Codebook - U
advertisement

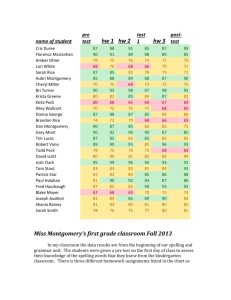
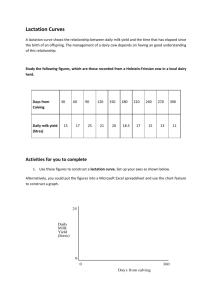
Codebook: Regions, Regional Power, and Status Attribution October 2009 Table of Contents Variables: ........................................................................................................................................ 2 Works Cited: ............................................................................................................................... 6 Appendices: Coding Processes ....................................................................................................... 7 Appendix 1: Process by which missing SIPRI data was imputed .............................................. 7 Appendix 2: Coding the Cultural Indicators ............................................................................. 16 Appendix 3: ISO Country Codes .............................................................................................. 18 Variables: cowabb1: 3 letter country abbreviation, state 1 cowabb2: 3 letter country abbreviation, state 2 ccode1: COW Country code, state 1 ccode2: COW Country code, state 2 iso1: ISO 3 letter country code, state1 iso2: ISO 3 letter country code, state2 year: Year of observation From COW’s CINC data: irst: Iron and steel production (thousands of tons) milex: Military Expenditures (thousands of current year US Dollars) milper: Military Personnel (thousands) energy: Energy consumption (thousands of coal-ton equivalents) tpop: Total Population (thousands) upop: Urban population (population living in cities with population greater than 100,000) cinc: Composite Index of National Capability (CINC) score From the SIPRI data: milexp: Military expenditure (in millions of 2005 USD) o missing data was imputed; process is listed in Appendix 1 From the WDI: (*need to check these explanations) gdp: GDP (how is this measured?) captl: market capitalization of domestic firms pop: total population resid: residual of regression population on GDP From EUgene: (*need to check these explanations) contig: Direct contig (1=Lnd, 2=1-12 miles watr, 3=13-24, 4=25-150, 5=151-400, 6=?) distance: Distance, from the capitol of country 1 to the capitol of country 2, in milse From the IDEA Events Data: statevisits: Number of state visits from state 1 to state 2 per year cc: sum of the absolute value on the Goldstein scale of events between country 1 and country 2 per year cc_nosv: Identical to cc, but excludes all state visits from state 1 to state 2 cc_count: A count of all events, conflictual, cooperative, and neutral, from state 1 to state 2 per year cc_countnosv: Identical to cc_count, but excludes all state visits from state 1 to state 2 coop: Sum of all cooperative events between state 1 and state 2 per year, using weighted values of events from the Goldstein scale coop_nosv: Identical to coop, but excludes all state visits from state 1 to state 2 conflict: Sum of all conflictual events between state 1 and state 2 per year, using weighted values of events from the Goldstein scale coop_count: Count of all cooperative events between state 1 and state 2 per year coop_countnosv: Identical to coop_count, but excludes all state visits from state 1 to state 2 conf_count: Count of all conflictual events between state 1 and state 2 per year From Goertz and Powers (2009): rei: 1 signifies the dyad shares membership to a common REI, 0 not; this data is coded from the list provided by Goertz and Powers (2009) From The Military Balance (MB) (range 2002-2005): milpers: number of active military personnel per country; countries for which ranges are given (e.g., 11-15000) are treated as missing data lowbound: if a range is given for military personnel, the lower bound of the range is listed highbound: if a range is given for military personnel, the upper bound of the range is listed milpersavg: lists the number of active military personnel per country, using the average if a range is given milperslow: lists the number of active military personnel per country, using the lower bound if a range is given (a more conservative measure of active personnel) milpershigh: lists the number of active military personnel per country, using the upper bound if a range is given (a more liberal measure of active personnel) milpersavg_th: identical to milpersavg, but divided by 1000 milperslow_th: identical to milperslow, but divided by 1000 milpershigh_th: identical to