Chemistry
advertisement
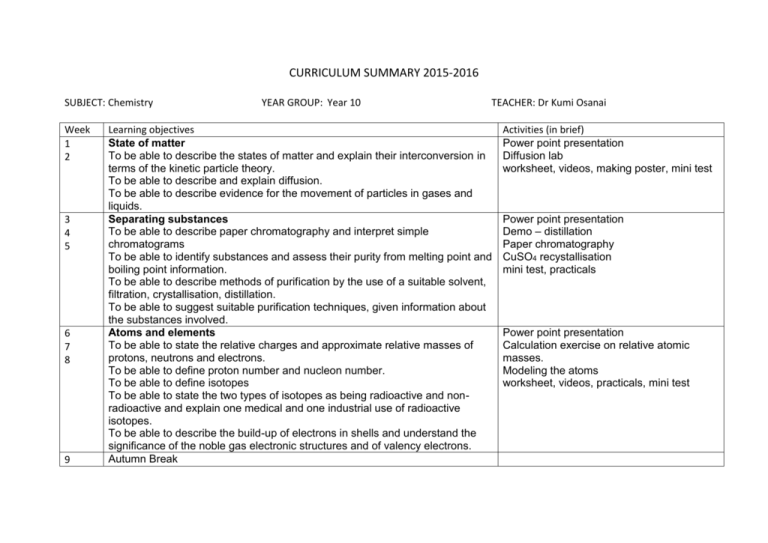
CURRICULUM SUMMARY 2015-2016 SUBJECT: Chemistry Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 YEAR GROUP: Year 10 TEACHER: Dr Kumi Osanai Learning objectives State of matter To be able to describe the states of matter and explain their interconversion in terms of the kinetic particle theory. To be able to describe and explain diffusion. To be able to describe evidence for the movement of particles in gases and liquids. Separating substances To be able to describe paper chromatography and interpret simple chromatograms To be able to identify substances and assess their purity from melting point and boiling point information. To be able to describe methods of purification by the use of a suitable solvent, filtration, crystallisation, distillation. To be able to suggest suitable purification techniques, given information about the substances involved. Atoms and elements To be able to state the relative charges and approximate relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons. To be able to define proton number and nucleon number. To be able to define isotopes To be able to state the two types of isotopes as being radioactive and nonradioactive and explain one medical and one industrial use of radioactive isotopes. To be able to describe the build-up of electrons in shells and understand the significance of the noble gas electronic structures and of valency electrons. Autumn Break Activities (in brief) Power point presentation Diffusion lab worksheet, videos, making poster, mini test Power point presentation Demo – distillation Paper chromatography CuSO4 recystallisation mini test, practicals Power point presentation Calculation exercise on relative atomic masses. Modeling the atoms worksheet, videos, practicals, mini test 10 11 12 13 14 15 Atoms combining To be able to describe the differences between elements, mixtures and compounds, and between metals and non-metals. To be able to describe an alloy, such as brass, as a mixture of a metal with other elements. To be able to describe the formation of ions by electron loss or gain. To be able to describe the formation of ionic bonds between elements from Group I and VII. To be able to describe the formation of single covalent bonds in H2, Cl2, H2O, CH4, and HCl as sharing of pairs of electrons. To be able to describe the giant covalent structures of graphite and diamond. Power point presentation Modeling the ionic compounds Practicals – finding chemical bondings worksheet, videos, practicals, mini test