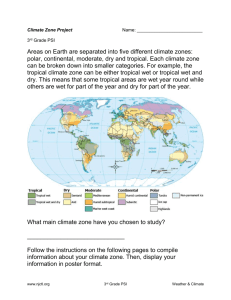
MULTIPLE CHOICE FINAL REVIEW Units 1
advertisement

MULTIPLE CHOICE FINAL REVIEW Units 1-9 1. The image below shows red blood cells in solution. Label the type of solution found in each sample, from left to right. a. Isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic b. Hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic c. Hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic d. Hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic Questions #2-3 refer to the following situation: In the 1890s, hunting reduced the northern elephant seal population to only 20 individuals. Due to conservation efforts, their population size today is above 30,000. 2. How would the genetic diversity of the northern elephant seal population compare to the genetic diversity of the southern elephant seal population, which was not heavily hunted? a. The northern elephant seal would have much less genetic variation than the southern elephant seal. b. The southern elephant sea would have much less genetic variation than the northern elephant seal. c. The two populations would have similar genetic variation. d. The southern elephant seal would have stable genetic variation because it is in HardyWeinberg equilibrium. 3. This is an example of what biological principle? a. Founder effect b. Allopatric speciation c. Bottleneck effect d. Microevolution 4. While eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells, metabolic requirements place upper limits on how large eukaryotic cells can become. Which of the following statements does not accurately describe this? a. If a cell is too large, there will not be enough surface area for the exchange or elimination of oxygen, nutrients, and wastes. b. The surface area to volume ratio must remain as large as possible. c. As multicellular organisms grow in size, they do not have larger cells; rather, they have a larger number of cells. d. As a cell increases in size, surface area grows faster than volume. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 5. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all composed of long chains of glucose molecules. While starch and glycogen are often branched, cellulose is always straight due to hydrogen bonding between neighboring strands. How is this structural difference advantageous for the function of cellulose? a. Cellulose is held tightly together in order to offer support in cell walls. b. Cellulose is used as long-term energy storage, held tightly together to take up minimal space. c. Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide, used as support in exoskeletons. d. The lack of branching allows cellulose to be easily hydrolyzed, enabling it to be used as quick energy. 6. Animal muscle is composed of a variety of different types of proteins. Muscles use ATP as the source of energy to create work. When an animal is stressed, ATP is depleted quickly in the muscles. This results in an environment that has a low pH and a high temperature. Under these conditions, muscle proteins may denature. If denaturation occurs, which of the following is not interrupted in the protein molecules? a. α helices b. disulfide bridges c. peptide bonds d. hydrophobic interactions 7. Using the graph comparing photosynthetic rate and absorption of different wavelengths of light, what can be concluded? a. Carotenoids absorb the narrowest range wavelengths of light b. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths at both ends of the spectrum c. The photosynthetic rate at 550 nm is the highest d. Chlorophyll b is associated with the greatest rate of photosynthesis. Questions #8-9 refer to the following information: Prairie dogs are a type of rodent that inhabit the grasslands of central and western North America. These burrowing animals live in large colonies and are an important component of the ecosystem. The prairie dog foraging technique increases plant diversity. Their burrows enable water to find underground aquifers, thereby conserving water. The act of burrowing into the ground mixes the soil, creating richer growing conditions. The open spaces maintained by prairie dogs increase the animal diversity found in the ecosystem. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 8. Prairie dogs are a keystone species for the Great Plains ecosystem. Which of the following is also true of this animal? a. They have a low biomass in the ecosystem. b. They are at the top of the food chain. c. Removal of the prairie dog will not have a large impact on the ecosystem. d. They do not experience competition. 9. To determine the effect of prairie dog on the Great Plains ecosystem, you create an exclusion experiment. You maintain several plots of land that have distinct borders to them. In one of the plots, you exclude prairie dogs. Which of the following is not a plausible result in the exclusion plot? a. Plant diversity decreases. b. Prolonged drought. c. Herbivore populations increase. d. Nutrient limitation in the soil. 10. All living organisms use DNA and RNA as their genetic code. Humans and roundworms, in fact, have 25% of their DNA in common while humans and chimpanzees have 98% in common. What type of evidence of evolution is this? a. Comparative embryology b. Fossil record c. Molecular homology d. Biogeography 11. Organisms have evolved a variety of adaptations that allow them to survive their environments. One aspect of survivorship involves the trade-off between the quantity and quality of offspring produced. What is a true statement regarding this type of adaptation? a. Organisms who follow r-selection favor quality over quantity. b. Organisms who follow K-selection experience high fecundity. c. Producing numerous offspring consumes energy but ensures that at least some will grow into reproducing adults. d. Organisms who favor quality have low parental involvement. 12. An RNA strand has the following sequence: 5’ – UAGCUGAC – 3’. How many molecules of water did it require to create this strand of nucleotides? a. 7 b. 8 c. 9 d. 10 www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #13-14 refer to the following image of a fruit fly oocyte. Bicoid protein concentration Highest Lowest A D B C 13. Based on the diagram, where would the anterior part of the fruit fly develop? a. A b. B c. C d. D 14. Bicoid protein is a type of egg-polarity gene that determines the body axes of the fruit fly. What is another name for this type of gene? a. Maternal effect gene b. Oncogene c. Molecular coordinate gene d. Homeotic gene 15. Cyclin and kinases are molecules that aid in cell cycle regulation. Which of the following is true concerning these molecules? a. They function independently of each other. b. Cyclin regulates the G1 and G2 checkpoints while kinases regulate the metaphase checkpoint. c. Kinases are only active when paired with cyclin. d. The concentration of cyclin within cells remains constant. 16. Which of the following cannot be determined from looking at a karyotype? a. The sex of the individual. b. Down syndrome, in which there is an extra copy of chromosome 21. c. Klinefelter syndrome, in which there is an abnormal number of sex chromosomes. d. The loci of specific genes. 17. Snakes evolved from ancestors who had the ability to walk. Some snakes, in fact, still have small pelvis and leg bones that are remnants from this ancestor. What are these called? a. Vestigial structure b. Homologous structure c. Sympatric structure d. Molecular homology www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #18-19 refer to the following cellular components: I. II. III. IV. V. Plasma membrane Nucleus Peroxisomes Ribosomes Chloroplasts 18. Ameobas and Chlamydomonas are two types of protists. Ameobas engulf food while Chlamydomonas are phototrophs, using the sun’s energy to create food. Which cellular component is not found in both types of protists? a. I b. III c. IV d. V 19. Which cellular components are found in all organisms? a. I and II b. II and IV c. I and IV d. I, II, and IV 20. Chemosynthetic autotrophs and photosynthetic autotrophs are similar in that they both capture free energy to produce organic compounds. Which of following correctly contrasts photosynthesis and chemosynthesis? a. In photosynthesis oxygen gas is the final electron acceptor while in chemosynthesis hydrogen sulfide is the final electron acceptor. b. In chemosynthesis water is a final product while in photosynthesis carbon dioxide is a final product. c. Photosynthetic organisms require solar radiation while chemosynthetic organisms require electromagnetic radiation. d. Chemosynthetic organisms capture energy from inorganic molecules while photosynthetic organisms capture energy present in sunlight. 21. Although they are both nucleic acids, RNA and DNA carry out different functions. Which statement describes a similarity between the two macromolecules? a. They are both composed of 5-carbon sugars. b. They are double stranded. c. They share two purines and two pyrimidines. d. They are self-replicating. 22. When an enzyme is noncompetitively inhibited, which of the following occurs? a. The enzyme is able to increase its activity. b. The active site will change shape. c. The active site will be occupied by the inhibitor molecule. d. Increasing substrate concentration will increase inhibition. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 23. Mendel’s law of independent assortment states that alleles for different traits are inherited independently from each other. To what type of gene does this law not apply? a. Codominant genes b. Dihybrid genes c. Linked genes d. Incompletely dominant genes Questions #24-26 refer to the following situation. An experiment was conducted to determine the factors affecting aerobic respiration in a bacterium. Under aerobic conditions, the rate of carbon dioxide production was measured at 5 minute intervals. In each treatment, a different molecule was added to the bacterial solution. A graph of the results is shown below. 1.2 1 0.8 Control 0.6 Citrate Added 0.4 ATP Removed 0.2 AMP Added 0 0 5 10 15 20 24. Which of the following best explains the above results? a. ATP and citrate are allosteric inhibitors in the cellular respiration process while the presence of AMP stimulates respiration. b. ATP and AMP stimulate respiration, while citrate inhibits this process. c. Citrate stimulates the production of CO2 by simulating fermentation in the bacterial cells. d. The presence of ATP and AMP have little effect on the process of cellular respiration. 