VSEPR Theory - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
advertisement

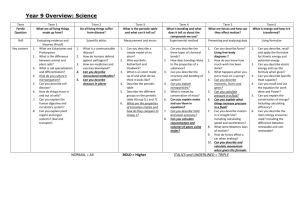
VSEPR Theory: VSEPR means Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory This theory is used to predict shapes of molecules. The basic idea is that the shape of the molecule depends on the number of electron pair that surround the central atom in the molecule. The rule that is applied is that the electron pairs around the central atom in the molecule will repel each other and go as far apart as possible. Multiple bonds (double or triple) count as one bonding pair for VSEPR predictions. Your knowledge of geometry will be used to determine how far apart the electron pairs about the central atom are when they are as far apart as possible. Number of and type Atoms (bonding or nonbonding atoms) 4 bonding pairs Shape Angles between bonding pairs Tetrahedral 109.5° 3 bonding pairs Triangular Pyramid and 1 non-bonding 107° pair 2 bonding pairs Bent or V-shaped and 2 non-bonding 104.5° pairs 2 bonding pairs Linear 180° 3 bonding pairs Triangular Planar 120° Diagram/Example VSEPR Theory: VSEPR means Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. This theory is used to predict shapes of molecules. The basic idea is that the shape of the molecule depends on the number of electron pair that surround the central atom in the molecule. The rule that is applied is that the electron pairs around the central atom in the molecule will repel each other and go as far apart as possible. Multiple bonds (double or triple) count as one bonding pair for VSEPR predictions. Fill out the attached chart from the class Powerpoint to understand how VSEPR theory determines shape, and consequently the polarity of covalent molecules. Number of and type Atoms (bonding or nonbonding atoms) 4 bonding pairs 3 bonding pairs and 1 non-bonding pair 2 bonding pairs and 2 non-bonding pairs 2 bonding pairs 3 bonding pairs Shape Angles between bonding pairs Diagram/Example Instructions: 1) Draw the molecule or compound in 3-D according to VSPER theory. (Use Lewis dot structures to determine how many bonding and nonbonding pairs are in the molecule or compound to determine the shape if needed.) 2) Name the shape. 3) Look up each atom’s electronegativity and calculate the ΔEN. 4) State if the bond type(s) as ionic, covalent polar, or covalent non-polar. Write in charges or dipoles (partial charges) as necessary. The atom with the higher EN will be negative (or partially negative) and the atom with lower EN will be positive (or partially positive). 5) State if the molecule/compound is ionic, polar or nonpolar overall. 6) Build the molecule/compound Examples: 1) CCl4 2) Na2O 3) H2O 4) BF3 5) NH3 Practice 1) Draw the molecule or compound in 3-D according to VSPER theory. (Use Lewis dot structures to determine how many bonding and nonbonding pairs are in the molecule or compound to determine the shape if needed.) 2) Name the shape. 3) Look up each atom’s electronegativity and calculate the ΔEN. 4) State if the bond type(s) as ionic, covalent polar, or covalent non-polar. Write in charges or dipoles (partial charges) as necessary. The atom with the higher EN will be negative (or partially negative) and the atom with lower EN will be positive (or partially positive). 5) State if the molecule/compound is ionic, polar or nonpolar overall. Click on the molecule's name to see the answer, but first try to do it yourself! (Note: Trigonal pyramidal is listed as tetrahedral. This is because it really is just a variation on the tetrahedral shape, and so is sometimes referred to as such. I expect you to differential between trigonal pyramidal and tetrahedral.) 1. AlCl3 - Aluminum Trichloride 2. CS2 - Carbon Disulfide 3. BeI2 - Beryllium Diiodide 4. NOCl - Nitrosyl Chloride 5. PO(OH)3 - Phosphoric Acid 6. SO2Cl2 - Sulfuryl Chloride 7. NOCl - Nitrosyl Bromide 8. BCl3 - Boron Trichloride 9. SiH4 - Silicon Tetrahydride 10. BeBr2 - Beryllium Dibromide 11. CH2O - Formaldehyde 12. NH2Cl - Chloramine 13. CH4 - Methane 14. SO2 - Sulfur Dioxide 15. AlF3 - Aluminum Trifluoride 16. NH3 - Ammonia 17. SeH2 - Hydrogen Selenide 18. H2O - Water 19. CO2 - Carbon Dioxide 20. SCl2 - Sulfur Dichloride 21. NO2F - Nitryl Fluoride 22. CSe2 - Carbon Diselenide 23. CCl4 - Carbon Tetrachloride 24. AlBr3 - Aluminum Tribromide 25. BeCl2 - Beryllium Dichloride 26. SO3 - Sulfur Trioxide 27. PCl3 - Phosphorus Trichloride 28. BeF2 - Beryllium Difluoride 29. BF3 - Boron Trifluoride (Source: http://www.tutorhomework.com/Chemistry_Help/Molecular_Geometry/Polar_Or_Nonpolar.html#problems )