Topic 1 - Muscles_Workbook Answers
Muscles Workbook
Types of muscles gall bladder skeletal intestines striated cardiovascular smooth smooth heart veins voluntary conscious extend cardiac organs skill
Complete the paragraphs below using the terms in the word bank above.
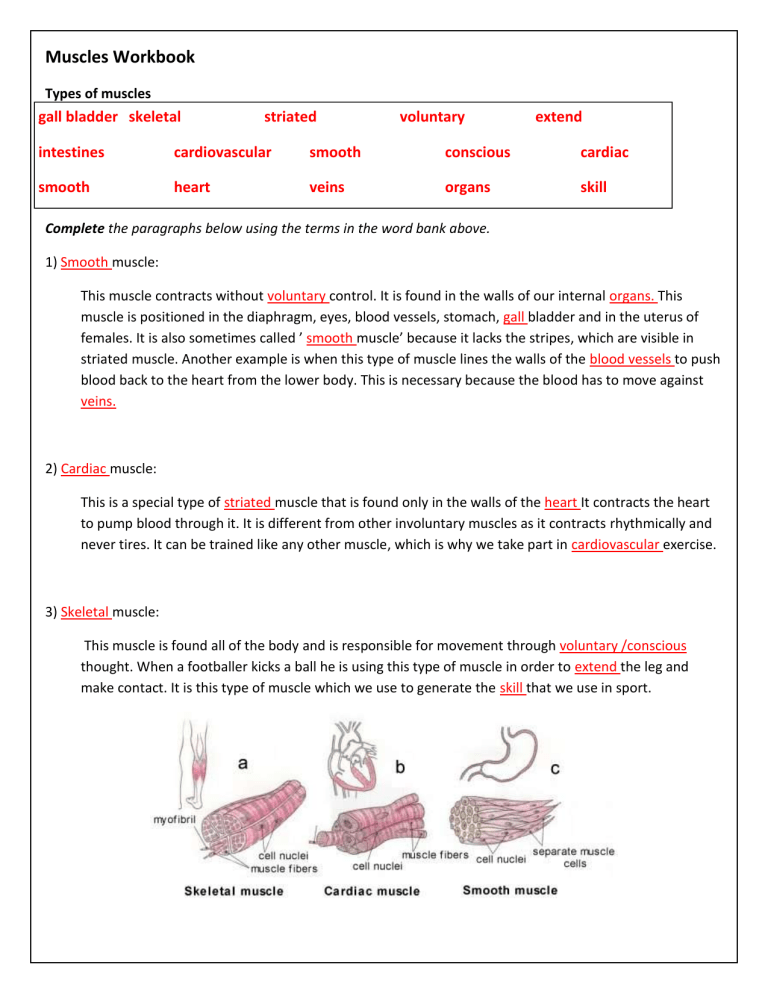
1) Smooth muscle:
This muscle contracts without voluntary control. It is found in the walls of our internal organs. This muscle is positioned in the diaphragm, eyes, blood vessels, stomach, gall bladder and in the uterus of females. It is also sometimes called ’ smooth muscle’ because it lacks the stripes, which are visible in striated muscle. Another example is when this type of muscle lines the walls of the blood vessels to push blood back to the heart from the lower body. This is necessary because the blood has to move against veins.
2) Cardiac muscle:
This is a special type of striated muscle that is found only in the walls of the heart It contracts the heart to pump blood through it. It is different from other involuntary muscles as it contracts rhythmically and never tires. It can be trained like any other muscle, which is why we take part in cardiovascular exercise.
3) Skeletal muscle:
This muscle is found all of the body and is responsible for movement through voluntary /conscious thought. When a footballer kicks a ball he is using this type of muscle in order to extend the leg and make contact. It is this type of muscle which we use to generate the skill that we use in sport.
Functions of muscles
Outline 4 functions of muscles
1.
Skeletal muscles contract exerting forces on the tendons. Tendons then pull on the bones causing joint movement.
2.
Generating body heat
3.
Postural muscles stabilize and maintain body positions
4.
