DSRIP Plan: UC San Francisco Medical Center / UCSF Benioff
advertisement

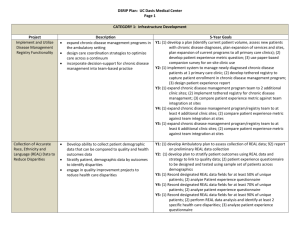
DSRIP Plan: UC San Francisco Medical Center / UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital Page 1 CATEGORY 1: Infrastructure Development Project Increase Primary Care Capacity Implement and Utilize Disease Management Registry Functionality Description Expand existing practices Opening at least one new UCSFMC primary care practice Recruiting the primary care clinicians needed for this expansion Implement the new EPIC EMR at UCSFMC 5-Year Goals Y1: (1) Appoint primary care strategic planning group to plan and implement UCSFMC primary care expansion; (2) Relocate General Medical Clinic to larger space at UCSFMC Mt. Zion Campus Y2: (1) Recruit 2 additional primary care provider FTEs; (2) Increase patient encounters at UCSFMC primary care clinics by 2,5000 relative to FY10 encounters Y3: (1) Recruit 2 additional primary care provider FTEs (total of 4); (2) Increase patient encounters at UCSFMC by 5,000 relative to FY10 encounters Y4: (1) Recruit 2 additional primary care provider FTEs (total of 6); (2) Increase patient encounters at UCSFMC by 7,500 relative to FY10 encounters Y5: Increase patient encounters at UCSFMC by 10,000 relative to FY10 encounters Y1: Review current registry capability and assess future needs Y2: (1) Populate registry with patient data at 2 of 5 (40%) primary care practices to create registry for patients enrolled in those practices; (2) Enter patient data into registry at these 4 practices for at least 75% of patients at the practice with diabetes and 75% of patient eligible for colorectal cancer screening (aged 50-75) Y3: (1) Populate registry with patient data at 4 of 5 (80%) primary care practices to create registry for patients enrolled in those practices; (2) Enter patient data into registry at these 4 practices for at least 75% of patients at the practice with diabetes and 75% of patient eligible for colorectal cancer screening (aged 50-75) Y4: (1) Populate registry w/ patient data at 5 of 5 primary care practices to create registry for patients enrolled in those practices with final practice included being pediatrics; (2)In addition to adult patient data entered in previous 4 primary care practices, enter patient data into registry at pediatrics practice to track immunization status, including registry data for at least 75% of active young children in the practice Y5: (1) Expand child immunization registry to include young children cared with medical homes at family medicine practice, so that 100% of UCSF primary care practices serving children have an immunization registry; Enhance Performance Improvement and Reporting Capacity DSRIP Plan: UC San Francisco Medical Center / UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital Page 2 (2) Enter patient data intro registry at all practices serving children to track immunization status, including registry data for at least 75% of active young children in the practice. Y5: Enter patient data into the registry for at least 65% of patients with diabetes who are assigned to a KMC primary care clinic as their medical home Y1: (1) Develop reporting methodologies that will enable continuous quality Conduct an inventory of the key data sources, improvement; (2) Participate in a collaborative reporting efforts and platforms Y2: (1) Hire/ train 2 staff in well proven quality and efficiency improvement Select an information technology solution to principles, tools and processes; (2) Implement quality improvement (QI) support data management and production of data systems, collection and reporting capabilities balanced scorecards Y3: (1) Hire/ train 1 staff in well proven quality and efficiency improvement Produce meaningful reports and templates principles, tools and processes; (2) Implement QI data systems, utilized to reflect performance and drive change. collection and reporting capabilities Starting with one or two initiatives, this Y4: (1) Participate in / present to quality performance improvement intervention will ultimately provide information conferences, webinars, learning sessions or other venues; (2) for all key initiatives in the “Bridge to Reform” Implement QI data systems, collection and reporting capabilities project set and other key organizational Y5: Create a quality dashboard or scorecard to be shared with initiatives. This will enable front line staff as well organizational leadership on a regular basis that includes patient as executive stakeholders to manage against satisfaction data, increase assigned accountability, adjust interventions/approaches based on data and celebrate success Retrain / recruit / hire / train staff to assist in achieving the plan Shift the manpower effort from data collection and manipulation to performance improvement activities CATEGORY 2: INNOVATION AND REDESIGN Expand Medical Homes Expand and redefine the roles of the primary care team members, focusing on training medical assistants to function in an expanded role as panel managers and training nurses in care management of high risk patients in all UCSFMC primary care clinics Link high need patients to primary care medical homes, focusing in particular on SPD patients, Y1: (1) Develop protocols for effectively communicating with patients and families during and post discharge to improve adherence to discharge and follow-up instructions; (2) Begin monthly data collection and reporting