Pancreas transplant
advertisement
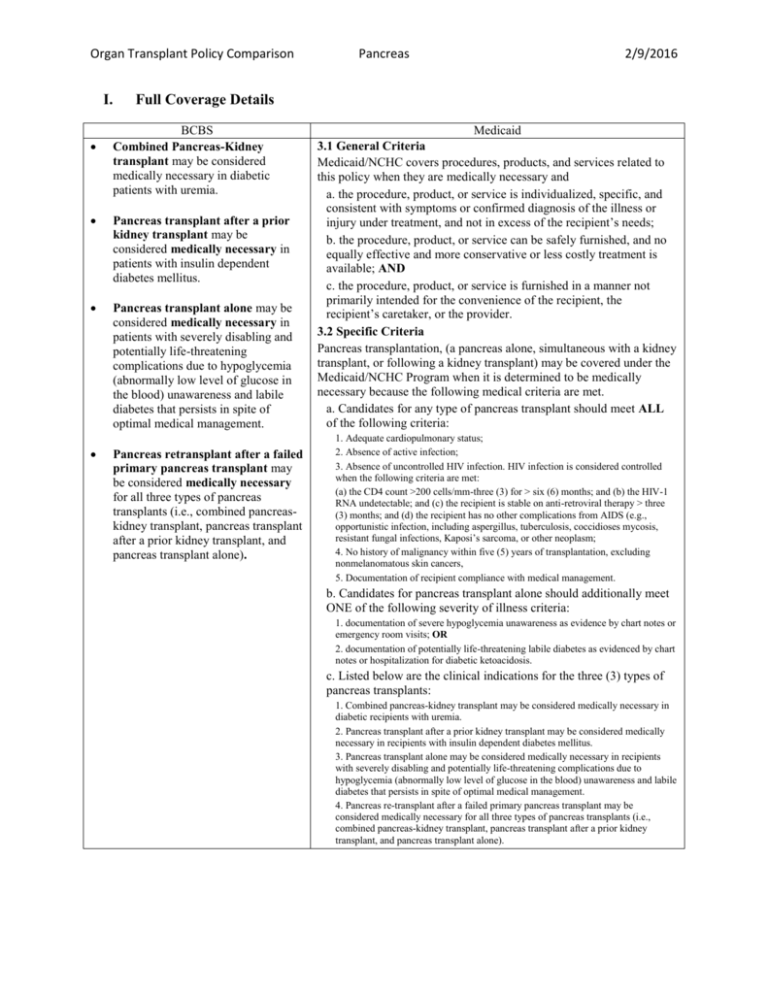
Organ Transplant Policy Comparison I. Pancreas 2/9/2016 Full Coverage Details BCBS Combined Pancreas-Kidney transplant may be considered medically necessary in diabetic patients with uremia. Pancreas transplant after a prior kidney transplant may be considered medically necessary in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Pancreas transplant alone may be considered medically necessary in patients with severely disabling and potentially life-threatening complications due to hypoglycemia (abnormally low level of glucose in the blood) unawareness and labile diabetes that persists in spite of optimal medical management. Pancreas retransplant after a failed primary pancreas transplant may be considered medically necessary for all three types of pancreas transplants (i.e., combined pancreaskidney transplant, pancreas transplant after a prior kidney transplant, and pancreas transplant alone). Medicaid 3.1 General Criteria Medicaid/NCHC covers procedures, products, and services related to this policy when they are medically necessary and a. the procedure, product, or service is individualized, specific, and consistent with symptoms or confirmed diagnosis of the illness or injury under treatment, and not in excess of the recipient’s needs; b. the procedure, product, or service can be safely furnished, and no equally effective and more conservative or less costly treatment is available; AND c. the procedure, product, or service is furnished in a manner not primarily intended for the convenience of the recipient, the recipient’s caretaker, or the provider. 3.2 Specific Criteria Pancreas transplantation, (a pancreas alone, simultaneous with a kidney transplant, or following a kidney transplant) may be covered under the Medicaid/NCHC Program when it is determined to be medically necessary because the following medical criteria are met. a. Candidates for any type of pancreas transplant should meet ALL of the following criteria: 1. Adequate cardiopulmonary status; 2. Absence of active infection; 3. Absence of uncontrolled HIV infection. HIV infection is considered controlled when the following criteria are met: (a) the CD4 count >200 cells/mm-three (3) for > six (6) months; and (b) the HIV-1 RNA undetectable; and (c) the recipient is stable on anti-retroviral therapy > three (3) months; and (d) the recipient has no other complications from AIDS (e.g., opportunistic infection, including aspergillus, tuberculosis, coccidioses mycosis, resistant fungal infections, Kaposi’s sarcoma, or other neoplasm; 4. No history of malignancy within five (5) years of transplantation, excluding nonmelanomatous skin cancers, 5. Documentation of recipient compliance with medical management. b. Candidates for pancreas transplant alone should additionally meet ONE of the following severity of illness criteria: 1. documentation of severe hypoglycemia unawareness as evidence by chart notes or emergency room visits; OR 2. documentation of potentially life-threatening labile diabetes as evidenced by chart notes or hospitalization for diabetic ketoacidosis. c. Listed below are the clinical indications for the three (3) types of pancreas transplants: 1. Combined pancreas-kidney transplant may be considered medically necessary in diabetic recipients with uremia. 2. Pancreas transplant after a prior kidney transplant may be considered medically necessary in recipients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. 3. Pancreas transplant alone may be considered medically necessary in recipients with severely disabling and potentially life-threatening complications due to hypoglycemia (abnormally low level of glucose in the blood) unawareness and labile diabetes that persists in spite of optimal medical management. 