UNIT 3.5: The Age of JacksonElection of 1824 Between 1816

UNIT 3.5: The Age of Jackson
• Election of 1824
• Between 1816 & 1824, U.S. had only one political party
(__________________________________)
• The “_______________________________________” would bring a different attitude to Washington.
• A new Democratic political party was born and Jackson’s inauguration showed that changes were coming.
• _________ candidates for President in 1824
•
_____________________________ won majority of electoral votes
•
Winner determined by
____________________________________
•
Speaker of the House Henry Clay &
_____________________________ made a deal.
• Adams won the vote in the House & ultimately won the election.
• Clay became the Secretary of State under Adams.
• Indian Removal
•
1823: Supreme Court rules Native Americans have
“_________________________” American lands
•
Natives lived in isolated pockets east of the
Mississippi River
•
Devastated by war, disease, and bad treaties
• The 5 “________________________________”
(Cherokee, Creek, Choctaw, Chickasaw and
Seminole)
had become “Euro-assimilated”
• 1830: Jackson supports
___________________________________
• Jackson/supporters cried
“________________________________”
•
Felt election was “stolen” from Jackson
•
Began plotting for the Election of 1828 & formed the
__________________________ Party.
•
Election of 1828
• ____________________ vs. ______________________
• Campaign buttons
•
Rallies
•
Slogans
•
Jackson won in a landslide
• Indians forced to give up land east of the Mississippi in exchange for land west of the Mississippi
(________________________________)
•
Led to the “_________________________”
•
Tariff of Abominations
•
The Protectionist Tariff of 1828
•
Increased tariffs to 37%
• Goal: ______________________________________
• Southerners (including VP John Calhoun) attacked the tariff as a “________________________________”.
•
They depended on imported British farm tools and textiles.
• Allowed Northern manufacturers to raise prices to just below the British costs and “gouge” Southerners.
•
____________________________ developed
_________________________ theory
•
Every state has right to reject unconstitutional federal laws
•
If federal gov’t refused nullification, state could secede from Union
• THE SEEDS OF CIVIL WAR ARE PLANTED!
• The Nullification Crisis
• Following a small lowering of the tariff (of Abominations) in
1832, SC called the Nullification Convention
•
South Carolina nullified the tariff and threatened
___________________________
•
President Jackson hated Calhoun & his threats, and began preparations for war.
•
_________________________________, “the Great
Compromiser” stepped in with the Compromise Tariff.
• SC hesitantly agreed & Civil War was avoided for a while longer
• The Bank of the U.S.
• Jackson hated the BUS and threatened to destroy it several times.
•
Election of 1832
•
__________________________ wanted to push the re-chartering of the BUS as a campaign issue, hoping
Jackson would veto it and lose the election.
•
Jackson vetoed the BUS and instead won great acclaim in the
_____________ and _____________ (it backfired on Clay)
• Bank of the U.S.
•
BUS’s charter due to expire in 1836
•
Jackson ordered his Secretary of the Treasury to create
“___________________________”
•
All gov’t funds placed in these new banks
• President of the BUS (______________________) reacted by calling in loans from these “pet banks”
• Also refused to _______________________________
•
As a result, many banks went _________________ & caused economic ______________ nationwide.
•
Biddle’s decision cost him much of his support. The BUS
____________________________.
•
Industrial Revolution
• 19 th Century: the U.S. followed ______________________ examples of Industrial Revolution.
• __________________________________
• est. the 1st textile mill in Rhode Island, which produced thread
• known as “_________________________________”
•
____________________________________________
•
Built a weaving factory in Mass., which used the thread to produce cloth.
• This sparked a major push for ______________ in
______________________, where citizens had depended heavily upon shipping & trade
• ________________________
•
Built the ___________________________
•
Cotton farming _________________
•
Slave prices ___________________ throughout the region.
• Introduced concept of ______________________________
•
Used ___________________________ identical parts, which allowed muskets to be assembled rapidly by unskilled workers.
•
The concept was adopted on a large scale by numerous U.S. manufacturers.
•
THE U.S. INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION HAD BEGUN!
• “Go To Texas!!!”
