Fricatives
advertisement

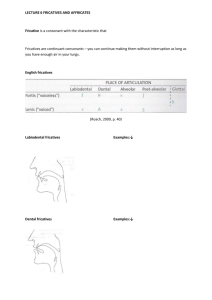
Fricatives Fricatives are produced when the air passes through a narrow passage where it causes friction of various types. Fricatives are continuant consonants, which means that they can be produced continually without interruption. There are nine fricatives in English such as /f, v,ϴ, ð, s, z, ʃ, ʒ and /h/. They can be described as follows: 1. /f/ labiodental, fricative, voiceless, fortis 2. /v/ labiodental, fricative, voiced, lenis 3. /ϴ/ dental, fricative, voiceless, fortis 4. /ð/ dental, fricative, voiced, lenis 5. /s/ alveolar, fricative, voiceless, fortis 6. /z/ alveolar, fricative, voiced, lenis 7. /ʃ/ post – alveolar, fricative, voiceless, fortis 8. /ʒ/ post – alveolar, fricative, voiced, lenis 9. /h/ glottal, fricative, voiceless Distribution of fricatives The fricatives /f, v, ϴ, ð, s, z/ and /ʃ/ ocuur initially, medially and finally. /ʒ/ occurs medially and finally but not ini8tially as in measure /meʒə/, garage /gəræʒ/. /h/ occurs initially and medially but not finally as in who /hu:/, behind /bihaind/. Phonologically, /h/ is a consonant. It is found before vowels. /h/ can be omitted in unstressed pronunciation of the words her, he, him, his and the auxiliary have, has, had The affricates Affricates are rather complex consonants. they begin as plosives and end as fricatives. Such sounds are /ʧ/ and /ʤ/ as illustrated in the word change /ʧeinʤ/ where it has /ʧ/ and /ʤ/. It should be noted that /ʧ/ and /ʤ/ are considered as single phonemes. Thus the word change transcribed above has four phonemes such as: /ʧ/,/ei/, /n/ and /ʤ/. It is impossible to class all sequences of plosive plus fricative as affricate. For example, the combination /k/ plus /f/ in the middle of the word breakfast is not affricate because /k/ and /f/ are produced with different articulators in that /k/ is produced when the back of the tongue touches the soft palate, whereas /f/ is produced when the lower lip touches the upper front teeth. On the other hand, /t/ and /ʃ/ are produced with same articulators, I,e. the blade of the tongue touches the alveolar ridge. This means that they are homorganic. Fortis consonants Fortis fricatives and plosives shorten the preceding vowels.thus, the diphthong /ai/ in ice /ais/ is shorter than /ai/ in eyes/aiz/. Similarly, fortis consonants such as /p/, /t/ and /k/ shorten the preceding consonants such as /l/, /m/, /n/ and /ŋ/ as in belt /belt/, bent /bent/ and so on. Voiced consonants such as /l, r, w j/ become voiceless when preceded by fortis consonants such as the plosives /p, t, k/ as in play /plei/ and so on.