Conceptual Questions
advertisement

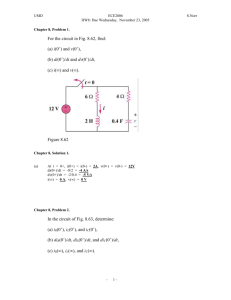
Physics 1402 Formula Sheet Chapter 19: Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields q1 q2 F k F qE r 2 q Ek EA cos r2 Qencl 0 Chapter 20: Electric Potential and Electric Potential Energy U q0 V Ex q r qq U k 1 2 r V V V , Ey , Ez x y z V k Q CV C 0 U A (parallel-plate capacitor) d 1 Q2 1 CV 2 QV 2 2C 2 1 uE 0 E 2 (energy density) 2 Chapter 21: Electric Current and Direct-Current Circuits I av Q t I lim Q t 0 t Pav U t P IV V IR P I 2R R V2 (for resistor) R L A Resistors and Capacitors in Series and Parallel 1 1 1 Series: Req R1 R2 RN Ceq C1 C2 Series: Parallel: 1 1 1 Req R1 R2 1 RN Parallel: Ceq C1 C2 RC Circuits Charging: t q (t ) C 1 e RC I t e RC R t Discharging: t RC q(t ) Q0 e Q I t 0 e RC RC t 1 CN CN Physics 1402 Formula Sheet Page 2 Chapter 22: Magnetism F q vB sin r B F ILB sin E (velocity selector) B v mv (uniform magnetic field) qB B 0 I (long, straight wire) 2 r B 0 nI (inside ideal solenoid) F 0 I 0 I1 I 2 L 2 d Chapter 23: Magnetic Flux and Faraday’s Law of Induction BA cos av N t Motional EMF I B v B v R B 2 2v R B2v2 2 P R F Inductance av I L t 1 U LI 2 2 Vp N2 L 0 n 2 A 0 A (solenoid) B2 uB (energy density) 2 0 Transformers Vs Np Ns Is N p I p Ns Physics 1402 Formula Sheet Page 3 Chapter 24: AC Circuits Root-mean-square Voltages and Currents I max V Vrms max 2 2 I rms 2 Pav I rms R 2 Vrms (average power dissipated in resistor) R Capacitors in AC Circuits 1 1 XC Vmax I max X C C 2 fC Vrms I rms X C Z R X Vrms I rms Z tan 1 X L L 2 fL Vrms I rms X L Z R X Vrms I rms Z tan 1 Z R2 X L X C Vrms I rms Z 0 RC Circuits 2 2 C Vmax I max Z Pav I rmsVrms cos XC R cos 1 (phase angle by which voltage lags current) Z R Inductors in AC Circuits Vmax I max X L RL Circuits 2 2 L XL R Vmax I max Z Pav I rmsVrms cos 1 R cos Z (phase angle by which voltage leads current) RLC Circuits and Resonance 1 LC X XC tan 1 L R 2 Vmax I max Z Pav I rmsVrms cos f0 1 2 LC 1 R cos Z (phase angle by which voltage leads current) Physics 1402 Formula Sheet Page 4 Chapter 25: Electromagnetic Waves Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1 c vf 0 0 Energy in Electromagnetic Waves 1 uE 0 E 2 2 utotal uE uB 0 E 2 U I av At P I A 1 uB 20 E cB Pav I c0 E 2 2 B U t Polarization 1 I trans I 0 (for unpolarized light hitting a polarizer) 2 Itrans I0 cos2 (Law of Malus) Chapter 26: Geometrical Optics Reflection of Light & Spherical Mirrors 1 r i (Law of Reflection) f R 2 hi d 1 1 1 m i (magnification) (Mirror Equation) d o di f ho do Refraction of Light c n v 1 1 1 (Thin-lens Equation) d o di f n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 (Snell’s law) Thin Lenses m hi d i (magnification) ho do Chapter 27 Refractive power = 1/f; f – number = f/D Magnifying glass M = N/f; or M = 1+ N/f; Microscope: M = -(di N)/(fefo); Telescope: M = fo/fe, L = fo+fe Chapter 28: Physical Optics 2 2 Superposition and Interference (condition for constructive interference) 1 m , m 0, 1, 2, 1 1 m , m 0, 1, 2, 2 (condition for destructive interference) Young’s Double-Slit Experiment d sin m , m 0, 1, 2, (constructive interference) 1 d sin m , m 0, 1, 2, 2 small-angle approximation: (destructive interference) y L tan Physics 1402 Formula Sheet Page 5 tan sin For thin film, you need to consider if there is a /2 change; also the changes in the medium to /n. Diffraction W sin m , m 1, 2, (destructive interference – single-slit diffraction) d sin m , m 0, 1, 2, (constructive interference – diffraction grating) Modern Physics E1 13.6 2 eV 2 n n t t N N 0e , R R0e ln 2 T1/2 , T1/2 ( 14C ) 5730 years rn n 2 r1 , r 1.2 1015 A1/3 (m) m0v p 1 v2 / c2 E 1 v / c K E E0 p E/c 2 2 , E0 m0 c 2 1 1 1 R 2 2 n m Wien ' s law f peak 5.88 1010 T p En nhf , n 0,1, 2, 3,... K max hf W0 f0 t h (1 cos ) me c L L0 1 v2 c2 N m2 k 9.00 109 0 8.85 1012 C2 1 k 4 0 C2 N m2 Tm 0 4 107 A 19 e 1.60 10 C (magnitude of charge on electron) me 9.111031 kg (mass of electron) m p 1.673 1027 kg (mass of proton) mn 1.675 1027 kg (mass of neutron) 1 eV 1.602 1019 J c 3.00 108 m/s (speed of light in vacuum) h 6.626 1034 J s (Planck’s constant) E hf Physical Constants h m0 c 2 En W0 (cutoff frequency) h t0 1 v2 c2 Physics 1402 Formula Sheet Areas & Volumes Circumference of a circle, radius r : C 2 r Area of a circle, radius r : A r 2 Surface area of sphere, radius r : A 4 r 2 4 Volume of sphere, radius r : V r 3 3 Area of lateral surface of a right circular cylinder, radius r , length Page 6 Volume of right circular cylinder, radius r , length Trigonometric Identities sin A B sin A cos B cos Asin B sin(t 90 ) cos t : V r 2 : A 2 r