Kinetics 2 - Woodland Hills School District
advertisement

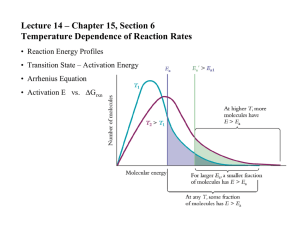
WOODLAND HILLS HIGH SCHOOL LESSON PLAN SAS and Understanding By Design Template Name: Naill Week: 04/18/14 Length of Lesson: 10 days Course: Chem II Edline updated Class website updated STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS LESSON TOPIC: Kinetics BIG IDEAS: (Content standards, assessment anchors, eligible content) objectives, and skill focus) Chemical reactions are predictable. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: According to the collision theory, what factors affect the rate of a chemical reaction? UNDERSTANDING GOALS (CONCEPTS): Students will understand: VOCABULARY: reaction rate, rate law, reaction order, integrated rate law, Arrhenius equation, activation energy, reaction mechanism, molecularity, rate limiting/determining step, transition state theory, reaction intermediates STUDENT OBJECTIVES (COMPETENCIES/OUTCOMES): Students will be able to understand and use the kinetics terminology. describe the factors that can affect the rate of reaction. relate the different possible ways of defining reaction rates and convert between them. calculate rates given data either graphically or in tabulated form. interpret a rate law in terms of reaction orders. use the method of initial rates to determine reaction orders. use concentration versus time data to determine reaction orders. describe the relationship between concentration and rate and use the differential rate law in calculations involving this relationship. describe the relationship between concentration and time and use the integrated form of the rate law in calculations involving this relationship. describe the relationship between temperature and rate and use the Arrhenius equation in calculations involving this relationship. provide a molecular level explanation for the factors affecting the rate of reaction using the concepts of collision theory. use transition state theory to explain the role of activation energy understand, interpret, and draw potential energy curves characterize a mechanism in terms of elementary reactions, molecularity, and slow and fast steps identify reactants, products, intermediates, and catalysts in a reaction mechanism. describe the relationship between a reaction mechanism is related to its rate law and use it to derive a rate law given a mechanism. STAGE II – ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE PERFORMANCE TASK: FORMATIVE ASSESSMENTS: Class discussion Assignments Tests/Quizzes Laboratory experience Observation Notetaking Asking/Answering questions Performing Lab STAGE III – LEARNING PLAN INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURES: MATERIALS & RESOURCES: INTERVENTIONS: Explicit Instruction Overhead/Board Lab material/equipment Handouts Content Area Reading Preferential seating Cooperative work Presentation Discussion Modeling Demonstration Prelab Active Engagement Note-taking Partnering Cooperative Education Higher Level Thinking Scaffolding Build on prior knowledge Build vocabulary MINI LESSON: intro to kinetics terminology and the factors that can affect the rate of reaction. relate the different possible ways of defining reaction rates and convert between them. interpret a rate law in terms of reaction orders. use the method of initial rates to determine reaction orders. describe the relationship between concentration and rate and use the differential rate law in calculations involving this relationship. describe the relationship between concentration and time and use the integrated form of the rate law in calculations involving this relationship. describe the relationship between temperature and rate and use the Arrhenius equation in calculations involving this relationship. provide a molecular level explanation for the factors affecting the rate of reaction using the concepts of collision theory. transition state theory and activation energy; describe and interpret potential energy curves characterize a mechanism in terms of elementary reactions, molecularity, and slow and fast steps identify reactants, products, intermediates, and catalysts in a reaction mechanism. describe the relationship between a reaction mechanism is related to its rate law and use it to derive a rate law given a mechanism. ASSIGNMENTS: A39. EOC 13: 1,6,8,25,26,28,34,37,40,48,49,53,57,63 A40. EOC 13: 11,12,30,62,65,70,72,76,79,93,100,106,104