Ch. 8 Guided Notes
advertisement

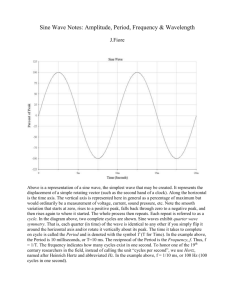
Name: ______________________________ Chapter 8 - AC circuits page 1 Alternating Voltage is a voltage that: 1. Continuously varies in ___________________ 2. Periodically _______________ in polarity Symbol for a _______________________________ source. The sinusoidal waveform _______ __________ is the fundamental alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage waveform. ____________ _______ ________ are named from the mathematical function with the same shape. Sinusoidal voltage sources Sinusoidal voltages are produced by ___ ___________ and electronic oscillators. When a conductor rotates in a constant magnetic field, a sinusoidal wave is generated. Fill in chart as we talk about it: N Motion of conductor S Conduc tor When the conductor is moving _______________ with the lines of flux, no voltage is induced. When the loop is moving __________________ to the lines of flux, the maximum voltage is induced. Sine waves are characterized by the __________________ and _____________. Page 2 1. The ______________ is the maximum value of a voltage or current. 2. The period is the ___________________________ ____________. 20 V 15 V The amplitude (A) of this sine wave is _________. 10 V 0V The period is :_________. t (s) 0 25 37.5 50.0 -10 V -15 V -20 V The period (T) of a sine wave can be measured between any ___________________________on the waveform. By contrast, the ______________ of a sine wave is only measured from the center to the maximum point. Frequency ( f ) is the _________________________ that a sine wave completes in one ___________. Frequency is measured in______________. If 3 cycles of a wave occur in one second, the frequency ______________. The smaller amount of cycles per second the ____________ frequency. The larger amount of cycles per second the _________ Frequency. The ___________ and ________________ are reciprocals of each other. Period and Frequency: f 1 T T 1 f If the period is 50 s, the frequency is (The 1/x key on your calculator is handy for converting between f and T.) Page 3 Period and Frequency problems: 1 f T T 1 f 1. Calculate the frequency for each of the following periods: a.) 4 s b.) 300 µs c.) 0.5 s d.) 2 ms 2. Calculate the period for each of the following frequencies: a.) 40 Hz b.) 3 kHz c.) 7 MHz d.) 300 MHz 3. How long does it take a 20 kHz sine wave to complete 200 cycles? 4. A sine wave has a frequency of 30 kHz. How many cycles does it complete in 6 ms? 5. A sine wave goes through 4 cycles in 8µs. What is its period? Page 4 Sine wave voltage and current values • Instantaneous value____ : __________ __ ___________at any point on the curve. • • Peak value (______ for voltage): The ____________of a sine wave. 20 V 15 V The peak voltage of the wave form is ______. 10 V 0V t (s) 25 0 37.5 50.0 t= micro seconds Below are the equations to find: Peak to peak value: Value from positive peak to negative peak. pp = peak to peak p = peak value -10 V -15 V -20 V V 2V PP Vpp = 2 (20v) = 40 Voltage I 2I P PP P RMS(Root mean square): Most ac voltmeters display rms voltage. The 120V at your wall outlet is an rms value. RMS (root mean square) value: Is the sinusoidal wave with the same heat value as a DC voltage source (known as the effective value) V 0.707V rm s P V 1.414V p vms I 0.707 I rm s P I 1.414 I p 15 V vms 10 V Vavg = 0.637Vp V = ______ 0V Vp = _____________ 30 Vpp = ___________ Vavg = ________________ Use the graph below to answer these questions. What is Vp = What is Vrms = ____________ __________________ What is Vpp = __________ Voltage (V) 10 0 What is Vavg = ___________ -20 -30 - 40 50.0 -20 V 20 -10 37.5 -15 V The rms voltage is =______ 40 t (s) 25 0 -10 V The peak-to-peak voltage is = _______ P 1. 20 V What is the period = ____________ What is the frequency = _____________ 2. Try this one yourself. Page 5 What is Vrms = ____________ What is Vpp = __________ What is Vavg = ___________ What is the period = ____________ What is the frequency = _____________ 60 V 45 V 30 V 0V t (s) 0 25 37.5 50.0 -30 V -45 V -60 V Homework p. 377 selftest 1-9 in complete sentences or if equations show your work! Also p. 378 2,6,9,10,15 all parts and show your work. Phase of a sine wave: Phase: Angular measurement that specifies the position on the sine wave relative to a reference point Phase Shift: Page 6 Occurs when a sine wave is shifted right or left in relation to the base/reference sine wave. Phase Shift: Lead and Lag Occurs when a sine wave is shifted right or left in relation to the base/reference sine wave. Add comments to graphs Poly Phase Power An important application of phase-shifted