Nathan`s discoveries and information…
advertisement
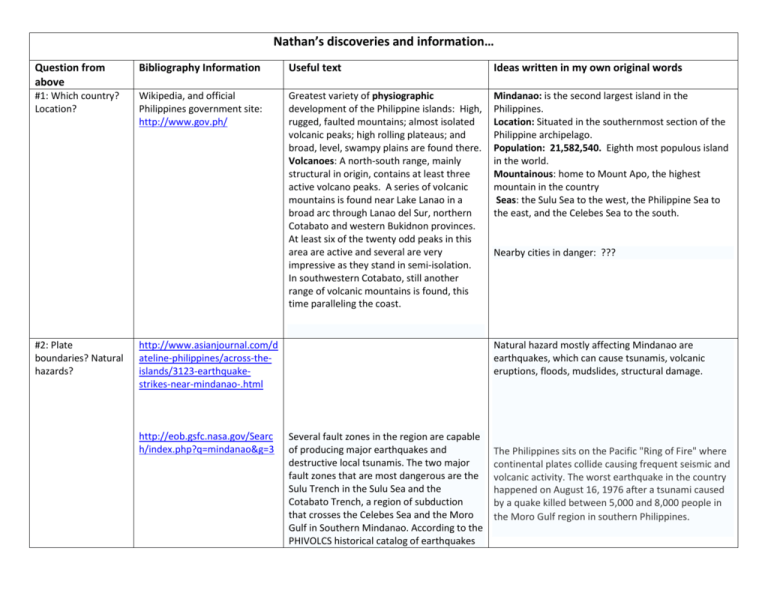
Nathan’s discoveries and information… Question from above Bibliography Information Useful text Ideas written in my own original words #1: Which country? Location? Wikipedia, and official Philippines government site: http://www.gov.ph/ Greatest variety of physiographic development of the Philippine islands: High, rugged, faulted mountains; almost isolated volcanic peaks; high rolling plateaus; and broad, level, swampy plains are found there. Volcanoes: A north-south range, mainly structural in origin, contains at least three active volcano peaks. A series of volcanic mountains is found near Lake Lanao in a broad arc through Lanao del Sur, northern Cotabato and western Bukidnon provinces. At least six of the twenty odd peaks in this area are active and several are very impressive as they stand in semi-isolation. In southwestern Cotabato, still another range of volcanic mountains is found, this time paralleling the coast. Mindanao: is the second largest island in the Philippines. Location: Situated in the southernmost section of the Philippine archipelago. Population: 21,582,540. Eighth most populous island in the world. Mountainous: home to Mount Apo, the highest mountain in the country Seas: the Sulu Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. #2: Plate boundaries? Natural hazards? http://www.asianjournal.com/d ateline-philippines/across-theislands/3123-earthquakestrikes-near-mindanao-.html http://eob.gsfc.nasa.gov/Searc h/index.php?q=mindanao&g=3 Nearby cities in danger: ??? Natural hazard mostly affecting Mindanao are earthquakes, which can cause tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, floods, mudslides, structural damage. Several fault zones in the region are capable of producing major earthquakes and destructive local tsunamis. The two major fault zones that are most dangerous are the Sulu Trench in the Sulu Sea and the Cotabato Trench, a region of subduction that crosses the Celebes Sea and the Moro Gulf in Southern Mindanao. According to the PHIVOLCS historical catalog of earthquakes The Philippines sits on the Pacific "Ring of Fire" where continental plates collide causing frequent seismic and volcanic activity. The worst earthquake in the country happened on August 16, 1976 after a tsunami caused by a quake killed between 5,000 and 8,000 people in the Moro Gulf region in southern Philippines. for the last 100 years, this region of the southern Philippines is characterized by moderate to high seismicity. The most recent earthquake along the Cotabato Trench region of subduction being the March 6, 2002 earthquake in Southern Mindanao http://www.nset.org.np/peer/p hilippines.html The archipelago makes up part of the "Pacific Ring of Fire" with over 200 volcanoes within its boundaries The Philippines is in a tectonically active region, lying between two major tectonic plates. The country lies west of the north western Pacific Ocean - the world's largest spawning ground of tropical Cyclones. The Philippines Archipelago is said to lie between the world's largest tectonic plates the Pacific and Eurasian Plates The so-called earthquake "generators" cause an average of five earthquake a day, most of which are imperceptible There has been 63 major earthquakes between 1589 and 1983 To date the worst earthquake (magnitude 7.7) happened in July 16, 1990 in Northern Luzon Why the Philippines is considered the most disasterprone country. #3: What type of natural hazards before? Will it happen again? #4: Climate? How has http://www.medco.gov.ph/me it changed? dcoweb/mindanao.asp Predictions? #5: How developed is the civilization? What’s it like? Other natural hazard: typhoons which can also result in floods, mudslides, structural damage. What is likelihood of more typhoons: ???? Climate and natural resources: Situated outside the typhoon belt, Mindanao enjoys a generally fair tropical climate, evenly distributed throughout the year. Its rich soil accounts for bountiful harvests of a variety of farm products. It grows most of the Philippines' major crops such as rubber (100% of national production), pineapple (91%), cacao (90%) as well as banana, coffee, corn and coconut (over 50%). The island also produces exotic fruits like pomelo, mangosteen and durian. Culture: The Cebuano language is spoken by the majority of people in Mindanao. Cebuano is generally the native language in most regions, except for the Muslim areas on the west coast and among the hill tribes. Although Mindanao sits outside of the typhoon belt, it does experience them occasionally. Find types of houses, buildings: ??? Are they building more earthquake-proof buildings??? Many poor people, therefore homes easily destroyed. Christians form the majority, with 63% of the population; Muslims are 32% of the population (mostly on the southern part of the island); 5% are affiliated with other religions. The native Maguindanaon and