milperhigh, but divided by 1000 Military Personnel Variables: milper_avg: combines the CINC milper variable (ranges from 1988-2001) and the MB’s, milpersavg_th variable (ranges from 2002-2005), to obtain a count of military personnel in thousands from 1988 to 2005 milper_h: identical to milper_avg, but uses the upper bound of the MB range milper_l: identical to milper_avg, but uses the lower bound of the MB range Barbieri Trade Data (Non-directed dyad bilateral trade data) flow1: imports of state 1 from state 2 (rename to imports) flow2: imports of state 2 from state 1 (rename exports) From CIA world fact book? langmaj: 1 if the majority language family of state 1 and state 2 is the same, 0 otherwise langmin: 1 if the minority language family of state 1 and state 2 is the same, 0 otherwise langminmaj: 1 if the minority language family of state 1 matches the majority language family of state 2, 0 otherwise langmajmin: 1 if the majority language family of state 1 matches the minority language family of state 2, 0 otherwise scriptmaj: 1 if the majority writing script of state 1 and state 2 is the same, 0 otherwise scriptmin: 1 if the minority writing script of state 1 and state 2 is the same, 0 otherwise scriptminmaj: 1 if the minority writing scrip of state 1 matches the majority script of state 2, 0 otherwise scriptmajmin: 1 if the majority writing scrip of state 1 matches the minority script of state 2, 0 otherwise religionmaj: 1 if the majority religion of state 1 and state 2 is the same, 0 otherwise religionmin: 1 if the minority religion of state 1 and state 2 is the same, 0 otherwise religionmajmin: 1 if the majority religion of state 1 matches the minority religion of state 2, 0 otherwise religionminmaj: 1 if the majority religion of state 1 matches the minority religion of state 2, 0 otherwise Our Opportunity and Willingness Measures: milexp_total: sum of all military expenditure in the system per year milpers_total: sum of all military personnel in the system per year milexp_cinc1: the military expenditure of country 1 (milexp) divided by the sum of all military expenditure in the system that year (milexp_total) milexp_cinc2: the military expenditure of country 2 (milexp) divided by the sum of all military expenditure in the system that year (milexp_total) milper_cinc1: the military personnel of country 1 (milper_avg) divided by the sum of all military expenditure in the system that year (milpers_total) milper_cinc2: the military personnel of country 1 (milper_avg) divided by the sum of all military expenditure in the system that year (milpers_total) military_cinc1: the average value of the military expenditure “cinc” score and the military personnel “cinc” score for country 1 military_cinc2: the average value of the military expenditure “cinc” score and the military personnel “cinc” score for country 2 captl_total: the total amount of capital in the system per year captl_cinc1: the amount of capital of country 1 (captl1) divided by the total amount of capital in the system captl_cinc2: the amount of capital of country 1 (captl1) divided by the total amount of capital in the system lofp_military: loss of power gradient for military strength (military_cinc1^log10[(distance/500) + 10 – e ] ) lofp_economic: loss of power gradient for military strength (captl_cinc1^log10[(distance/500) + 10 – e ] ) milpower_comp: a comparison of country 1’s military power at home versus at country 2’s capital (lofp_military / military_cinc1) econpower_comp: a comparison of country 1’s economic power at home versus at country 2’s capital (lofp_econmic / captl_cinc1) mil_opp: coded 1 if country 1 has at least 50 % of its military power at country 2’s capital as compared to its military power at home (mil_opp = 1 if milpower_comp > .5; 0 if milpower_comp ≤ .5) econ_opp: coded 1 if country 1 has at least 50 % of its economic power at country 2’s capital as compared to its economic power at home (mil_opp = 1 if milpower_comp > .5; 0 if milpower_comp ≤ .5) mill_will: coded 1 if country 1 directs at least 1 event towards country 2 econ_will: coded 1 if country 1 and country 2 trade at least 1 USD worth mil_oxw: military opportunity times military willingness; 1 indicates countries are able and willing to interact diplomatically/militarily) econ_oxw: economic opportunity times military willingness; 1 indicates countries are able and willing to interact economically) max_oxw: the maximum value of mil_oxw and econ_oxw Works Cited: Barbieri, Katherine, Omar Keshk, and Brian Pollins. 