25. When oxygen is removed from the environment, CO2 continues to be produced at low levels. What type of bacterium is being used in the experiment? a. Obligate anaerobe b. Obligate aerobe c. Facultative anaerobe d. Oxidative anaerobe 26. How many treatments are being used in this experiment? a. 1 b. 3 c. 4 d. 8 27. Which of the following is not evidence for the existence of LUCA? a. Living organisms use a universal genetic code. b. Proteins are built using the same 20 amino acids. c. Nucleic acids are used as the energy source. d. Lipid bilayers are used in cellular membranes. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 28. In an experiment, scientists transfer fibroblasts, a type of connective tissue cell, to two cultures with different growth mediums. Both growth mediums contain glucose, amino acids, salts, and antibiotics. Culture #2, however, also includes protein called PDGF. After incubating the cultures at 37⁰ C for 24 hours, culture #1 shows no cell division while the cells of culture #2 have extensively divided. What can the scientists conclude about PDGF? a. It is capable of binary fission. b. It is a growth factor for fibroblasts. c. It is only effective at high temperatures. d. It prevents anchorage dependence. 29. The difference between a negative feedback loop and a positive feedback loop is that in a negative feedback loop the new signal will _______________ the stimulus. a. Slow down b. Accelerate c. Promote d. Reverse 30. Willows are a type of deciduous tree found in temperate climates. Although plants generally reproduce sexually, if a stem from a willow is placed in moist soil, a new tree will grow. This new tree will be genetically identical to the parent tree. This is an example of what type of reproduction? a. Binary fission b. Budding c. Fragmentation d. Spores Question #31 refers to the image below depicting the genes found on chromosome 4 of fruit flies. Bent wings Eyeless Shaven bristles Sparkling eyes 31. Which of the following gene pairs would have the highest recombination frequency? a. Bent wings and sparkling eyes b. Shaven bristles and sparkling eyes c. Bent wings and eyeless d. Eyeless and shaven bristles www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 32. Which of the following is an example of a positive feedback loop? a. High body temperature is sensed by neurons, blood vessels in the skin dilate, and sweat glands are activated, lowering the body temperature. b. Low blood glucose levels triggers the hydrolysis of glycogen, releasing glucose into the blood, raising the blood glucose level. c. Bleeding triggers the release of enzymes that activate platelets in the blood. Activated platelets release chemicals to activate more platelets, leading to a blood clot. d. Partially digested food in the intestines stimulates the liver to reduce the amount of digestive enzymes. 33. A pentose is the general name for a 5-carbon sugar. The carbonyl groups of some pentoses are located at the end of the carbon chain. These molecules are called aldopentoses. The carbonyl groups of other pentoses are located within the carbon chain. These molecules are called ketopentoses. Regardless of carbonyl group location, all pentoses will have the following molecular formula: O -C – H Carbonyl Group a. b. c. d. C10H20O10 C5H3O4 C10H8O9 C5H10O5 34. Before RNA polymerase can begin transcription, transcription factors must first bind to the promoter region. Of what is this an example? a. Allosteric regulation b. Alternative splicing c. The specificity of enzymes d. Regulation of gene expression 35. Having a widow’s peak (W) is dominant over not having one (w). John has a widow’s peak, but his mother does not. What is a correct statement about the widow’s peak gene of John’s father? a. He must be homozygous recessive for the treat. b. He must have at least one dominant allele. c. He must be heterozygous for the trait. d. He is incompletely dominant for the trait. 36. Steroids, a type of lipid, include the sex hormones that are synthesized and stored in the testes and ovaries. The testes and ovaries, therefore, are rich in what organelle? a. Ribosomes b. Rough ER c. Mitochondria d. Smooth ER www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Question #37 refers to the following information: An experiment was conducted to measure the reaction rate of the human salivary enzyme alphaamylase. Ten mL of a concentrated starch solution and 1.0 mL of alpha-amylase solution were placed in a test tube. The test tube was inverted several times to mix the solution and then incubated at 25 degrees C. The amount of product (maltose) present was measured every 10 minutes for an hour. The results are given in the table below. 37. Why was a change in the reaction rate observed after 30 minutes? a. The rate increases as the substrate concentration declines. b. The rate decreases as the substrate concentration declines. c. The product is increased. d. The enzyme is buffered. 38. Many herbicides act on different stages of photosynthesis. If a particular herbicide disrupts the action of ATP synthase, which is also true? a. More ATP than usual is formed. b. Chlorophyll cannot absorb photons. c. The citric acid cycle cannot be completed. d. Cyclic electron flow can still occur. 39. Which one is not a type of physical pathway between adjacent cells to aid in communication and transfer of substances? a. Tight junctions b. Quorum junctions c. Plasmodesmata d. Adhering junctions 40. Innate immunity is general immunity that all animals have. Which of the following is not part of innate immunity? a. Skin b. Mucus c. Antibodies d. Inflammation www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #41-43 refer to the following codon table: Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:06_chart_pu3.gif 41. Leucine can be coded for by CUU, CUC, CUA, or CUG; however, these same codons will never code for any amino acid other than leucine. What does this indicate about the genetic code? a. It is redundant but not ambiguous. b. It can be recombined to form a variety of products. c. It is ambiguous but not redundant. d. It is strictly regulated. 42. This table would be used to decipher the bases on what molecule? a. DNA template b. tRNA anticodon c. mRNA d. rRNA large subunit 43. Errors during gene expression often result in mutations in proteins. Which of the following codons would have the largest impact on the resulting protein? a. UGU b. UGA c. UGG d. AUG 44. Which of the following provides a similarity between stem cells and cancer cells? a. They are able to reproduce indefinitely. b. They cause diseases. c. They are only found in the bone marrow. d. They replicate via binary fission. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #45-46 refer to the following scenario: In pea plants, there are two genes that code for flower color, P and C. Each gene codes for a different step of flower pigment production. If either gene is homozygous recessive, the flower will be white. Otherwise, the flower is purple. 45. If a PPCc plant is crossed with a Ppcc plant, what phenotypic ratio will result? a. 3 purple: 1 white b. 3 white: 1 purple c. All white d. 1 purple: 1 white 46. This situation, in which more than one gene affects one trait, is referred to by what name? a. Codominance b. Epistasis c. Pleiotropy d. Linked genes 47. Margarine is produced from plant oil that has undergone hydrogenation. In the process of hydrogenation, most of the carbon double bonds are removed. As a result of hydrogenation, the melting point of the product is elevated. An example of hydrogenation is illustrated below: Which of the following statements is incorrect based on this information? a. Hydrogenation produces trans fats. b. Hydrogenation creates fats that are healthier than the starting product. c. Margarine is solid at room temperature. d. Consumption of hydrogenated fats affects HDL levels. 48. Morphine is a commonly used drug prescribed for severe pain. Patients who use morphine on a long-term basis often experience a drug tolerance to it. This means that the effect of morphine slowly lessons and a higher dosage is required to induce the same level of pain relief. One theory that explains drug tolerance involves varying pathways that lesson the amount of receptors that will accept the drug. This is an example of what type of process? a. Antibiotic resistance b. Upregulation c. Downregulation d. Neural incompatibility www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #49-51 refer to the following scenario: You are given a u-tube filled with two solutions separated at the bottom by a semi-permeable membrane. You do not know the compositions of the solutions and are asked to determine which solution has a higher initial solute potential. You decide to observe the u-tube over several hours. Illustrated below are the initial and final diagrams of the u-tube. Solution A Solution B Source: http://course1.winona.edu/sberg/ILLUST/fig8-10.GIF 49. What is an accurate description of the initial conditions in the u-tube? a. Solution A is hypertonic compared to Solution B. b. Solution A is hypotonic compared to Solution B. c. Solution A and Solution B have reached osmotic equilibrium. d. Not enough information. 50. What is an accurate description of the final conditions in the u-tube? a. Solution A is hypertonic compared to Solution B. b. Solution A is hypotonic compared to Solution B. c. Solution A and Solution B have reached osmotic equilibrium. d. Not enough information. 51. It turns out that Solution A had an initial solute potential of -0.25 bar. Which of the following is a possible initial solute potential for Solution B? a. 0.25 bar b. -0.12 bar c. -0.25 bar d. -0.58 bar 52. Which of the following is not something that happens during a cell-mediated response? a. The infected cell is flagged to alert immune cells of the infection. b. Histamines increase blood flow. c. Helper T cells attach to anitgens. d. Cytotoxic T cells destroy infected cell. