Reducing the amount of carbon dioxide
advertisement

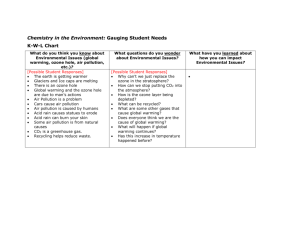
Chapter 15 Water Management The water issue Water in its liquid from is the material that makes life possible on Earth. All living organisms are composed of cells that contain at least 60 percent water. Furthermore, their metabolic activities take place in water solution.Organisms can exist only where they have access to adequate supplies of water. The hydrologic cycle All water is locked into a constant recycling process called the hydrologic cycle. Two important processes involved in the cycle are the evaporation and condensation of water. Evaporation involves adding energy to molecules of liquid so that it becomes a gas in which the molecules are farther apart. Condensation is the reverse process in which molecules of a gas give up energy, get closer together, and become a liquid. Human influences on the hydrologic cycle Human activities can significantly impact evaporation, runoff, and infiltration. When water is used for cooling in power plants or to irrigate crops, the rate of evaporation is increased A major concern in urban areas is providing ways to carry storm water away rapidly. Water withdrawals are measurements of amount of water taken from a source. Water that is incorporated into a product or lost to the atmosphere through evaporation or evapotranspiration cannot be reuse in the same geographic area and is said to be consumed. Kinds of water use - Domestic use of water - Agricultural use of water - Industrial use of water - In-Stream use of water Kind and source of water pollution Water pollution occurs when something enters water that changes the natural ecosystem or interferes with water use by segments of society. Dissolved organic matter is a significant water pollution problem because it decays in the water. The amount of oxygen required to decay certain amount of organic matter is called the biochemical oxygen demand. If too much organic matter is added to the water, all of the available oxygen will be used up. Anaerobic respiration produces chemicals that have a foul odor. Effect of organic waste on dissolved oxygen When a source of pollution can be readily identified because ithas a definite source and place where it enters the water, it is said to come from a point source. Diffuse pollutants, such as from agricultural land and urban paved surfurban paved surfaces , acid rain and runoff, aye said to come from nonpoint sources and are much more difficult to identify and control. -be aware that many chemicals commonly used around the home are toxic -buy chemical only in the amount you expect to use, and apply them only as directed. -take unwanted household chemicals to hazardous waste collection centers. -Never pour unwanted chemicals on the ground. -Used water-based products whenever possible Municipal water pollution Manicipalities arw faced with the double-edged problem of providing suitable drinking water and disposing of wastes. Wastes from homes consist primary of organic matter from garbage, food preparation. Cleaning of clothes and dishes, and human wastes. Facal coliform bacteria are also present in the wastes of other warm - blood animals Agricultural water pollution Agricultural activities are a primary cause of a water pollution problems. One of the largest waterpollution problem is agricultural runoff for large expanses of open field. Industrial water pollution. Factories and industrial complexes frequently dispose of some or all of their into municipal sewage systems. A special sources of industrial water pollution is mining. Thermal pollution : many industries use water for cooling, thermal pollution can be a problem. Thermal pollution occurs when an industry removes water from a souce Marine oil pollution : has many sources. One source is accidents, such as oil -drilling blowouts or oil tanker accidents. Groundwater pollution : make agricultural products, underground storage tanks, landfills, septic tank, surface impoundments. Water-use planning issue Water diversion is the physicalprocess of transferring water from one area to another, the aqueducts of ancient Rome are early example of water diversion. 1. Developing facilities to store surface water and pump water into aquifers. 2. Developing wetland to treat municipal and agricultural runoff. 3. Using clean wastwwater to recharge aquifers. 4. Reducing the amount of water lost through levees Wastewater treatment : because water must be clean before it is released, most companies and municipalities in the developed world maintain waste water treatment facilities. Salinization : another water-use problem results from salinization, an increase in a salinity caused by growing salt concentrations in soil ,Groundwater mining means that water is removed from aquifer faster than it is replaced. It is common in area of the western USA., and throughout the world. Preserving scenic water areas and wildlife habitats : the way in which the land adjacent to the water is used must be consistent with preserving these scenic areas. Chapter 16 Global Pollution and climate changes Atmospheric layers The atmosphere is composed of layers and composed of 78.1 percent nitrogen, 20.9 percent oxygen, and a number of other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor that total about 1 percent Pollution of the atmosphere is any addition of matter or energy that degrades the environment for humans and other organism. Bacause human action are the major cause of pollution we can do something to prevent it. Categories of air pollutants - Carbon Monoxide Particulate Matter Sulfur Dioxide Nitrogen Dioxide Lead The Atmosphere The description of the Earth's Atmosphere is now in its own section: Atmosphere Air Pollution Primary air pollutants : pollutants emitted directly Secondary air pollutants : pollutants created from reactions between primary air pollutants Criteria air pollutants 6 pollutants regulated by the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) carbon