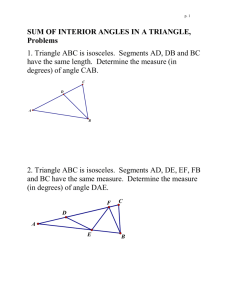
Solving Right Triangles: Procedures & Examples
advertisement
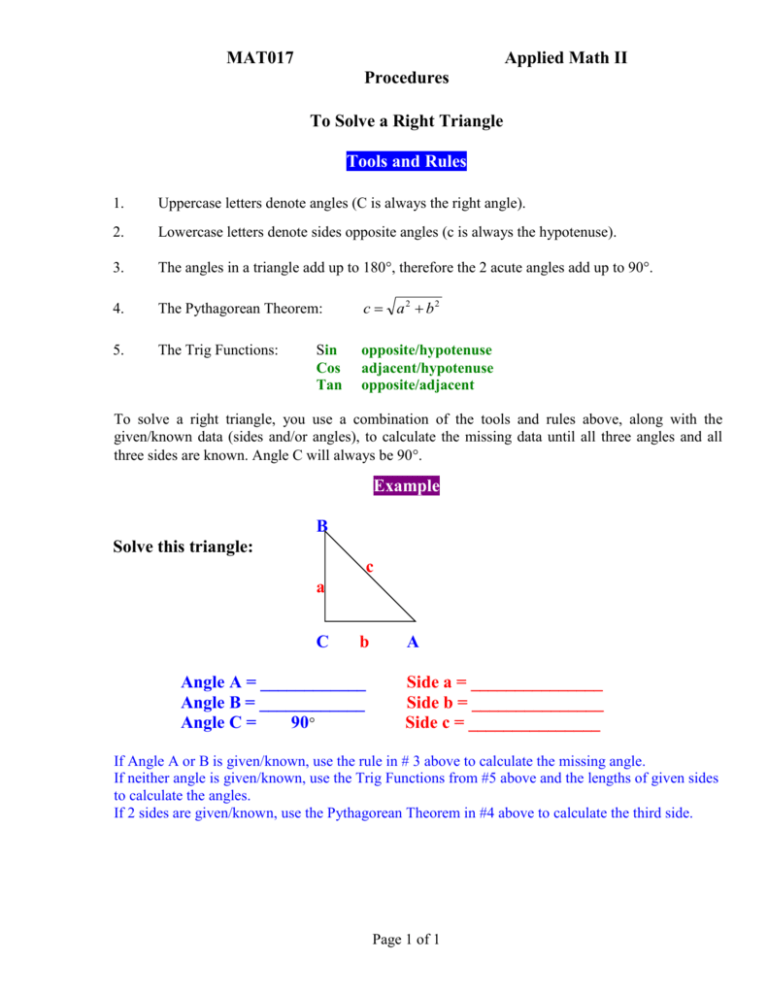
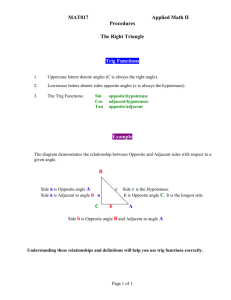
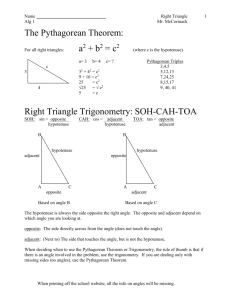
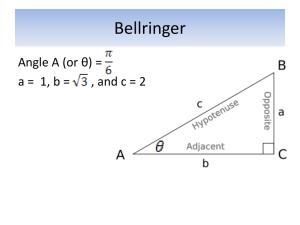
MAT017 Applied Math II Procedures To Solve a Right Triangle Tools and Rules 1. Uppercase letters denote angles (C is always the right angle). 2. Lowercase letters denote sides opposite angles (c is always the hypotenuse). 3. The angles in a triangle add up to 180, therefore the 2 acute angles add up to 90. 4. The Pythagorean Theorem: c a2 b2 5. The Trig Functions: opposite/hypotenuse adjacent/hypotenuse opposite/adjacent Sin Cos Tan To solve a right triangle, you use a combination of the tools and rules above, along with the given/known data (sides and/or angles), to calculate the missing data until all three angles and all three sides are known. Angle C will always be 90. Example B Solve this triangle: c a C b Angle A = ____________ Angle B = ____________ Angle C = 90 A Side a = _______________ Side b = _______________ Side c = _______________ If Angle A or B is given/known, use the rule in # 3 above to calculate the missing angle. If neither angle is given/known, use the Trig Functions from #5 above and the lengths of given sides to calculate the angles. If 2 sides are given/known, use the Pythagorean Theorem in #4 above to calculate the third side. Page 1 of 1