Fume Hood SOP: Biological Science Safety
advertisement

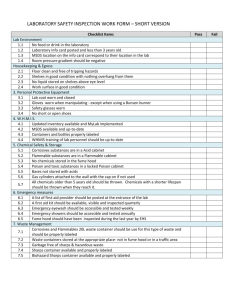
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Procedure: School/Department: SOP prepared by: Use of Fume Hood School of Biological Science Angela Nikolic, Nick Coleman SMB edit M Joseph Section 1 - Personal Protective Equipment • lab coat and enclosed shoes: always • hair tied back if long • safety glasses: if risk of squirt/splash of toxic, corrosive or biohazard liquids • gloves: if handling toxic, corrosive or biohazard compounds Section 2 – Potential Hazards + Safety precautions 1. Harmful vapours (toxic, corrosive, stench) may escape from hood if it is not set up correctly. Keep the glass sash at the front of the hood down as far as possible when in use (approx 20 cm gap is appropriate) – this ensures a strong airflow into the hood, and provides protection against toxic inhalation. 2. Use of a Bunsen burner or other ignition source in hood can lead to a fire. Never use Bunsen burners or other ignition sources in a fume hood – fires in this location can get out of control quickly due to chimney effect, and the common use of fume hoods to store solvents and solvent wastes. Instead, use an electric heating element if you need to heat an item in the hood. Section 3 – Procedure 1. Ensure you have 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. read the MSDS of any chemicals you are using in the hood and understand the risks. Know the location of the nearest spill kit, eyewash, safety shower, fire extinguisher and fire blanket Ensure hood fan is switched ON before use. Keep hood clear of clutter and mess, and keep amount of equipment and chemicals in hood to a minimum to maintain good air flow. Wear personal protective equipment as appropriate. Keep the glass sash at the front of the hood down as far as possible when in use (approx 20 cm gap is appropriate). Don’t use the hood as a long-term storage location for chemicals and wastes - it is designed for experimental procedures, not storage. Never use Bunsen burners or other ignition sources in a fume hood. Section 4 – Disposal / Spills / Incidents 1. Organic waste and other types of waste generated from working inside the fume hood should not be stored long-term in the hood. Instead, this waste should be appropriately labelled and disposed of through the hazardous waste system. 2. Any broken glassware should go into a dedicated broken glass disposal system (either the large cardboard boxes, or yellow plastic sharps containers). See “Use and Disposal of Sharps” SOP and risk assessment. Section 5 – Repairs / Certification / Validation 1. Fume hoods are certified annually by NATA certified contractors. 2. Report faulty hoods to the Resources Officer immediately, so that repairs can be arranged. Faulty hoods should not be used. Section 6 – Relevant Material safety data sheets and References 1. Read the relevant MSDS for all chemicals used inside the fume hood. 2. Risk assessment for Fume Hood, risk assessment and SOP for flammables, toxic Issue date: 20/11/12 Review date: 20/11/13 Page 1 of 2 chemicals, corrosives, chemical wastes. SOP Training Confirmation By signing below, these individuals confirm that they have read and understood the SOP, and agree to always follow the instructions in this SOP when performing this procedure. Position Name Signature Date Supervisor employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student employee / student WHS Committee Approval Representative: A. Prof Frank Seebacher Chair Safety Committee Signature: ........................................................ Date: ..................................... Issue date: 20/11/12 Review date: 20/11/13 Page 2 of 2