Chapter 17 Electricity Review the model of an atom and the names
advertisement
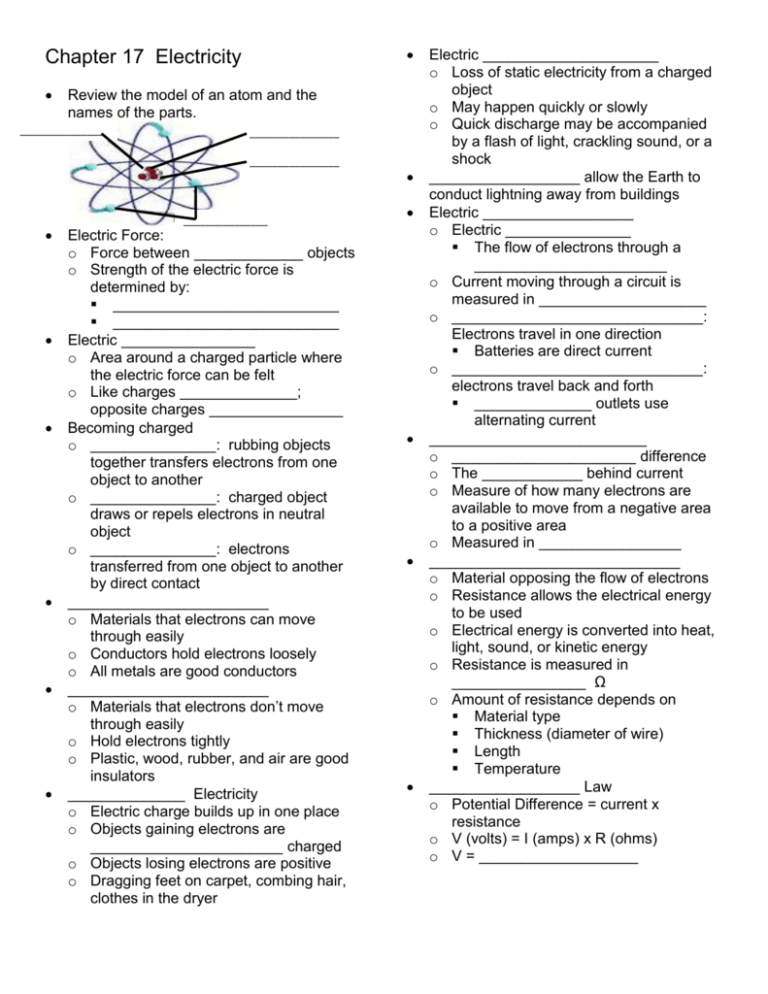
Chapter 17 Electricity Review the model of an atom and the names of the parts. _______________ _ ________________ ________________ _______________ _ Electric Force: o Force between _____________ objects o Strength of the electric force is determined by: ___________________________ ___________________________ Electric ________________ o Area around a charged particle where the electric force can be felt o Like charges ______________; opposite charges ________________ Becoming charged o _______________: rubbing objects together transfers electrons from one object to another o _______________: charged object draws or repels electrons in neutral object o _______________: electrons transferred from one object to another by direct contact ________________________ o Materials that electrons can move through easily o Conductors hold electrons loosely o All metals are good conductors ________________________ o Materials that electrons don’t move through easily o Hold electrons tightly o Plastic, wood, rubber, and air are good insulators ______________ Electricity o Electric charge builds up in one place o Objects gaining electrons are _______________________ charged o Objects losing electrons are positive o Dragging feet on carpet, combing hair, clothes in the dryer Electric _____________________ o Loss of static electricity from a charged object o May happen quickly or slowly o Quick discharge may be accompanied by a flash of light, crackling sound, or a shock __________________ allow the Earth to conduct lightning away from buildings Electric __________________ o Electric _______________ The flow of electrons through a _______________________ o Current moving through a circuit is measured in ____________________ o ______________________________: Electrons travel in one direction Batteries are direct current o ______________________________: electrons travel back and forth ______________ outlets use alternating current __________________________ o ______________________ difference o The ____________ behind current o Measure of how many electrons are available to move from a negative area to a positive area o Measured in _________________ ______________________________ o Material opposing the flow of electrons o Resistance allows the electrical energy to be used o Electrical energy is converted into heat, light, sound, or kinetic energy o Resistance is measured in ________________ Ω o Amount of resistance depends on Material type Thickness (diameter of wire) Length Temperature __________________ Law o Potential Difference = current x resistance o V (volts) = I (amps) x R (ohms) o V = ___________________ Electric _____________________ o All circuits consist of 3 parts: _____________________ to provide electrons _____________________ to convert electricity to work _____________________ to connect the load to the power source o Circuits may also have a ________________: An open switch is off and a closed switch is on. o ______________ Circuit All parts are connected in a _____________________________ o ______________ Circuit An electrical circuit that provides _____________________________ for the electrical current to follow. o Circuit safety Wires are coated with an ____________________ to prevent electric shock and fire Wires that are drawing too much current may overheat and start a fire A _______________ has a thin strip of metal that melts when overheated and breaks the connection shutting off the circuit. ___________________________ are a switch that turns off when the circuit is drawing too much current. Ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) Measures the difference in current from one side of the outlet to the other, shuts off immediately if there is a difference Electrical Power and Energy o ______________: how quickly work is done Rate that electric energy is changed into another form of energy Unit for power = ________________ Power = current x voltage Watt = ampere x volts o Electrical Energy Energy – the ability to do work Electrical energy measured in _____________________________ Energy = power x time