Exam questions - The Grange School Blogs
advertisement

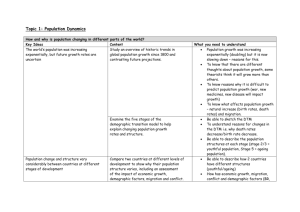
Population Revision Booklet AS LEVEL GEOGRAPHY 1 Checklist: I can… No Sort of Yes Define population key terms such as fertility rate, infant mortality and life expectancy Describe and explain how population has increased over the past 250 years Annotate a diagram of the Demographic Transition Model and explain what it shows Apply the DTM to different countries and show what Stage countries are in based solely on birth and death rate data Interpret population pyramids for LEDC and MEDC countries Relate population pyramids to different stages of the DTM Describe the key theories of Malthus, Boserup and the Club of Rome Describe push and pull factors leading to migration and relate this to a case study Explain what is meant by the dependency ratio Give advantages and disadvantages of an ageing population and relate this to a case study Give advantages and disadvantages of a youthful population and relate this to a case study Explain the causes and impacts of different population management strategies Define and give examples of urbanisation Define and give examples of counter-urbanisation Show how the urban characteristics change from the inner city through to rural areas Explain the term social welfare and relate this to an urban case study 2 Opening questions on an exam often ask you to define a key term, or show you can distinguish the difference between key terms. Write a definition for each of the following key terms. Birth rate Natural Increase Infant mortality rate Fertility rate Population density Death rate Life Expectancy Child mortality rate Total fertility rate Migration rate 3 This graph shows the increase in population since 1750. Describe the pattern shown: Annotate the map above to show the areas of highest and lowest population density. In your annotations include some explanation as to why this could be (think climate, resources). Exam questions 1) Outline the reasons for rapid population growth over the past 200 years (4 marks) 2) Explain why some areas of the world have higher population densities than others (6 marks) 4 Annotate your demographic transition model (DTM) to show: The 5 stages (Stage 1, Stage 2 etc) Labelled axes (Time/Development and Birth/Death rates per 1000 people) Birth Rate; Death rate; Total population Descriptions of the 5 stages – High fluctuating; Early Expanding; Late Expanding; Low fluctuating and Declining Examples of countries/places that fit each of these Stages (e.g., Mali; tribes of the Amazon; UK; Japan; Egypt) Stage 1 2 3 4 5 Birth rate Death rate Natural Increase Write the words HIGH; LOW; DECREASING; INCREASING in the table above. It is really important that you understand what the DTM shows you. The DTM represents a large part of the course and it is very likely that there will be questions on the exam about it. 5 Stage 1: Example of place: Birth rate is __________ because… Death rate is __________ because… Stage 2: Example of place: Birth rate is __________ because… Death rate is __________ because… Stage 3: Example of place: Birth rate is __________ because… Death rate is __________ because… Stage 4: Example of place: Birth rate is __________ because… Death rate is __________ because… Stage 5: Example of place: Birth rate is __________ because… Death rate is __________ because… 6 1600 1700 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000 Birth rate (per 1000 per year 38 35 35 26 18 12 8 Death rate (per 1000 per year) 37 34 18 15 12 10 10 Population (millions) Approximate Stage 2 3 7 15 21 26 28 To answer the question below it is useful to plot at which stage the country was at each date. Then, use information from page 6 to answer the question below. Exam questions 3) The table shows some population data for a country since 1600. With reference to the DTM, describe and explain the changes in the population shown by the data (10 marks) Usefulness of the DTM: The data behind the DTM was from more developed countries, so the model works well for these countries. How does the UK fit into the DTM – when did the UK go through each of the stages? Comparison between countries… Forecasting future population growth… (why are these important?) Limitations of the DTM: Originally no Stage 5… Doesn’t take into account education and role of women… Religious practices can influence progression through stages… No migration included… Population control policies… (for each, briefly explain how it could influence progression through the Stages of the DTM) 7 Population structures (pyramids) and the DTM: Draw and annotate a population pyramid for Stage 5 of the DTM: You need to know the shape of these population pyramids and what they show. Wide base = high birth rate Narrowing quickly = high death rate Wide top = ageing population Narrowing base = low birth rate You should be able to relate these facts to the population pyramids and the DTM. Exam questions 4) Discuss the uses and limitations of the DTM (15 marks) 5) Describe the differences between the population structures of countries at different stages of the DTM (10 marks) 8 There are three main population theories that you should be aware of: Malthus, Boserup and the Club of Rome. To show off to an examiner you could also write about Julian Simon. Theory: Thomas Malthus Main features: What would happen at the crisis point (the intersection of pop growth and food supply (see graph below)? Ways of stabilising the population: Preventative checks (reducing birth rate) Positive checks (increasing death rate) For each give examples of ‘checks’. Positives and negatives of the Malthusian theory: Positives – where it works Negatives – where it doesn’t work 9 Theory: Ester Boserup Main features: Using the cartoon below and the graph to the left as prompts, explain how Boserup felt that population could continue to rise: Positives and negatives of the Boserup theory: Positives – where it works Negatives – where it doesn’t work 10 Theory: Club of Rome Main features: What is the graph on the left showing you? Prompts: what will happen to resources, population in the future + why? Positives and negatives of the Club of Rome theory: Positives – where it works Negatives – where it doesn’t work Exam questions 6) Comment on contrasting population growth theories (15 marks) 7) To what extent is the theory postulated by Malthus supported by evidence in today’s world? (8 marks) 11 Quick facts: Migration _____________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Immigration_____________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Emigration _____________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Look