2008. Correlates of War Project Trade Data Set Codebook, Version 2.0. Online: http://correlatesofwar.org. Goertz, Gary, and Kathy L. Powers. 2009. “The economic–institutional construction of regions: conceptualization and operationalization.” COW SIPRI Military Balance IDEA Events Data EUgene Data WDI indicators ATOP data? Appendices: Coding Processes Appendix 1: Process by which missing SIPRI data was imputed Added data is color coded in excel and details for each added entry are listed below by country in the order which they appear in the revised SIPRI dataset. For countries with red numbers, data was calculated for the missing state (state A) using expenditures of the neighboring state with the largest military expenditures (state B) for all years missing in state A. The ratio of State B to State A's military expenditures was calculated using data from the correlates of war. That ratio was then multiplied by the SIPRI data for State B. The resulting figure was entered for the missing value of State A for each year available. For countries with green 0's, COW data was not available for the missing state. These missing points typically correspond with periods of domestic turmoil and conflict, or the missing entry falls after 2001. For countries with blue numbers, data was provided in a previous version of SIPRI, but the most recent version of SIPRI has removed that entry for review. Libya 88-92; 94-96 extrapolated from Libya-Algeria COW ratio 93 data coded 0, missing in COW Angola 88-91; 93-97 extrapolated from Angola-Zambia COW ratio 92 data coded 0, missing in COW 98 extrapolated from Angola-Namibia COW ratio Benin 91-92; 94-98 extrapolated from Benin-Nigeria COW ratio 93 data coded 0, missing in COW Cape Verde 89-90 data coded 0, missing in COW 91-92 extrapolated from Cape Verde-Senegal COW ratio Central African Republic 88-90; 97-01 extrapolated from Central African Republic-Cameroon COW ratio Chad 88-92 extrapolated from Chad-Nigeria COW ratio Congo 88-90; 92; 94-00 extrapolated from Congo-Cameroon COW ratio 91; 93 coded 0, missing in COW Congo, Dem. Rep. 88-92; 93-95; 01 extrapolated from Cong, Dem. Rep.-Sudan COW ratio 92; 02 coded 0, missing in COW Cote d'Ivoire 95 extrapolated from Cote d'Ivoire-Ghana COW ratio 98-01 extrapolated from Cote d'Ivoire-Guinea COW ratio 02 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Equatorial Guinea 88-93 coded 0, missing from COW 96-01 extrapolated from Equatorial Guinea-Cameroon COW ratio 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Eritrea 88-92 coded "." Eritrea not a state 04-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Gabon 88-90; 94-99 extrapolated from Gabon-Cameroon COW ratio 91-93 coded 0, missing in COW Guinea 88-90; 95-96 extrapolated from Guinea-Senegal COW ratio 05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Guinea-Bissau 88; 91-93 coded 0, missing in COW 90; 99 extrapolated from Guinea-Bissau-Senegal COW ratio 04 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Liberia 88-91;93-97; 00 extrapolated from Liberia-Sierra Leone COW ratio 92 coded 0, missing in COW 01-02 coded from 06 SIPRI data 03 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Mali 91-92 extrapolated from Mali-Algeria COW ratio Namibia 88-89 coded "." not a state 90 coded from 06 SIPRI data Niger 88-93 extrapolated from Niger-Algeria COW ratio Sierra Leone 98-99 extrapolated from Sierra Leone-Guinnea COW ratio Somalia 88-90; 95-01 extrapolated Somalia-Ethiopia COW ratio 91-94 coded 0, missing in COW 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Sudan 89 extrapolated from Sudan-Egypt COW ratio Tanzania 88 extrapolated from Tanzania-Kenya COW ratio Togo 96 coded from 06 SIPRI data 97-01 coded from Togo-Ghana COW ratio 02 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Zambia 98; 00 coded from 06 SIPRI data 01 extrapolated from Zambia-Angola COW ratio 02-03 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Cuba 88-91;94-01 extrapolated from Cuba-USA COW ratio 92-93 coded 0, missing from COW 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Haiti 88-92; 95-01 extrapolated from Haiti-Dominican Republic Ratio 93-94 coded 0, missing from COW 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Jamaica 88-89 extrapolated from Jamaica-Dominican Republic Trinidad and Tobago 88;90;93 coded 0, mising in COW 89 extrapolated from