PP 32: Alkanes
advertisement

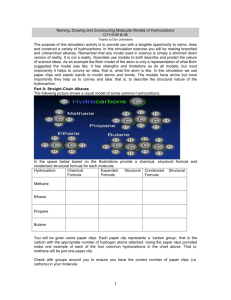
PP 32: Alkanes Drill: Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram for C6H8 Alkanes: Hydrocarbons containing only single covalent bonds or saturated hydrocarbons • • All hydrocarbons with no multiple bonds end with the suffix -ane Prefix: Alk- any length carbon chain Organic Prefixes: 1 = meth2 = eth3 = prop4 = but5 = pentAlkanes: 1 = methane: 2 = ethane: 3 = propane: 4 = butane: 5 = pentane: 6 = hexane: 7 = heptane: 8 = octane: 9 = nonane: 10 = decane: 6= 7= 8= 9= 10 = hexheptoctnondec- CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 C7H16 C8H18 C9H20 C10H22 CH4 H3C-CH3 H3C- CH2-CH3 H3C- CH2- CH2-CH3 H3C- CH2- CH2- CH2-CH3 H3C- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2-CH3 H3C- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2-CH3 H3C- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2-CH3 H3C- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2-CH2- CH2- CH2-CH3 H3C- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2-CH3 General Alkane Formula: CnH2n+2 Drill: Draw each of the following: C3H8 C3H6 C3H4 Name & give the molecular formula for alkanes with 1, 2, 3, 4, & 5 carbons: Name each of the following: C5H12 C3H8 C8H18 Saturated Hydrocarbon: • A hydrocarbon with the maximum number of hydrogens possible • A hydrocarbon with only single bonds • All non-cyclic hydrocarbons are saturated Unsaturated Hydrocarbon: • A hydrocarbon with less than the maximum number of hydrogens possible • A hydrocarbon with at least one multiple bond (double or triple bond) • Carbon Chains: Any continuously bonded group of carbons in a hydrocarbon is called a carbon chain. Types of Formulas: (We will use butane as our example) • Molecular Formula: Simplest: (C4H10) • Symbols of elements present & subscripts telling how many of each • Condensed formula: (bonds between Cs & Hs understood) • • Bonds between Cs & Cs also understood: (CH3CH2CH2CH3) • Bonds between Cs & Cs shown: (CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3) • Repeating items in (): (CH3-(CH2-CH2)2-CH3) Skeletal Formula: (Hs & bonds to Hs understood) • • C-C-C-C Complete structural formula: (All elements & bonds are shown as in Lewis Dot Diagrams) HHHH H-C-C-C-C-H HHHH • Stick structures or minimal formulas: (Only bonds shown all Cs & Hs that are not part of a functional group are understood) • • • Line ends & joints represent carbons Hydrogens understood Others draw Alkane Shapes: • • • In 2 dimensions we draw bond s as 90o The true bond s are 109.5o Tetrahedral in shape • Draw each of the following in four diffenent ways: • • Propane butane octane methane hexane heptane pentane ethane