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 53. James Watson and Francis Crick worked together to determine the structure of DNA. They created their model of DNA structure based on the x-ray diffraction picture taken by Rosalind Franklin. Which of the following supports their idea that a purine always pairs with a pyrimidine in the DNA molecule? a. A purine plus a pyrimidine is the only pairing whose width matched the measurements of the x-ray picture. b. Covalent bonding is only possible between a purine and a pyrimidine. c. A pyrimidine bonded to a pyrimidine would have created a pairing that was too wide for their DNA data. d. In a given DNA molecule, the amount of cytosine molecules present always equaled the amount of adenine molecules. Questions #54-55 refer to the following phylogenetic tree: Source: http://www.vanderbilt.edu 54. The elephant and the crocodile evolved from a common ancestor. Which characteristic do they have in common? a. Amniotic egg b. Subdermal fat stores c. Gizzard d. Ability to see UV light 55. When constructing this phylogenetic tree, several different options were possible. The tree with the least number of evolutionary changes is the one that was chosen as most probable. What is this called? a. Least parsimony b. Modern synthesis c. Temporal equilibrium d. Maximum parsimony www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 56. Yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y) in pea plants. A yellow seed plant is crossed with a green seed plant. The F1 generation is composed entirely of yellow seeds. What is the name of this procedure? a. Dihybrid cross b. Testcross c. Trihybrid cross d. Chi-squared test 57. The cell cycle is tightly regulated by various mechanisms, such as checkpoints at specific times of both interphase and the mitotic phase. Which of the following is not an example of a factor involved in cell cycle control? a. Density b. Growth factors c. Substratum d. Independent assortment Questions #58-59 refer to the following karyotype: Source: http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k2humancsomaldisorders.html 58. The karyotype portrays Edward’s syndrome. Infants born with this condition usually only survive for a few months. This condition is an example of what type of event? a. Polyploidy b. Fragmentation c. Nondisjunction d. Monosomy 59. How does this type of event occur? a. Chromosome duplication errors during interphase b. Inaccurate separation of chromosomes during meiosis c. Lack of independent assortment during meiosis d. Incomplete separation of sister chromatids during mitosis www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #60 refer to the following diagram of the trp operon: Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lac_Operon.svg 60. In order for tryptophan production to stop, what needs to occur? a. An inducer needs to block the promoter region, which will inhibit further tryptophan production. b. Alternative splicing needs to change the introns present, thereby inhibiting tryptophan production. c. Tryptophan needs to bind to the repressor molecule, which in turn will bind to the operator region, inhibiting further tryptophan production. d. Tryptophan needs to bind to the promoter region, thereby prohibiting the binding of RNA polymerase and the production of further tryptophan. 61. Although animals and plants are both able to defend themselves against pathogens, the methods of defense differ greatly. Which of the following describes a difference between animal and plant immunity? a. Each plant cell must defend itself against pathogens. b. An outer membrane provides an initial line of defense in plant cells. c. In animals, a signaling cascade results in an immune response. d. As a last line of defense, infected cells are killed in animals. 62. Scientists who understand the structure of DNA were able to create the gel electrophoresis procedure. During this procedure, an electrical current forces DNA to move from the negative end to the positive end. What structural component of DNA allows this to occur? a. The specific order of bases on the inside of the molecule b. The negatively-charged backbone of DNA c. The solubility of deoxyribose d. The positively-charged phosphate groups 63. Which of these statements is correct regarding the complimentary sequence to this DNA strand: 5’ – GCGA – 3’ a. It will have one uracil. b. It will start with a 5’ end. c. It will have one purine. d. It will have three 2-ring bases. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #64-65 refer to the following information: Deer mice are usually found in the woods and are dark brown in color. The deer mice that live in the Sand Hills of Nebraska, however, have evolved a lighter coloring, the result of a change in one gene. 64. The initial population of deer mice in the Sand Hills was probably dark brown, like all other deer mice. What was the driving force behind the evolution of this population? a. Mutation b. Speciation c. Equilibrium d. Predation 65. A scientist decides to move a population of brown deer mice to a habitat composed of a mixture of sandy areas and dark rocks. After monitoring the population for several generations, she finds that it is composed of a mixture of very light and very dark colored mice. What type of selection has occurred? a. Adaptive b. Disruptive c. Directional d. Stabilizing 66. Towards the end of pregnancy, the uterus becomes more sensitive to the oxytocin, a hormone that causes uterine contractions. This sensitivity is accomplished by acquiring additional oxytocin receptors. What is this process called? a. Quorum sensing b. Downregulation c. Allosteric regulation d. Upregulation 67. Stomata are pores on the surface of plant leaves that allow for gaseous exchange. The chart below shows the density of stomata on the leaf surfaces of three species of plants. Based on this information, which statement is incorrect? Plant Elodea Water Lily Black Walnut Stomata Density (# of stomata/mm2) In Upper Epidermis In Lower Epidermis 0 0 420 0 0 465 a. In Elodea’s aquatic environment, stomata are not used to control gas exchange. b. Since water lilies live on the surface of water, transpiration occurs from the upper epidermis because that is where it is in contact with air. c. Since black walnut trees thrive on land, stomata are located on lower surface to decrease the amount of water lost in the heat of the sun. d. Since Elodea does not have any stomata, it does not carry out photosynthesis. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #68-69 refer to the following diagram: Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Replication_complex_a.png 68. The diagram shows single-stranded binding proteins, helicase, and topoisomerase located near the replication fork. What common function do these molecules share? a. The addition of new nucleotides. b. Unwinding DNA and maintaining it in an unwound position. c. Proofreading the new nucleotides. d. Protecting DNA from degradation. 69. Where would one find Okazaki fragments? a. Behind topoisomerase. b. In the leading strand. c. Hydrogen bonded to the single-stranded binding proteins. d. In the lagging strand. 70. Hemophilia is a recessive sex-linked disorder carried on the X chromosome. The disorder affects the ability of the blood to clot. A female, who does not have hemophilia, has children with a male who has hemophilia. They have four children: one male with hemophilia, one healthy male, one female with hemophilia, and one healthy female. What is true about the mother? a. She has two normal alleles for the hemophilia gene. b. She has one normal gene on the X chromosome and one recessive gene on the Y chromosome. c. She passed on at least one hemophilia allele to each child. d. She is a carrier for hemophilia. 71. Bdelloid rotifers are a group of organisms that inhabit a variety of environments. They solely reproduce via asexual means. Which of the following is not a benefit derived from this lifestyle? a. They are able to reproduce faster than sexually reproducing organisms. b. They do not need to spend time and energy attracting mates. c. The offspring are genetically varied due to random fertilization. d. They do not use energy to produce sex cells. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 72. Some strains of Staphylococcus aureus are resistant to antibiotics. This bacteria is able to create an enzyme that prevents the antibiotic from binding to the active site, rendering it useless. Which of the following is responsible for conferring resistance in bacteria? a. F plasmids b. Pili c. R plasmids d. Capsule 73. A recent study exposed some seeds to increased amounts of gibberellin, with a control group of untreated normal seeds. What would be a reasonable result of such a study? a. Treated seeds grew to show increased phototropism. b. Treated plants germinated faster. c. Treated plants grew slower. d. Treated and untreated plants show no differences in growth patterns. Question #74 refers to the diagram below: 74. In what direction will the net flow of water occur? a. Water will move to side A because side A contains the higher concentration of NaCl and sucrose. b. Water will move to side B because side B contains the least concentration of NaCl and sucrose. c. Water will accumulate on side B when NaCl and sucrose diffuse through the membrane. d. Water will move toward side A because side A contains the least concentration of NaCl and sucrose. 75. Which is the correct order of a signal transduction pathway? a. Reception, transduction, response b. Reception, response, transduction c. Transduction, reception, response d. Transduction, response, reception www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #76-77 refer to the following information: Planktonic copepods are small crustaceans that float with sea currents in the ocean. Usually only 1-2 mm in length, they feed on phytoplankton also present in the surface waters. Copepods are very sensitive to contamination by metals and are often used as bioindicators for water pollution. 76. Which of the following is not an abiotic factor that affects planktonic copepods? a. Copper concentrations b. Phytoplankton concentrations c. Water temperature d. Ocean currents 77. Copepods follow r strategies for reproduction. Which of the following is a true statement concerning organisms such as these? a. They value quality over quantity of offspring. b. They mature at a later age. c. They live in an unstable environment. d. Population size is constant. 