• 1820s: ______________________ advertised for Americans settlers to populate its northern border
• Goal: _____________________________________
•
U.S. repeatedly offered to buy the territory, but Mexico refused
•
Land agents, or “
______________________,”
were given huge tracks of free land to divide and sell to American settlers inexpensively
•
In exchange Americans had to agree to do 2 things:
• _____________________________________
• _____________________________________
•
Tensions Build
•
Problems:
• Most settlers were _____________________
• Refused to speak Spanish
• Refused to honor Mexico’s abolishment of slavery.
•
In 1830, Mexico attempted to seal its border, but the flood of
Americans was too much.
•
By 1834, the Anglo population of Texas
___________________.
•
1833: empresario
_______________________________
traveled to Mexico City to present petitions for increasing TX self-gov’t. Pres. Santa Anna imprisoned him for “inciting revolution.”
• Texas Revolution
•
President __________________________ revoked local powers in Texas and other Mexican states
•
Attempting to enforce his new laws, Santa Anna w/ a 4,000 strong army, marched on ________________.
•
Meanwhile, Austin issued a call for Texans to arm themselves!
• 1835, Texans attacked Santa Anna and his men @ a small
Catholic mission (____________________), but were eventually defeated. “REMEMBER THE ALAMO!!!”
• __________________________________
• Texans, led by _____________________________
•
Killed over 600 and captured Santa Anna.
•
Pres. Santa Anna was freed after signing over
____________________________ in the Treaty of
Valasco.
•
September 1836, the
________________________________________ was born
• 1838: Texas ________________________ by the U.S. as the
“Lone Star State” by pro-slavery President James K. Polk.
• Manifest Destiny
•
_____________________ gripped the country as Americans believed that the movement westward was “destined” and
“ordained by God.”
•
Following the annexation of Texas, a newspaper editor stated that it was “the fulfillment of our manifest destiny to overspread the continent…for the free development of our yearly multiplying millions.”
•
Many Americans adopted the phrase to express their own beliefs.
• War With Mexico
•
December 1845: __________________ became 28th state
•
Dispute: where is the border with Mexico?
• Mexico: ____________________________________
• U.S.: _____________________________________
•
President Polk orders US forces led by _________________ and __________________ to march to Rio Grande
•
Goal: _______________________________________
•
American settlers in California declared independence, created the __________________________
•
Ran Mexican troops out of Cali
• American troops led by Officers ____________________ and
__________________________
• General Winfield Scott captured Mexico City in 1847
•
_________________________________________ ended the war (1848)
•
US gained valuable fighting experience that they would use on each other in the Civil War
•
GOLD!!
•
The US gave 15 million in exchange for the
“Mexican Cession.”
• January 1848: James Marshall discovered gold at
___________________________ (California)
• Gold Fever swept the nation
•
1848: _________________ people migrated to Cali
•
1850: _________________ people migrated to Cali
•
_________________________: people who flocked west in
1849 gold rush
• Asia, South America, Europe
• Impact:
•
San Francisco’s population exploded
•
New populations settled in the West (Chinese, Free Blacks)
• ___________________: California became a state
Immigration & the Rise of Cities
• Immigrants Fuel Industry
•
As U.S. industrialization began to reach its stride in the
1830s & ‘40s, the “first wave” of foreign immigrants began to flood in from Europe.
•
The need for labor steadily rose
•
__________________ & __________________ immigration increased
•
Women were plentiful, cheap and __________________ even cheaper, small and expendable.
• Nativism
• Issues with Immigration
• ________________________________
•
Poverty
•
______________________
• Disease
• ______________________
• Rise of _______________________
•
Favoring native-born Americans over immigrants
•
__________________________________________ (aka American
Party) formed in 1854
•
Roots in a secret organization (“I Know Nothing”)
• The 2nd Great Awakening
•
Mid 1800s: a new wave of _________________ religion reacted violently to a new age of reason.
•
Huge “camp meetings” lasting days helped thousands “get
___________” and “get _______________”
• esp. ______________ and _______________
• Traveling preachers used personal conversion not predestination
• New denominations were created while ____________ and
___________ differences split churches (especially over the issue of slavery).
• Religion Leads to Reform
•
American ______________________ took it upon themselves to reform society during this period.
•
Known commonly as __________________, this phenomenon included reforms in ________________, women's rights, _________________________, and many other questions faced by society.
