Ammonia Chemistry Worksheet: Properties & Reactions
advertisement

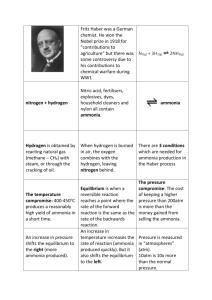
Ammonia Fill In the blanks Q Complete the statements by selecting correct word from the brackets. (i) The gas most difficult to liquiefy is __________ [nitrogen/ammonia/hydrogen]. (ii) Ammonia in liquid form is __________ [basic/neutral/acidic]. (iii) The salt solution which gives white ppt. on the addition of ammonium hydroxide solution is __________ [sodium sulphate/potassiam nitrate/magnesium chloride]. (iv) Excess of ammonia reduces chlorine to ________ [NH4Cl/ N2/HCl]. (v) The alkaline behaviour of liquor ammonia is due to the presence [+ ions/OH– ions/H3O+ ions] of __________ [NH4 Q Choose the correct word from the brackets for each sentence and write a balanced equation for the same. (a) Ammonium chloride is a soluble salt prepared by ______ (precipitation, neutralization). (b) When ammonium chloride is heated, it undergoes thermal ______ (decomposition / dissociation). Q Choose the correct word from the bracket and write a balanced equation for the same : Heating ammonium chloride with sodium hydroxide produces ______ [ammonia / nitrogen]. Give one word for/ Name the following Q Why nitrogenous matter produces ammonia? State a liquid source of ammonia. Q Why is ammonia not obtained in laboratory from NH4NO3 and NaOH? [2] Q How is density of ammonia compare with air? Name two gases lighter than ammonia. [2] Q Ammonia gas is highly soluble in water. Name two more gases showing similar solubility. [1] Q Name in industrial process which uses a catalyst, ammonia and oxygen as reactants. Q What is the chemical name of aqueous solution of ammonia? By giving reasons, explain, how is it prepared? [3] Q Name the catalyst which is used in the oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide. Name the other product of the oxidation reaction. Q Name the gas evolved by choosing from letters A, B, C and D in the following statements. A. N2O B. NO C. N2 D. NO2 (i) Ammonium nitrite undergoes a thermal decom-position. (ii) A greenish yellow gas reacts with excess of ammonia. (iii) Dry ammonia and oxygen are ignited. (iv) Dry ammonia and oxygen are passed over heated platinum and then allowed to cool. (v) Ammonia gas is passed over heated litharge. [5] Q A gas X is formed when a substance Y is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid. The gas X turns wet blue litmus paper red and gives dense white fumes with ammonia. (i) Name gas X and substance Y. (ii) Write balanced chemical equation between Y and cone. H2SO4. (iii) Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction between gas X and ammonia. (iv) What is the nature (acidic or basic) of gas X? Give an evidence to justify your answer. Q Q Name a gas (other than hydrogen chloride gas) which gives dense white fumes with ammonia. Name one compound of ammonia which is used in (i) dry cell (ii) explosives (iii) fertilizers (iv) medicine as stimulant Q From the list of substances given – Ammonium sulphate, Lead carbonate, Chlorine, Copper nitrate, Ferrous sulphate – State : A compound which on heating with sodium hydroxide produces a gas which forms dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride. Q Name two chemicals required for the laboratory preparation of ammonia gas. Q Name the drying agent used for drying ammonia. Q Select the correct compound from the list given – Ammonia, Copper oxide, Copper sulphate, Hydrogen chloride, Hydrogen sulphide, Lead bromide – which matches the description given below: Although this compound is not a metal hydroxide, its aqueous solution is alkaline in nature. Q From the gases – ammonia, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulphide, Sulphur dioxide – Select the following: (a) When this gas is bubbled through copper sulphate solution, a deep blue coloured solution is formed. (b) This gas burns in oxygen with a green flame. Q Select the most probable substance from D, E, F, G and H which must be added to distinguish between: (i) Ammonium sulphate from ammonium chloride acid.