Document 7096119
advertisement

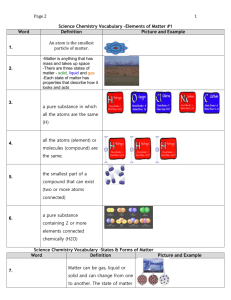
1 Page 2 Word Science Chemistry Vocabulary –Elements of Matter #1 Definition Picture and Example An atom is the smallest particle of matter. 1. Atom -Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space -There are three states of matter - solid, liquid and gas -Each state of matter has properties that describe how it looks and acts 2. Matter 3. Element a pure substance in which all the atoms are the same (H) 4. Pure Substance all the atoms (element) or molecules (compound) are the same. 5. Molecule the smallest part of a compound that can exist (two or more atoms connected) 6. Compound a pure substance containing 2 or more elements connected chemically (H2O) Science Chemistry Vocabulary –States & Forms of Matter Word Definition Picture and Example 7. States of Matter Matter can be gas, liquid or solid and can change from one to another. The state of matter 2 Page 2 can change because of temperature or pressure A substance in which 8. Mixture components are mixed but don’t blend together 9. Homogenous Mixture A substance in which components are mixed and evenly blend together 10. Heterogeneous Mixture A substance in which components are mixed but don’t blend together 11. Physical Change A change in substances that have had a chemical reaction. The original substance is changed to a new substance and cannot easily be changed back Describe how chemicals react 12. Chemical Change with one another – chemical reactions, solubility, acidity, heat, flammability, oxidation (rust), toxicity Science Chemistry Vocabulary –Mixtures & Solutions # 3 Word Definition 13. Solution -When one substance is evenly mixed with another -also known as a homogeneous mixture Picture and Example 3 Page 2 -The substance being dissolved 14. Solute -A solute is dissolved into a solvent -Ex: sugar (sugar dissolved into hot water) -What something is being dissolved 15. Solvent into -Ex: the water (sugar being dissolved into hot water) 16. Saturated a solution that cannot hold any more solute at a given temperature 17. Suspension a mixture in which the component are dispersed but large enough to see and to settle out 18. Decanting Process for separation -To pour off the top layer without disturbing the layers below 19. Filtering Process for separation –To separate the solid from a liquid by poring it through a filter (such as paper or a sieve) 20. Distillation Process for separation - the process of vaporizing then condensing a liquid (to separate the parts) 21. Gas Photo #1 Draw a photo of sugar + glass of water Photo #2 Draw a photo of sugar dissolved Point arrow to the layer sugar on bottom Photo #1 Draw a photo of corn starch + glass of water Photo # Draw a photo of dissolved cloudy liquid of water and corn starch 4 Page 2 22. Liquid 23. Solid Size, Colour, State of Matter, etc., 24. Physical Property Ability to oxidize, Ability to be stable Radioactivity, toxicity, Flammability, 25. Chemical Property Relationship of the mass of a substance to the space it takes up 26. Density A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. Atom Chemical Change Physical Change Chemical Property Physical Property Compound Decanting Density Distillation Element Filtering Gas Heterogeneous Mixture N. O. P. Q. R. S. T. U. V. W. X. Y. Z. Homogenous Mixture Liquid Matter Mixture Molecule Pure Substance States of Matter Saturated Solid Solute Solution Solvent Suspension