•
Education Reform
• The typical one room school with ill trained/stern female teachers taught “readin’, writin’+’rythmitic.” (3 R’s)
• Reformers like ___________________ and
_____________________ proposed changes.
•
Pushed for better school-houses,
____________________, longer terms, more
_______________ and “public schools.”
•
Small Liberal Arts colleges, mostly religiously affiliated developed in the West and East.
•
Women’s colleges and seminaries also developed
•
Led by Emma ________________ and Mary
_________________.
• Women’s Reform
•
Many women involved in multiple reform movements.
•
____________________________ personified the
“reformer” with her crusade against cruelty in prisons and hospitals/asylums for the sick.
•
The _________________ sisters of SC championed women’s education and the anti-slavery movement.
• ____________ was blamed for many social ills including low work productivity, spousal and child abuse etc.
• __________________ societies developed and quickly spread forcing 9 states to go “dry.”
• Seneca Falls
•
Women lacked many rights including ______________, holding office, __________ rights, inheritance
•
Were basically owned by their husbands like slaves
(aka “____________________________”)
•
Women made strides particularly in ____________ as pupils and teachers, as well as temperance reform, abolition & womens’ __________________.
• Lucretia ______________, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, &
____________________ organized the ________ Falls
Conference (1848)
• Wrote the “_____________________________” demanding certain rights for women, which sparked the “_______________” movement in U.S. History.
• Abolition!
•
Northern outcries against slavery came about with the 2nd
Great Awakening.
•
_____________________ papers and _________________ flooded the south.
•
William Lloyd Garrison’s
____________
caused him to be beaten by northerners who saw him as a radical
• Created the American Anti-Slavery Society and
___________________________, which sought to return freed slaves to Africa.
•
Abolitionist ______________________ was also an icon for women’s rights.
•
Frederick Douglass was an escaped slave who was taught to read & write by his former master’s wife.
•
After secretly writing a number of editorials for abolitionist papers, he penned his
Narrative of the Life of Frederick
Douglass,
which led to his career as a publisher, lecturer and
__________ of the abolitionist movement.
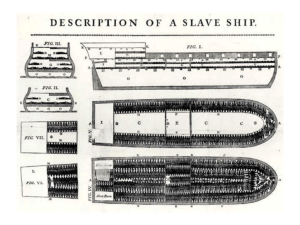
• Institution of slavery
• _______ in ______ whites owned slaves
• Billions of $ were invested and many “poor white” farmers dreamed of slave ownership.
•
Slaves were forbidden to __________, learn to _________ and write, to be ___________, and to assemble under the harsh “slave codes.”
•
Poor whites supported the system to keep blacks “in their place.”
•
Slave Rebellion!
• Nat Turner was a slave preacher in VA, who believed he had been chosen to lead his people out of __________________.
• In 1831, following a solar eclipse, he led _______ followers to attack _____ plantations and kill nearly 60 whites before being captured.
• Turner hid for weeks, but was captured, tried & hanged.
•
Over 200 slaves were killed in __________________!
•
This event ___________________ the resolve of Southern whites to defend the institution of slavery.
• Abolition!
•
Many slaves escaped to the north and freedom along the
___________________________.
•
Helped by Harriett Tubman and many other “conductors” such as ______________, they followed the North Star.
•
Southerners considered them _____________________ and
“slave-catchers” made a large profit.
• 250,000 free blacks lived in the north especially near
________________, Massachusetts
• Many racial northerners (______________), resented and terrorized free blacks and refused to educate or employ them.
• The Wilmot Proviso
•
A resolution authored by _________________________ of
Pennsylvania, proposed no ___________ in the Mexican
Cession Territories.
•
Passed twice by the House, never passed the
______________.
•
Set the stage for political debate in the
__________________________ period.
• North & South Compromise
• As _______________ spread, the North and South grew further apart
•
U.S. gov’t attempted to keep the peace
•
The _______________________________
•
Passed under ____________________
• One free state admitted to Union for every slave state
• ______________ enters as free, ________________ enters as a slave state
• Compromise of 1850
•
_____________________ (free) applies for statehood
• ________________ and ___________ allowed to vote on issue of slavery
(__________________________________)
•
Slave trade banned in _____________________
•
Stronger fugitive slave laws in the North