Unit 8: Population and Community Ecology
advertisement

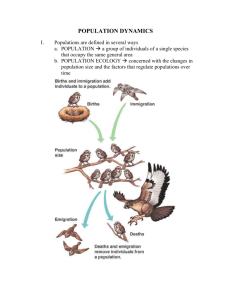
Chapter 35: Population and Community Ecology Concept 35.1: A population is a local group of organisms of one species I. Defining Populations A. A populations size is determined by the _______________ and space, weather conditions, and __________________________ B. When scientists study populations they must determine its ________________________, such a lake, a state or the whole country II. Population Density A. Population Density is the _____________________________ ______________________________________________________ B. Population density is useful when comparing two populations in different areas III. Sampling Techniques A. Since it is impossible to count every member of a population scientists use sampling techniques to estimate the size of a population 1. _________________________- scientists mark off a square boundary at several locations and take an average 2. Indirect Counting_____________________________ __________________ instead of the organisms themselves 3. ________________- scientists trap and mark individuals B. Most sampling techniques involve making __________________ about the populations being studied Concept 35.2 -There are limits to population growth I. Exponential Growth of Populations A. A population’s ability to grow partly depends on the ________ which its organisms can ____________________________ B. ________________________________ is when the population multiplies at a constant factor at constant time intervals i.e. bacteria doubling every 20 minutes II. Carrying Capacity A. A population may start to grow exponentially, but eventually one or more environmental factors will limit its growth B. A ________________________________________ is a condition that can restrict a population’s growth C. The carrying capacity is ___________________________ ___________________________________________________ III. Factors Affecting Population Growth A. ________________________________________ is a factor that limits a population more as a population density increases B. Density-Independent Factors are factors that limit population but are ____________________________________________ IV. Population Growth Cycles A. A “boom” and “bust” growth cycle is one that _____________ rapidly followed by a ____________________________ B. Other growth cycles are influenced by those of other populations in their environments V. Survivorship curves are graphic representations of the age structure of a given population. They are used to predict the future growth of the population. A. Type_____ - reflect relatively low death rates early in life and through midlife, with a sharp increase in death rate among older-age groups (e.g., _____________________). B. Type ______ - illustrate a fairly even mortality rate throughout the life span of the organism (e.g., ______________________________________________________). C. Type _______ - Populations with high death rates early in life followed by a sharp decline of death rates for the survivors are represented by Type III survivorship curves (e.g., _______________________________________________________________). Survivorship Curves- Type I, II, & III Concept 35.3-Biologists are trying to predict the impact of human population growth I. History of Global Population Growth A. For most of human history, the human population has grown __________________________________________ B. Human population growth depends on _______________ rates and ____________ rates C. The introduction of ________________ has provided a stable ___________________________ so birth rates have gone up D. Advances in _____________________________________ ______________________ have caused death rates to go down E. These factors have caused the human population to increase dramatically II. Predicting Future Population Growth A. The ___________________________ of a population is the proportion of people in different age groups B. Prediction of future growth varies because of the difficulty predicting future ________________ rates of various countries C. The question remains whether or not Earth will have the capacity for the human population Concept 35.4-Species interact in biological communities I. Competition Between Species A. B. C. D. Members of a population may compete for the same limited resource Within a community, ________________________ takes place when two or more species rely on the same limited resource __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ _______________________________ competitive exclusion A ____________________includes an organisms living place, its food source, the time of day it is most active and many other factors that are specific to that organism’s way of life II. Predation A. Predation ________________________________________ B. Eating and avoiding being eaten are important to survival and predators and prey have developed many adaptations 1. Predator adaptations include: _____________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ 2. _______________________ include: retreating or fleeing from predators, camouflage, defensive coloring, mimicry, secreting poisonous chemicals, having spines and thorns III. Symbiotic Relationships A. A symbiotic relationship is when two species _____________ ________________________________________________ B. There are three main types of symbiotic relationships 1. _____________________- A parasite gets it’s food at the expense of another organism, i.e. mosquitos and humans 2. ________________________- Both organism benefit from the relationship, i.e. E.Coli and humans 3. _________________________- One organism benefits and the other is neither hurt nor helped, i.e. sharks and remoras Concept 35.5-Disturbances are common in communities I. Disturbances to Communities A. Natural Disturbances are events such as ________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ B. Disturbances can be either positive or negative C. ________________also have an impact on communities which can be either positive or negative II. Ecological Succession A. The ___________________________________________, often following a disturbance is known as ecological succession B. There are two types of succession: 1. 2. Primary succession which is when new community arises from _________________________________ i.e. plants growing on a volcanic island Secondary succession is when ____________________ ______________________ i.e. a forested are which has been cleared and abandoned III. Human Activities and Species Diversity A. ______________ of the Earth’s land is used by humans, mainly for cropland or rangeland B. Humans usually have a negative effect on species in two ways 1. ___________________________- Humans clear vast amounts of land to make way for farming and building 2. _____________________________________ are species that are moved from one location to another either accidentally or on purpose. These new species may take over an area and prey on native species or drive them from their niches