other native Muslim/non-Muslim groups of Mindanao have a culture that is different from the main cultures of the Southern Philippines #6: PPP? (Predict, Prepare, protect???) Current hazard relief and PREPAREDNESS organizations: http://www.nset.org.np/peer/p hilippines.htm NDCC in Philippines a. NDCC The National Disaster Coordinating Council or NDCC, is the policy-making and coordinating body for disasters management at the national level. It directs all disaster preparedness planning, as well as disaster response operations and rehabilitation, both in the public as well as private sectors. It advises the President on matters related to natural calamities and disasters, including recommendations for the declaration of a state of calamity in disaster-affected areas. It is composed of the heads of fourteen national ministries, the Chief of Staff of the Armed Forces of the Philippines, the Secretary-General of the Philippine National Red Cross, and the Administrator of the Office of Civil Defense. The Defense Minister, or Secretary of National Defense, serves as the Chairman of the NDCC, with the Civil Defense Administrator as Executive Officer. PEER coordinates with the National Disaster Coordinating Council. All council members with search and rescue and medical first response mandates are de facto partner agencies of PEER. PEER in Philippines Philippines was one of the member from the beginning of OFDA-funded Program for Enhancement of Emergency Response (PEER) phase I (1998-2003) and an active member in the current PEER phase II (20032008). There are six countries Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Nepal, Pakistan and the Philippines who have a high risk of seismic b. PEER vulnerability. PEER implements activities in Philippines under the coordinating authority of the National Disaster Coordinating Council, with which the program has a Memorandum of Understanding. The designated training institution for Medical First Responder (MFR) and Collapsed Structure Search and Rescue (CSSR) training is the NDCC. The designated training institution for Hospital Preparedness for Emergencies (HOPE) is the Philippines General Hospital, which falls under the authority of the University of the Philippines. 7. Example of one company’s earthquake Preparedness Plan in Mindanao Pacific Tsunami Warning Centre: http://www.prh.noaa.gov/ptwc /?region=1&id=pacific.2009.10. 04.111147 PREDICTION Government assistance: http://www.usaid.gov/our_wor k/humanitarian_assistance/disa ster_assistance/publications/pr ep_mit/mods/program_update s/philippines_preparedness.pdf PROTECTION & PREPARTIONS http://www.drj.com/drworld/ content/w1_116.htm Facility Evacuation “I cannot overemphasize the importance of periodic evacuation drills,” he said. Because all the employees were cognizant of the nearest exits, the spontaneous evacuation was successful; while all employees escaped serious injury, many others trapped in buildings in Baguio were crushed. Facility Power PREPARATIONS Electricity, power, water, etc. should be well planned and duty personnel should be well trained on emergency shut-down procedures, Locke says. “If we have a case where perimeter mains of a significant size are totally collapsed, I can well assure you that reservoirs can be drained in a relatively short period of time unless the pumps are manually turned off,” he said. Communications In an event such as a large-scale earthquake, communications are almost certain to be either hindered or temporarily destroyed. Thus, backup communications are vital. “The Motorola cellular phone that I carried to Baguio was key to our limited communication,” said Locke. Ham radio and VHF radios could also be used. Site Plans and Drawings It is important to know the precise layout and location of routing for water mains, sewer mains, gas lines, and underground power lines, to name a few, Locke stresses. “When initiating repairs, it could be of vital importance from an expediency viewpoint to have detailed drawings of the total factory structure available at each site.” Insurance Claims Only a limited number of employees were involved in incidents that involve a substantial claim. However, Locke observed that it would be prudent to consider a detailed check-off list and maybe a video tape that could be made available to each factory site for quick reference and training. 8. Recent earthquake activity Cool Site ! PROTECTION To see seismic activity on a Most recent seismic activity: seismograph: http://www.ga.gov.au/bin/eart hquake.pl?title=Mindanao%2C+ Philippines&magnitude=5.6&de pth=60&xy=124.505,6.500&dat e=18,09,2009&time=11,53,54& bg1=eqrisk_lm&zoom=500&sta tion=MTN Last week, Nov. 11. Another one just happened, Nov 17, 5.2 on Richter Scale, just after midnight. NOTES TO ME: Will do video for Utube? Need resources from: books, newspaper, magazine. Visit Philippine Embassy for pamphlets to pass around? Make food to create mood in class? Candies? Small and practical dish?