Extreme Environments Project (2)
advertisement

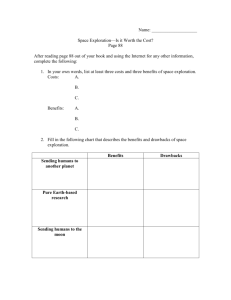
Extreme Environments Project Name; ____________ Using the computer, research the answers to the questions for your environment. Define the terms related to your environment Keep a daily Expedition journal of 1-2 things you learned or accomplished in that part of your learning journey. Also, comment on your team’s progress. Demonstrate all the information you have gathered to answer the questions and define the terms on a poster board. 3-D models are also welcome. Divide up the work evenly and note each day who accomplished various tasks Present your poster to the class in an appropriate exploration suit for your environment. You will be assessed on your journal, the poster board, the presentation and your contribution to the workload Ocean Volcano a) Why is the ocean an extreme environment? b) Give an example of a plant or animal that lives deep in the oceans. What adaptations does it have to survive? c) What is buoyancy? d) What happens to the amount of pressure as you go deeper into the ocean? e) How do humans breathe in diving suits? f) How do they take samples to study? Can living samples be collected without being destroyed? a) What makes a volcano? b) What are the different kinds of volcanoes? What makes them different? c) Where are volcanoes located around the world? d) When active, do volcanic areas allow humans to visit easily? Why or why not? e) Can volcanoes be studied from a long distance away or do people have to go there to learn about it? f) What is known about plant and animal life in the following time frames: Right after an eruption? 3 – 6 months after an eruption? One year after an eruption? g) How are rocks formed? h) What are tectonic plates? How do they move? i) Describe Earth’s crust, mantle, and core. Vocabulary: fluid, pressure, dark, pressurized environment, payload, acceleration Technologies: What technologies exist that help us with underwater exploration? Explore submarines, Newtsuit. What are the benefits and drawbacks with using technology in the exploration of your environment? (Journal) Vocabulary: lava, magma, subduction zone, mid-ocean range, convection current, tectonic plates, igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic, hot spots Technologies: What technologies help us with tectonic plate exploration? Explore fibre-optics, ROPOS. What are the benefits and drawbacks with using technology in the exploration of your environment? (Journal) Space Polar Ice a) What are some obstacles to space exploration? b) What are the harmful conditions that humans need to be protected from? How is this done? c) What prevents humans from further explorations? d) How does zero gravity affect someone in space? e) How do astronauts hold and grip tools? f) Should samples be collected and brought back to Earth for testing? Explain a) Where are the polar regions? b) What makes them polar regions? c) What is the climate of these regions? (weather, temperature, etc.) d) What conditions make it difficult to survive in the polar regions? e) What are the obstacles to exploring this environment? f) Tell about past exploration of this environment. (Who went on the missions, when, and what did they find out?) Vocabulary: vacuum, microgravity, contained atmosphere, airlocks, gravitational pull Technologies: What technologies exist that help us with space exploration? Explore rockets, Canada arm. What are the benefits and drawbacks with using technology in the exploration of your environment? Vocabulary: polar, extreme cold, heavy ice, glaciers Technologies: What technologies exist to help us with arctic exploration? Explore icebreakers, hot water drill. What are the benefits and drawbacks with using technology in the exploration of your environment? (Journal) (Journal)