Movement of substances within the body e.g. peristalsis
Properties of muscles
Describe the following properties of muscles contractility excitability extensibility elasticity
ability to receive and respond to stimuli via generation of an electrical pulse, which causes contraction of the muscle cells ability to shorten ability to be stretched or extended ability of a muscle fiber to recoil and resume its resting length
Investigating The Effects of Temperature on Muscle Function
Materials:
Ice
Pen or pencil
1. Write your signature 3 times under the column labelled “Normal”.
2. Obtain a handful of ice and hold it in your writing hand (over a sink!)
3. Write your signature 3 times under the column labelled “Cold”.
3. Place your hands under warm running water for a few minutes and massage your hands
4. Write your signature 3 times under the column labelled “Warm”.
Warm Normal Cold
Analysis
• What effect did the changes in temperature have on your hand muscles?
• How could you explain this effect?
• Why do you think dancers wear leg warmers and baseball pitchers wear jackets before pitching?
Origin and Insertion of muscles
Complete the paragraph below and annotate the diagram
When a muscle contracts, only one bone moves leaving the other stationary. The points at which the tendons are attached to the bone are known as the origin and the insertion .
The origin is where the tendon of the muscle joins the stationary bone(s).
The insertion is where the tendon of the muscle joins the moving bone(s).
The ulna and radius are the moving bones- insertion
The humerus and scapula are stationary bones- origin
Muscles of the body
Label the diagram below
How muscles work
Complete the paragraphs below using words from the word bank – you can use them more than once if necessary.
Muscles work in pairs. As one muscle contracts , the other relaxes Muscles that work together are called agonist and antagonist (reciprocal inhibition) .
Muscles have to work in pairs because a ____________ can only ………………………. on a bone, it can push the bone back to its ………………………. ……………………….- the other muscle is responsible for this.
A good example of this pairing is the biceps brachii and the triceps brachii . As the biceps brachii contracts, the triceps brachii relaxes and the elbow joint is flexed/shortened To straighten the arm, the biceps brachii relaxes and the triceps brachii contracts.
Other muscles support the agonist in creating movement and these are called synergist . (neutralizer). fixator
(stabilizer) muscles allows the agonist to work, stabilising the origin.
WORD BANK antagonistic pairs stabilizer contracts biceps brachii pull relaxes relax muscle fixator triceps brachii flexed original position
Muscles of the trunk
Muscle Location Movement Origin Insertion
Rectus
Abdominus
Flexion Pubis Sternum and 5
& 7 th ribs
Strengthening exercise
Crunches
Exeternal
Obliques
Flexion Lower 8 ribs Ilium
Broomstick twist
Muscle Location Movement Origin Insertion Strengthening
Erector Spinae Extension Ribs, vertebrae, ilium exercise
Ribs, vertebrae Chest raises
Muscle
Deltoid
Pectoralis
Major
Biceps brachii
Location
Muscles of the upper extremity
Movement Origin
Flexion, extension and abduction of the shoulder
Clavicle and scapula
Insertion Strengthening exercise
Lateral
Humerus
Back Press
Deltoid raises
Flexion, adduction of the shoulder
Clavicle, sternum, anterior ribs
Humerus Pec Dec
Bench Press
Flexion Scapula Radius and ulna
Biceps curls
Muscle
Triceps
Brachii
Location Movement Origin
Extension Scapula and humerus
Insertion Strengthening exercise
Ulna Tricep extensions
Latissimus
Dorsi
Adduction and extension of the shoulder
Sacrum, ilium, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
Humerus Pull-ups
Trapezius Extension of the shoulder
Cervical and thoracic vertebrae, base of skull
Clavicle and
Scapula
Shrugs
Muscles of the lower extremity
Muscle Location
Iliopsoas
Movement Origin
Flexion of hip Ilium and lumbar vertebrae
Insertion Strengthening exercise
Inner femur Sit ups
Sartorius Flexion, abduction and lateral rotation of hip
Ilium Medial tibia Walking lunges
Quadriceps
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedius
Flexion,
Extension