[ D. Conc. Hydrochloric] (ii) Potassium sulphate from ammonium sulphate. [E. Ammonia gas] (iii) Copper (II) oxide from Cu(II) chloride [F. Sodium hydroxide] (iv) Liquior ammonia from liquid ammonia [G. Barium chloride] (v) Ammonia and sulphur dioxide gas [H. Phenolphthalein]. Q (i) What are the products formed when ammonia is oxidized with copper oxide. (ii) From the following gases – ammonia, chlorine, hydrogen chloride, Sulphur dioxide, select the gas that matches the description given below: (a) The gas [B] turns moist red litmus paper blue. What is the name of gas [B]? Q Name a gas whose solution in water is alkaline. Q Name the ion other than ammonium ion formed when ammonia dissolves in water. Q The questions below are related to the manufacture of Ammonia 1. Name the process 2. In what ratio must be the reactant 3. Name the catalyst used 4. Give balanced chemical equation for manufacture of ammonia 5. Give one equation to explain reducing nature of ammonia Q Name a simple method you would employ to prepare ammonium salts in your laboratory. Q Q Which compound is normally used as a drying agent for ammonia ? Name a substance used for drying ammonia. Q Name [formula is not acceptable] the gas produced on warming ammonium sulphate with sodium hydroxide solution. Q Ammonia can be obtained adding water to : [select the correct word] A: Ammonium chloride B: Ammonium nitrate C: Magnesium nitride D: Magnesium nitrate. Q Name: An alkaline gas ‘A’ which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride. Give reason Q State why an aqueous solution of ammonia turns red litmus blue? Q Why is the aqueous solution of ammonia a weak base and weak electrolyte? [2] Q Why cannot drying agents such as conc. H2SO4, anhydrous calcium chloride and phosphorus pentoxide be used for drying ammonia? Support your answer with a chemical equation? [3] Q Why should the apparatus for the collection of ammonia gas be perfectly dry? Q Name the chemical for drying ammonia. Why the chemicals such as CaCl2, P2O5 and conc. H2SO4 is not used for drying ammonia. Support your answer by chemical equations. Q How is ammonia collected? Why is ammonia not collected over water ? Chemical Equations Q Write a word equation and balanced molecular equation for the laboratory preparation of ammonia from ammonium chloride. Q Write chemical equations for preparing ammonia from ammonia sulphate by using two different alkalis. [2] Q How is ammonia collected? Why is ammonia not collected over water ? Write a chemical equation when the chemicals named in (i) react. Q Write the equation for the reaction when a mixture of ammonium chloride and slaked lime is heated. Q Write the chemical equations for (i) Ammonia gas reacts with excess of chlorine gas. (ii) Ammonia gas reacts with limited amount of chlorine gas. Q (i) The following reactions are carried out : A : Nitrogen + Metal → Compound X. B : X + Water → Ammonia + Another compound. C : Ammonia + Metal oxide → Metal + Water + N2. (i) One metal that can be used for reaction A is magnesium. (a) Write the formula of the compound X formed. (b) Write the correctly balanced equation for reaction B where X is the compound formed. (c) What property of ammonia is demonstrated by reaction C. (ii) Write the equation for the formation of ammonia by the action of water on magnesium nitride. (iii) Write the equation for the reaction of Aluminium nitride and water. Q i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. Q What is the purpose of Haber’s Process. Name the gaseous inputs of the Haber’s process and state the ratio by volume in which the gases are mixed. What is done to increase the rate of the reaction in the Haber’s Process. Give two different ways by which the product can be separated from the reactant. Write the equation for the reaction in the Haber’s Process that forms ammonia. State the purpose of liquefying the ammonia produced in the process. With reference to Haber’s Process for the preparation of ammonia, write the equation and the conditions required. (i) Write equation for the following: (a) Burning of ammonia in oxygen (b) Catlytic oxidation of ammonia. (ii) What do you observe in (a)? (iii)Name the catalyst used in (b). (iv)In the reaction referred to in (b), the catalyst glows red hot. Why?What is the name of the industrial process which starts with the reaction referred to in (b). Q Q Write an equation for the reaction of chlorine with excess of ammonia. Write a balanced chemical equation to illustrate the reducing nature of ammonia. Q What property of ammonia is demonstrated by the Fountain Experiment. Write the balanced equation for the reaction between ammonia and sulphuric acid. Q Q Give balanced equations for the following conversions. [3] (i) NH4OH to (NH4)2SO4 (ii) (NH4)2SO4 to 2NH3 (iii) NH3 to N2 Copy and complete the following table relating to an important industrial process. Output refers to the product of the process not the intermediate steps. Name of process Inputs Haber process Hydrogen + Catalyst Equation for catalyzed reaction Output Q Write the equation for the following reaction: Aluminium nitride and water. Q Write an equation for solutions of ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide are heated. Q Write the equation for the preparation of NH3 from ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide. Q Write fully