Populations, Communities, and Biodiversity Powerpoint Questions 1
advertisement

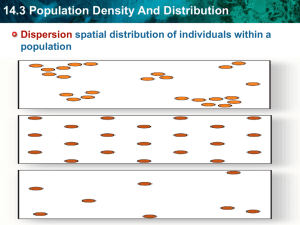
Populations, Communities, and Biodiversity Powerpoint Questions 12. The limit to population size that a particular environment can support is called ________________________(k). 1. Define Population Density. 13. What will eventually happen to the human population as it grows? 2. Define Spatial Distribution and state the 3 main types of dispersion. 14. Our growth rate will start to look like most organisms, which is the __________ Growth Model. 3. The primary cause of dispersion is ___________________________. 15. State 3 facts about the Logistics Growth Model. 4. The population growth rate depends on how fast a given population ________. 5. State the 4 factors that influence population growth . 16. Populations will stop increasing when (state 2 conditions). 6. Density-independent factors are factors that limit _______________________, regardless of population density, and these are usually ______________ factors such as (state 6 examples.) 17. Can the carrying capacity be raised or lowered? If so, how (give two examples)? 7. Define density-dependent factors. 18. Give two cycles to show when populations do not reach “k” as smoothly as in the logistics graph. 8. Density-dependent factors are usually biotic factors such as (stat 4 examples). 9. The Exponential Growth Model is also called the _____________ growth or __________ growth; its first growth phase is _________ and called the _______ phase and the second growth phase is _________ and called the _____________ growth phase. 10. What is Population Density? 11. _____________ follows as nutrients and resources are used up. 19. State 5 descriptions about species that follow the Boom-and-Bust Life Cycle. 20. Draw the graph to represents the population growth of species that have longer life spans, produce few offspring, and are larger organisms. 28. During Primary Succession, small _________ plants and other organisms are established, and as these organisms die, additional ________ is created. 29. __________ brought in by animals, water and wind begin to grow in the soil. Eventually enough soil is present for ___________ and ____________ to grow. 30. The stable, mature community that eventually develops from bare rock is called a __________________________________. 31. What are some disturbances that can disrupt a community? 21. A ________________ is a group of interacting populations that occupy the same area at the same time. 32. After a disturbance, new ___________ of plants and animals might occupy the habitat. 22. Describe what are limiting factors to communities? 33. Pioneer species in secondary succession are usually _________ that begin to grow in the disturbed area; this is much ___________ than primary succession. 34. Why can’t we predict the end point of an ecological succession? 23. The Range of Tolerance is the _________ within which an organism can exist. 24. ____________ _______________ is the change in any ecosystem that happens when one community replaces another as a result of changing biotic and abiotic factors. 25. State the two types of ecological succession. 26. Describe Primary Succession. 27. The first organisms to arrive in Primary Sucession are usually __________ or __________, which are called pioneer species. They secrete _________ that can break down rock and their dead, decaying organic materials, along with bits of sediment from the rock make up ________. 35. Define Biodiversity and state the 2 main types. 36. The gradual process of becoming extinct is known as ____________ extinction. _______________________ occurs when a large percentage of all living species become extinct in a relatively short period of time. 37. State the 5 most recent mass extinctions.