sine waves is in electrical power systems. o • Electrical utilities generate ac with three phases that are separated by 120 . • 3-phase power is delivered to the user with three hot lines plus neutral. The voltage of each phase, with respect to neutral is 120 V. Add Current to graph Sine Wave equation: page 7 Instantaneous values of a wave are shown as____________. The equation for the ___________________ voltage (v) of a sine wave is v V p sin Where Vp = Peak Voltage Θ(theta) = Angle in Radians or degrees. If the peak voltage is 25 V, the instantaneous voltage at 50 degrees is A certain sine wave has a positive-going zero crossing at 0° and an peak value of 40V. Calculate its instantaneous voltage for the degrees listed below for the sine wave below. 45°, 125°, 180°, 220°,325° Show your work! Homework problem 16 all parts, pay close attention to the Voltage. Can you use Vrms to calculate Instantaneous voltage! Page 8 Phasor (aka Phase Vector): Representation of a ______ _______ whose amplitude (A) and __________ frequency (ω - omega) are a ___________ rate. Power in resistive AC circuits: A sinusoidal voltage produces a Kirchhoff’s _________ _____applies to AC circuits just like DC circuits _______________ current. Power in AC circuits is calculated using RMS values for ___________ and ____________. Finish picture! The formula’s are: The dc and the ac sources produce the same power to the bulb: P Vrms I rms 2 Vrms P R 2 P I rms R ac or dc source Bulb WHY? Page 9 Assume a sine wave with a peak value of 40 V is applied to a 100 resistive load. What power is dissipated? 40 V 30 Voltage (V) 20 10 rms = 0.707 x V = p 0 -1 0 -2 0 -3 0 - 40 Homework Page 379 #21 all parts AC Generators (alternators) • Generators convert rotational energy to_____________ _____________. • • The __________ has an induced voltage, which is connected through ______ _____ and brushes to a ______. • • The armature loops are wound on a __________ _______.(not shown for simplicity). • Small alternators may use a ____________ magnet. Others use Use ______ coils to produce ____________ _______. • Increasing the number of________ increases the number of _________ per revolution. • A _________ ________ generator will produce _______ complete cycles in each revolution. An output Frequency of an AC Generator f Ns 120 f – frequency (Hz) N – number of poles s - speed in RPM Alternators: page 10 • In vehicles, alternators_________ ___, which is converted to dc for operating _____________ _______and charging the battery. • • AC is more ____________ to produce and can be easily____________, hence it is generated and converted to DC by____________. Housing The _________ is taken from the ________ through the ______ rings. Stator coils Rotor Diode plate AC Motors There are two major classifications of ac motors. 1. _____________ motor. Diodes Slip rings 2. _________________ motor. Both types use a _____________ field in the __________ windings. Induction motors work because __________ is induced in the rotor by the changing _________ in the ________. This current creates a ______________ ________ that reacts with the __________ field of the stator, which develops a __________ and causes the __________ to turn. Synchronous motors have a ___________ for the rotor. In small motors, this can be a _______________ magnet, which keeps up with the ___________ field of the stator. Large motors use an _________________ in the rotor, with external dc supplied to generate the magnetic field. Induction verses Stator p. 358 Pulse Definitions p. 11 Ideal Pulses Leading (rising) edge Leading (falling) edge Trailing (falling) edge Trailing (rising) edge Baseline Am plitude Am plitude Baseline Pulse width (a) Positive-going pulse Pulse width (b) Negative-going pulse Repetitive pulse Waveforms • • • • • • • Periodic waveforms repeat at __________ intervals. Pulse repetition frequency: _______ at which the pulses _________. _________________ – Ratio of pulse width (t ) to the period (T). w Add formulas to picture below. Define these terms on page 359, Rise time: Fall time: Pulse Width: Voltage Ramp: page 12 Ramp – Linear increase or decrease in voltage or current. Slope = Yaxis V I or Xaxis t t Triangular and Sawtooth waves Triangular and sawtooth waveforms are formed by __________ or ____________ current ramps (linear increase/decrease). ____________waveforms have T T T positive-going and negative-going ramps of ______ duration (same slope either increasing or decreasing). T The sawtooth waveform consists of ____ ramps, _____ of much longer duration than the other. (_________ slopes in either direction). Find the T, Vp, Vpp, Vrms for each graph A.) B.) C.) D.)