Study Guide for Plant Taxonomy Quiz on Wednesday October 29
advertisement

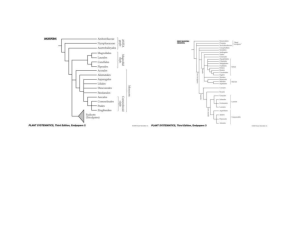
Study Guide for Plant Taxonomy Quiz on Wednesday October 29, 2014 Keep an eye to the BIG PICTURE—I may ask a question or two about how everything fits together! Be able to diagram a simple phylogeny of angiosperms. Angiosperms: ANITA (ANA) Grade : Basal Angiosperms What is the ANITA Grade and what do the letters stand for? How do the plants of the ANITA grade differ from the Core Angiosperms? How are the carpels fused? What are columellate pollen, ethereal oils and why are they important? Be VERY clear on angiosperm synapomorphies and be able to list several. Discuss the level of differentiation of flower parts in general in the ANITA grade. Have a general understanding of Amborella, Nymphaeales, Illiaceae (Austrobaileyales). Which had no vessels? What group has air spaces in the stems? How prevalent is the apocarpous state and poorly differentiated stamens? Magnoliid Clade What characters resolve magnoliids into a separate clade (for example: molecular synapomorphies and secondary chemistry), monophyletic group including the Magnoliales, Laurales, Canellales & Piperales, perianth parts spiral or whorls of 3, sources of spices, stamens frequently poorly differentiated, be able to describe the foliage & calyx & corolla & androecium & gynoecium & fruit of the Magnoliaceae, Myristicaceae, Lauraceae, Piperaceae, Aristolochiaceae, and Saururaceae (see separate study guide) General Monocots: Embryo with a single cotyledon– remains the best morphological synapomorphy of monocots Other monocot characteristics (but not necessarily synapomorphies since there are many exceptions) : parallel veined leaves, adventitious roots, herbaceous habit, scattered vascular bundles, leaves formed at the basal end of the leaf primordium (= intercalary meristem), monosulcate pollen, DNA sequence evidence, flower parts in 3’s. What is a cotyledon (leaf or leaves developed at first embryonic node) and how do they differ from endosperm? Ploidy level of endosperm vs. cotyledons. No vascular cambium (i.e., no wood) in monocots although they can grow thicker by virtue of anomalous (secondary thickening) meristem Know the foliage/calyx/corolla/androecium/gynoecium/fruit for Lilliaceae. Family Magnoliid Clade Magnoliaceae Myristicaceae Lauraceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit Trees/shrubs blade with pellucid dots containing ethereal oils (aromatic terpenoids) bark exudes reddish sap; blades with pellucid dots containing ethereal oils; contains myristicin (=hallucinogen Tepals distinct Tepals distinct Many undifferentiated stamens Numerous distinct, superior aggregate of follicles, seed red, dangles Three connate tepals Three connate tepals filaments connate into a solid column; stamens 2 to numerous one ovule, ovary superior leathery follicle, large seed, colorful aril contain ethereal oils (made from 5 carbon Usually 6 tepals Usually 6 tepals filaments with nectar producing appendages; one carpel, ovary superior Drupe or one seeded berry Piperaceae fragment called terpenoid) contains ethereal oils stamens 3-12 Aristolochiaceae ethereal oils with pellucid dots and aristolochic acids, bitter yellow nitrogenous compounds Saururaceae with ethereal oils Family Monocots (nonCommelinoid Clade) Liliaceae No perianth! Spikes of thick, minute flowers connate, showy, dull red, mottled No perianth! Spikes of thick, minute flowers missing filaments distinct; stamens 1-10 1 ovule per gynoecium, superior drupe filaments adnate to style; stamens 6-12 4-6 carpels, inferior ovary Septicidal capsule Absent-Flowers with a single petaloid bract Absent-Flowers with a single petaloid bract 3-8 distinct stamens 3-4 carpels united at the base; superior capsule Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit bulbs or rhizomes, parallel venation Six distinct tepals Six distinct tepals Stamens 6, filaments distinct 3 connate carpels, ovary superior Loculicidal capsule Plant Taxonomy Plant ID list 2014: WEEK 1 Euphorbia (term to know: cyathium) EUPHORBIACEAE Tribulus (terms to know: schizocarp, mericarp, opposite, alternate, distinct, adnate, connate) ZYGOPHYLLACEAE WEEK 2 Ipomopsis (term to know: exserted) POLEMONIACEAE Castilleja (term to know: hemiparasite) OROBANCHACEAE Malva (term to know: monadelphous) MALVACEAE Hesperidanthus (terms to know: tetradynamous, silique) BRASSICACEAE Desmodium (term to know: loment) FABACEAE Commelina (term to know: spathe) COMMELINACEAE WEEK 3 Melampodium (terms to know: disc flower, ray flower) ASTERACEAE Argemone (term to know: merosity, plant alkaloids) PAPAVERACEAE Cucurbita (terms to know: pepo, inferior ovary) CUCURBITACEAE Datura (terms to know: salverform, funnelform) SOLANACEAE Oenothera (term to know: inferior ovary) ONAGRACEAE WEEK 4 Agastache (term to know: zygomorphic) LAMIACEAE Dieteria (terms to know: phyllary, achene) ASTERACEAE Scirpus (terms to know: sedge, monocot) CYPERACEAE Thalictrum (term to know: dioecious) RANUNCULACEAE Guilleminia (term to know: bract) AMARANTHACEAE WEEK 5 Persicaria (term to know: ochrea) POLYGONACEAE Typha TYPHACEAE Maclura (term to know: multiple fruit) MORACEAE Boerhavia (term to know: anthocarp) NYCTAGINACEAE Mentha LAMIACEAE WEEK 6 Ericameria (terms to know: discoid, lanate) ASTERACEAE Gutierrezia (term to know: radiate) ASTERACEAE Polanisia CLEOMACEAE Croton (term to know: dioecious) EUPHORBIACEAE Salsola (term to know: whole plant is dispersal mechanism) CHENOPODIACEAE WEEK 7 Ephedra (term to know: Gnetophyte) EPHEDRACEAE Portulaca (term to know: circumscissile) PORTULACACEAE Mollugo (term to know: whorled) MOLLUGINACEAE Allionia NYCTAGINACEAE Dimorphocarpa BRASSICACEAE Stachys LAMIACEAE