Population Growth
advertisement

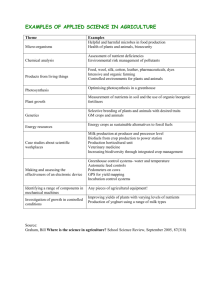
Population Growth including farming methods, fertilisers and pesticides The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum size of population it can support. This is when birth rate + death rate. The rapid growth rate (exponential) of the human population started in mid 1800s. Factors contributing to this huge increases are; Food availability Improved hygiene and sanitation Improved medical treatment Increase in female fertility. The study of human population statistics is known as demography. A change in a country’s population depends on four factors: Births Deaths Immigration Emigration It is suggested that birth control is the best way to control human population but there are problems with this due to religious beliefs, medical care, cultural and social backgrounds. Food and Population In natural cycles plants die and decay. The mineralisation of the plants in the soil replaces the nutrients as fast as they are used. This along with materials excreted by plants and animals is a source of natural fertilisers. In ideal circumstances this is how nutrients would be cycled. However, in order to meet ever-increasing food demands large fields of monocultures (one plant) are created. When these large fields are harvested this balance is disturbed and synthetic fertilisers like nitrates have to be added. Synthetic fertilisers disturb the soil structure and may be leached into surrounding water causing eutrophication. This in turn leads to an algal bloom which causes a decrease in oxygen by: Blocking light and preventing photosynthesis Providing nutrients for bacteria which multiply using up oxygen. Indicator species This is a species whose presence/absence shows the level of pollution in an area. Species mayfly Rat-tailed maggot Level of oxygen in water high low Level of pollution low high Uses of minerals Mineral Use nitrate Building protein and growth Phosphate Respiration and growth potassium Respiration and photosynthesis magnesium photosynthesis Deficiency symptoms Poor growth and yellow leaves Poor root growth and discoloured leaves Poor flower and fruit growth, discoloured leaves Yellow leaves Explanation All amino acids contain nitrogen. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein A component of DNA molecules and cell membranes Must be present for photosynthesis and respiration enzymes to work Chlorophyll molecules contain magnesium ions. It is the magnesium that makes chlorophyll green. Vigorous weeds often compete with crops for light, space and nutrients. Farmers apply herbicides to avoid this. Monocultures provide ideal conditions for pests and parasites. Pesticides are used to avoid these. Fungicides are used against fungi and insecticides combat insects. Some chemicals used in pesticides kill helpful insects e.g. bees. Some pesticides take a long time to break down e.g. DDT which builds up in organisms as you go along a food chain. This is known as bioaccumulation. It often reaches fatal level. DDT also causes the thinning of birds’ eggs. The use of DDT has been banned despite it being an effective pesticide. Some farmers use organic methods to get rid of pests: Spraying natural chemicals obtained from plants on to their crops Picking pest off by hand Placing natural predators of the pests onto crops Growing plants that repel the insects amongst the crops. Some farmers may use genetically modified crops, such crops are resistant to particular pests. These methods may involve: Bacterial carriers Gene silencing Gene splicing Viral carriers Many farmers are moving away from intensive farming using artificial fertilisers and pesticides and developing organic farming methods. Organic farming techniques Technique Manure Replaces Fertiliser Crop rotation Single crop Weeding Herbicides Nitrogen-fixing plants Nitrogen fertilisers Advantage Recycles waste, improves soil structure Reduces disease and damage to soil composition Less environmental damage or health risk Cheaper, longer lasting Disadvantage Difficult to apply and cannot control mineral content Less productivity. Less efficient to grow different crops Labour intensive Reduces area for growing crops if part of crop rotation