monoxide particulate matter sulfur dioxide nitrogen dioxide ozone lead Sulfur Dioxide and Acid Rain Sulfur Dioxide Sulfur is oxidized to sulfur dioxide: S + O2 → SO2 This can then be combined with water in the atmosphere to form sulfur dioxide: 2SO2 + O2 + 2H2O → H2SO4 Source: burning of sulfur-containing compounds including coal and oil smelting of metal ores Cu2S + O2 → 2Cu + SO2 (metal ore) Direct Effect Absorbed by moist respiratory tissue causing restriction of airway especialy severe in people with asthma Environmental Effect Acid Deposition The fallout of sulfuric acid either in rain or as dry particles is called acid deposition or, more commonly, acid rain. Effects: Destruction of concrete and stone structures The sulfuric acid converts calcium carbonate to calcium sulfate which is more soluble: CaCO3 + H2SO4 Acid rain events on a stone monument Acidification of forests, rivers, and lakes Some lakes have natural buffering, but many do not. Acidified water causes death of fish and other organisms, due to both the lower pH directly and the leaching of metal, especially aluminum. It also causes damage to trees and other plants. Acid rain damage on woodlands in Czech Republic Nitrogen dioxide, ozone, and smog Nitrogen Dioxide Nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) are formed from high temperature combustion. low temperature combustion: CH4 + O2 + N2 → CO2 + H2O + N2 high temperature combustion: CH4 + O2 + N2 → CO2 + H2O + NO Nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide are together called NOx (read as nox). Health Effects: lung irritation increases susceptibility to lung disease The flask contains nitrogen dioxide. It is this that gives the characteristic brownish color to smog Ozone Nitrogen dioxide reacts with sunlight to form nitric oxide and atomic oxygen. This oxygen reacts quickly with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone. Ozone can then react with nitric oxide to regenerate nitrogen dioxide. NO2 + hν → NO + O O + O2 → O3 O3 + NO → NO2 + O2 Note The ozone formed here is tropospheric ozone ("bad ozone"), not to be confused with stratospheric ozone ("good ozone") Health Effects: lung problems eye irritation Environment Effects: damage to plants and trees Ozone damage to plants. The top row shows normal plants, the bottom row show plants exposed to ozone. Photochemical Smog Tropospheric ozone reacts with organic chemicals to produce photochemical smog. Smog is a toxic soup of NOx, ozone, peroxyacyl nitrates (PANs), aldehydes, and other organic chemicals. Smog in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Thermal inversions Under certain conditions a layer of warm air can occur above cold air. This causes any pollutants to be trapped and not dispersed. Smoke rising in Lochcarron, Scotland is stopped by an overlying layer of warmer air Winter smoke in Shanghai A good animation of thermal inversion can be found here. Particulate matter (PM) and Aerosols Particulate Matter Small solid and liquid particles which remain suspended in the atmosphere. burning field producing particulate matter (smoke) Sizes are up to 10 micrometers in diameter. Sources: dust from construction, agriculture, and roads forest fires burning of solid and liquids -- especially from coal, wood, and diesel fuel clearing of land for agriculture Effects: The small particles can get trapped in the lining of the lung causing irritation, inflammation, or cancer Inflammation Silicosis (silica dust) Black Lung disease (coal dust) Cancer Asbestos Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) Tar from incomplete combustion and tobacco smoke Asbestos micrograph showing the fibers Toxic air pollutants Carbon Monoxide (CO) Car exhaust contains carbon monoxide (note CO is colorless, the white color is steam) Source: incomplete burning of organic materials complete combustion: CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O incomplete combustion: CH4 + 1.5O2 → CO + 2H2O Effects: binds with hemoglobin to form carboxyhemoglobin. This carboxyhemoglobin cannot transfer oxygen to the cells. Lead Sources: paint smelters batteries leaded gasoline Effects: memory loss learning difficulties nervous system damage damage to bones and kidneys accumulative poison Mercury Mercury amalgam from small-scale gold mining. This will be heated to evaporate the mercury Sources: burning of coal small-scale gold mining Effects: mental effects ("mad-hatter's" disease) kidney disease Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC's) Definition: Organic compounds which rapidly evaporate. Examples: benzene acetone solvents formaladehyde (from building materials) Effects: varies widely depending on substance eye, nose, and throat irritation dizziness and headaches damage to liver, kidney, and nervous system actual toxicity varies widely Indoor Air Pollution Indoor air pollution is air pollutants found in your home, office, etc. Examples: formaldehdye chlorinated solvents pesticides tobacco smoke radon Naturally radioactive gas. A decay product of radium (which is a decay product of uranium). Uranium and radium can be found naturally in some rocks especially granite. Radon can then enter houses built on such rocks. Ozone Depletion As stated above, the stratosphere contains a layer of ozone which protects the Earth from dangerous ultraviolet radiation. Chlorinated and brominated hydrocarbons can travel unreacted up to the stratosphere. The most important of these are the chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's). CCl3F + hν → CCl2F + Cl This free chlorine then reacts with the ozone. Cl + O3 → ClO + O2 This depletes the amount of ozone present. These ozone depleting chemicals include: chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's) hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFC's) halons (bromochloroflurocarbons) methyl bromide Montreal Protocol In the 1980's, it was found the ozone layer was thinning. In 1987 a treaty called the Montreal