Second Semester Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement

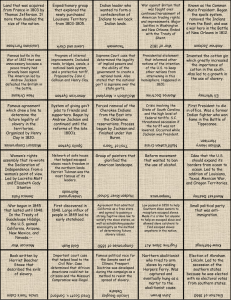
Second Semester Final Exam Study Guide People and Terms 1. States’ Rights (7) belief that state power should be greater than federal power 2. Judicial Review (9) Supreme Court’s power to declare acts of Congress unconstitutional 3. Secession (9) act of formally withdrawing from the Union 4. Louisiana Purchase (9) land deal that doubled the size of the United States 5. James Monroe (10) president during the “Era of Good Feelings” 6. Indian Territory (10) area of land containing most of what is now Oklahoma 7. Whig Party (10) political organization that supported the idea of a weak president and a strong legislature. 8. Eli Whitney (11) invented the Cotton Gin 9. Mass Production (11) the making of large numbers of identical goods 10. Nativists (11) U.S. citizens who opposed immigration 11. Abolition (12) an immediate end to slavery 12. Frederick Douglass (12) ex-slave who published The North Star and became one of the most important African American leaders of the 1800’s 13. Seneca Falls Convention (12) convention that launched the organized women’s rights movement 14. Brigham Young (13) led Mormons to Salt Lake City, Utah 15. The Alamo (13) old Spanish mission that was occupied by Texas rebels 16. Sam Houston (13) former governor of Tennessee who was elected president of the Republic of Texas 17. Popular Sovereignty (14) principle that would allow voters in a particular territory to decide whether they wanted to ban or permit slavery 18. Dred Scott Decision (14) Supreme Court ruling that denied that African Americans had rights as citizens 19. Battle of Antietam (15) the bloodiest single day battle in U.S. history 20. Pickett’s Charge (15) event in which 15,000 Confederates went up Cemetery Ridge 21. Freedmen’s Bureau (16) federal agency established to provide relief for all poor people in the south 22. Jim Crow Laws (16) laws that enforced segregation 23. Andrew Johnson (16) vice-president under Abraham Lincoln who was sworn in as president after Lincoln’s assassination Chapter 9 24. What major battle occurred two weeks after the U.S. and Great Britain signed a peace treaty?(9) Battle of New Orleans 25. Who was sent to explore the Missouri River area to establish peaceful relations with American Indians?(9) Lewis and Clark 26. Who was the Supreme Court Justice whose ruling established the principle of Judicial Review?(9) John Marshall 27. What impact did Marbury v. Madison have on the Supreme Court?(9) Established the principle of Judicial Review 28. Who were the War Hawks?(9) Members of Congress who wanted war with Britain during the war of 1812 Chapter 10 29. What is the concept of nullification?(10) States had the right to not obey any federal law with which they disagreed. 30. Who often represented the concerns of the slave states and was very popular with the common people?(10) Andrew Jackson 31. How did Georgia respond to the Supreme Court ruling in Worcester v. Georgia?(10) Georgia defied the ruling and removed the Cherokee from their land. 32. What did the Monroe Doctrine state?(10)it declared that the U.S. would not allow European nations to create American colonies or interfere with the free nations of Latin America. Chapter 11 33. Describe the impact of the Cotton Gin.(11) It increased the demand for slaves 34. What did the Missouri Compromise state?(11) Allowed Missouri and Maine to enter into the Union 35. Why did Nat Turner begin a slave revolt?(11) He believed that God had called upon him to end slavery. 36. What was the platform of the Know-Nothing Party?(11) They wanted to exclude Catholics and foreigners from public office Chapter 12 37. What was the function of the Underground Railroad?(12) A network of people who helped fugitive slaves 38. Who was William Lloyd Garrison and what was The Liberator?(12) One of the most outspoken leaders of the abolitionist movement/ an antislavery newspaper Chapter 13 39. After what battle was Santa Anna forced out of Mexico City thus ending the Mexican War?(13)Battle of Chapultepec 40. What did the term manifest destiny mean?(13) The belief that the U.S. was meant to expand across the continent Chapter 14 41. Why was John Brown’s raid at Harper Ferry unsuccessful?(14) No slaves would join for fear of punishment 42. What does the term sectionalism mean? A devotion to the interests of one region rather than to those of the entire country 43. Who was elected president of the Confederate States of America?(14) Jefferson Davis 44. Who wrote Uncle Tom’s Cabin and what was it about?(14) Harriet Beecher Stowe – The evils of slavery/slave being mistreated by his master 45. Who was the Union commander that refused to leave Fort Sumter?(14) Robert Anderson Chapter 15 46. What event triggered the Battle of Gettysburg?(15)confederate soldiers searching for shoes 47. Why did Union leaders want control over the Mississippi River?(15) To cut the Confederates off from supplies 48. Describe the total war strategy used by Sherman?(15) Targeting both civilian and military resources to destroy the South’s ability to fight 49. What did the Emancipation Proclamation do?(15) Declared slaves free in those areas controlled by the Confederacy 50. Who first introduced iron clad ships and why?(15) The Confederacy/in an attempt to overcome the Unions superiority at sea/to break the naval blockade 51. What was the 54th Massachusetts Infantry?(15)pg.527 A regiments consisting mainly of African Americans who played a key role in the attack on Fort Wagner, South Carolina Chapter 16 52. Northern Republicans that wanted to move to the south were often called what?(16) Carpetbaggers 53. What made slavery illegal throughout the United States?(16) 13th Amendment 54. What was the definition of Reconstruction?(16) The process of reuniting the nation and rebuilding the southern states without slavery 55. What is the definition of segregation?(16) The forced separation of whites and African Americans in public places Chapter 18 56. Why did skilled workers form trade unions?(18) Because competition with cheaper manufactured goods had reduced their wages and created poor working conditions and child labor 57. What is the purpose of a strike?(18) refusal to work until employers meet workers’ demands