Third Grade Science Pacing Guide
advertisement
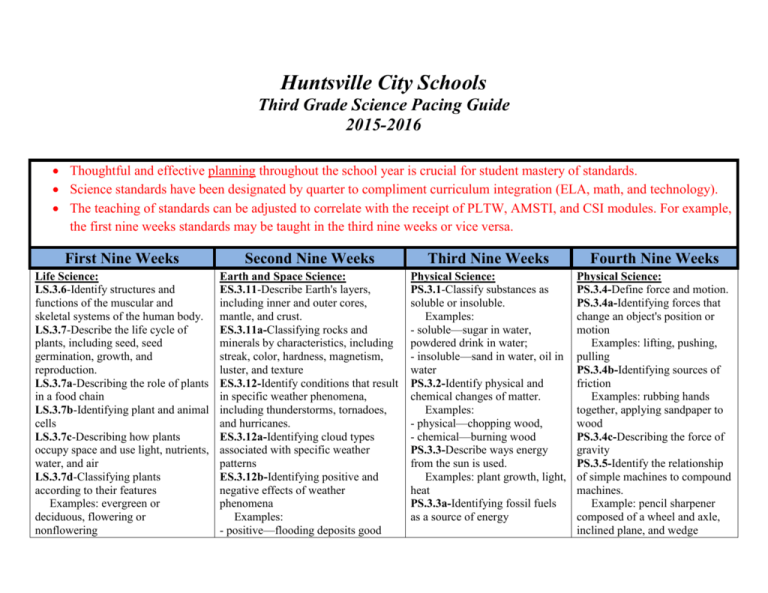
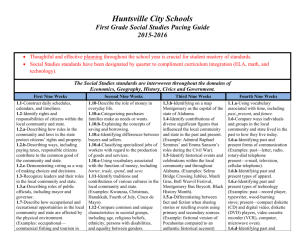
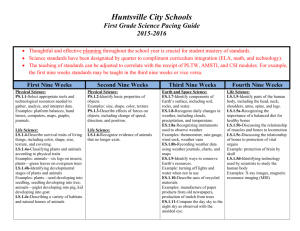
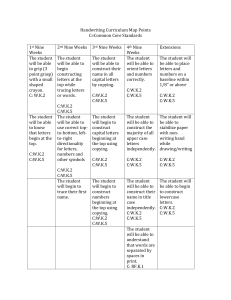
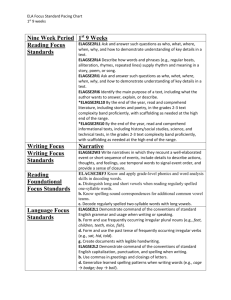
Huntsville City Schools Third Grade Science Pacing Guide 2015-2016 Thoughtful and effective planning throughout the school year is crucial for student mastery of standards. Science standards have been designated by quarter to compliment curriculum integration (ELA, math, and technology). The teaching of standards can be adjusted to correlate with the receipt of PLTW, AMSTI, and CSI modules. For example, the first nine weeks standards may be taught in the third nine weeks or vice versa. First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks Life Science: LS.3.6-Identify structures and functions of the muscular and skeletal systems of the human body. LS.3.7-Describe the life cycle of plants, including seed, seed germination, growth, and reproduction. LS.3.7a-Describing the role of plants in a food chain LS.3.7b-Identifying plant and animal cells LS.3.7c-Describing how plants occupy space and use light, nutrients, water, and air LS.3.7d-Classifying plants according to their features Examples: evergreen or deciduous, flowering or nonflowering Earth and Space Science: ES.3.11-Describe Earth's layers, including inner and outer cores, mantle, and crust. ES.3.11a-Classifying rocks and minerals by characteristics, including streak, color, hardness, magnetism, luster, and texture ES.3.12-Identify conditions that result in specific weather phenomena, including thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes. ES.3.12a-Identifying cloud types associated with specific weather patterns ES.3.12b-Identifying positive and negative effects of weather phenomena Examples: - positive—flooding deposits good Physical Science: PS.3.1-Classify substances as soluble or insoluble. Examples: - soluble—sugar in water, powdered drink in water; - insoluble—sand in water, oil in water PS.3.2-Identify physical and chemical changes of matter. Examples: - physical—chopping wood, - chemical—burning wood PS.3.3-Describe ways energy from the sun is used. Examples: plant growth, light, heat PS.3.3a-Identifying fossil fuels as a source of energy Physical Science: PS.3.4-Define force and motion. PS.3.4a-Identifying forces that change an object's position or motion Examples: lifting, pushing, pulling PS.3.4b-Identifying sources of friction Examples: rubbing hands together, applying sandpaper to wood PS.3.4c-Describing the force of gravity PS.3.5-Identify the relationship of simple machines to compound machines. Example: pencil sharpener composed of a wheel and axle, inclined plane, and wedge LS.3.7e-Identifying helpful and harmful effects of plants Examples: - helpful—provide food, control erosion; - harmful—cause allergic reactions, produce poisons LS.3.7f-Identifying how bees pollinate flowers LS.3.7g-Identifying photosynthesis as the method used by plants to produce food LS.3.8-Identify how organisms are classified in the Animalia and Plantae kingdoms. LS.3.9-Describe how fossils provide evidence of prehistoric plant life. Example: plant fossils in coal or shale providing evidence of existence of prehistoric ferns LS.3.10-Determine habitat conditions that support plant growth and survival. Examples: deserts support cacti, wetlands support ferns and mosses soil when waters recede, - negative—flooding kills crops ES.3.12c-Identifying technology used to record and predict weather, including thermometers, barometers, rain gauges, anemometers, and satellites ES.3.12d-Explaining symbols shown on a weather map ES.3.12e-Organizing weather data into tables or charts ES.3.13-Describe ways to sustain natural resources, including recycling, reusing, conserving, and protecting the environment. ES.3.13a-Recognizing the impact of society on human health and environmental conditions ES.3.14-Describe the position of Earth, the moon, and the sun during the course of a day or month. ES.3.14a-Describing various forms of technology used in observing Earth and its moon Science utilizes a variety of standards and may be cross-referenced, integrated, and assessed in both subject areas. Informational Text RI 3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RI 3.2 Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. RI 3.3 Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to time, sequence, and cause/effect. RI 3.4 Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 3 topic or subject area. RI 3.5 Use text features and search tools (e.g., key words, sidebars, hyperlinks) to locate information relevant to a given topic quickly and efficiently. RI 3.6 Distinguish their own point of view from that of the author of a text. RI 3.7 Use information gained from illustrations, other visual elements (e.g., maps, photographs), and the words in a text to demonstrate understanding of the text (e.g., where, when, why, and how key events occur). RI 3.8 Describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text (e.g., comparison; cause and effect; first, second, third in a sequence). RI 3.9 Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in two texts on the same topic. RI 3.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including historical, scientific, and technical texts, in the grades 2–3 text complexity band independently and proficiently. Writing W.3.2 Write informative or explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly. W.3.6 With guidance and support from adults, use technology to produce and publish writing (using keyboarding skills) as well to interact and collaborate with others. W.3.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic. W.3.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories. W 3.10 Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. Speaking and Listening SL 3.1 Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 3 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. SL 3.2 Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. SL 3.3 Ask and answer questions about information from a speaker, offering appropriate elaboration and detail. SL 3.4 Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at an understandable pace. SL.3.6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Math – Measurement and Data 3.MD.3 Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. 3.MD.4 Generate measurement data by measuring lengths using rulers marked with halves and fourths of an inch. Show the data by making a line plot where the horizontal scale is marked off in appropriate units – whole numbers, halves, or quarters.