78. Cladograms are diagrams that show relationships between different organisms. Each branch of a cladogram indicates a common ancestor. By studying the cladogram below, determine which two organisms share the greatest genetic relationship. a. b. c. d. Flies and moths Butterflies and bees Beetles and wasps Ants and flies 79. The mechanisms of transcription and translation are virtually identical in species from all three domains, Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Which of the following hypotheses could be best supported by this evidence? a. The mechanisms of transcription and translation presently found in living organisms are the only mechanisms that could effectively convert heredity information into protein structures. b. The mechanisms of transcription and translation are universal processes and therefore suggest a common ancestor for all forms of life. c. The similarity in these processes in all organisms suggests that convergent evolution has occurred. d. This evidence does not support a hypothesis because the products of transcription and translation vary widely. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #80-81 refer to the following information: The hemoglobin protein consists of four subunits. Each subunit contains separate binding sites for carbon dioxide and oxygen. When one oxygen (or carbon dioxide) binds to a subunit, a conformation change occurs in the other three subunits allowing them to more readily accept oxygen (or carbon dioxide). When oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, the protein cannot bind carbon dioxide. The oxygen-binding site, however, has a higher affinity for carbon monoxide than it does for oxygen. If carbon monoxide is present, hemoglobin will bind to it instead of oxygen. This can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in which the victim suffocates.. 80. Although hemoglobin is not an enzyme, it shares several properties with enzymes. Which of the following is not a similar feature of both hemoglobin and enzymes? a. Allosteric regulation b. Competitive inhibition c. Noncompetitive inhibition d. Three levels of structure 81. What animal would have a hemoglobin gene most similar to that found in humans? a. Chimpanzees b. Hatchet fish c. Deer mouse d. Eagle 82. The functions of respiratory and circulatory systems are interrelated. Which statement is not true? a. Respiratory systems get rid of the lactic acid that builds up during strenuous exercise. b. Molecules that enter the body via respiration enter the blood stream of the circulatory system via diffusion. c. The respiratory system gets rid of carbon dioxide created during cellular respiration. d. The circulatory system carries oxygen from the respiratory system to mitochondria for cellular respiration. 83. Homologous chromosomes are matching chromosomes found in diploid organisms. They share similar shape and genetic loci. In a diploid organism, where would homologous chromosomes not be found? a. Somatic cells b. Prophase I c. Interphase prior to mitosis d. Metaphase II 84. In 1953, Stanley Miller created a simulation of early Earth’s atmosphere. He was able to create simple compounds, amino acids and hydrocarbons. Which of the following was not one of the molecules that Miller used in his “atmosphere”? a. CH4 b. H2S c. H2O d. NH3 www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 85. What statement accurately describes the illustration below? Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Phage_Reproduction_Cycle.jpg a. b. c. d. A virus is reproducing inside a host cell, ending in the death of the host cell. A retro virus is invading a bacterial cell. A virus is coexisting inside a host cell. A virus is being attacked by restriction enzymes. 86. When making wine, yeast is added to grape juice. As time passes, the yeast consumes all of the oxygen in the flask, but continues to thrive and produce alcohol. Which of the following statements best explains this process? a. Yeast has evolved the ability to uses other electron acceptors in the absence of oxygen. b. Yeast is a facultative anaerobe, able to switch to fermentation in the absence of oxygen. c. In the absence of oxygen, yeast participates in a symbiotic relationship with anaerobic bacteria. d. Fructose stimulates alcohol production in yeast. 87. In gel electrophoresis, the smallest DNA fragments will travel the farthest. Why does this consistently occur? a. Small fragments have less charge on them and therefore travel farther. b. Small fragments are the first to leave the well and have more time to travel than the larger fragments. c. The higher molecular weight of larger fragments makes them sink. d. Small fragments move more freely through the agar gel. 88. In pea plants, stem length can be either tall or dwarf, with tall (T) being dominant to dwarf (t). What would be the phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross for this trait? a. 3 tall : 1 dwarf b. All tall c. 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt d. 3 dwarf : 1 tall www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 89. All of the following scenarios are examples of barriers that distinguish separate species. Which is not a postzygotic barrier? a. Two species of ladybugs live in the same habitat. Although they mate at the same time of year, their genitals are physically incompatible. b. Two species of fish inhabit the same stream. They are capable of mating and producing healthy offspring. The offspring, however, are infertile. c. Two species of opossums inhabit the same forest. Although they are capable of mating, no offspring ever survive development. d. Two species of mice coexist in a forest habitat. They are capable of mating and producing offspring. The offspring, however, are frail and die young. Questions #90-91 refer to the following graphs: 90. What can be concluded about P. aurelia and P. caudatum? a. They both follow exponential growth models. b. When grown together, P. aurelia competitively excludes P. caudatum. c. P. aurelia is parasitic to P. caudatum. d. When grown together, P. caudatum reaches its carrying capacity sooner than P. aurelia. 91. If nutrients and water are continually added to a sample containing both P. caudatum and P. aurelia, both species survive. When combined with the information in the graphs above,what does this indicate? a. P. aurelia competes better for food than P. caudatum. b. Predation causes P. caudatum populations to crash in the absence of nutrition. c. In the presence of nutrition, P. caudatum and P. aurelia become facultative symbionts. d. P. aurelia is a dominant species. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions 92-93 refer to the following: Many scientists postulate that the following four steps brought about the evolution of simple cells: 1) Small, organic molecules were created from inorganic sources. 2) The small molecules combined to form macromolecules. 3) The macromolecules were packaged into protobionts that were able to maintain an internal chemistry separate from their surroundings. 4) Self-replicating molecules were created and made inheritance possible. 92. The protobionts described in step 3 had a membrane that separated the internal and external environments. What current macromolecule did this membrane probably resemble? a. Triglycerides b. Nucleotides c. Lipids d. Proteins 93. What self-replicating molecule do many scientists postulate came first? a. Proteins b. Amino acids c. Glycerol d. RNA 94. Remoras are marine fish that have a modified fin in the shape of a sucking disc that can attach to the skins of other marine animals, such as sharks and manta rays. Remoras eat the leftover food from their hosts’ meals. The host is neither harmed nor benefitted by the remora’s presence. How would this relationship be characterized? a. Parasitism b. Obligate c. Commensalism d. Neutralism 95. Which of the following statements does not describe the role of auxin in phototropism? a. Auxin causes cell elongation. b. In response to light, auxin moves away from the source. c. As the concentration of auxin on the darker side of the plant increases, the elongation of those cells also increases and the plant bends toward the light. d. In the presence of light, auxin is activated to stunt cell growth. 96. Cyanide is a highly toxic molecule. It bonds to a cytochrome in the electron transport chain located in the mitochondria, rendering the electron transport chain useless. The ingestion of cyanide, therefore, results in death due to which of the following? a. Inability to take in oxygen through the lungs. b. Build up of lactic acid. c. Starvation, due to an inability to create glucose. d. Cellular death from lack of energy. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Answer #97-98 based on an AaBb x aabb cross that results in 20 offspring. 97. In a laboratory setting, this cross is conducted with the following results: 6 AaBb, 5 Aabb, 6 aaBb and 3 aabb. What is the chi-squared value? a. 0 b. 0.05 c. 1.67 d. Not enough information. 98. Use the chi-squared chart below and a p value of 0.05 to make a conclusion about the experiment. a. The difference between the observed and expected results is statistically significant. b. You should accept the null hypothesis. c. The difference between the observed and expected results was not due to random chance. d. The experiment should be rerun, using a larger sample size. 99. Spirochaetes are free-living, anaerobic bacteria that contain spiral-shaped cells. Nematodes are roundworms that are incredibly diverse and, as a group, have adapted to survive in all environments. Which of the following statements accurately describes the DNA of both groups? a. The spirochaete genome is smaller than the nematode genome. b. Nematode DNA is circular. c. Spirochaete chromosomes are composed of just DNA while nematode chromosomes also include specialized proteins. d. Spirochaete DNA is linear. 