4. Pancreas re-transplant after a failed primary pancreas transplant may be considered medically necessary for all three types of pancreas transplants (i.e., combined pancreas-kidney transplant, pancreas transplant after a prior kidney transplant, and pancreas transplant alone). Organ Transplant Policy Comparison II. Pancreas 2/9/2016 Coverage Exclusion BCBS poor physiologic age; significant emotional problems that may impair the patient’s ability to adhere to follow-up; recent substance abuse; current tobacco use (impairs wound and microvascular healing); history of non-compliance with medical management; lack of support to the extent that adequate follow-up and adherence to post operative treatment plan is impaired; other major organ system disease or infection, including major vascular disease; morbid obesity; uncontrolled HIV positive patients. Medicaid 4.1 General Criteria Procedures, products, and services related to this policy are not covered when a. the recipient does not meet the eligibility requirements listed in Section 2.0; b. the recipient does not meet the medical necessity criteria listed in Section 3.0; c. the procedure, product, or service unnecessarily duplicates another provider’s procedure, product, or service; or d. the procedure, product, or service is experimental or investigational. 4.2 Specific Criteria a. Pancreas transplantation is not covered for: 1. indications other than those cited above. 2. organs sold rather than donated to a recipient. 3. artificial organs or human organ transplant service for which the cost is covered or funded by governmental, foundation, or charitable grants. b. Contraindications for the combined pancreas/kidney transplantation include the following: 1. significant emotional problems that may impair the recipient’s ability to adhere to follow-up; 2. recent substance abuse; 3. current tobacco use (impairs wound and microvascular healing); 4. history of non-compliance with medical management; 5. lack of support to the extent that adequate follow-up and adherence to post operative treatment plan is impaired; 6. other major organ system disease or infection, including major vascular disease; 7. morbid obesity; or 8. uncontrolled HIV positive recipients. Organ Transplant Policy Comparison III. Pancreas 2/9/2016 BCBS Policy Guidelines It is recommended that all transplant requests be reviewed by the Plan Medical Director or his or her designee. Only those patients accepted for transplantation by an approved transplantation center and actively listed for transplant should be considered for precertification or prior approval. Guidelines should be followed for transplant network or consortiums, if applicable. Guidelines should be followed for transplant networks, where applicable. Candidates for any type of pancreas transplant should meet ALL of the following criteria: A.) Adequate cardiopulmonary status, and B.) Absence of active infection, and C.) Absence of uncontrolled HIV infection. HIV infection is considered controlled when the following criteria are met: 1) the CD4 count >200 cells/mm-3 for >6 months; and 2) the HIV-1 RNA undetectable; and 3) the patient is stable on anti-retroviral therapy >3 months; and 4) the patient has no other complications from AIDS (e.g., opportunistic infection, including aspergillus, tuberculosis, coccidioses mycosis, resistant fungal infections, Kaposi’s sarcoma, or other neoplasm; and D.) No history of malignancy within 5 years of transplantation, excluding nonmelanomatous skin cancers, and E.) Documentation of patient compliance with medical management. Candidates for pancreas transplant alone should additionally meet one of the following severity of illness criteria: 1) documentation of severe hypoglycemia unawareness as evidence by chart notes or emergency room visits; OR 2) documentation of potentially life-threatening labile diabetes as evidenced by chart notes or hospitalization for diabetic ketoacidosis. IV. None. Medicaid Policy Guidelines