for chosen metrics Y2: (1) Develop a staffing and implementation plan to accomplish the goals/ objectives of the care transitions program; (2) Implement standard care transition processes in one additional patient population; Y3: (1) Conduct an assessment and establish linkages with community- Increase Specialty Care Access / Redesign Referral Process DSRIP Plan: UC San Francisco Medical Center / UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital Page 3 including young adults with childhood-onset based organizations to create a support network for targeted patients disabling conditions who use UCSFMC specialist post-discharge; (2) Implement standard care transition processes in two services but do not have a primary care medical additional patient populations; home Y4: (1) Train 3 additional MEAs / health workers in panel management and health coaching, deploy in UCSFMC clinics; (2) Train 1 additional RN case Perform population health management by manager in case management of high risk patients and deploy in identifying and reaching out to patients who UCSFMC primary care clinics; (3) Link at least 75 additional SPD patients need preventive and chronic care services, with without UCSFMC primary care visits in FY10 to primary care medical an emphasis on newly trained panel managers homes; (4) Panel managers / health coaches actively managing registries and nurse care managers using the registry for colorectal cancer screening for at least 1,500 UCSFMC primary care functionality as a tool for more effective patients and registries for chronic care for 1,000 UCSFMC primary care population management and outreach patients with diabetes; (5) 150 high risk HCSFMC primary care patients have assigned care manager teams Y5: (1) Train 1 additional RN case manager in case management of high risk patients and deploy in UCSFMC primary care clinics; (2) Link at least 50 additional SPD patients without UCSFMC primary care visits in FY10 to primary care medical homes; (3) Panel managers / health coaches actively managing registries for colorectal cancer screening for at least 2,000 UCSFMC primary care patients and registries for chronic care for 1,500 UCSFMC primary care patients with diabetes; (5) 250 high risk HCSFMC primary care patients have assigned care manager teams Y1: Designate personal / team to support and manage the specialty access Redesign the specialty referral process for a process subset of UCSFMC specialty clinics in order to Y2: (1) Develop and implement standardized referral evaluation and reduce the appointment scheduling lag to less processing guidelines for 4 specialty clinics; (2) Complete a planning than and reduce the 3rd available appointment process and submit a plan to implement electronic referrals; (3) Develop time, thus improving access for new patients the technical capabilities to facilitate electronic referrals Develop and implement an e-referral program in Y3: (1) Develop and implement standardized referral evaluation and a subset of UCSFMC specialty clinics processing guidelines for 2 additional specialty clinics; (2) Measure wait times for specialty care appointments in the 4 initial specialty clinics; (3) Implement specialty care access programs; e-referral in at least 2 specialty clinics Y4: (1) Measure wait times for specialty care appointments in 2 additional clinics%; (2) Develop and implement standardized referral evaluation and processing guidelines for 2 additional specialty clinics; (3) Implement specialty care access programs; e-referral in at least 2 additional specialty clinics Y5: (1) Measure the number of specialty care referrals that result without a clinic visit; (2) Achieve standards for specialty care access Implement / Expand Care Transitions Program DSRIP Plan: UC San Francisco Medical Center / UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital Page 4 Y1: (1) Develop protocols for effectively communicating with patients and Early identification of needs: enhanced families during and post discharge to improve adherence to discharge assessment for post-discharge needs will be and follow-up instructions; (2) begin monthly data collection and conducted at the time of admission by a case reporting for chosen metrics manager Multi-disciplinary teams with clearly defined roles Y2: (1) Develop a staffing and implementation plan to accomplish the goals/objectives of the care transitions program; (2) Implement will prepare the patient for discharge standard care transition processes in one additional patient population; Individual target plans will be developed for high Y3: (1) Conduct an assessment and establish linkages with communityrisk patients to mitigate risks and crease post based organizations to create a support network for targeted patients discharge care plans that will be communicated post-discharge; (2)Implement standard care transition processes in two and coordinated without patient partners additional patient populations Revision of discharge materials and education will Y4: (1) Redesign the process in order to be more effective; incorporating be addressed learnings, at least one new element into the process based on the Medication reconciliation will be done for every assessment, using the process modification process to include the patient specificity needed as learnings are discovered in Year 3; (2) Begin Post discharge appointments will be made within monthly data collection and reporting for chosen