Geography Unit 1 Study Guide—6 th Grade
advertisement
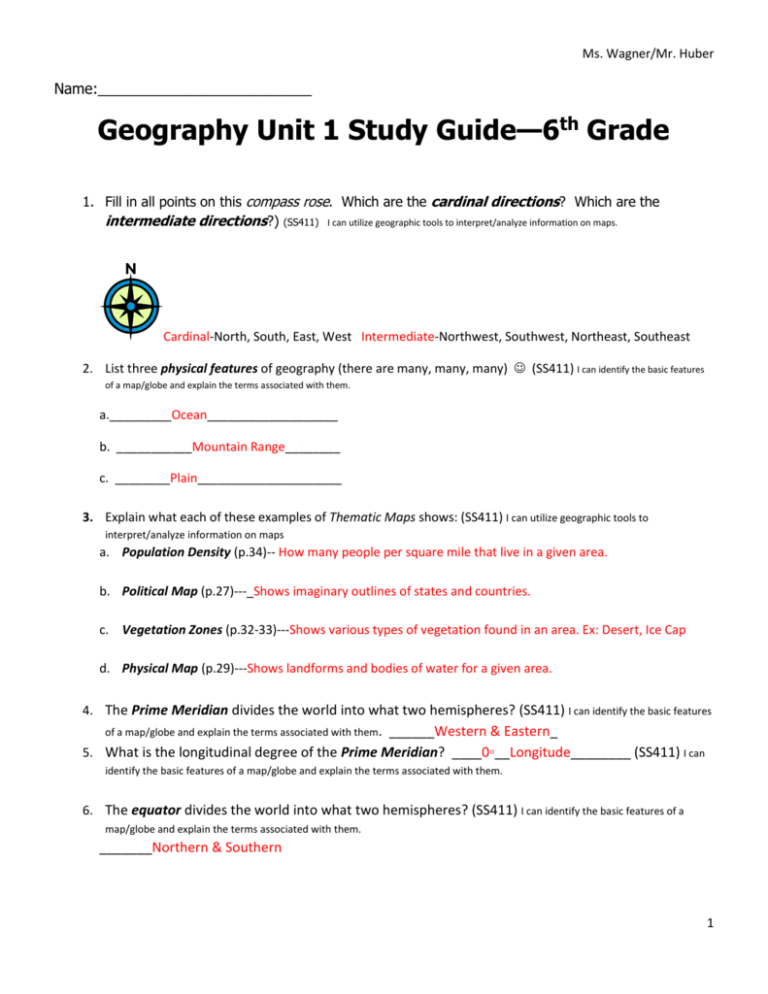
Ms. Wagner/Mr. Huber Name:__________________________ Geography Unit 1 Study Guide—6th Grade 1. Fill in all points on this compass rose. Which are the cardinal directions? Which are the intermediate directions?) (SS411) I can utilize geographic tools to interpret/analyze information on maps. Cardinal-North, South, East, West Intermediate-Northwest, Southwest, Northeast, Southeast 2. List three physical features of geography (there are many, many, many) (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. a._________Ocean___________________ b. ___________Mountain Range________ c. ________Plain_____________________ 3. Explain what each of these examples of Thematic Maps shows: (SS411) I can utilize geographic tools to interpret/analyze information on maps a. Population Density (p.34)-- How many people per square mile that live in a given area. b. Political Map (p.27)---_Shows imaginary outlines of states and countries. c. Vegetation Zones (p.32-33)---Shows various types of vegetation found in an area. Ex: Desert, Ice Cap d. Physical Map (p.29)---Shows landforms and bodies of water for a given area. 4. The Prime Meridian divides the world into what two hemispheres? (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. ______Western & Eastern_ 5. What is the longitudinal degree of the Prime Meridian? ____0◦__Longitude________ (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. 6. The equator divides the world into what two hemispheres? (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. _______Northern & Southern 1 Ms. Wagner/Mr. Huber 7. What is the latitudinal degree of the equator? (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. _____0◦_Latitude_____________ 8. What are possible characteristics of a country with a low population density? Example: climate, vegetation, job opportunities, etc… (SS442) I can explain cause and effect relationships between the physical geography of an area and its social and economic development. *Extreme climate *Lack of vegetation or job opportunities *Difficult landforms (Mountains) *Unstable food supply 9. Define absolute location. Provide an example. (SS411) I can identify absolute location of places on Earth’s surface. _The exact location of an area on Earth. Ex: An address, coordinates 10. Explain relative location. Provide an example. (SS411) I can identify absolute location of places on Earth’s surface. The location of one place compared to another. Ex: RECCA is behind Walgreens and across from McDonald’s 11. What is the most accurate way to show the earth? Globe or Map? (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. A globe is the most accurate way because it does not distort the oceans or continents. 12. Define distortion. Provide a common example of distortion found on a map. (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. Changes on a map in the size, shape or distance of an area. 1. North Pole 2. South Pole 3. Pacific Ocean 13. Label the continents and oceans on the attached map. Highlight the equator and Prime Meridian. (SS411)I can identify absolute location of places on Earth’s surface. 2 Ms. Wagner/Mr. Huber 14. What is a climagraph? The bars on a climograph stand for what? The line stand for what? (SS442) I can explain the cause and effect relationships between the physical geography of an area and its social and economic development. A graph that shows the climate of a specific area. Remember the bars represent precipitation and the line represents temperature. 15. What does urban mean? Urban areas are usually found by what physical feature? Would an urban area have a high or low population density? (SS421) I can explain cause and effect relationships between the physical geography of an area and its social and economic development. 1. Found in the city. 2. Urban areas are usually found by or on water. 3. High Population Density 16. Falmouth and California, KY, have a low population density and have farmland. They are examples of what? (SS421) I can explain cause and effect relationships between the physical geography of an area and its social and economic development. _Rural Areas 17. Define suburb and give a local example. (SS421)I can explain cause and effect relationships between the physical A developed area at the edge of an urban area. Alexandria, Southgate, Ft. Thomas, Cold Spring, etc… geography of an area and its social and economic development. 18. How are weather and climate different? (SS442)I can explain cause and effect relationships between the physical geography of an area and its social and economic development. Weather Changes in a short period of time Climate Changes at a much slower rate (think seasons) 3 Ms. Wagner/Mr. Huber Hard to predict Predictable What is happening now What should happen 19. Give 4 examples of human geography (think culture). (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. Food, language, religion, government, economics, clothing, etc…. 20. Each continent can be found in at least how many hemispheres? (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. 2 21. What do the following geographic tools tell a map reader? (SS411) I can identify the basic features of a map/globe and explain the terms associated with them. a. Map Scale-The distances between places. b. Title-The topic of the map and the type of map that it is. c. Map Key-What symbols mean on a map. 4