2013-Three-Level-Questions-grid-1
advertisement

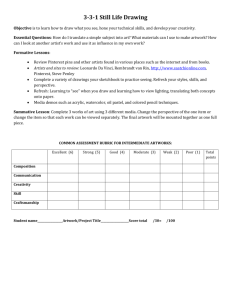
BLOOMS HoTs CCEs 3 level questions DOL Analysing /Applying /Understanding Remembering / recall Who,What,When,Where,Why? 1. Recognising words, letters and other symbols, 11. Compiling lists/statistics, 12. Recording/noting data, 13. Compiling results in a tabular form, 14. Graphing, 18. Substituting in formulae 26. Classifying 31. Extrapolating 46. Observing systematically 42. Perceiving patterns 44. Identifying shapes in two and three dimensions 45. Searching and locating items/information 48. Manipulating/operating/using equipment 4. Interpreting the meaning of words or other symbols, 5. Interpreting the meaning of pictures/illustrations, 6. Interpreting the meaning of tables or diagrams or maps or graphs, 22 Explaining to others 27. Interrelating ideas/themes/issues 28. Reaching a conclusion which is necessarily true provided a given set of assumptions is true 37 Analysing 38. Synthesising 16 Estimating numerical magnitude 23. Expounding a viewpoint 29. Reaching a conclusion which is consistent with a given set of assumptions 30. Inserting an intermediate between members of a series 31. Extrapolating 32. Applying strategies to trial and test ideas and procedures 33. Applying a progression of steps to achieve the required answer 34. Generalising from information 35. Hypothesising 36. Criticising 37 Analysing 38. Synthesising 43. Visualising 47. Gesturing LITERAL D2 – acquire and integrate (gathering/researching relevant information) helping students acquire and facilitate new knowledge is another important aspect of learning. When students are learning new information, they must be guided in relating the new knowledge to what they already know, organising that information, and then making it a part of their long-term memory. When students are acquiring new skills and processes they must learn a model, or set of steps, then shape the skill or process to make it efficient and effective for them. They must finally internalise or practice the skill or process so they can perform it easily. INTERPRATIVE Identify the over-arching ideas, themes and issues in a mind-map. Identify the associated/hidden ideas, themes and issues (may use mind map) Identify the audience of the text/work/product Identify conventions of interrelating ideas/themes/issues – contextual; required outcome; desired grouping principle….etc. Review concepts being studied. Interrelating skills – making observations; identifying patterns, trends; look for anomalies D3 – extend and refine (draw inferences from analysing gathered information) Learners develop in-depth understanding through the process of extending and refining their knowledge, by making new distinctions, clearing up misconceptions and reaching conclusions. They analyse what they have learned by applying reasoning processes that will help them extend and refine the information. Evaluating / creating 7. Translating from one form to another, 19. Setting out/presenting/arranging/displaying 20. Structuring/organising extended written text 21. Structuring/organising a mathematical argument 23. Expounding a viewpoint 24. Empathising 25. Comparing, contrasting 27. Interrelating ideas/themes/issues 28. Reaching a conclusion which is necessarily true provided a given set of assumptions is true 39. Judging/evaluating 41. Justifying 49. Sketching/drawing APPLICATION D4 – use meaningfully (apply new knowledge in evaluating) The most effective learning occurs when we use knowledge to perform meaningful tasks. Making sure that students have the opportunity to use knowledge meaningfully is one of the most important parts of planning a unit of instruction. Creating Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things Designing, constructing, planning, producing, inventing. Evaluating Justifying a decision or course of action Checking, hypothesising, critiquing, experimenting, judging Analysing Breaking information into parts to explore understandings and relationships Comparing, organising, deconstructing, interrogating Applying Using information in another familiar situation Implementing, carrying out, using, executing Understanding Explaining ideas or concepts Interpreting, summarising, paraphrasing, classifying, explaining Remembering Recalling information Recognising, listing, describing, retrieving, naming, finding Remembering - level 1 questions - LITERAL Recalling information Recognising, listing, describing, retrieving, naming, finding Locate Identify Recall Memorise Relate Show Locate Distinguish Give example Reproduce Group Outline Group Choose Label Select Underline Cite Sort Repeat Recite Review Quote Record Match Understanding - level 2 questions - INTERPRATIVE Explaining ideas or concepts Interpreting, summarising, paraphrasing, classifying, explaining Discuss Retell Research Annotate Translate Paraphrase Reorganise Associate Describe Report Recognise Review Observe Interpret Give main idea Estimate Define Account for Give examples Outline Restate Applying – level 2 questions - INTERPRATIVE Using information in another familiar situation Implementing, carrying out, using, executing Translate Manipulate Exhibit Illustrate Interpret Practice Apply Demonstrate Interview Change Compute Calculate Sequence Show Solve Collect Dramatise Construct Adapt Draw Analysing – level 2 questions - INTERPRATIVE Breaking information into parts to explore understandings and relationships Comparing, organising, deconstructing, interrogating Distinguish Question Appraise Inspect Examine Probe Separate Inquire Arrange Test Investigate Research Calculate Criticize Compare Contrast Survey Detect Group Order Sequence Relate Dissect Categorise Discriminate Debate Draw diagram Evaluating – level 3 questions - APPLICATION Justifying a decision or course of action Checking, hypothesising, critiquing, experimenting, judging Judge Rate Validate Predict Assess Discriminate Revise Infer Determine Prioritise Explain why Compare Defend Select Measure Choose Conclude Deduce Debate Justify Recommend Reject Appraise Value Argue Decide Criticise Rank Creating – level 3 questions - APPLICATION Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things Designing, constructing, planning, producing, inventing. Compose Assemble Invent Compile Forecast Devise Construct Generate Prepare Develop Originate Imagine Formulate Improve Predict Produce Blend Devise Concoct Plan Art Appraising Task levels Steps Art criticism Art history Suggested questions LITERAL Description Literal qualities and/or formal qualities (elements of art) Make an inventory listing the subject matter and/or the elements of art found in the work. Determine when, where and by whom the work was completed. What is it? What is it made from? Who made it? How was it made? Where was it made? When was it made? What does it look like? INTERPRATIVE Analysis Formal qualities (principles/ concepts of art) Determine how the work of art is organised or put together; concern centres on how the art principles/concepts have been organised in relation to the art elements. Identify the features in the work of art and compare these with features found in other works to determine its artistic style. What type of lines, shapes, colours and texture appear in the artwork? How have the art and design concepts been produced and what relationship do they have to the art and design elements? What is the dominant element/concept in the composition and how and why is it produced? Compare and contrast this work with another of a similar theme. Interpretation Expressive qualities Determine the possible feelings, moods or ideas communicated by the artwork. Investigate the influences of time and place upon the artist. What is the artist trying to express in this work? What is the story or meaning of the artwork? Why was it made? Why is it made from these materials? Is the style of work representational or non-representational? Why? Does the style and form of the work increase what the artist wants to say? What other works influenced this work? How is the mood or atmosphere of the work created and how does it relate to the meaning of the work? Does the work relate to a cultural or historic context? How? What influence does the time and place have on the meaning of the work? Judgment and Evaluation Make decisions about the artistic merit of the artwork. This decision takes into account all you have learned about the work during the previous art criticism steps. Make decisions about the work’s importance in terms of its historical and cultural context, and justify decisions. How is the artwork successful in communicating its meaning? Why are the art and design elements and concepts positioned in the work in a certain compositional structure? Why were these materials chosen and how do they relate to the influence and style of the work? Why does the artist choose this particular process and how is it unique? How does the genre of the work influence or determine the style? Why is the work significant historically and culturally? APPLICATION