at the population pyramid for the UAE. Describe and explain the pattern shown: Focus on men aged 20-54 and the increase of 0-9 year olds. This is a case of international migration – migration between different countries. You will also need to know about internal migration (within a country), see the Section on urbanisation and counter-urbanisation. Push and Pull factors Push = forces you out of your country/place Push Factors Pull = encourages you into a country or place Pull factors 12 Case study: Poland to UK (You could also your case study about Mexico-USA migration) Historical background Push and Pull factors Push Factors Pull factors Advantages/Disadvantages to UK/Poland (think Social; Economic and Environmental) Advantages for UK Disadvantages for UK Advantages for Poland Disadvantages for Poland Exam questions 8) With specific reference to a case study explain the impacts of international migration (15 marks) 13 . Quick facts: The dependency ratio is___________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ The dependency ratio is a useful term when discussing ageing and youthful populations. Use this term and ‘elderly dependents’; ‘young dependents’ and ‘working age’ in your exam answers. Case study: Japan’s ageing population (You could also consider the ageing population of UK, but again you will need specific facts). Describe and explain what this population pyramid shows: Social, economic and environmental impacts of ageing population (specific facts!): (+ve and –ve) Social Economic Environmental Possible management solutions: 14 Youthful population pyramids are a common feature of LEDC countries. Describe and explain the features of this population structure: Case study: Uganda’s ageing population Almost any LEDC country will do for a case study so long as you include specific facts in an exam! Fact box: Uganda High dependency ratio. 50% under 15 years of age High fertility rate (6.7 per mother) affecting health of mothers and children Pressure on health services: 6000 women die in childbirth each year Unprotected sex leads to spread of sexual diseases e.g., HIV/AIDS Early child bearing means fewer women in education, restricting their opportunities Overcrowding and rural-urban migration leads to growth of shanty town settlements Land degradation due to overuse and demand for trees for fuel Low life expectancy – just 52 years of age The box above shows many of the negative aspects of a youthful population. What are the opportunities for a country with a youthful population? Exam questions 9) Distinguish between the problems faced by governments of youthful and ageing populations (15 marks) 15 Case study: China’s One Child Policy Remember to include specific facts and figures in your exam about the One Child Policy. You can also refer to population management in Kerala, India (focussing on education to reduce the fertility rate) and Singapore (where the government has provided incentives to encourage people to have fewer children). This is the population structure of China in 1970 (before the One Child Policy). Referring to page 15 – what are the key problems faced by the country? These should directly link to the causes of the 1CP. Use terms like overpopulation and explain its meaning Impacts of the One Child Policy: As geographers you should refer to both the positives and negatives and refer to SEE. Exam questions 10) Compare the two population pyramids. To what extent have China been successful in their One Child Policy? (6 marks) 16 China 2010 Quick facts: Pro-natalist means _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Case Study: France France realised that it had an ageing population by the 1990s, and so needed to increase its population so that in the future it could support its elderly dependents. It did this through a number of incentives. Incentives by French Government to increase birth/fertility rates: (be specific!) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) France fertility change from 1960s to present: Fertility rates 1960s 2.7 1990s 1.7 2010s 2.0 To what extent has the population management strategies used by the French Government been successful in achieving their aims? 17 NB: The birth rate in France is 1.9 – the second highest in Europe. Exam questions 11) What problems could a temporary increase in fertility rates cause in the future (4 marks) Quick facts: Urbanisation is __________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Counter-urbanisation is ___________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Case Study: Urbanisation LEDC: From rural areas of India to Dharavi, Mumbai MEDC: Isle of Purbeck (Dorset) to Southampton Annotate the cartoon to the right to show the problems associated with urbanisation in LEDCs. How would the problems differ in MEDC countries? 18 Consider the problems faced in the rural area. Include information from push and pull factors. How does the population pyramid for Cornwall compare to that of the UK average? Case Study: Counter-urbanisation Cornwall from major cities in the UK. Counter-urbanisation is almost exclusively found in MEDC countries. Using the pictures above, describe the pull factors that encourage people to Cornwall: What impacts will the migration of people have – social, economic and environmental? 19 Refer to the types of people (demography) that are immigrating. Exam questions 12) Explain the push factors that facilitate urban-rural migration (6 marks) Case Study: Differences between urban and sub-urban areas Use London – Canning Town v Richmond-upon-Thames. You will need to be able to comment on: Housing Ethnicity Age Structure Wealth Employment Provision of Services Locate Canning Town and Richmond-upon-Thames on the map above As bullet points, use specific facts to highlight the differences between the inner city and suburban areas Canning Town (inner city) Richmond-upon-Thames (surburban) Housing Ethnicity Age Structure Wealth 20 Employment Provision of services 21 Exam questions 13) Choose any two areas. Using only the photographs, contrast the characteristics of the two settlement areas chosen (4 marks) Quick facts: Social welfare is ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ For any question on social welfare you need to comment on the living conditions and the things that affect these. For example, the level of education, health, unemployment, crime rates, types of jobs Using key facts from page 20, how does social welfare differ between different urban areas? Key Term Definition 22 Use this space to make notes – perhaps things you need to focus on for your revision. You could also attempt some of the exam questions in this space… 23 24 25