balanced equations for the following reactions : (i) Aluminium nitride is treated with warm water. (ii) Ammonium sulphate crystals are warmed with sodium hydroxide. (iii) Ammonium chloride is warmed with slaked lime. (iv) Magnesium nitride is treated with warm water. Starting from (i) magnesium, (ii) calcium and (iii) aluminium how can you obtain ammonia gas. Support your answer by chemical equations. [9] Q Q Write a balanced equation for the burning of ammonia in oxygen and state your bservations. [2] Q By writing chemical equations, explain how can you prepare ammonium chloride from hydrochloric acid by two different methods. [4] Q Write chemical equations for the conversion of : (i) Ammonia to nitric acid. (ii) Ammonium hydroxide to ammonium sulphate. [4] Q Write balanced chamical equations for reducing action of ammonia with (i) lead(II) oxide (ii) excess of chlorine Q State how ammonium hydroxide solution is used in identifying (i) Fe2+, (ii) Fe3+ , (iii)Zn2+ , (iv) Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions. Q By stating all experimental conditions write an equation for the conversion of ammonia into nitric oxide. [2] What do you observe Q A flask contains 2(vols) of oxygen and 1(vol.) of ammonia. If the flask is lowered a coiled wire of platinum and its ends are connected to a battery through a switch. The flask is sealed and electric current is switched on for 1 minute. Describe your observation and explain by writing balanced chemical equations. Q State five tests for ammonia, where colour change is involved. [5 Q (i) What do you observe when ammonia gas is bubbled through red litmus solution. (ii) State what you observe when a piece of moist red litmus paper is placed in a gas jar of ammonia. Q How would you distinguish between Zn2+ ans Pb2+ using ammonium hydroxide solution. Q State what is observed when excess of ammonia is passed through an aq. solution of lead nitrate. Q How will you confirm that a gas jar is completely filled with ammonia gas? [1] Q Give one test for the gas evolved in [1] Q Give your observation when- Ammonia gas is bubbled through red litmus solution. Direct questions Q State two physical properties of ammonia which enable its separation from a mixture of NH3, H2 and N2. [2] (5) What property of ammonia is illustrated by its reaction with CuO? Q State the chemical name and formulae of the following salts and a reason for their use : (i) smelling salt (ii) sal ammonic used in dry cells. Q By stating experimental conditions and writing chemical equations, write how the nitrogen gas reacts with the following : [6] (i) Hydrogen gas (ii) Oxygen gas (iii) Magnesium powder. Q Nitrogen can be prepared directly from air by removing oxygen and other impurities. Answer the following questions : (i) How are the acidic impurities such as carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, etc., removed from the air? (ii) How are the water vapours present in the air removed? [1] (iii) How is oxygen removed from the air? Support your answer by an equation. [2] (iv) How is nitrogen gas collected? [1] (v) The vapour density of nitrogen so collected is more than the vapour density of nitrogen collected by chemical reactions. Why is it so? [2] Miscelleneous Q Nitrogen gas is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite solutions. (i) Write a fully balanced equation for the above reaction. [1] (ii) Why is nitrogen not prepared by directly heating ammonium nitrite? [1] (iii) How is the drawback in (ii) overcome in reaction (i)? (iv) If instead of sodium nitrite, sodium hydroxide is added, name the gas evolved and write a fully balanced equation. [2] (v) How will you test the gas evolved in (iv)? [1] (vi) If instead of sodium nitrite, conc. sulphuric acid is added, name the gas evolved? Write fully balanced equation in support of your answer. [2] Q Ammonium salts decompose on heating. What other property do ammonium salts have in common? Numericals Q In the preparation of ammonia in industry, the raw materials are nitrogen and hydrogen. These are mixed together in the correct proportions needed to form ammonia. (i) Write the balanced equation for the manufacture of ammonia. [1] (ii) How much hydrogen would there be in 400 litres of gaseous mixture required for the manufacture of ammonia? [2] (iii) 1. If all nitrogen and hydrogen used were converted into ammonia, find the volume of ammonia formed. [1] 2. How would the volume of ammonia formed compare with the volume of original mixture? [1] (iv) The formation of ammonia from its elements is an exothermic reaction. What is meant by exothermic? (v) Ammonia produced is removed from unchanged gases in one of the two possible ways. Mention the two ways. [2]