Third Grade Social Studies Pacing Guide
advertisement

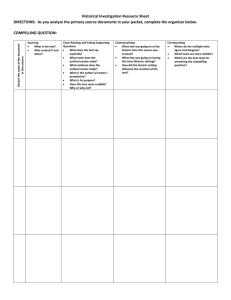
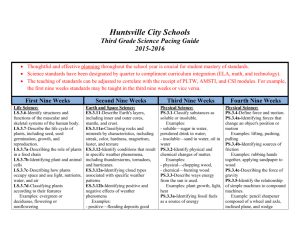
Huntsville City Schools Third Grade Social Studies Pacing Guide 2015-2016 Thoughtful and effective planning throughout the school year is crucial for student mastery of standards. Social Studies standards have been designated by quarter to compliment curriculum integration (ELA, math, and technology). The Social Studies standards are interwoven throughout the domains of Economics, Geography, History, Civics and Government. First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks 3.1-Locate the prime meridian, equator, Tropic of Capricorn, Tropic of Cancer, International Date Line, and lines of latitude and longitude on maps and globes. 3.1.a-Using cardinal and intermediate directions to locate on a map or globe an area in Alabama or the world 3.1.b-Using coordinates to locate points on a grid. 3.1.c-Determining distance between places on a map using a scale. 3.1.d-Locating physical and cultural regions using labels, symbols, and legends on an Alabama or world map. 3.3-Describe ways the environment is affected by humans in Alabama and the world. Examples: crop rotation, oil spills, landfills, clearing of forests, replacement of cleared lands, restocking of fish in waterways. 3.3.a-Using vocabulary associated with human influence on the environment, including irrigation, aeration, urbanization, reforestation, erosion, and migration. 3.4-Relate population dispersion to geographic, economic, and historic changes in Alabama and the world. Examples: geographic—flood, hurricane, tsunami 3.11-Interpret various primary sources for reconstructing the past, including documents, letters, diaries, maps, and photographs. 3.11.a-Comparing maps of the past to maps of the present. 3.12-Explain the significance of representations of American values and beliefs, including the Statue of Liberty, the statue of Lady Justice, the United States flag, and the national anthem. 3.13-Describe prehistoric and historic American Indian cultures, governments, and economics in Alabama. 3.10-Recognize functions of the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution of the United States. 3.10.a-Describing the process by which a bill becomes law. 3.10.b-Explaining the relationship between the federal government and state governments, including the three branches of government. 3.10.c-Defining governmental systems, including democracy, monarchy, and dictatorship. 3.1.e-Describing the use of geospatial technologies. Examples: Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS) 3.1.f-Interpreting information on thematic maps. Examples: population, vegetation, climate, growing season, irrigation 3.1.g-Using vocabulary associated with maps and globes, including megalopolis, landlocked, border, and elevation. 3.2-Locate the continents on a map or globe. 3.2.a-Using vocabulary associated with geographical features of Earth, including hill, plateau, valley, peninsula, island, isthmus, ice cap, and glacier. 3.2.b-Locating major mountain ranges, oceans, rivers, and lakes throughout the world. 3.7-Describe the relationship between locations of resources and patterns of population distribution. Examples: presence of trees for building homes, availability of natural gas supply for heating, availability of water supply for drinking and for irrigating crops. 3.7.a-Locating major natural resources and deposits throughout economic—crop failure historic—disease, war, migration. 3.4.a-Identifying human and physical criteria used to define regions and boundaries. Examples: human—city boundaries, school district lines physical—hemispheres, regions within continents or countries. 3.5-Compare trading patterns between countries and regions. 3.5.a-Differentiating between producers and consumers. 3.5.b-Differentiating between imports and exports. Examples: imports—coffee, crude oil exports—corn, wheat, automobiles. 3.6-Identify conflicts within and between geographic areas involving use of land, economic competition for scarce resources, opposing political views, boundary disputes, and cultural differences. 3.6.a-Identifying examples of cooperation among governmental agencies within and between different geographic areas. Examples: American Red Cross, Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), World Health Organization (WHO) Examples: prehistoric— Paleo-Indian, Archaic, Woodland, Mississippian historic—Choctaw, Chickasaw, Cherokee, Creek. 3.13.a-Identifying roles of archaeologists and paleontologists. the world on topographical maps. 3.7.b-Comparing present-day mechanization of labor with the historical use of human labor for harvesting natural resources Example: present-day practices of using machinery versus human labor to mine coal and harvest cotton and pecans. 3.7.c-Explaining the geographic impact of using petroleum, coal, nuclear power, and solar power as major energy sources in the twentyfirst century. 3.8-Identify geographic links of land regions, river systems, and interstate highways between Alabama and other states. Examples: Appalachian Mountains, Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway, Interstate Highway 65 (I65), Natchez Trace Parkway 3.8.a-Locating the five geographic regions of Alabama. 3.8.b-Locating state and national parks on a map or globe. 3.6.b-Locating areas of political conflict on maps and globes. 3.6.c-Explaining the role of the United Nations (UN) and the United States in resolving conflict within and between geographic areas. 3.9-Identify ways to prepare for natural disasters. Examples: constructing houses on stilts in flood-prone areas, buying earthquake and flood insurance, providing hurricane or tornado shelters, establishing emergency evacuation routes. Social Studies utilizes a variety of standards and may be cross-referenced, integrated, and assessed in both subject areas. Informational Text: RI.3.1-Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RI.3.2-Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. RI.3.3-Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to time, sequence, and cause/effect. RI.3.4-Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 3 topic or subject area. RI.3.5-Use text features and search tools (e.g., key words, sidebars, hyperlinks) to locate information relevant to a given topic quickly and efficiently. RI.3.6-Distinguish their own point of view from that of the author of a text. RI.3.7-Use information gained from illustrations, other visual elements (e.g., maps, photographs), and the words in a text to demonstrate understanding of the text (e.g., where, when, why, and how key events occur). RI.3.8-Describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text (e.g., comparison; cause and effect; first, second, third in a sequence). RI.3.9-Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in two texts on the same topic. RI.3.10 -By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including historical, scientific, and technical texts, in the grades 2–3 text complexity band independently and proficiently. Writing: W.3.1-Write opinion pieces on topics or texts, supporting an ongoing of view with reasons. W.3.2-Write informative or explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly. W.3.3–Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, descriptive details, and clear event sequences. W.3.4-With guidance and support from adults, produce writing in which the development and organization are appropriate to task and purpose. W.3.5-With guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, and editing. (Editing for conventions should demonstrate command of the first three Language standards in Grades K-3). W.3.6-With guidance and support from adults, use technology to produce and publish writing (using keyboarding skills) as well as to interact and collaborate with others. W.3.7-Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic. W.3.8-Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories. W 3.10-Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. Speaking and Listening: SL.3.1-Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 3 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. SL.3.2-Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. SL.3.3-Ask and answer questions about information from a speaker, offering appropriate elaboration and detail. SL.3.4-Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at an understandable pace. SL.3.5-Create engaging audio recordings of stories or poems that demonstrate fluid reading at an understandable pace; add visual displays when appropriate to emphasize or enhance certain facts or details. SL.3.6-Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification.