Years 5 and 6 Cycle A Ancient Greece Classes: Falcon, Flamingo

Years 5 and 6 Cycle A
Ancient Greece
Classes: Falcon, Flamingo & Owl Start Date: April 2015 End Date: End Term 5 – May 2015
Attainment Targets
to create sketch books to record their observations and use them to review and revisit ideas
to improve their mastery of art and design techniques, including drawing, painting and sculpture with a range of materials [for example, pencil, charcoal, paint, clay]
about great artists, architects and designers in history.
I know how to report unacceptable uses of technology
I can spot acceptable and unacceptable behaviour when using technology.
I know who to tell if I find something that upsetting on the internet.
I know what the internet is.
I know what searching the internet means.
I can search for information on the internet.
I can work out which search is the most relevant.
I can use present my findings using a computer program.
I can make a simulation of a physical system.
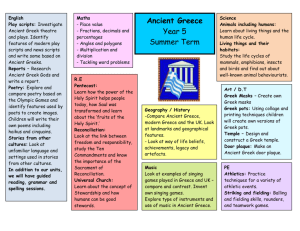
Teaching and Learning Focus
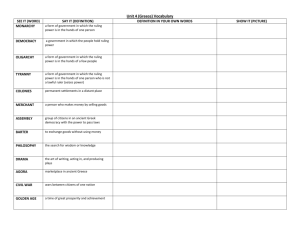
Ancient Greek pottery
- Studying examples of ancient Greek pottery, looking at colour, style and design
- Painting terracotta pots (or creating own from clay) in the style of ancient Greek pottery
Ancient Greek Soap Sculptures
- Exploring examples of ancient Greek sculpture
- Exploring soap as a sculpture material
- Replicating an ancient Greek sculpture using soap instead of marble
Ancient Greek multiple choice quizzes
- Using a variety of sources including ICT to research questions and answers for a multiple choice quiz
- Using the PowerPoint to create a multiple choice quiz
- How to manipulate PowerPoint slides (including use of background, colour, fonts, transitions and hyperlinks)
Retelling Aesop’s Fables
- Finding out who Aesop was and what his fables are
- Using ICT to research some of Aesop’s fables?
- Using ICT to retell one of Aesop’s fables either by creating digital storybooks or posters
Attainment Targets
use research and develop design criteria to inform the design of innovative, functional, appealing products that are fit for purpose, aimed at particular individuals or groups
generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through discussion, annotated sketches, cross-sectional and exploded diagrams, prototypes, pattern pieces and computer-aided design
select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing], accurately
select from and use a wider range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their functional properties and aesthetic qualities
investigate and analyse a range of existing products
evaluate their ideas and products against their own design criteria and consider the views of others to improve their work
understand how key events and individuals in design and technology have helped shape the world
Teaching and Learning Focus
Designing, making and evaluating a model of the Parthenon
- Studying the Parthenon and its design
- Exploring ways of strengthening materials
- Using a variety of materials and techniques to design. make and evaluate a model of the Parthenon
Attainment Targets
locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of
Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities
name and locate counties and cities of the
United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time.
human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water
use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied
Teaching and Learning Focus
What is Greece like today?
- Exploring the physical geography of Greece e.g. size, location, rivers, mountains, climate, landscape, etc.
- Using maps and secondary sources of information
What is modern Greek culture like?
- Finding out about the population of Greece
- Researching various aspects of Greek culture e.g. food, music, clothes, leisure, etc.
Attainment Targets
Ancient Greece
– a study of Greek life and achievements and their influence on the western world
The legacy of Greek or Roman culture
(art, architecture or literature) on later periods in British history, including the present day
Teaching and Learning Focus
Who and where were the ancient Greeks?
- Placing the ancient Greeks on a timeline
- Locating Greece on a map
- Exploring what Greece is like today as a tourist destination
What were the differences between Athens and Sparta?
- Finding out what city states were in ancient Greece
- Exploring similarities and differences between Athens and
Sparta e.g. in government, trade, women, education, etc.
What was ancient Greek warfare like?
- Investigating why city states needed armies and navies
- Using artefacts to find out about warfare in ancient Greece
- Exploring the types of armour, weapons, ships, etc., that were
Used
What did the ancient Greeks believe?
- Investigating the Olympians and the Titans and their relationship
- Finding out who the Olympian gods and goddesses were
- Exploring how Greek myths show beliefs about their gods
What was daily life like in ancient Greece?
- What do you know about daily life in ancient Greece from what we have found out so far?
- Using a variety of sources of information to research what life was like for the citizens of Greece
What impact did the ancient Greek civilisation have on the world?
- Exploring how the ancient Greeks affected future civilisations
- Exploring which ancient Greek inventions and developments
(e.g. the Olympics, the marathon, universities, etc.) are still around today
What have we learnt about life in ancient Greece?
- What are the most interesting things you have found out about ancient Greece?
- Summarising everything that has been learnt about ancient
Greece
- Displaying knowledge of ancient Greece in a variety of ways
Attainment Targets
listen attentively to spoken language and show understanding by joining in and responding
explore the patterns and sounds of language through songs and rhymes and link the spelling, sound and meaning of words
engage in conversations; ask and answer questions; express opinions and respond to those of others; seek clarification and help*
speak in sentences, using familiar vocabulary, phrases and basic language structures
develop accurate pronunciation and intonation so that others understand when they are reading aloud or using familiar words and phrases
listen with attention to detail and recall sounds with increasing aural memory
appreciate and understand a wide range of high-quality live and recorded music drawn from different traditions and from great composers and musicians
Teaching and Learning Focus
Recap on vocabulary and phrases already learnt to establish starting point.
Ensure secure knowledge and understanding of basics, such as greetings, numbers, colours.
Reinforce correct pronunciation.
Introduce a few key classroom instructions and responses.
Sing songs related to subjects studied.
Tout le Monde L2, Modules 3, 4 and 5 ( covering vocabulary for the family, pastimes, countries and transport, houses – rooms, furniture.)
Investigating music linked to ancient Greek theatre.
Attainment Targets
Rounders
I can perform the skills of rounders with accuracy, confidence and control, focusing on dribbling
I am beginning to understand the role of fielders and batters.
I can perform the skills of rounders with accuracy, confidence and control, focusing on throwing, catching and hitting.
I can find and use space in a rounders match to help their team
I can look for specific things in a game of rounders and explain how well they are being done
I know and understand the basic principles of warming up, and understand why it is important for a good-quality performance
I can practice the different techniques for throwing a ball.
I can throw a ball while running.
I can receive a ball correctly and safely.
I can begin to throw and catch a ball during a game situation.
I can respond consistently in the games I play, choosing and using skills which meet the needs of the situation
I recognise parts of a performance that could be improved, and identify practices that will help
I can suggest ideas for warming up, explaining their choice
Teaching and Learning Focus
Children will learn:
To throw and catch a ball accurately.
To develop batting skills in rounders.
To develop range of fielding techniques.
To develop the understanding of the rules of rounders.
To develop the understanding of the rules of rounders.
Attainment Targets
Describe the differences in the life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird
Describe the life process of reproduction in some plants and animals.
Describe how living things are classified into broad groups according to common observable characteristics and based on similarities and differences, including micro-organisms, plants and animals
Give reasons for classifying plants and animals based on specific characteristics
To be able to explain the differences in the life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird.
Teaching and Learning Focus
To be able to explain the life cycle of a mammal.
To be able to explain the life cycle of a bird.
To be able to explain the life cycle of an insect.
To be able to describe the life process of reproduction in some animals.
To be able to describe the life process of reproduction in some plants.
To be able to describe the life process of reproduction in some plants.
SEAL – Relationships.
I can find out about people who are important to me
I can give and receive a compliment
I can tell you about a time when I felt embarrassed and what it felt like.
I know some things to do when I feel embarrassed that will not make things worse
I can tell you about a time when I felt embarrassed and what it felt like.
I know some things to do when I feel embarrassed that will not make things worse
I can think about what embarrasses me and learn something about me that I didn’t know before.
I know some things to do when I feel embarrassed that will not make things worse.
I can set myself goals or challenges