Trinidad and Tobago-Guyana COW ratio 91-92; 96-01 extrapolated from Trinidad and Tobago-Venezuala COW ratio 94-95 coded from 2006 SIPRI data 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Belize 88; 98-99 extrapolated from Belize-Mexico COW ratio Costa Rica 88-99 extrapolated from Costa Rica-Panama COW ratio 00-01 extrapolated from Costa Rica-Nicaragua COW ratio 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Honduras 88-99 extrapolated from Honduras-Guatemala COW ratio Nicaragua 88;90 extrapolated from Nicaragua-Guatemala COW ratio 89 coded 0, missing in COW Panama 00-01 extrapolated from Panama-Colombia COW ratio 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Bolivia 88 extrapolated from Bolivia-Chile COW ratio Guyana 97-01 extrapolated from Guyana-Brazil COW ratio 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Paraguay 88 coded from the 06 SIPRI data Peru 88 extrapolated from Peru-Chile COW ratio Venezuala 88-90 extrapolated from Venezuala-Brazil COW ratio Kazakhstan 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, missing in COW data 92 extrapolated from Kazakhstan-Russia COW ratio Kyrgyzstan 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, missing in COW data Tajikistan 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, missing in COW data 05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Turkmenistan 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, missing in COW data 92-93; 00-01 extrapolated from Turkmenistan-Iran COW ratio 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Uzbekistan 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91-93 coded 0, missing in COW data 98l 00 extrapolated from Uzbekistan-Kazakhstan COW ratio 02; 04-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 North Korea 88-94; 98-04 coded from the 06 SIPRI data 95-97 coded "0" COW ratio unreliable relative to SIPRI data Laos 88;90-91 coded 0, missing in COW data 89 extrapolated froms Laos-China COW ratio Mongolia 88-89 extrapolated from Mongolia-Russia COW ratio Myanmar 88-01 extrapolated from Myanmar-China COW ratio 02-05 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Vietnam 88-94 coded from 06 SIPRI data 95-01 extrapolated from Vietnam-China COW ratio 02 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Afghanistan 88-89; 91-94 coded 0, missing in COW 90; 95-01 extrapolated from Afghanistan-China COW ratio 02 coded 0, COW ends in 01 Tongo 88 coded "." state does not exist Albania 88-89; 91 extrapolated from Albania-Greece COW ratio Armenia 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 extrapolated from Armenia-Turkey COW ratio 94 coded 0, missing in COW Azerbaijan 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 extrapolated from Azerbaijan-Iran COW ratio Belarus 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, missing in COW Bosnia-Herzegovina 88-91 coded "." state does not exist 92-01 extrapolated from Bosnia-Herzegovina-Croatia Ratio Croatia 88-91 coded "." state does not exist Czech Republic 88-92 coded "." state does not exist Czechoslovakia 88-92 extrapolated from Czechoslovakia-Germany 93-05 coded "." state does not exist EStonia 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, missing in COW Georgia 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91-95 coded 0, COW data unreliable Germany, DR 88-89 extrapolated from Germany, DR-Germany FR COW ratio 90 coded 0, COW data missing Latvia 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, COW data missing 92 extrapolated from Latvia-Russia COW ratio Lithuania 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91 coded 0, COW data missing 92 extrapolated from Lithuania-Russia COW ratio Macedonia 88-92 coded "." state does not exist 93-95 coded from 06 SIPRI data Moldova 88-90 coded "." 91-92 coded 0, COW data unreliable Montenegro 88-05 coded "." state does not exist Russia 91 coded from 06 SIPRI data Serbia/Yugoslavia 88-91 coded as 0, COW data unreliable 92-95 coded using 06 sIPRI data Slovak Republic 88-92 coded "." state does not exist Slovenia 88-81 coded "." state does not exist Ukraine 88-90 coded "." state does not exist 91-92 coded 0, COW data unreliable Iran 88 coded from 06 SIPRI data Iraq 88-01 extrapolated from Iran-Iraq COW ratio 02-04 coded 0, COW data missing Lebanon 89 extrapolated from Lebanon-Israel COW ratio Qatar 88; 91; 93-01 extrapolated from Qatar-Saudi Arabia COW ratio 89-00; 92 coded 0, COW data missing 02-05 coded 0, COW