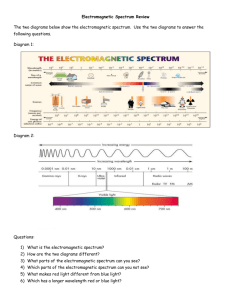
Electromagnetic Spectrum Questions Worksheet
advertisement

Some Harder Electromagnetic Spectrum Questions: The number of available marks is indicated at the end of each question. What type of electromagnetic radiation radiates from warm objects? Infrared [1] Describe surfaces that are good absorbers of radiation and those that are good reflectors of radiation. Good absorbers = dark, matt surfaces Good reflectors = light, shiny surfaces [2] A good absorber is also a good emitter – true or false? True. Dark, matt surfaces are good at both emitting and absorbing radiation [2] A good emitter is also a good reflector – true or false? False. Dark, matt surfaces are good emitters, but light shiny surfaces are good reflectors. [2] Which type of wave has the highest frequency in the Electromagnetic spectrum? Gamma [1] Which type of wave has the lowest frequency in the Electromagnetic spectrum? Radio waves [1] Which 2 Electromagnetic waves are adjacent (next to) Visible light in the Electromagnetic spectrum? Ultraviolet and Infrared [2] Which 2 Electromagnetic waves lay between Visible light and Gamma waves in the Electromagnetic Spectrum? Ultraviolet and X-rays [2] How fast do Electromagnetic waves travel? 300,000,000m/s [1] Which of the Electromagnetic waves is used in sun beds? Ultraviolet [1] List 2 uses of Microwaves. Cooking and Communication [2] How can Electromagnetic waves cause, detect and cure cancer? Energetic Electromagnetic waves may cause damage to cells, leading to cancer X-rays can be used to detect tumours Gamma waves and X-rays can be used to destroy cancerous tissue [4] Which of the Electromagnetic waves is used in optical fiber communication? Give other uses for these waves. Infrared; can also be used in TV remote controls, heat lamps, thermal imaging and night vision. [3] What is meant by the frequency of a wave? The number of waves passing a particular point in 1 second [1] Wavelength can be described as the distance from 1 wave crest to the next. Give a more general definition than this. Wavelength is the distance from a particular point on the wave to the equivalent point on the next wave [1] If you measure the height of a wave from the trough to the crest, how does this relate to the amplitude? Twice the amplitude [1] TOTAL MARKS: /27