04b-Tabulation Metho..
advertisement

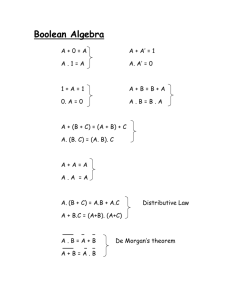
IKI10201 04b-Simplification of Boolean Functions Bobby Nazief Semester-I 2005 - 2006 The materials on these slides are adopted from Prof. Daniel Gajski’s transparency for Principles of Digital Design. Tabulation Method • • • Map method is a trial-and-error procedure Tabulation method performs thorough search It starts with SOM and consists of 2 steps: – PIs generation • group minterms by number of 1s • compare minterms & find pairs that differ in 1 variable • generate subcubes • repeat the above 3 steps to generate subcubes until no more subcubes can be generated – Minimal cover generation • find EPIs through a selection table • find minimal cover through the POS of PIs 2 Example: simplify w’y’z’ + wz + xyz + w’y • K-map representation: yz 00 01 wx 00 01 11 10 • 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 10 1 1 0 0 PIs generation: – 0-subcubes 3 Example: simplify w’y’z’ + wz + xyz + w’y (cont.) – 1-subcubes – 2-subcubes 4 Example: simplify w’y’z’ + wz + xyz + w’y (cont.) • Minimal cover generation: – EPIs selection • • • – PI list: EPI list: POS: w’z’, w’y, yz, wz w’z’, wz (P2 + P3)(P2 + P3) = P2 + P3 Minimal cover expressions: • F1 = w’z’ + wz + w’y • F2 = w’z’ + wz + yz 5 Another example • K-map representation: yz 00 01 wx 00 01 11 10 • 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 11 0 1 1 0 10 1 1 0 0 PIs generation: – 0-subcubes, 1-subcubes 6 Another example (cont.) • Minimal cover generation: – EPIs selection • • • – PI list: EPI list: POS: w’yz’, x’y’z, w’xy, wx’z, xyz, wyz w’yz’, x’y’z (P3 + P5)(P4 + P6)(P5 + P6) = (P3 + P5)(P4P5 + P5P6 + P4P6 + P6) = P3P4P5 + P4P5 + P3P6 + P5P6 Minimal cover expressions: • F1 = w’yz’ + x’y’z + wx’z + xyz • F2 = w’yz’ + x’y’z + w’xy + wyz • F3 = w’yz’ + x’y’z + xyz + wyz 7 Technology Mapping for Gate Arrays • Gate arrays contain only one type of m-input gate (such as 3-input NAND, 3-input NOR) • Technology mapping is a transformation of Boolean expressions into a logic schematic containing only this type (NAND or NOR) of gate – SOP/POS NAND/NOR gate implementation 8 Conversion & Optimization • Conversion: • Optimization: • Conversion procedure: replace AND & OR gates with NAND (NOR) gates by using Rules 1 & 2 (3 & 4), and eliminate double inverters whenever possible 9 Translation standard forms to NAND/NOR schematics 10 Conversion to NAND (NOR) gates 11 Technology Mapping for Custom Libraries • Libraries contain gates with different functions and different delays • Technology mapping means covering schematic with library gates • Minimize delay on critical paths • Minimize cost on non-critical paths 12 Example design with custom libraries • F = w’z’ + z(w + y) • AND-OR implementation (delay = 7.2ns, cost = 28) • NAND implementation (delay = 5.2ns, cost = 22) 13 Example design with custom libraries (cont.) • Alternatif A (delay = 5.4ns, cost = 20) • Alternatif B (delay = 3.8ns, cost = 20) • Alternatif B-optimized (delay = 3.8ns, cost = 18) 14 Design with static 1-hazard Timing Diagram 15 Hazard-free design Timing Diagram 16