Water in the Atmosphere/Precipitation Water Vapor is water
advertisement

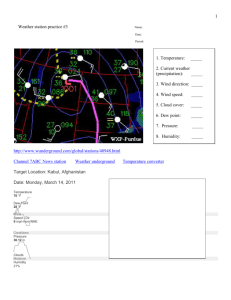
Water in the Atmosphere/Precipitation Water Vapor is water evaporating and entering the atmosphere. Water vapor is lighter than nitrogen or oxygen. Humidity is water vapor in the air. Specific humidity is the actual amount of water vapor in the air at a given time & place (grams of vapor per kilogram of air). Relative humidity (abbreviated RH) Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air compared to what the air can “hold” at that temperature. Relative humidity depends on temperature and pressure. Relative humidity is measured with a psychrometer. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Warmer air can hold more water vapor than cooler air. As humidity increases, pressure decreases because water molecules are less massive than air. Relative humidity is measured with a psychrometer. The dew point is the temperature at which water vapor turns into a liquid. This is where the air is saturated or the relative humidity is 100%. The dew point is associated with relative humidity. A high relative humidity implies that the dew point is closer to the current air temperature. Relative humidity of 100% indicates the dew point is equal to the current temperature and that the air is maximally saturated with water. At temperatures below the dew point, water will leave the air. The condensed water is called dew when it forms on a solid surface. The condensed water is called either fog or a cloud, depending on its altitude, when it forms in the air. An air temperature of 22° with a relative humidity of 75% would have a dew point of 17°C. The same air temperature with a lower humidity of 60% would have a lower dew point of 14°C. The lower the relative humidity, the lower the temperature must drop to reach the dew point. When the air temperature is high, the body uses evaporation of perspiration to cool down, with the cooling effect directly related to how fast the perspiration evaporates. The rate at which perspiration can evaporate depends on how much moisture is in the air and how much moisture the air can hold. If the air is already saturated with moisture, perspiration will not evaporate. The body's cooling system will produce perspiration in an effort to keep the body at its normal temperature even when the rate it is producing sweat exceeds the evaporation rate. So even without generating additional body heat by exercising, one can become coated with sweat on humid days. It is the unevaporated sweat that tends to make one feel uncomfortable in humid weather. The frost point is similar to the dew point, in that it is the temperature to which a given parcel of humid air must be cooled, at constant barometric pressure, for water vapor to be deposited on a surface as ice without going through the liquid phase. Freezing occurs when a liquid changes to a solid. Melting occurs when a solid changes into a liquid. Evaporation occurs when a liquid changes to a gas. Condensation occurs when a fas changes into a liquid. Sublimation occurs when a solid changes directly to a gas. Deposition occurs when a gas changes directly to a solid.