Glossary - The Birman Cat Club
advertisement

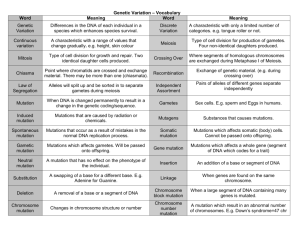
Glossary Allele: alternative forms of the same gene Allelic heterogeneity: the existence of many different disease-causing alleles at a locus Amino acid: building block of proteins, there are 20 of these Autosome: any chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes X and Y Back cross: where a son or daughter is mated back to one of its parents or grandparents Candidate gene: a gene that is suspected of being the disease gene Chromosome: Contains the main information carrying single piece of double stranded DNA Codon: a nucleotide triplet Congenital: existing at birth, not inherited Congenital disorder: may be the result of genetic abnormalities, the inter-uterine environment, errors of development, infection during pregnancy, chromosomal abnormalities Compound heterozygote: an animal with two different mutant alleles at one locus Constitutional: a genotype, abnormality or mutation that was present in the fertilised egg and is therefore present in all the cells of that animal Diploid: having two copies of each type of chromosome, the normal constitution of most human somatic cells DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid Dominant negative: a mutant gene whose product can inhibit the function of the normal wild-type gene when present in one copy Dominant: in genetics any trait that is expressed in the heterozygous form ES cells: Embryonic stem cells. These are cells that can differentiated into any cell type found in the body Exon: a segment of a gene F1 generation: first generation progeny from a cross F2 generation: second generation progeny from a cross Founder effect: high frequency of a particular allele in a population because the population was derived from a small number of founders Frameshift mutation: a mutation that alters the normal translational reading frame by adding or deleting nucleotides such that the normal reading frame of multiples of 3 is altered Genotype: the genetic constitution of an individual Germ cells/gametes: sperm cells and egg cells Haploid: describing a cell (typically a gamete) which has only a single copy of each chromosome Haplotype: a series of alleles found next to each other (linked) on a single chromosome Hemizygous: having only one copy of a gene or DNA in diploid cells. Males are hemizygous for most genes on the sex chromosomes Heterozygote: an individual having two different alleles at a given locus Homozygote: an individual having two identical alleles at a particular locus Inbreeding: marrying a blood relative Intron: non-coding DNA that separates exons Karyotype: summary of chromosome constitution of cell or individual (male human is 46,XY; female human is 46, XX; male cat is 36, XY; female cat is 46,XX) Linkage disequilibrium: a statistical association between particular alleles at separate but linked loci Matrilineal inheritance: inheritance from just the mother to the children of either sex (mitochondrial inheritance) Missense mutation: a change in the DNA that results in the change of one amino acid for another Nonsense mutation: a mutation that results in the substitution of an amino acid for a stop codon Nucleotide: building blocks of DNA and RNA, there are four for RNA and four for DNA Penetrance: the frequency with which a genotype manifests itself in a given phenotype Phenotype: the observable characteristics of a cell or organism Point mutation: usually a single nucleotide change Polymorphism: the existence of two or more alleles/variants present at a significant frequency in the population Recessive: a character is recessive if it is manifest only in the homozygote form i.e. has to be inherited from both parents RNA: ribonucleic acid Semi-dominant: an allele in the heterozygote produces a phenotype intermediate between the wild type and the homozygote Sibs: siblings (brothers and sisters) Somatic cell: any cell in the body apart from the gametes Synonymous substitution: a substitution that replaces one codon for another but does not change the amino acid Stop codon or termination codon: There are three of these. They act as protein full stops Transition: Type of mutation in DNA where G and A are swapped or C and T are swapped Transversion: Type of mutation in DNA where G and A replaced by C or T and vice versa X inactivation: the inactivation of one of the two X chromosomes in females