BT0064A02
advertisement

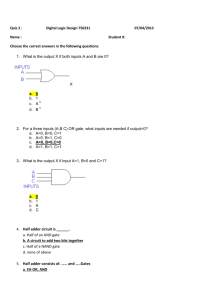
CUSTOMER_CODE SMUDE DIVISION_CODE SMUDE EVENT_CODE JULY15 ASSESSMENT_CODE BT0064_JULY15 QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 5712 QUESTION_TEXT What are shift registers? Explain SISO shift registers. Shift registers is a group …… activated (1 mark) SISO(serial-in-serial-out) Destructive readout: These are……and lost (1 mark) The data are stored…..4-Bit register (1 mark) SCHEME OF EVALUATION To give idea of…..output pin and so on(2 mark) So the serial output of entire….right most bit (2 mark) Non-destructive readout: Non destructive readout can be……end of the register(2 mark) However, when the R/W ….lost from the system(1 mark) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 5713 QUESTION_TEXT Write a short note on flip-flop. SCHEME OF EVALUATION Flip flops can be either simple …..some gating mechanism (2 mark) The more advanced …….falling edge(2 mark) Clocked flip flops are ……independent of clock (2 mark) Flip flops can be divided …….output, Q (3 marks) A flip flop is a ……..bit of information (1 mark) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 72385 QUESTION_TEXT Explain universal gates along with their truth tables. SCHEME OF EVALUATION The NAND gate is a digital logic gate that behaves in a manner that corresponds to the truth table to the left. A LOW output results only if both the inputs to the gate are HIGH. If one or both inputs are LOW, a HIGH output results. The NAND gate is a universal gate in the sense that any Boolean function can be implemented by NAND gates. Digital systems employing certain logic circuits take advantage of NAND's functional completeness. In complicated logical expressions, normally written in terms of other logic functions such as AND, OR, and NOT, writing these in terms of NAND saves on cost, because implementing such circuits using NAND gate yields a more compact result than the alternatives. NAND gates can also be made with more than two inputs, yielding an output of LOW if all of the inputs are HIGH, and an output of HIGH if any of the inputs is LOW. These kinds of gates therefore operate as n-ary operators instead of a simple binary operator. (4 marks) (2 marks) The NOR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW (0). If one or both inputs are is HIGH (1), a LOW output (0) results. NOR is the result of the negation of the OR operator. NOR is a functionally complete operation - combinations of NOR gates can be combined to generate any other logical function. By contrast, the OR operator is monotonic as it can only change LOW to HIGH but not vice versa. (3 marks) (1 mark) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 118224 QUESTION_TEXT List out any ten theorems in Boolean Algebra. The important theorems are: Theorem-1: X + X = X SCHEME OF EVALUATION Theorem-2: X • X = X Theorem-3: X + 0 = X Theorem-4: X • 1 = X Theorem-5: X • 0 = 0 Theorem-6: X + 1 = 1 Theorem-7: (X + Y)’ = X’ • Y’ Theorem-8: (X • Y)’ = X’ + Y’ Theorem-9: X + X•Y = X Theorem-10: X •(X + Y) = X Theorem-11: X + X’Y = X+Y Theorem-12: X’ • (X + Y’) = X’Y’ Theorem-13: XY + XY’ = X Theorem-14: (X’+Y’) • (X’ + Y) = Y’ Theorem-15: X + X’ = 1 Theorem-16: X • X’ = 0 QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 118226 QUESTION_TEXT Write a note on Excess-3 code and its properties. Excess–3 code theory explanation Properties SCHEME OF EVALUATION (4 marks) (6 marks) Excess–3 binary coded decimal (XS–3), also called biased representation or Excess–N, is a numeral system used on some older computers that uses a pre–specified number N as a biasing value. It is a way to represent values with a balanced number of positive and negative numbers. The smallest binary number represents smallest value. The greatest binary number represents the largest value. The primary advantage of XS–3 coding over BCD coding is that a decimal number can be nines’ complemented(for subtraction) as easily as a binary number can be ones’ complemented; just invert all bits. Adding Excess–3 works on a different algorithm than BCD coding or regular binary numbers. When you add two XS–3 numbers together, the result is not an XS–3 number. QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 118227 QUESTION_TEXT Explain the working of multiplexers and de-multiplexers. Multiplexers: In electronics, a multiplexer or mux is a device that performs multiplexing; it selects one of many analog or digital input signals and outputs that into a single line. An electronic multiplexer makes it possible for several signals to share one expensive device or other resources(4 marks) SCHEME OF EVALUATION Digital Multiplexers: In digital circuit design, the selector wires are of digital value. In the case of a 2–to–1 multiplexer, a logic value of 0 would connect I0 to the output while a logic value of 1 would connect I1 to the output. In larger multiplexers, the number of selector pins is equal to 2n where n is the number of inputs. (4 marks) De–multiplexers: In electronics, a demultiplexer is a device taking a single input signal and selecting one of many data–output–lines, which is connected to the single input. A multiplexer is often used with a complementary demultiplexer on the receiving end. A demultiplexer as a single–input, multiple–output switch. (2 marks)