Equine Rhinopneumonitis
advertisement

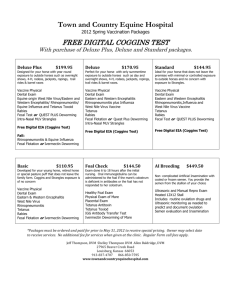
Equine Rhinopneumonitis Disease Name: Equine Rhinopneumonitis Species Affected: Equidae About the Disease: Equine Rhinopneumonitis is highly contagious viral disease of horses characterized by upper respiratory tract infection. The severity of respiratory disease varies with the age of the horse and the level of immunity resulting from previous vaccination or natural exposure. This disease is an OIE Reportable Disease as in the Disease Category 4. Animals Affected: Horses and donkeys. Cause: Equine Rhinopneumonitis is caused by caused by either of two members of the Herpesviridae family Equine herpesvirus -1 (EHV-1) and Equine herpesvirus -1 4 (EHV-4). Both viruses are endemic in most equine populations. Infection by either EHV-1 or EHV-4 is characterized by a primary respiratory tract disease of varying severity that is related to the age and immunological status of the infected animal. Infections by EHV-1 in particular are capable of progression beyond the respiratory mucosa to cause the more serious disease manifestations of abortion, perinatal foal death, or neurological dysfunction. Source of infection: Affected or Carrier animals are usually the source for new infection .The virus is spread via aerosolized secretions from infected coughing horses, by direct and indirect (fomite) contact with nasal secretions, and in contact with aborted fetuses, fetal fluids, and placentae associated with abortions. Symptoms: Equine Rhinopneumonitis is characterized (rhinopneumonitis) of varying severity. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Nasal discharge Fever Cough Discharge from the eyes Depression Loss of appetite by a primary respiratory tract disease 7. Perinatal foal death 8. Neurological dysfunction 9. Abortion 10. Death. Control and Management: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Isolation and quarantine of newly brought animal in the herd. Isolation of infected horses. Annual vaccinations and good sanitary practices provide the best preventive treatment. Good Stable hygiene is always recommended. Slaughtering and proper disposal of infected animals is advisable for the risk of further transmission. Vaccines: In India no potent vaccines is available and the immunity derived from vaccination for Equine Rhinopneumonitis is short lived so a booster vaccination should be given to extend immunity for this disease. In other countries, both live attenuated and inactivated viral vaccines of varying composition are commercially available. Multiple vaccines are available ( Duvaxyn EHV1,4, EquiGuard, EquiVac EHV-1/4, etc.), most in an inactivated virus form. Meteorological Occurrence: Its distribution occurs in world wide. Prepared by: Dr. Peter N JRF, NADRS, Manipur. Disease Investigatory Laboratory Directorate of Veterinary, & A.H. Services, Manipur