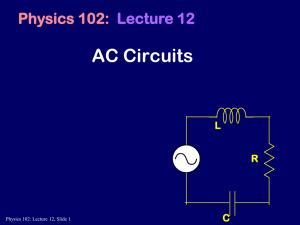
AC Voltages and Phasors Resistors, Inductors and Capacitors in AC Circuits RLC Circuits
advertisement

AC Voltages and Phasors Resistors, Inductors and Capacitors in AC Circuits RLC Circuits Power and Resonance Transformers AC sources have voltages and currents that vary sinusoidally. The current in a circuit driven by an AC source also oscillates at the same frequency. The standard AC frequency in the US is 60 Hz (337 rad/s). v(t ) Vmax sin(t ) 1 2 T f Consider a sinusoidal voltage source: v(t ) Vmax sin(t ) This source can be represented graphically as a vector called a phasor: v(t) Vmax b b Vmax v(t) t T a c -Vmax e d t c a e d v - vR 0 Vmax sin t vR iR I max vR Vmax sin t I max sin t R R Vmax vR I max R sin t R Since both have the same arguments in the sine term, iR and vR are in line, they are in phase. iR I max sin t P (t ) RiR RI max sin 2 t 2 2 P (t ) RiR RI max sin 2 t 2 Pav RI max I rms 2 2 1 2 I rms R 2 I max 0.707 I max 2 Vrms Vmax 0.707Vmax 2 v - vL 0 Vmax sin t L di iL di dt Vmax sin tdt L iL di - Vmax cos t L For a sinusoidal voltage, the current in the inductor always lags the voltage across it by 90°. Vmax sin t - L 2 I max Vmax Vmax L XL X L L Inductive Reactance vL - I max X L sin t v vC Vmax sin t I max CVmax q CVmax sin t dq CVmax cos t dt iC CVmax sin t 2 iC For a sinusoidal voltage, the current in the capacitor always leads the voltage across it by 90°. XC 1 C Vmax XC Capacitive Reactance vC I max X C sin t v Vmax sin t i I max sint - vR I max R sin t VR sin t vL I max X L sin t VL cos t 2 vC I max X C sin t - -VC cos t 2 v vR vL vC Vmax VR VL - VC 2 2 I max R 2 I max X L - I max X C 2 Vmax Vmax I max R 2 X L - X C 2 I max Vmax R2 X L - X C 2 Z R2 X L - X C 2 Vmax I max Z X L - XC R tan -1 Impedance R = 425 W L = 1.25 H C = 3.5 mF = 377 s-1 Vmax = 150 V vR 124V sin 377t 1 1 758W C 377 s -1 3.5mF Z R2 X L - X C 2 I max 425W2 471W - 758W2 Vmax 150V 0.292 A Z 513W X L - XC R tan -1 -1 471W - 758W tan -34 425 W VL I max X L 0.292 A471W 138V VC I max X C 0.292 A758W 221V X L L 377s -1 1.25H 471W XC VR I max R 0.292 A425W 124V 513W vL 138V cos 377t vC -221V cos 377t P iv I max sint - Vmax sin t P I max Vmax sin t cos - cos t sin sin t P I max Vmax sin 2 t cos - I max Vmax sin t cos t sin 1 Pav I max Vmax cos 2 Pav I rms Vrms cos vR Vmax cos I max R Vmax Pav I rms 2 I max R I max R I rms 2 Vmax Pav I rms R 2 No power loss occurs in an ideal capacitor or inductor. For a purely resistive load, =0 Pav I rms Vrms A circuit is in resonance when its current is maximum. I rms Vrms Z I rms Vrms R2 X L - X C 2 Irms=max when XL-XC=0 X L XC 1 0 L 0 C 0 1 LC Resonance Frequency Pav I rms 2 V 2 rms R R Z2 X L - X C 2 Pav Pav,max 2 1 L2 2 2 L 2 - 0 C Vrms 2 R 2 R L - 0 2 Vrms 2 R 2 R2 X L - X C 2 2 2 Vrms R 0 0 L Q R 2 2 2 =0 Quality Factor 2 V1 - N1 d B dt d B V2 - N 2 dt N2 V2 V1 N1 I1V1 I 2 V2 V1 I1 Req V2 I2 RL 2 N1 RL Req N2 Power is transmitted in high voltage over long distances and then gradually stepped down to 240V by the time it gets to a house. 22 kV 230 kV 240 V 20 106W I 87 A 3 V 230 10 V For 22kV transmission: P I 2 R 87 A 2W 15kW Total Cost = $4100 Pg P g= 20 MW Cost = 10¢/kWh 2 TotalCost 15kW 24h$0.1 $36 Midterm 2 Review on Tuesday Midterm 2 on Wednesday Reading Assignment for Thursday Chapter 34 – Electromagnetic Waves WebAssign: Assignment 11 (due Tuesday, 5 PM)