metrics 7-14 days or as appropriate for the patient Y5: (1) Report shared learnings of the care transitions program to local or condition national stakeholders; (2) Begin monthly data collection and reporting Routine directed post discharge phone calls will for chosen metrics be the standard of care Earlier introduction of Palliative Care Consultation as a care option Leverage technology to standardize transition of care information flow and reports. CATEGORY 4: URGENT IMPROVEMENT IN CARE Improve Severe Sepsis Detection and Management implement Sepsis Management and Resuscitation Bundle Reduce avoidable harm or deaths due to severe sepsis to patients receiving inpatient services Y1: (1) Conduct and report a gap analysis of recommended practices compared to UCSFMC practices; (2) Establish UCSFMC sepsis mortality baseline using the Integrated Nurse Leadership Program (INLP) definitions Y2: (1) Implement the Sepsis Resuscitation Bundle; (2) Report at least 6 months of data to SNI for baseline / benchmarks; (3) Report results to the state Y3: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with sepsis resuscitation bundle; (2) share data and practices with SNI for benchmarking across public hospitals; (3) Report results to the state Y4: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with sepsis resuscitation bundle; (2) share data and practices with SNI for benchmarking across public hospitals; (3) Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infection (CLABSI) Prevention Surgical Site Infection DSRIP Plan: UC San Francisco Medical Center / UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital Page 5 Report results to the state Y5: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with sepsis resuscitation bundle; (2) share data and practices with SNI for benchmarking across public hospitals; (3) Report results to the state Y1: Implement a process of care to improve performance improve compliance with central line insertion Y2: (1) Implement the Central Line Insertion Practices (CLIP); (2) Report at bundle least 6 months of data collection on CLIP to SNI for baseline / Reduce avoidable harm or deaths and costs of benchmarks; (3) Report at least 6 months of data collection on CLABSI care due to central-line associated blood stream to SNI for baseline / benchmarks ; (4) Report CLIP results to state infections Y3: (1)achieve TBD% compliance with CLIP; (2) share data and practices with SNI; (3) report CLIP and CLABSI results to State Y4: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with CLIP; (2) reduce central line bloodstream infections by TBD%; (3) share data and practices with SNI; (4) report CLIP and CLABSI results to State Y5: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with CLIP; (2) reduce central line bloodstream infections by TBD%; (3) share data and practices with SNI; (4) report CLIP and CLABSI results to State Y1: Establish an institutional surgical site infection and complication profile improve surgical site infection prevention baseline for general surgery, vascular surgery and selected specialty surgical cases using the American College of Surgeon’s National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) Y2: (1) Report at least 6 months of data collection on SSI to California Health Care Safety Net Institute (SNI) for purposes of establishing the baseline and setting benchmarks ; (4) Report results to state Y3: (1) Reduce the rate of surgical site infection for Class 1 and 2 wounds by X, where “X” will be determined in Year 2 based on baseline data; (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (3)Report results to the state. Y4: (1) Reduce the rate of surgical site infection for Class 1 and 2 wounds by X, where “X” will be determined in Year 2 based on baseline data; (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (3)Report results to the state. Y5: (1) Reduce the rate of surgical site infection for Class 1 and 2 wounds by X, where “X” will be determined in Year 2 based on baseline data; (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (3)Report results to the state. Hospital-acquired Pressure Ulcer (HAPU) Prevention Stroke Management Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention & Treatment Falls with Injury Prevention DSRIP Plan: UC San Francisco Medical Center / UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital Page 6 Y1: Educate at least 100 nurses on pressure ulcer prevention and wound Use a multi-disciplinary team approach to the care. Education will focus on prevention, identification, treatment and prevention of pressure ulcers using evidencecase review analysis based recommendations from the national Y2: (1) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (2) Report HAPU prevalence results to the state Y3: (1) Achieve HAPU prevalence of less than 2.2%: (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (3)Report HAPU prevalence to the state. Y4: (1) Achieve HAPU prevalence of less than 1.7%: (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (3)Report HAPU prevalence to the state. Y5: (1) Achieve HAPU prevalence of less than 1.1%: (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (3)Report HAPU prevalence to the state. Not a selected intervention by UCSF Medical Center Prevent VTE by checking patients for risk of blood Not a selected intervention by UCSF Medical Center clots and taking appropriate prevention steps Not a selected intervention by UCSF Medical Center