Bacterial Genetic Transfer: 3D Model Project
advertisement

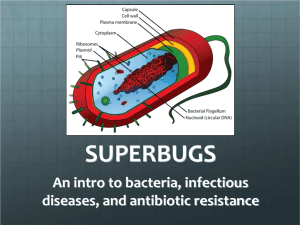
Bacterial Mechanisms of Genetic Transfer 3D Models Project Background Information: Streptococcus pneumonia, commonly referred to as pneumococcus, is a bacterium commonly found in the back of the nose in healthy people. Occasionally, pneumococcal bacteria spread to other parts of the body and cause diseases such as ear infections, sinus infections, pneumonia and meningitis. Before the introduction of penicillin, in the 1930’s, a person might die from a pneumococcal infection. After the introduction of penicillin, pneumococcal infections were effectively treated. However, strains of pneumococcal bacteria resistant to penicillin were discovered in the 1960’s. Since then, new strains of pneumococcal bacteria resistant to multiple antibiotics have been emerging. Over the last decade, almost every type of bacteria known to cause disease has become stronger and less responsive to antibiotic treatment. Antibiotic resistant bacteria are threatening communities with strains of infectious diseases. Tuberculosis, gonorrhea, malaria, skin infections (staph), pneumonia, strep throat and ear infections are just a few of the diseases that have become harder to treat. For this reason, antibiotic resistance is one of the Centers for Disease Control’s top concerns. In this project, you will investigate the mechanisms by which DNA from one bacterial cell is transferred to another bacterial cell. When the DNA that is transferred carries an antibiotic resistant gene, the intercellular transfer enables the new cell to become antibiotic resistant. Over time, one bacterial cell containing an antibiotic resistant gene could lead to an army of superbugs. There are three main mechanisms used by bacteria to transfer genetic material – transformation, transduction, and conjugation. Bacterial Mechanisms of Genetic Transfer 3D Models Project Essential Understanding: Bacterial cells use multiple pathways to gain resistance to antibiotics. Essential Question: What methods do bacteria use to share antibiotic resistant genes? Performance Objectives: I can research a genetic transfer mechanism that bacteria use to share antibiotic resistant genes I can create a design plan for building a 3D model demonstrating one of the genetic transfer mechanisms that bacteria use to share antibiotic resistant genes I can create a 3D model demonstrating one of the genetic transfer mechanisms used by bacteria to share antibiotic resistant genes I can effectively present one genetic transfer method used by bacteria to my peers Daily Project Schedule: Friday Sept. 19th: Research your team’s mechanism of genetic transfer and the steps involved Meet with project team and brainstorm possible designs and materials to use Decide as a group which design (or a combination of designs) will be used to build the model. Draw a design of your model o Once main design has been agreed upon by the group & approved by Mrs. Stewart, you may build. Monday Sept. 22nd: Build your model Practice your presentation Tuesday Sept. 23rd: Present models to class. Take notes on other presentations to learn the mechanisms used by bacteria to transfer genetic material and share antibiotic resistance. Grading Information: This project is worth a total of 100 points. 75 points come from the model and the presentation (see rubric) 25 points come from peer evaluations (see rubric) Bacterial Mechanisms of Genetic Transfer 3D Models Project Model and Presentation Rubric Category Presentation Accuracy of final product Detail of final product Creativity of final product 5 points 4 points 3 points 2 points 1 point Presentation is clearly organized into a logical sequence and shows a high level of preparation among group. Presentation is highly professional, engaging and it very effectively presents information to class. Final product shows highly indepth, accurate information; including all steps and structures involved Presentation is organized into a logical sequence and shows preparation among group. Presentation is professional, engaging and it effectively presents information to class. Presentation is organized. Presentation is somewhat professional. Presentation either lacks engagement or it ineffectively presents information to class. Presentation is organized. Presentation lacks two of the following: professionalism engagement and/or concise information. Little or no logical organization; presentation is unclear and/or confusing; does not adequately present information; poor professionalism Final product shows in-depth accurate information, including all steps and structures involved Final product shows accurate information, but omits a step or structure involved Final product shows deficient or inaccurate information ; missing one step or structure involved Highly detailed structures and sequence of steps on model. Model is easy to decipher/under stand and is highly visually appealing Somewhat detailed structures and sequence of steps on model. Model is easy to decipher/under stand and is visually appealing Model shows creativity in use of items and display Detailed structures and sequence of steps on model. Model is not easy to decipher/under stand or is not visually appealing. Model is creatively displayed OR has creative use of items, but not both. Structures and sequence of steps on model are present. Model is hard to decipher and/or not visually appealing Final product shows deficient or inaccurate information ; missing more than one step or structure involved – model not complete Model is missing one or more steps, or structures; model not complete Model shows high creativity in use of items and display Model is not creatively displayed NOR is creative in items used to construct Final Grade (out of 75 possible points) Multiply for final point value X4 X5 X4 Model not complete X2 Total points