Weather Factors Vocabulary
advertisement

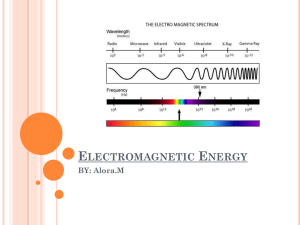
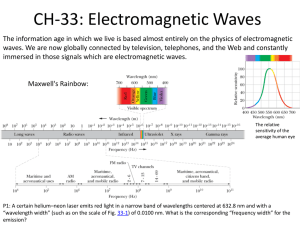
Weather Factors Vocabulary 1. Electromagnetic waves- waves that transfer electric and magnetic energy through space 2. Radiation-the direct transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves 3. Infrared radiation- electromagnetic waves with wavelength that are longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves 4. Ultraviolet radiation- electromagnetic waves with wavelength that are shorter than visible light but longer than X rays 5. Scattering – reflection of light in all directions 6. Greenhouse effect- the process by which heat is trapped in the atmosphere by gases that form a “blanket” around Earth 7. Temperature- a measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to a referenced point 8. Thermometer- an instrument used to measure heat 9. Heat- transfer of thermal energy from one object to another 10. Conduction-the direct transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another 11. Convection- the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a fluid 12. Convection currents- the circulation of a fluid as it alternately heats up and cools down 13. Wind- the horizontal movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure 14. Anemometer-an instruments used to measure wind speed 15. Wind-chill factor- a measure of cooling combing temperature and wind speed 16. Local winds- winds that blow over short distances 17. Sea breeze- the flow of cooler air from over an ocean or lake towards land 18. Land breeze- the flow of air from land to a body of water 19. Global winds- wind that blow steadily from specific directions over long distances 20. Coriolis effect- the change that Earth’s rotation causes in the motion of objects & that explains how wind curve 21. Jet stream- bands of high-speed winds about 10 km above Earth’s surface 22. Humidity- the amount of water vapor in a given volume of air 23. Relative humidity- the percentage of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount of water vapor that air can contain at a particular temperature. 24. Psychrometer- an instrument used to measure relative humidity 25. Dew point- the temperature at which condensation begins 26. Cirrus- wispy, feathery clouds made of ice crystals that form at high levels 27. Cumulus- fluffy, white clouds with flat bottoms 28. Stratus- clouds that form in flat layers of often cover much of the sky 29. Cloud seeding- a method of changing precipitation 30. Rain gauge – an instrument used to measure precipitation