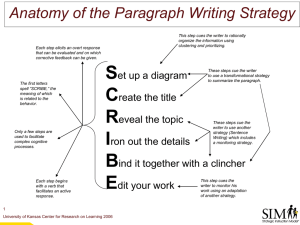
Intermediate II (54 hours)
advertisement

BAR ILAN UNIVERSITY – EFL UNIT TROM (INTERMEDIATE) 2 SYLLABUS (54 hours) 05 LEVEL For Pre-Advanced Level Students (Psychometric: 95 – 99) EXIT REQUIREMENTS Upon completion of the pre-advanced level course, the student will be able: i. to read and comprehend English texts of general interest at a basic academic level (approximately 1,500 words) to extract information and draw inferences from the text in order to demonstrate comprehension of the texts to write short answers varying from a few words to a complete sentence in English. ii. iii. The student will acquire the following skills: i. reading skills (at word, sentence, and paragraph and text level) ii. to general language skills (listening, speaking and writing sufficient participate in the lesson, communicate with the teacher and write short answers to language and comprehension questions). READING SKILLS A. Skim and scan a text to anticipate its content and structure, and get the gist. B. Recognise the structure and development of a text via transitions and other organisational markers, and understand the relationship between ideas as they are expressed across several paragraphs. C. Identify the main idea of a text and the purpose of the writer; identify the point of view or attitude of the writer. D. Identify the main idea of a paragraph; understand the development of ideas in a paragraph via common rhetorical devices such as general statement and illustrative support, listing, comparison and contrast, cause and effect, problem and solution. E. Infer meaning at both sentential and discourse levels. F. Develop conscious awareness of cognitive strategies as tools in reading. LANGUAGE SKILLS G. Build and master vocabulary adequate for reading texts at the preacademic level and deduce meanings of other words via morphological, syntactic and context clues. H. Understand the meaning of a sentence with the help of syntactic clues. I. Identify the meanings of references and ellipses within and between sentences. READING SKILLS SKILL A: Skim and scan a text to anticipate its content and structure, and get the gist. a. Skim opening and closing paragraphs to get the main idea or conclusion of the writer. b. Read first sentence of each paragraph to get the gist of the text. c. Scan for dates, names, and numbers. SKILL B: Recognise the structure and development of a text via transitions and other organisational markers, and understand the relationship between ideas as they are expressed across several paragraphs. Identify the function of paragraphs as they relate to each other and to the text as a whole. SKILL C: Identify the main idea of a text and the purpose of the writer; identify the point of view or attitude of the writer. 1. Identify the purpose of the writer by recognising direct statements of intent or by recognising other clues of intent such as type of text, style and use of language, and overall tone. 2. Identify the point of view or attitude of the writer by distinguishing between fact and opinion, between the writer’s own view and his/her presentation of other views, between a neutral tone and an ironic tone. SKILL D: Identify the main idea of a paragraph; understand the development of ideas in a paragraph via common rhetorical devices such as general statement and illustrative support, comparison and contrast, cause and effect. 1. Recognize the markers of comparison and contrast. Identify comparison and contrast of ideas. Recognise what two things are being compared or contrasted and what is the point of the comparison or contrast. 2. Recognize the markers of cause and effect. Identify cause and effect relationships, distinguishing the cause or reason from the result or effect, and connecting the cause with its particular result. 3. Recognise other common markers such as: markers of frequency, listing and problem and solution. SKILL E: Infer meaning at both sentential and discourse levels. 1. Infer the main idea of a text when it is not stated directly by using general knowledge and textual clues. 2. Infer the tone of a text (ironic, humorous, sceptical, sarcastic) from indirect statements and stylistic devices such as exaggeration, understatement and inflated language. 3. Infer the writer’s point of view/position from references to opposing viewpoints and tone of personal statements. SKILL F: Develop conscious awareness of cognitive strategies as tools in reading. 1. Recognise that high cognitive strategies combine with lower decoding strategies in reading comprehension. 2. Make conscious use of reading skills. LANGUAGE SKILLS SKILL G: Build and master vocabulary adequate for reading texts at the basic-academic level and deduce meanings of other words via morphological, syntactic and context clues. 1. Make predictions while reading so that expectations give meaning to unknown words. 2. Be aware of idioms and figurative language. 3. Recognize which words are more important for the general meaning of the passage and which words are less important. SKILL H: Understand the meaning of a sentence with the help of syntactic clues. 1. Use markers to understand the logical relationship between the main clause and the other clauses, i.e., the type of information conveyed by each clause. 2. Understand the meaning conveyed by grammatical structures (tenses, modals, conditionals, and verbals (gerund and participle non-verb forms). 3. Read sentences in meaningful units. SKILL I: Identify the meanings of references and ellipses within and between sentences. 1. Recognize ellipses, relative pronouns, reduced adjective clauses and other instances of ellipsis within and between sentences. 2. Deduce the meanings of unknown words by recognising the writer’s use of references.