Activity Worksheets: Getting to Know Assessment Design Patterns
advertisement
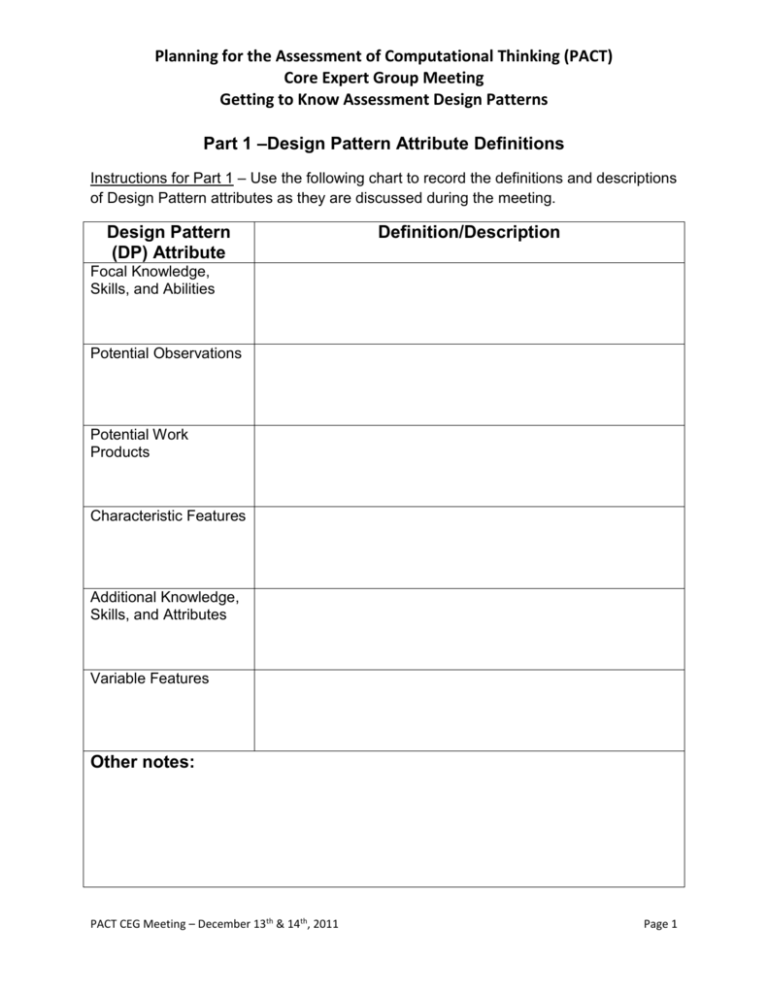
Planning for the Assessment of Computational Thinking (PACT) Core Expert Group Meeting Getting to Know Assessment Design Patterns Part 1 –Design Pattern Attribute Definitions Instructions for Part 1 – Use the following chart to record the definitions and descriptions of Design Pattern attributes as they are discussed during the meeting. Design Pattern (DP) Attribute Definition/Description Focal Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities Potential Observations Potential Work Products Characteristic Features Additional Knowledge, Skills, and Attributes Variable Features Other notes: PACT CEG Meeting – December 13th & 14th, 2011 Page 1 Planning for the Assessment of Computational Thinking (PACT) Core Expert Group Meeting Getting to Know Assessment Design Patterns Part 2 – Matching DP Attributes with Messick’s Assessment Argument Instructions for Part 2 – Select the generic Design Pattern attributes (on the left) that match with each of the components of Messick’s Assessment Argument (on the right). Briefly explain why you selected the particular attributes. Remember to refer to your resource materials for more information about Messick’s Assessment Argument. Generic Design Pattern Attributes Messick’s Assessment Argument Student Model/Claim Focal Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities Additional Knowledge, Skills, and “What construct (complex of student Attributes attributes) should be assessed?” Potential Observations Potential Work Products Characteristic Features Variable Features Why did you select these particular attributes? Evidence Model/Actions Focal Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities Additional Knowledge, Skills, and “What behaviors should reveal the Attributes construct?” Potential Observations Potential Work Products Characteristic Features Variable Features Why did you select these particular attributes? Task Model/Situation Focal Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities Additional Knowledge, Skills, and “What tasks should elicit those behaviors?” Attributes Potential Observations Potential Work Products Characteristic Features Variable Features Why did you select these particular attributes? PACT CEG Meeting – December 13th & 14th, 2011 Page 2 Planning for the Assessment of Computational Thinking (PACT) Core Expert Group Meeting Getting to Know Assessment Design Patterns Part 3 – Working with Design Pattern Attributes Instructions for Part 3 – The major design pattern attributes referenced throughout the meeting appear in the left column of the chart on the following page. In the right column are excerpts taken from an attribute entry in a design pattern on “Solving Complex Mathematical Problems”. Match each excerpt with the design pattern attribute that is the best fit by drawing a line between them. PACT CEG Meeting – December 13th & 14th, 2011 Page 3 Planning for the Assessment of Computational Thinking (PACT) Core Expert Group Meeting Getting to Know Assessment Design Patterns Part 3 – Working with Design Pattern Attributes Example – The attribute “Additional Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities” matches with the excerpt “Ability to identify and use the tools required to solve a problem” DESIGN PATTERN (DP) ATTRIBUTES ATTRIBUTE EXCERPTS FROM SOLVING COMPLEX MATHEMATICAL PROBLEMS DP 1. Focal Knowledge, Skills, and Attributes (KSAs) Efficiency of path taken to solve the problem 2. Additional Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities (KSAs) Ability to identify and use the tools required to solve a problem 3. Potential Observations Number of steps needed to solve the problem 4. Potential Work Products Present non-routine problems where a substantial part of the challenge is in deciding what to do and which mathematical tools to use 5. Characteristic Features Ability to make conjectures about the form and meaning of the solution 6. Variable Features Written response showing steps taken to solve the problem PACT CEG Meeting – December 13th & 14th, 2011 Page 4 Planning for the Assessment of Computational Thinking (PACT) Core Expert Group Meeting Getting to Know Assessment Design Patterns Part 4 – Generating Design Pattern Attributes Below is an example item measuring mathematical ability, specifically the ability to frame and solve complex problems in geometry (from Appendix C of the Math Content Specifications from the Smarter Balance Assessment Consortium). Ms. Olsen is having a new house built on Ash Rd. She is designing a sidewalk from Ash Road to her front door. Ms. Olsen wants the sidewalk to have an end in the shape of an isosceles trapezoid, as shown. The contractor charges a fee of $200 plus $12 per square foot of sidewalk. Based on the diagram, what will the contractor charge Ms. Olsen for her sidewalk? Show your work or explain how you found your answer. PACT CEG Meeting – December 13th & 14th, 2011 Page 5 Planning for the Assessment of Computational Thinking (PACT) Core Expert Group Meeting Getting to Know Assessment Design Patterns A. Please fill in the table below with possible attributes that would come from the Design Pattern this item could have been built from. Design Pattern Attribute Description Focal KSAs Additional KSAs Potential Observations Variable Features Characteristic Feature B. Pick one Variable Feature you identified and explain how the manipulation of this attribute may affect the emphasis or difficulty of the item. PACT CEG Meeting – December 13th & 14th, 2011 Page 6




![Best-fit Decisions [, 25 KB]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006613263_1-62a61f810693250e9828b38f77c693b2-300x300.png)