100. A virus is considered an obligate intracellular parasite. What does this mean? a. It can only reproduce inside a host cell. b. It can switch between the lytic and lysogenic cycles. c. It can use either DNA or RNA as its genetic material. d. It is dependent upon reverse transcriptase inside the bacterial host cell. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #101-104 refer to the following information: Nitrogen is the most limiting nutrient for most plants, including Azolla, an aquatic fern. Azolla has formed a relationship with the cyanobacterium Anabaena azollae. This cyanobacteria fixes atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by Azolla. In return, Azolla supplies nutrients to the cyanobacteria. 101. How would the relationship between Azolla and Anabaena azollae be classified? a. Commensalism b. Competition c. Parasitism d. Symbiosis 102. Azolla is used in rice paddies as a natural fertilizer. When paddies are flooded, Azolla are allowed to grow on the surface. As rice grows, it eventually overshadows Azolla, causing it to die. How would this be beneficial to the rice? a. When Azolla dies, the cyanobacteria can transfer usable nitrogen to the rice. b. The decomposition of Azolla supplies nutrients to the growing rice. c. The death of Azolla give the rice more room to grow. d. The oxygen expelled by the Azolla enables the rice to grow. 103. Which of the following is a density independent factor that would affect Azolla? a. A long winter freeze b. Predatory fish c. A similar aquatic plant that inhabits the same space d. A disease that affects aquatic ferns 104. Large Azolla blooms are prevalent in areas with high phosphorous concentrations. What does this indicate about Azolla? a. Phosphorous is toxic to Azolla. b. Phosphorous is toxic to the cyanobacteria. c. The cyanobacteria are also able to fix phosphorous. d. Phosphorous is a limiting nutrient for Azolla. 105. Why is a closed circulatory system more efficient? a. Muscular movement assists the transport of materials. b. The transport of nutrients and removal of wastes is accomplished rapidly. c. Oxygen can enter directly into the blood via diffusion across the skin. d. Body organs and tissues are continuously in contact with blood. 106. Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease for which there currently is no cure. Alzheimer’s results from an accumulation of misfolded proteins. In some instances, β pleated sheets form instead of α helices. At what level of structure is this error occurring? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Quaternary www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 107. Eukaryotes are a diverse group that have evolved several differences from their prokaryotic ancestors. Which of the following statements does not accurately describe a difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? a. Eukaryotes have organelles suspended in their cytoplasm. b. Eukaryotes have smaller cells which enable them to be more efficient. c. Eukaryotes contain their DNA in a nucleus. d. Most eukaryotes are multicellular. 108. Due to advances in biotechnology, scientists are able to produce insulin in a laboratory setting. This enables people who suffer from diabetes to replace the insulin that their bodies are not producing. During the laboratory procedure, the insulin gene is isolated and then amplified. What process is used to amplify the insulin gene? a. Recombinant DNA b. Splicing c. Electrophoresis d. Polymerase chain reaction Question #109 refers to the image below of cells extracted from the bronchioles of a patient. Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tripolar_Mitosis_-_bronchial_wash.jpg 109. The cell in the middle of the picture shows tripolar mitosis, indicating that the cell is cancerous. Tripolar mitosis explains what aspect of cancer? a. Cancer cells do not respond to cell cycle checkpoints. b. Cancer cells have extra copies of chromosomes. c. Cancer cells are oncogenes. d. Cancer cells do not exhibit anchorage dependence. 110. The medium ground finch is one of Darwin’s finches that inhabit an island in the Galapagos. It has a small beak that it uses to eat small, soft seeds. In 1977, a drought eliminated all but the hard, large seeds. The birds who had larger beaks were able to find food and survive to reproduce while the birds who had small beaks could not find food and died. Within a few generations, the beak size of the medium ground finch increased by 10%. What type of selection is this? a. Disruptive b. Stabilizing c. Directional d. Sympatric www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #111-112 refer to the following situation: A plant found in Yosemite National Park is found to have two varieties: red flowers and blue flowers. To determine the type of inheritance pattern found in this species, red flowers are crossed with blue flowers. 111. What flowers would result if flower color has incomplete dominance? a. Red flowers b. Purple flowers c. Blue flowers d. Red and blue spotted flowers 112. What flowers would result if flower color has codominance? a. Red flowers b. Purple flowers c. Blue flowers d. Red and blue spotted flowers 113. An unknown lab sample is subjected to hydrolysis. The results include a combination of hydrocarbon chains, glycerol molecules, and phosphate groups. What was in the original sample? a. Cholesterol b. Phospholipids c. Trans fats d. Triglycerides 114. The cellular membrane is composed of a variety of proteins, each with different functions. Which of the following is not a function of membrane proteins? a. Energy storage b. Transport c. Signal transduction d. Cell-cell recognition 115. After transcription, pre-mRNA undergoes processing that ensures, among other things, that it will be safely transported to the cytoplasm and protected from hydrolytic enzymes. Which of the following is not something that occurs during mRNA processing? a. Poly-A tail b. Recombination c. 5’ cap d. Splicing 116. Crossing over was first described in 1909 by Belgium professor Frans Alfons Janssens. It is a phenomenon that has important implications for evolutionary change in populations. What is the result of this phenomenon? a. It creates chromosomes with genetic combinations unique from parental chromosomes. b. It creates chiasma between nonhomologous chromosomes. c. It allows for independent assortment to occur. d. It creates stability in recombinant chromosomes. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Questions #117-118 refer to the following food web: Source: http://alaska.usgs.gov/science/biology/seabirds_foragefish/marinehabitat/index.php 117. Which organism is a producer in this food web? a. Cephalopod b. Phytoplankton c. Fox d. Zooplankton 118. If the salmon population crashes as a result of overfishing, which of the following is not a plausible result? a. The fox population may increase. b. The zooplankton population may increase. c. Puffins may eat larger amounts of sand lances. d. The cephalopod population may increase. 119. Mendel did most of his work during the mid-1800s. He grew and observed over 5,000 pea plants and, from these studies, identified the law of independent assortment and the law of segregation. Evidence for the law of segregation was later uncovered in the late 1800s by other scientists. What process would provide evidence for the law of segregation? a. Mitosis b. Crossing over c. Meiosis d. Epistasis 120. Which of the following statements regarding cellular respiration rate is correct? a. At 10oC, a gecko will have a higher rate of cellular respiration than a rat. b. At 10oC, a gecko and a mouse will have equal rates of cellular respiration. c. At 25oC, a mouse will have a higher rate of cellular respiration than a human. d. At 25oC, a human will have a higher rate of cellular respiration than a mouse. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 121. When Charles Darwin visited the Galapagos Islands, he observed the marine iguana. He later decided that the marine iguana evolved from the terrestrial iguana found on the mainland of South America. The marine iguana differs from the terrestrial iguana in several ways. The marine iguana has a flat tail, long claws and sharp teeth while the terrestrial iguana has a round tail, short claws and flat teeth. The marine iguana became a separate species after being geographically isolated on the Galapagos Islands for several years. What type of speciation is this? a. Adaptive b. Allopatric c. Sympatric d. Geographic 122. Structure and function is a recurring theme in biology. How does the structure of tRNA relate to its function? a. The anticodon pairs with mRNA while the amino acid attached to the other end bonds with the growing polypeptide chain. b. The three loops of the tRNA molecule are each able to pair to a different amino acid, making translation efficient. c. Allosteric control of tRNA can occur at any of the three anticodon locations, thereby regulating translation. d. The three loops of the tRNA molecule allow it to fit snugly into each of the three openings in the rRNA molecule. 123. During translation, the growing peptide chain resides in the P site of rRNA with the next amino acid in the chain waiting in the A site. Erythromycin, a common antibiotic, prevents the tRNA at the A site from moving into the P site. How does this result in the death of the bacteria? a. This terminates the replication of DNA. b. This prevents the translation of proteins necessary for life. c. This prevents the generation of RNA from DNA. d. This creates a breakdown in metabolism, resulting in starvation of the bacteria. 124. Eukaryotes include all of the following organisms, except for one. Which organism is not eukaryotic? a. Euglena, a unicellular flagellate protist b. Methanogens, bacteria that produce methane and live in the intestines of other organisms c. Mold, a multicellular organism that often grows on the surface of food d. Duckweed, an aquatic plant that grows on the surface of ponds 125. You are studying two variations of banana slugs. They have similar coloration and live in the same habitat. Although they are physically able to mate, there are no offspring that survive embryologic development. What can you conclude about the banana slugs? a. Prezygotic barriers have forced them to be separate species. b. They are in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. c. Microevolution is occurring in both variations. d. They are two separate species. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 126. The image below illustrates the process of cytokinesis in animals (1) and plants (2). Why are there two different methods for the same process? Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cytokinesis.png a. The cell wall of a plant cell prevents the contraction necessary for cleavage. b. Animals evolved after plants and therefore developed a more efficient method of cytokinesis. c. Plants undergo fission, a slightly different version of mitosis. d. The cell plate in plants pushes outwards, resisting the formation of a cleavage furrow. QUANTITATIVE 1. A triglyceride is formed from a glycerol molecule, C3H8O3, and three identical fatty acids, C7H14O2. How many hydrogen molecules are in the triglyceride? 2. Suppose an artificial “animal-type” cell was constructed out of dialysis tubing and contained 0.5M of a NaCl solution. If the cell is stored at 273 degrees Kelvin, what is the water potential of the cell? 3. A microrespirometer was used to collect data on the respiration of unsprouted seeds. Calculate the rate of cellular respiration, in cm/min, during last five minutes of the experiment. Total Time (min) Total distance fluid has moved (cm) 0 0 0 5 3.6 3.6 10 7.4 3.8 15 9.6 2.2 www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Change in fluid position (cm) Final Review 4. The influenza virus is spherical in shape with a genome of eight different RNA molecules. It can have a diameter of up to 200 nm. The animal cells that it infects have a cell diameter of about 10 µm. How big is the average animal cell in nm? 5. The illustration below refers to the results from gel electrophoresis. In the unknown sample, what is the size of the DNA fragment that was closest to the positive electrode while the gel was being run? 6. The hemoglobin found in adult humans is composed of four polypeptide subunits. There are two α subunits, composed of 141 amino acids each, and two β subunits, composed of 146 amino acids each. How many nucleotides compose the codons necessary to translate this important protein? Do not include the nucleotides used in start and stop codons. 7. The common earthworm has 36 chromosomes. How many different ways can these chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate during meiosis I? 8. In pea plants, flowers axial flower position (A) is dominant to terminal flower position (a), inflated pods (I) are dominant to constricted pods (i) and purple flowers (P) are dominant to white flowers (p). In a cross of pea plants that are heterozygous for all traits, how many of the 480 offspring are also heterozygous for all traits? www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 9. In fruit flies, wild type flies have gray bodies and normal wings. Mutant flies have black bodies and vestigial wings. A test cross between wild type and mutant flies, results in the following: 1,930 wild type 1,888 mutant 412 gray, vestigial 370 black, normal What is the recombination frequency for the traits body color and wing type? 10. A population of wildflowers consists of two flower colors. Yellow flowers (Cy) are completely dominant to white flowers (Cw). If the frequency of the Cy allele is 70%, what is the frequency of the Cw allele? 11. The table below shows the biomass per square meter of a pond ecosystem. What is the production efficiency of the primary consumers? Trophic Level Tertiary consumers Secondary consumers Primary consumers Primary producers Biomass (kg/m2) 1.2 10 41 512 12. Kruger National Park is home to a population of elephants that are protected within the park boundaries. In 1992, the elephant population was 603. By 2007, the elephant population had grown to 3,158. If the population continues to grow at this same rate, in what year will the population reach the park’s theoretical carrying capacity of 7,000? FREE RESPONSE 1. Phospholipids are important components to living systems. The diagrams below show two phospholipid models and 2 models of phospholipid aggregations (groupings). a. When in the presence of water, phospholipids can aggregate into a planar bilayer or a liposome formation. Describe how the structure of phospholipids leads to both of these formations. b. Explain the importance of phospholipids in the origin of life. http://www2.chemistry.msu.ed u/faculty/reusch/VirtTxtJml/Ima ges3/bilyrstr.gif www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 2. Plants lose water from their above ground surfaces in the process of transpiration. Most of this water is lost from stomata, microscopic openings in the leaves. Excess water loss can have a negative effect on the growth, development, and reproduction of a plant. Severe water loss can be fatal. Environmental factors have a major impact on the rate of plant transpiration. a. Use the structure of the water molecule to explain why transpiration rate increases from 20⁰C to 27⁰C. b. Why does transpiration rate decrease after 27⁰C? 3. Himalayan rabbits carry the C gene, which is required for the development of pigments in the fur, skin, and eyes. The C gene is inactive above 35°C, and it is maximally active from 15°C to 25°C. The rabbits below have the same alleles for the C gene. a. Describe the environments each of these rabbits were reared in. Provide the evidence that supports your choice of environment. b. Describe the type of ecological factor that regulates pigmentation in Himalayan rabbits. 4. Ricin is a protein found in the seeds of the castor plant (Ricinus communis). It is one of the most potent poisons of eukaryotic cells. As shown in the diagram, the pathway for internalization of ricin involves endocytosis by coated pits/vesicles (1) or by smooth pits/vesicles (2). Some ricin molecules are returned to the cell surface via exocytosis (3). Other molecules fuse with lysosomes where the ricin is destroyed (4). If ricin vesicles fuse with the Trans Golgi Network (5) there is a chance that they may return to the cell surface via exocytosis (6). Ricin toxicity occurs when ricin penetrates the Trans Golgi Network membrane and is liberated into the cytosol (7). Once inside the cytosol, ricin catalyzes the depurination (removal of a nucleic base from the 28S ribosomal RNA) of the ribosomes, halting protein synthesis. http://www.ansci.cornell.edu/plants/toxicagents/images/cell.gif a. How does impairment of ribosomal RNA halt protein synthesis? b. Describe the type of immune response described in the steps 2-4 of the above diagram. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 5. The crested phenotype in rock pigeons is defined as neck and occipital feathers growing towards the top of the head and not down the neck of the pigeon. Some strains of the rock pigeon (Columba livia) with the crested (figure B) or non-crested phenotype (figure A) are shown. Figure C shows variants for a part of the protein EphB2 sequence, a kinase that is involved in producing both phenotypes during embryonic development, in different organisms. Genomic Diversity and Evolution of the Head Crest in the Rock Pigeon, Science 1 March 2013: 339 (6123), 1063-1067.Published online 31 January 2013 A. Non-Crested Rock Pigeon(+) B. Crested Phenotype in Rock Pigeon(cr) a. Describe how a change in just one letter in Figure C can result in a change in phenotype. b. There are 350 different breeds of Columba livia, with 80 of them displaying the crested phenotype. Does it make more sense that the EphB2 mutation evolved separately several different times or that it evolved once and was passed on to all of the crested breeds? What theory supports your answer? www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 6. ATP Synthase The diagram shows the integral membrane protein complexes responsible for electron transport and proton translocation in oxygenic photosynthesis. The structures are from thermophilic cyanobacterial sources. Lumen (p) and stromal (n) -side soluble electron transfer proteins are plastocyanin (PC) or cytochrome c6, ferredoxin (Fd), and ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (FNR). Structure of the Cytochrome b6f Complex of Oxygenic Photosynthesis: Tuning the Cavity Genji Kurisu, Huamin Zhang, Janet L. Smith, and William A. Cramer Science 7 November 2003: 302 (5647), 1009-1014 Rotary model of how the E. coli F1F0 ATP synthase catalyzes the synthesis of ATP. The protonmotive force drives rotation of a ring composed of 12 c subunits (10 in the yeast). Protons enter the assembly through a periplasmic inlet channel and bind to the Asp61 carboxylate (open circle) of the c subunits. The protonated binding site (filled circle) then moves from the a1b2 stator component to the lipid phase of the membrane. After 12 steps the protons reach an outlet channel on the F1-binding (cytoplasmic) side of the membrane. Molecular Rotary Motors Robert H. Fillingame Science 26 November 1999: 286 (5445), 16871688. a. Describe how an absence of water would affect ATP generation. b. How would the ATP synthase be oriented in above model? www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 7. These images show an erythroid (red blood cell) enhancer that promotes the expression of BCL11A. This protein represses fetal globin genes (HBG1, HBG2) in adults. The images show the effects of normal, mutated and deleted erythroid enhancers on sickle cell disease. GWAS to Therapy by Genome Edits? Ross C. Hardison and Gerd A. Blobel Science 11 October 2013: 342 (6155), 206-207 a. Sickle cell disease occurs as a result of a mutation in the hemoglobin gene. In terms of protein structure, describe how a single mutation could lead to the disease. b. Sickle cell disease offers some resistance to malaria. Individuals with the sickle cell formation have fewer symptoms and are better able to survive the disease. Sickle cell disease is hereditary, following a codominant inheritance pattern. For individuals who live in an area with high levels of malaria, would it be more advantageous to have sickle cell disease or to be heterozygous for the trait? 