data ends in 01 Yemen 88-89 coded "." state does not exist Yemen, Arab Rep 88-90 extrapolated from Yemen, Arab Rep-Saudi Arabia COW ratio 91-05 coded "." state does not texist Yemen, PR 88-89 extrapolated from Yemen, PR-Saudi Arabia COW ratio 90-05 coded "," state does not exist Yugoslavia (former) entry merged with Serbia for consistency with COW country codes Appendix 2: Coding the Cultural Indicators Majority language family: Refers to single biggest language in the country – not the language family. For example, the population of the Cote d’Ivorie speak Niger-Congo languages. However, there are more than 250 different languages in the CDI, spoken by a varying number of people. Instead, French is the language spoken by the most Ivorians, and the CDI is coded as a “Majority Romance” country. Once the majority language has been identified, it is assigned to one of a number of broad categories. If it does not fit into any of them, it is called an “Isolate”. The most prominent isolates are Celtic and Hebrew. A country can only have one majority language. If it has several official languages, the most widespread one is coded as the majority language; the others become minority languages. Minority language families: Includes any language beyond the majority language spoken by at least 10% of the population. These are coded in the same way the majority languages. If there are no languages beyond the official one spoken by at least 10% of the population, this category is coded “0”. A country can have any number of minority languages. Majority script: Refers to the alphabet used to write the majority language. Once the majority script has been identified, it is assigned to one of a number of broad categories. If it does not fit into any of them, it is called an “Isolate”. The most prominent isolates are Greek and Hebrew. A country can only have one majority script. If several alphabets are used, the most widely used is coded as the majority script. Generally, all African and Latin American native languages were converted to Latin characters under colonial administration. Thus, though pre-colonial alphabets exist for many of these languages, they currently use Latin characters and are coded as “Latin script”. Minority scripts: Includes any alphabet(s) beyond the one used by the majority language. These are coded in the same way the minority languages. A minimum of 10% of the population must use the script, otherwise it is coded as “0” A country can have any number of minority scripts. Majority religion: This category refers to the country’s religion with the most followers. Once the majority religion has been identified, it is assigned to one of a number of broad categories. If it does not fit into any of them, it is called an “Isolate/Local/Tribal”. The most prominent isolates are voodoo in the Caribbean and animism and ancestor worship in Africa and SE Asia. A country can only have one majority religion. If a country has several official religions, the largest of these is coded as the “Majority religion”. If a country has an official religion, but this religion is smaller than another religion, the largest religion is still coded as the “Majority religion”. Minority religions: Includes any religion beyond the majority religion practiced by at least 10% of the population. These are coded in the same way the majority religion. If there are no religions beyond the official one practiced by at least 10% of the population, this category is coded “0”. A country can have any number of minority religions. Special: All categories are binary. States are or are not members of each category – this is represented, respectively, with a “1” or a “0”. Countries are not coded as both “Majority” and “Minority” if their languages belong to the same broad language families. The same applies to scripts. The one exception to this rule is Eritrea. Most Eritreans speak Tigrinya written in the Ge’ez alphabet, while a minority speak and write Arabic. Both languages belong to the Afro-Asiatic category, but the languages and the alphabets are mutually unintelligible. Eritrea is thus coded as both majority and minority Afro-Asiatic, with a majority Ge’ez and a minority Perso-Arabic scripts. Appendix 3: ISO Country Codes Countries without ISO codes—pre-2008 East Germany West Germany Czechoslovakia South Yemen (Democratic Republic of Yemen) North Yemen (Yemen Arab Republic) Yugoslavia/Serbia and Montenegro/Serbia