Factors Influencing Al(III) Adsorption onto Silicate Clay Minerals
advertisement

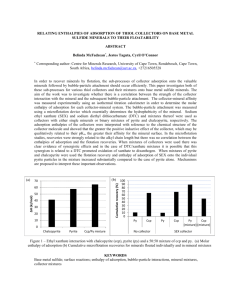
Factors Influencing Al(III) Adsorption onto Silicate Clay Minerals Wencui Chai, Yanfang Huang, Guihong Han∗, Jiongtian Liu School of Chemical Engineering and Energy, Zhengzhou University, Zhouzheng 450001, Henan Province, P.R.China (*Corresponding author: guihong-han@hotmail.com) ABSTRACT In the beneficiation process, the metal ions could adsorb onto clay mineral surface or interact with flotation chemicals, and then result in changing the flotation behavior of desired minerals. Al3+ is a dominating ion existing in the bauxite flotation system. In this research, the adsorption behavior of Al 3+ on two silicate clay minerals (including bentonite and kaolin) were investigated by means of UV-Vis spectra, Zeta potential testing, and SEM analysis. The adsorption experiment results show that the amount of Al3+ adsorption increases with initial metal ion concentration, contact time, and solution pH. Moreover, there are some different adsorption behaviours for different clays. Increasing the clay amount decreases the adsorption amount for bentonite, while increases first then decreases for kaolin. The temperature of the system also has a distinct effect on adsorption amount. Higher temperature favours the adsorption of Al3+ on bentonite but goes against for kaolin. The adsorption amounts of Al3+ on bentonite and kaolin reach to 12.48 mg·g-1 and 0.875mg·g-1 under the condition of the initial pH 5. Zeta potential results show that the adsorption of Al3+ on two clays is characterized by electrostatic attraction and ion exchange. Figure 1 – Adsorption rate of Al(III) and Zeta potential changing of clay minerals with solution pH KEYWORDS Bentonite, Kaolin, Al(Ⅲ), Adsorption, Clay Minerals