Protocol was signed. It bans the use of ozone depleting chemicals. This has stabilized the ozone layer, though it will take many years for the ozone layer to return to previous levels Global Warming Recent Climate Change The global temperature of the Earth has increased over the last century. Current temperatures are 0.6 °C over the 1950-1980 average. All objects emit heat in the form of infrared (IR) radiation. Gases in the atmosphere absorb the IR radiation from the Earth and reradiate it back to the surface. This regulates the temperature. The natural greenhouse effect allows life to survive on Earth. But problems occur when humans cause additional greenhouse effects. Major human-generated greenhouse gases [1]: Carbon dioxide 76% of all greenhouse gas emissions Methane 16% Nitrous Oxide 8% F-gases (see below) 1% Carbon Dioxide Carbon dioxide is by far the largest cause of global warming. Largest sources of carbon dioxide: Burning of carbon-based fuels Deforestation and burning grasslands for crop production Methane Methane is at lower concentrations, but has a stronger greenhouse effect. Largest sources of methane: Agriculture, Cattle and other ruminants Manure Rice farming Nitrous Oxide Nitrous Oxide (N20) is at low concentrations and has a strong greenhouse effect. Largest sources: Natural denitrification in soils Breakdown of fertilizers Fluorinated Gases Fluorinated gases (F-gases) which contribute to climate change include: Hydrofluorocarbons (HFC's) - used as substitutes for CFC's and HCFC's (HFC's do not destroy the ozone) Perfluorocarbons (PFC's) - used in electronics and other industries Sulfur Hexaflouride (SF6) - used in high-voltage switches Impacts of Global Warming Changing of the weather. Global warming will cause shift in climate .An animation of how the Earth's climate would change can be found here Generally, more hot days and fewer cool days. Tropics will get less precipitation. Polar regions will get more precipitation. Temperate regions will shift no Sea level rise The melting of the ice sheets and glaciers causes the amount of seawater to increase. Also heating water causes it to expand. Models estimate that sea levels will rise 0.18 - 0.59 m. 10 percent of world's population lives less than 10 m above sea level. Some island countries may no longer exist. Wildlife Global warming can also affect wildlife. It can affect their distribution. Some species have already migrated towards the poles. This is a especially a threat to endangered species. Permafrost melting Permafrost is soil which remains frozen all year. Melting of permafrost is a feedback mechanism. It releases methane, which increases global warming, which in turn causes more permafrost melting creating a loop. Ocean Acidification This effect is due to the carbon dioxide directly and not temperature change. Carbon dioxide dissolves in the ocean to create acid conditions. This in turn has an effect on marine organisms. Acidic conditions increase the solubility of calcium carbonate in shells of shellfish, coral, etc. Mitigation Reducing the amount of carbon dioxide Methods of mitigation energy conservation renewable energy sources changing transport carbon tax - taxing companies for each ton of carbon dioxide they produce reforestation carbon sequestering ? - capturing CO2 and then pumping it underground note that we are still producing carbon dioxide, but then burying it underground the technology is untested. What happens if leaks occur and will changing acidity cause problems? geoengineering - mega projects to reduce effects of global warming examples: setting huge mirrors in outer space, adding huge quantities of iron filings to the ocean, injecting aerosols of sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere problems: hugely expensive, most are not technically feasible with today's technology, may have undetermined consequences, and questions about governance Adaptation Measures to reduce the effects of global warming Examples Building sea walls Changing crop types Generating a fund to help low income countries (the most talked about adaptation measure) Chapter 17 Solid waste management and disposal 1.Municipal solid waste landfill is typically constructed above an impermeable clay layer this is lined with an impermeable membrane and includes mechanisms for dealing with liquid and gas materials generated. Methods of wastes disposal Landfills have historically been the primary Method of waste disposal because this method is the cheapest and most convenient, and the threat of groundwater contamination was not initially recognized. Advantage - Cheapest and the most convenient. -Can use methane to generate electricity Disadvantage - Groundwater contamination 2.Incineration is the process of burning waste in the incinerator. Most incinerators can produce electricity. Mass burn is the technology to burn unprocessed Municipal Solid Waste Advantage - Reduce Municipal Solid Waste(90% by volume and 75% by weight). - Electricity Disadvantage - More costly - Air Quality and the toxicity - Disposal of the ash. 3. Producing mulch and compost Mulch is organic material that is used to cover the soil. Composting is using natural decomposition to transform organic material into compost(humus-like material) Mulch for example Branches, Bark, and other organic materials are chopped into smaller pieces Advantage - Fertilizer - Can be done at home 4. Source Reduction is the method of designing, manufacturing, purchasing, and using in the way to reduce the amount of waste and toxicity. Such as reducing the use of packaging, careful manufacturing, purchasing necessary amount reuse etc. Advantage - Saving natural resource - Reduce the toxicity - Reduce cost 5. Recycling is one of the best environmental success stories of the late twentieth century. Advantage - Resource conservation - Pollution reduction - Energy saving - Job creation - Reduced need for landfills and incinerators. Disadvantage - Different plastics cannot be recycled together