Supplementary figures - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement

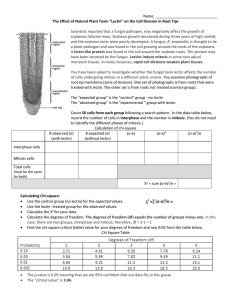
Supplementary figures Fig.1. Multiple sequence comparison of insecticidal fungal lectins Fig.1. (a) Amino acid sequence alignment of the recSRL with native SRL (SRL-ACN89784.1) as well as other fungal lectins such as Agaricus bisporus lectin (ABL-AAA85813.1), Xerocomus chrysenteron lectin (XCLAAL73235.1), Clitocybe nebularis lectin (CNL- ACD47153.1), Sclerotinia sclerotiorum agglutinin (SSAABE97202.1) and Rhizoctonia solani agglutinin (RSA-AGL80208.1). (b) Phylogenetic tree analysis of recSRL with native SRL and other fungal lectins Fig.2. Purification of recSRL Fig.2. (a) Fractionation of recombinant Sclerotium rolfsii lectin (recSRL) by ion exchange chromatography on a DEAE column, equilibrated in TB 7.5 pH, and the bound proteins were eluted by gradient elution using 25 mM TB pH 7.5 with salt gradient from 0 to 500 mM NaCl fractions of 3.0 ml were collected at a flow rate of 25 ml /h. (b) Purification of recSRL by gel filtration chromatography using Superdex G-75 column, equilibrated in PBS 7.5 pH and the bound lectin was eluted with PBS buffer, pH 7.5, fractions of 3.0 ml were collected at a flow rate of 18 ml /h. (c) SDS-PAGE analysis of recSRL. Crude extract of BL-21 cells without lectin gene insert (lane I; 20 µg), Crude extract of BL-21 cells with lectin gene insert (lane II; 37 µg), DEAE eluted recSRL (III; 12 µg), Purified recSRL (IV; 7 µg), Pre-stained protein molecular weight marker (V). Fig.3. PCR analysis of putative T0 plants using nptII gene specific primer Fig.3. PCR analysis of putative T0 transgenic plants using nptII gene specific primer: (M) 100 bp marker, (Lanes 1-7) putative transgenic T0 lines, Positive control (PC), Negative control (NC) Fig.4.The result of hemagglutination assay of all T0 lines Fig.4. Hemagglutination assay of T0 lines; A- Negative control plant, B-G1, C-G2, D-G3, E-G4, F-G5, G-G6, and H-G7