Ilium –
Rectus
Femoris
Femur -
Vastus
Lateralis,
Vastus intermedi us, Vastus medialis
Tibia Squats
Muscle
Gluteus Maximus
Location Movement
Extension and rotation of the hip
Origin
Posterior ilium, sacrum and coccyx
Insertion Strengthening exercise
Femur One legged dead lifts
Tibialis Anterior Dorsiflection and plantarflexion
Lateral tibia
1 st metatarsal and 1 st cuneiform
Toe raises
Hamstrings
Biceps Femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Flexion, extension
Biceps femoris –
Ischium, femur
Semitendi nosus –
Ischium
Semimem bransosus
- Ischium
Biceps
Femoris –
Fibula, lateral tibia
Semitendinos us – Medial tibia
Semimembra nosus –
Medial tibia
Muscle
Gastrocnemius
Location Movement Origin
Dorsiflexion and plantarfexion
Posterior femur
Insertion Strengthening exercise
Calf raises Calcaneus via
Achilles tendon
Soleus Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion
Posterior tibia and fibula
Calcaneus via
Achilles tendon
Seated calf raise
Hierarchy of skeletal muscle structure
Skeletal muscle structure
Fasiculli
Sarcomere
Muscle fiber
Myofilaments
Myofibril
Actin and myosin myosin oskeletmuscle structure
Structure of skeletal muscle
Define the following terms: hypertrophy: an increase of myofibrils; and increase in muscle atrophy: a decrease in myofibrils/muscle mass; If you don’t use it, you lose it. Reversible in healthy young individuals.
Skeletal Muscle matching activity Answers – B, F, C, A, G, D, E
Structure of a neuron
Answers – B, C, D, E, A
The Reflex Arc
2. Sensory neuron 3. Relay neuron 4. Motor neuron
Label the diagram of a reflex arc using the words below: motor neuron grey matter spinal chord white matter effector relay neuron sensory neuron receptor
Different types of motor unit/muscle fibers
Fiber type Slow Twitch (Type I)
Contraction time
Fatigue resistance
Used for: slow high
Aerobic activity
Fast twitch A
(Type IIA) fast intermediate
Capillary density
Mitochondria density
High
High
Fast twitch B
(Type IIB)
Very fast
Low
Long term anaerobic
Intermediate
Short term anaerobic
Low
High Low
The neuromuscular junction
The role of neurotransmitters
Outline the role of acetylcholine and cholinesterase in the stimulation of skeletal muscle contraction
See keynote slides
Synaptic transmission
Outline the process of synaptic transmission on the diagram below
Muscle cell microscopy
Draw a section of muscle tissue in the box provided
Remember your rules for drawing microscope images!
Use only pencil
State the title, date and total
Magnification on your drawing
No colors
The diagram should take up
All the space provided
Microanatomy of a skeletal muscle cell (see Anatomy Physiology Review of Skeletal Muscle Tissue Video
Workbook)
Structure of a sarcomere
B, C, A, D, F, G, H, E
Muscle Contraction
1.
In the table below, record the following measurements:
Sarcomere Section Length (±1mm)
Relaxed
Sarcomere
Contracted
Sarcomere
Sarcomere
Myosin filament
Actin filament
Sarcomere
Myosin filament
Actin filament
Sliding Filament Theory
See Keynote slides
3. When the muscle contracts, do the actin and myosin filaments shorten? Support your answer with data from the table in #1 above.
3. Explain how the sarcomere shortens when the parts that make it up don’t shorten.
Complete the flow chart below
A nerve impulse is sent from the brain through motor neurons or nerves to stimulate muscle contraction
The nerve impulse travels down the motor neuron , generating an action potential which causes calcium ions to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Ca+ ions diffuse into the sarcomere and attach to troponin Which changes shape.
As troponin changes shape it pulls tropomyosin away from the myosin binding sites on the actin – which are now exposed!
When the nerve impulse stops, the calcium gates close, Ca+ ions are removed via the sarcoplasmic reticulum and troponin returns to normal shape
Tropomyosin covers the myosin binding sites and the muscle relaxes
Myosin heads use ATP to pull themselves along the actin molecule, forming cross bridges at each binding site before breaking and Power stroking to the next one.
The sarcomere shortens – Z lines moves closer together – the muscle is contracting






