Chemistry Unit 2 Review: States of Matter & Changes
advertisement
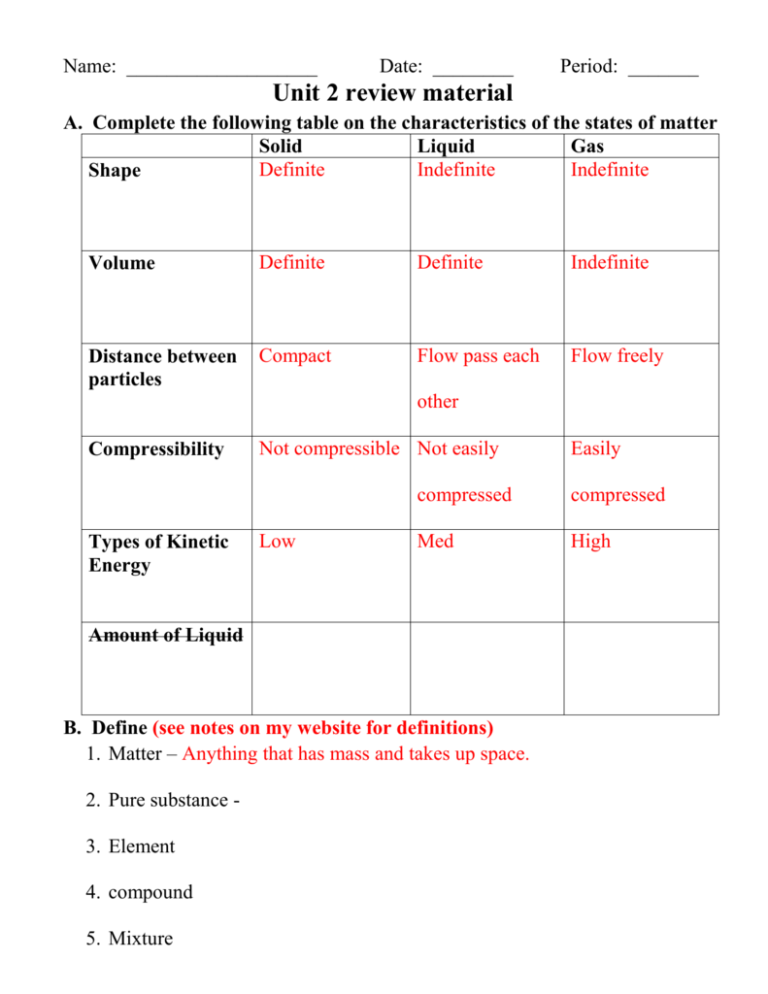
Name: ___________________ Date: ________ Period: _______ Unit 2 review material A. Complete the following table on the characteristics of the states of matter Solid Liquid Gas Definite Indefinite Indefinite Shape Volume Definite Definite Indefinite Distance between particles Compact Flow pass each Flow freely other Compressibility Types of Kinetic Energy Not compressible Not easily Low compressed compressed Med High Amount of Liquid B. Define (see notes on my website for definitions) 1. Matter – Anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. Pure substance 3. Element 4. compound 5. Mixture Easily 6. Homogeneous mixture 7. Heterogeneous mixture 8. Filtration 9. Distillation 10. Evaporation 11. Manual separation C. Classification of Matter Classify each as an element, compound, homogeneous mixture or a heterogeneous mixture. 1. table salt C 11. Salad dressing HE 21. Iron E 2. gold E 12. Water HM 22. Helium E 3. the air in DHS 13. hydrogen chloride (HCl) C 23. Wood HE 14. carbon E 24. Blood HE 4. carbon E 15. beach sand HE 25. Milk HE 5. copper E 16. water from water fountain 26. oily water HE HM 6. mercury E HM 27. soil (dirt) HE 7. Kool-aid HM 17. A root-beer float HE 28. oxygen E 8. fruit salad HE 18. Lucky charms cereal HE 29. pure water C 9. city air HE 19. sodium chloride C 30. sodium E 10. glucose C 20. Flat soda HM Classify each as a chemical or Classify each as a chemical or physical physical change property 1. boiling water P 1. Copper is a good conductor of heat and 2. burning gasoline C electricity 3. cooking an egg C 2. ice melts at 0°C. 4. ironing a shirt P 3. a piece of sulfur is burned. 5. evaporating alcohol P 4. 02 is a gas. 6. rusting iron C 5. Iron can rust 7. water evaporates. P 6. titanium is an inert metal. 8. Ripping paper P 7. He is very nonreactive. 9. Steel turns red when heated P 8. Na is a soft, shiny metal. 10. fermenting orange juice C 9. ice melts at 0°C 11. rocks are ground to sand. P 10. water has a high specific heat. 12. silverware tarnishes. C 11. Alcohol burns in presence of a flame 13. digesting a pizza C 12. gold is a yellow metal 14. an ice melting in a drink 13. silver is a soft metal. 15. decomposing meat 14. gold is a very dense metal. 16. evaporating water 15. Hydrogen peroxide will break down 17. sulfur is burned. into water and oxygen 18. a nail rusts. 16. Sodium is highly reactive with water 19. Carrots rot. 17. Water condenses at 100°C. 20. Bread it cut into slices 18. With electricity water with break down 21. Iron rust into oxygen and hydrogen C. Both elements and compounds are examples of a pure substance, how are they different from each other? Compounds consists of two or more elements. D. What are the 4 different separation techniques? Give an example for a use of each! Chromatography – separation based on solubility Distillation – separating saltwater from pure water Filtration – process by which solid materials are removed from a fluid mixture Manuel separation – (ex) using a magnet to separate iron filings from sand. E. Phase and Temperature Diagrams: label the points on the diagrams below Phases of Matter present at point A Solid E liquid I gas If energy is increasing what is happening at points C melting G evaporation If energy is decreasing what is happening at points C freezing G Condensation What happens to the temperature of a substance during a phase change? Stays constant What happens to the temperature of a substance when all of it is in the same phase and energy (heat is added)? Phase changes occur