Grade 8 Module 2 – Lesson 13
advertisement

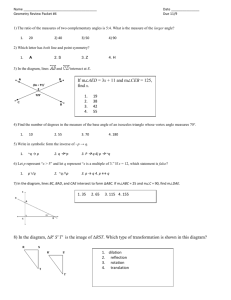
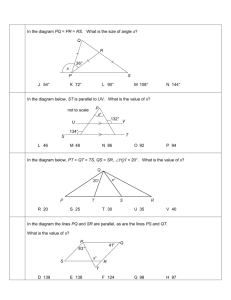
Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ Grade 8 Module 2 – Lesson 13 ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How can algebraic concepts be applied to geometry? G5: Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angles of a triangle. A. INQUIRY LAB: SUM OF THE INTERIOR ANGLES OF A TRIANGLE STEP 1: Using a pair of scissors, cut a triangle out of the bottom corner of the paper. STEP 2: Inside the triangle label each of the three angles with a letter STEP 3: Tear off the three angles of the triangle, being sure to tear the letter too. C A B STEP 4: Rearrange the torn pieces so that all three vertices (angles) meet at one point. STEP 5: Sketch the arrangement you made below. What do you notice about these three angles when they are all put together? What about your partner? Did s/he get the same results? Page 1 Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ CONCLUSIONS: The sum of the measures of the three angles of a triangle always equals_______ degrees, or a(n) _______________ angle. 𝑚∠1 + 𝑚∠2 + 𝑚∠3 = ________° 45° 90° 𝑚∠1 + 𝑚∠2 + 𝑚∠3 = ________° _________ + ________ + ________ = ________° If one angle of a triangle measures 32 degrees, and another angle measures 107 degrees, then show work to find the measure of the third angle. The name of this triangle by its angles is __________, and by its sides is _________________. In a right triangle, an acute angle measures 50 degrees. Show work to determine the measure of the other acute angle. Page 2 Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ B. INQUIRY LAB: SUM OF THE EXTERIOR ANGLES OF A TRIANGLE STEP 1: Record the measurements of angles A, B, and C on the diagram. Angle A = 43⁰, Angle B = 42⁰, and Angle C = 95⁰. STEP 2: Using each vertex angle ONCE, extend a ray out from each vertex. (One of the three is drawn for you) STEP 3: Once done drawing these rays, label the three new angles D, E, F. (One of the three is done for you) A B D C Angle D is known as a REMOTE angle or an exterior angle of the triangle. STEP 4: Record the measurements of angles D, E, and F on the diagram. Angle D = 138⁰, Angle E = 85⁰, and Angle F = 137⁰. Let’s see if we can find a relationship among these angles. What do you notice? If you know the measures of the interior angles, are there ways to determine the measure of the exterior angles? SUM OF THE EXTERIOR ANGLES OF A TRIANGLE The measure of an exterior angle is equal to the sum of its two REMOTE interior angles. Angle F = angle _____ + angle _____ Angle D = angle _____ + angle _____ Angle E = angle _____ + angle _____ Page 3 Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Find the value of angle X. X 22 134 Find the value of angle X. X 120 58 Find the value of angle X. X 125 170 Page 4 Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ 1) In the diagram below, line 𝐴𝐵 is parallel to line 𝐶𝐷, i.e., 𝐿𝐴𝐵 ∥ 𝐿𝐶𝐷 . The measure of angle ∠𝐴𝐵𝐶 = 28°, and the measure of angle ∠𝐸𝐷𝐶 = 42°. What is the measure of angle ∠𝐶𝐸𝐷? _________________ Explain why you are correct by presenting an informal argument that uses the angle sum of a triangle and what you know about corresponding angles and alternate interior angles. 2) In the diagram below, line 𝐴𝐵 is parallel to line 𝐶𝐷, i.e., 𝐿𝐴𝐵 ∥ 𝐿𝐶𝐷 . The measure of angle ∠𝐴𝐵𝐸 = 38°, and the measure of angle ∠𝐸𝐷𝐶 = 16°. What is the measure of angle ∠𝐵𝐸𝐷? _________________ Explain why you are correct by presenting an informal argument that uses the angle sum of a triangle and what you know about corresponding angles and alternate interior angles. [Hint: Find the measure of angle ∠𝐶𝐸𝐷 first, and then use that measure to find the measure of angle ∠𝐵𝐸𝐷.] Page 5 Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ 3) In the diagram below, line 𝐴𝐵 is parallel to line 𝐶𝐷, i.e., 𝐿𝐴𝐵 ∥ 𝐿𝐶𝐷 . The measure of angle ∠𝐴𝐵𝐸 = 56°, and the measure of angle ∠𝐸𝐷𝐶 = 22°. (Hint: Extend the segment 𝐵𝐸 so that it intersects line 𝐶𝐷.) What is the measure of angle ∠𝐵𝐸𝐷? _________________ Explain why you are correct by presenting an informal argument that uses the angle sum of a triangle and what you know about corresponding angles and alternate interior angles. [Hint: Extend the segment 𝐵𝐸 so that it intersects line 𝐶𝐷.] 4) What is the measure of ∠𝐴𝐶𝐵? _________________ Page 6 Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ 5) What is the measure of ∠𝐸𝐹𝐷? _________________ 6) What is the measure of ∠𝐻𝐼𝐺? _____________ 7) What is the measure of ∠𝐴𝐵𝐶? ______________ 8) Triangle 𝐷𝐸𝐹 is a right triangle. What is the measure of ∠𝐸𝐹𝐷? _________________ Page 7 Name _________________________________Period ___ Date ______________ 9) In the diagram below, lines 𝐿1 and 𝐿2 are parallel. Transversals 𝑟 and 𝑠 intersect both lines at the points shown below. What is the measure of ∠𝐽𝑀𝐾? __________________ Explain how you know you are correct. Page 8