8. The illustration below shows proteolysis (enzymatic cutting of protein chains) at the metaphaseanaphase transition. A model is presented for how anaphase-promoting complex (APC) participates in the breakdown of both mitotic cyclins and anaphase inhibitors. The model summarizes findings from various organisms. Although some substrates have been identified in only a single organism, the APC appears to have a universal role in mitotic proteolysis in eukaryotes. In this model, cyclin B accumulates during interphase to activate CDC2 (dotted arrow), producing an active mitotic cyclindependent kinase (CDK) that triggers entry into prophase, resulting in the eventual formation of the mitotic spindle and metaphase plate. The mitotic CDK also leads to the activation of the APC by an undefined pathway. Once the APC is activated, it catalyzes the ubiquitination (adding ubiquitin, a small 76 amino acid protein, to other proteins) of several substrates, including the anaphase inhibitors PDS1 (budding yeast) and CUT2 (fission yeast). Proteins that have been tagged with ubiquitin are slated to be broken down by the proteasome (an organelle that cuts proteins and aids www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review in protein recycling among other functions). The APC also mediates proteolysis of cyclin B, which is universally required for exit from telophase (cytokinesis). a. If a mutation results in the inability of a cell to produce cyclin B, what will be the fate of that cell, in terms of the cell cycle? b. How does ubiquitination affect anaphase inhibitors? How does this affect the cell cycle? 9. The human large intestine harbors a complex community of microbiota that affect many aspects of our physiology and health. Germ-free mice inoculated with microbiota from obese or lean human twins take on the microbiota characteristics of the donor. Those receiving the obese microbiota had an increase in adiposity (fat cell size), whereas those receiving the lean microbiota remained lean. Gut Microbiota from Twins Discordant for Obesity Modulate Metabolism in Mice Vanessa K. Ridaura, Jeremiah J. Faith et. al. Science 6 September 2013: 341 (6150), 1241214 a. Describe a control group that could have been used for this experiment? b. Using the graph labeled E, which mice had greater www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review changes in body mass- and what do the larger errors on the top curve (obese twin) than the bottom curve mean? 10. Waardenburg syndrome (WS) is an inherited birth defect in which a baby will suffer from hearing loss and problems with the pigment in the skin and hair. It is an autosomal dominant disease. The hearing loss in WS is present from birth (congenital). The hearing loss is typically not progressive, can be in one or both ears, and of the sensorineural (nerve) type. The hearing loss can vary from moderate to severe to profound. The following are additional signs and symptoms that may be seen in WS, noting that the child may not have all of these characteristics. The pigment (color) of the eyes and skin are affected causing two differently colored eyes or white areas of the skin (albinism). The bridge of the nose may be wide and the eyes may appear to be spaced far apart. The hairline may be low on the forehead. Hair may become gray early in life, often before 30 years of age. There may be patches of white hair such as a “white forelock”, which is a white lock of hair growing above the forehead. Type I WS includes the above signs and symptoms. Type II WS also has the above signs but has hearing loss and differently colored eyes more commonly than in type I. On the other hand, the white forelock, early graying of the hair, and albinism occur less commonly than in type I. Type III has the above signs, plus malformations of the upper limbs. Type IV has the above signs, as well as Hirschsprung disease, which is a digestive disorder where certain nerve cells in the large intestine are missing that causes problems passing stool. www.i-am-pregnant.com a. A woman with WS marries a man whose family has no history of the disease. They have a daughter with WS and two normal phenotype sons. One son marries a woman whose family has no history of the disease. They have two daughters. Create a pedigree for this family. b. What is the probability that the granddaughters will have the disease? Suppose that the daughter of the original couple marries a man with no family history of WS. What is the probability that they will have a child affected with the disease? 11. Double-gene knockout (removal of DNA or its functionality) mice (V1a–/–V1b–/–) and wild-type mice (WT) are examined for their behavioral rhythms under experimental jet-lag conditions. The mice were housed in a light-controlled isolator with food and drink available, and their body movement activity was recorded by infrared (heat) sensors. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review The small, dark bands in the above figures are evidence of activity or movement by the mice. When they were maintained in a 12-hour light/12-hour dark (LD) cycle, both WT and V1a–/–V1b–/– mice exhibited high locomotor activity during the dark phase (12-0 hours). After 2 weeks of recording behaviors (-5 to 0 days), LD cycles were advanced by 8 hours. In WT mice, this advance evoked a gradual shift of locomotor activity rhythms, which took 8 to 10 days for complete adjustment to the new LD schedule. This slow resetting of locomotor activity rhythm was expected, as it is the typical sign that mice are experiencing jet lag. Every subsequent day after the LD cycle advance, the WT mice will start their activity slightly earlier, to finally align, after 8 to 10 days, to the beginning of the night. In contrast, V1a–/–V1b–/– mice showed almost immediate readjustment within only 2 to 4 days of transition. a. Suppose that an equal number of each type of mice is released into an ecosystem that experiences random fluctuations of day and night. How would natural selection alter the alleles in the population of mice? b. In this new ecosystem, the fluctuations of day and night cause an unstable environment, in which the mice have relatively short lives. Describe the type of survivorship strategy that would be used by the mice in this environment. 12. These graphs show the results of laboratory feeding experiments of the snail T. funebralis. The experiment tested the feeding preference of the snails for the vegetative blades (V) and sporophylls (S) of the brown seaweed A. marginata. Graph A Ten large (wet weight, about 10 g) T. funebralis (snails) were offered equal weights (about 10 g each) of A. marginata sporophylls and vegetative blades in 36-liter aquaria. After 48 hours, the algae were weighed again. Control aquaria contained algae but no snails. Graph B For total phenolic content and tanning ability measurements, fresh algal tissue was ground in 50 % methanol in a tissue macerator and extracted in the dark for 24 hours. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review Graph C Organic nitrogen content refers to proteins and amino acids. Graph D The toughness of the blades and sporophylls refers to how easy it can be cut or punctured. Algal Chemical Defense Against Herbivores: Allocation of Phenolic Compounds in the Kelp Alaria marginata PETER D. STEINBERG Science 27 January 1984: 405-407 a. Based on the data, which part of brown seaweed is preferred by the snails? Describe your rationale. b. During the experiment, why was the algae weighed a second time, 48 hours after placement in the aquaria? 13. The Miller-Urey experiment showed amino acids can be produced from gases in the Earth’s early atmosphere and environmental conditions (heat and lightning). These amino acids could then go on to be used as reactants in the synthesis pathway for RNA and DNA. This evolution of genetic material allowed the progression of life on Earth. a. It is highly likely that amino acids evolved before either RNA or DNA. Which molecule most likely followed amino acid evolution? Explain your reasoning. b. The classic Miller-Urey experiment tested the hypothesis that organic molecules such as amino acids could be created from lightning in the early atmosphere. Describe two other possible sources of organic molecules. c. In the evolution of prokaryotic cells into eukaryotic cells, several organelles are thought to have been taken in by other cells along with their DNA. Name one of these organelles and explain this theory. 14. During microscopic examination of human tissue samples, a student observed the following. a. The tissue in this sample is ideally suited for the exchange of materials with the environment. Propose a location in the human body where this tissue may be found and describe its function. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review b. How does the structure of the above tissue relate to its function of material exchange? c. Suppose that three blocks are composed of agar, phenolphthalein and base solution. They are cut into differing sizes (1 cm3, 2 cm3 and 3 cm3) and placed in an acid solution for a set amount of time. After the blocks are retrieved from the acid solution, they are cut in half to measure the distance of diffusion. Describe the results expected. How does size relate to diffusion rate? 15. The diagram shows a phylogenetic tree made from the amino acid sequences of the complete haemocyanin molecules of Sepia officinalis (SoH1-SoH3, cuttlefish), Enteroctopus dofleini (OdHA, OdHG, Giant Pacific octopus), Nautilus pompilius (NpH, nautilus) and Haliotis tuberculata (HtH1, HtH2, green ormer (sea snail)). The split of gastropoda (snails and slugs) and cephalopoda (mollusks) about 550 ± 50 millions of years ago (mya) was used as calibration point to estimate the DNA sequence mutation rate. Included are the exon-intron (rectangles-line) structures of the haemocyanin of N. pompilius, E. dofleini and S. officinalis. Grey bars indicate the 95% HPD (highest posterior density) or the confidence interval of the estimated age. The number under the root of each branch is the estimated age of gene duplication in mya. Haemocynanin is an oxygen-binding, cylindrical protein complex made from at least 10 subunits. a. If you would look at the sequence alignment of the sequences used to make this phylogenetic tree, which 2 sequences would be the most similar? Describe the evidence to support your choice. b. The exon-intron structure of the Haliotis tuberculata haemocynanins would be expected to be more similar to which species? Describe the evidence to support your choice. c. This phylogenetic tree is based on what type of homologies? Name and describe one other type of homology that could be used to build a phylogenetic tree. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 16. Spartina anglica is a salt marsh grass found along the coasts of the British Isles. S. anglica is a very tolerant plant that can withstand periodic inundation and water-saturated soils. Because of these adaptations, it is used extensively for stabilizing mudflats. In general, S. anglica is the most seaward grass found in a salt marsh. Molles, Manuel C. "Competition." Ecology: Concepts and Applications. Boston: WCB/McGraw-Hill, 1999. 237. Print. The distribution of S. anglica in a salt marsh depends on several factors. Tidal fluctuations determine the upper and lower limits of distribution, with the grass being found between the mean high water spring tide and the mean high water neap tide. A second factor that determines distribution is the fetch of the estuary. The larger the fetch (distance over which wind can blow) the higher S. anglica must live in order to avoid wave disturbances. In the upper intertidal zone, S. anglica are replaced by other marsh grasses which are better able to compete for resources in those areas of the marsh. a. The distribution of S. anglica at the upper and lower levels of the intertidal zone are determined by different factors. For each location, describe the environmental factors affecting S. anglica as biotic or abiotic and density-dependent or density-independent. b. Describe the interaction occurring in the upper intertidal zone between S. anglica and other marsh grasses. c. To further investigate the interaction between S. anglica and other marsh grasses, an exclusion experiment is run. Describe how this would work, including possible results. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review ANSWER KEY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. www.njctl.org D A C D A C B A C C C A D A C D A D C D A B C A C B C B D C A C D D B D B C B C A C B A D B 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. B C B C D B A A D B D C B C A B C D B D D B D D C C B B A B C A B D A A D B A B D A A B A C PSI AP Biology 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 112. 113. 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. 123. 124. 125. 126. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. D C D D C B A A D B A D B B B D A C B D B A B A A A C C B A B B D A 44 22.7 bars 0.44 cm/min 10,000 nm 1500 bp 1722 6.9 x 1010 60 17% 30% 8% 2014 Final Review 1. Phospholipids a. Water molecules are polar. The phosphate head of a phospholipid is polar while the tail is nonpolar. The head is attracted to water while the tail is repelled by water. This causes the heads to aggregate beside water molecules while the tails form a middle layer. b. Phospholipids made it possible for the existence of micro-environments that were isolated form an outer environment. In these micro-environments, evolution was able to occur. 2. Transpiration a. Water molecules are held strongly together via hydrogen bonds. In order for water to evaporate, energy must first go into breaking the hydrogen bonds. As temperature increases, the amount of hydrogen bonds that are broken also increases, allowing transpiration rate to increase. b. At temperatures above 27⁰C, stomata begin to close to conserve water, leading to a lower transpiration rate. 3. Rabbits a. The rabbit with the black tips was raise in an environment where the temperature was between 15°C to 25°C, while the totally white was reared in an environment above 35°C. The C gene is inactivate above 35°C and therefore would be able to affect the color of the fur in the defined regions of the rabbit. b. Temperature is the factor that regulates pigmentation in Himalayan rabbits. It is an abiotic factor. 4. Ricin a. Ribosomal RNA is the location where nucleotides are joined to a growing polypeptide chain. By impairing the function of rRNA, protein synthesis would no longer occur. b. Phagocytosis is a part of innate immunity. Phagocytosis occurs when pathogens are taken into the cell via endocytosis. Vesicles with the pathogen are fused with lysosomes where the pathogen is destroyed. 5. Pigeons a. The sequence of letters represents the amino acid sequence of protein variants. A change in one amino acid results in a change in the folding of that protein, resulting in different function and, therefore, phenotype. b. The theory of maximum parsimony supports the idea that the mutation occurred once and was passed on to all of the crested breeds that followed. 6. Photosynthesis a. Water provides the stream of electrons that are given to photosystem II to create the proton gradient to generate ATP and the reducing powering in NADPH. Without water, this ATP generation will fall. b. The ATP synthase would be situated in the membrane with rotors facing up or into the lumen of thylakoids and the ATP-binding site facing out or into the stroma of the chloroplast. 7. Hemoglobin a. The single mutation causes a change in a codon for an amino acid in the synthesis of proteins related to red blood cells. Amino acid sequence is the primary structure of proteins. A change at this level of structure affects all other levels, causing conformational changes in the final protein. b. It would be best to be heterozygous. This would allow some resistance to malaria while also giving the individual a mixture of healthy and sickle cell hemoglobin instead of all sickle cell hemoglobin. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 8. Cyclins a. Cyclin B is necessary to trigger entry into prophase. Without an accumulation of cyclin B, the cell will remain in the G2 phase and the cell will not divide. b. Ubiquitination causes the anaphase inhibitors to be broken down. This means that anaphase is not inhibited and the cell will continue through the cell cycle and divide successfully. 9. Twin Mice a. A control group would have been mice that received neither microbiota treatment. b. The obese twin pair inoculations had greater changes in fat mass than the lean inoculations. The larger error bars on the curve show that some mice show more fat mass gain than other mice that gain fat mass. The larger error bars signify that possibly there other factor that contribute to body mass index, such as bacterial strain fluctuations in the composition of the microbial population. 10. Heredity a. b. 0%; 50% 11. Mice a. The mutated mice would have an advantage because they are able to adapt faster to changing conditions. These mice would survive to reproduce more so than the wild type mice. In the following generations, a majority of alleles will be provided by the mutated mice. b. The mice would use r-selection (or Type III survivorship) survivorship strategies. They would have high fecundity, early maturation and low parental care. 12. Snails a. The snails prefer the vegetative blade of the brown kelp. The vegetative blade has a much lower level of phenols. b. In order to determine the amount of algae eaten by the snails, the weight of the algae would need to be recorded before placement and after placement in the aquaria. The after value would be subtracted from the before value to calculate the amount eaten. 13. Miller Urey a. RNA probably evolved before DNA. Although both molecules can store genetic information, RNA can catalyze reactions and can reproduce itself and create DNA. b. Organic molecules could also be created via volcanic eruptions on early Earth. Other theories postulate that meteorites brought important molecules to Earth. c. Chloroplasts and mitochondria are thought to have been free-living bacteria that were taken in by other cells. Known as the endosymbiotic theory, the DNA of the bacteria were incorporated into the larger cell’s genome and eventually became a permanent part of that cell. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review 14. Human Tissue a. Answers may vary. Example: the lining of the small intestine where nutrients from food diffuse into blood vessels to be carried throughout the body. b. The folds of the tissue increase the surface area to volume ratio of the tissue. This allows a maximum amount of materials to be exchanged with the environment in a given amount of time. c. The smallest block (1cm3) will show the highest diffusion rate, followed by the 2cm3 block and then the 3cm3 block. The 1cm3 block has the highest surface area to volume ratio while the 3cm3 block has the lowest ratio. The higher the surface area to volume ratio, the faster the rate of diffusion. 15. Phylogenetics a. Enteroctopus dofleini (OdHA, OdHG, Giant Pacific octopus) sequences would be most similar, because the time from their duplication is the smallest; phylogenetic trees are calibrate on amount of mutations between all sequences involved in the study. b. The exon-intron structure of the Haliotis tuberculata haemocynanins would be most similar to Nautilus pompilius (NpH, nautilus). The nautilus heamocyanin gene has the g1g2 and s1s2 exon duplications like the sequence leading to the mollusks but does not have the exons b, e, f duplicated. c. This tree is based on molecular homology. Structural homology could also be used. This compares the anatomical structure of the animal, both as an adult and as an embryo. 16. Marsh a. Upper intertidal zone: biotic, density-dependent; Lower intertidal zone: abiotic, densityindependent b. Competitive exclusion is occurring between S. anglica and other marsh grasses. Other grasses are better able to compete for resources, thereby excluding S. anglica from growing there. c. Answers may vary slightly. For an exclusion experiment, upper intertidal plots would be built and studied. 1) a plot with only S. anglica. 2) a plot with both S. anglica and another common grass. If S. anglica grows in the exclusion plot but not in the combined plot, then this shows that the other grass is a better competitor for resources. If S. anglica does not grow well in either plot, then the limiting factor is environmental and not due to the other grass. www.njctl.org PSI AP Biology Final Review