File
advertisement

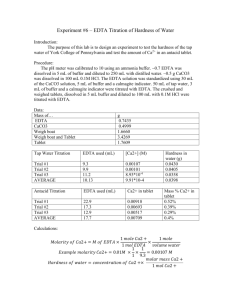
Almarzooqi 1 An Analysis of Water Hardness for Different Commercial Brands Using EDTA and AA Samar Almarzooqi 11/14/12 Chem 111 Section 105 Group Members: Laura Bleiel, Mariam Ahmad, Taylor Blackford TA: Jamie Bingaman Almarzooqi 2 Introduction Water hardness defines the sum of the concentrations of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions in a sample of water, measured by the amount of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Water is often defined in terms of water hardness in order to measure the overall quality of the water. Water with a large concentration of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions is said to be ‘hard’ while water with a small concentration of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions is defined as ‘soft’.1 Water levels containing concentrations of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions above 100 milligrams per liter (mg/l) are classified as hard while those below are classified as soft.2 Hard water is not a health hazard, and the minerals present in hard water are a part of the daily nutrients people need.3 Hard water causes complications in industries when hard water is heated, leaving behind the crystalline CaCO3, causing complications in heat transfer and further malfunctions and damage.4 The formation of scale, the CaCO3 crystalline deposit, is expensive to remove, which is why industries are concerned about measuring the hardness of the water used. Hard water also results in scum when Ca2+ ions bind with the soap, creating an insoluble compound. To eliminate the hardness of the water by removing the Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions, water softeners are often used in the form of the addition of lime and washing soda. These compounds bind with either the Mg2+ or Ca2+ ions and precipitate them out of solution, making them insoluble salts that can be Thompson, Stephen. PSU CHEMTREK: Small-Scale Experiments for General Chemistry. New Jersey: Hayden McNeil, 2012. Print 2 FAQ. SCBWA: State College Borough Water Authority. Web. 11 Nov. 2012. <http://www.scbwa.org/pages/faq> 3 Robillard, Sharpe, and Swistock. Water Softening. State College: The Pennsylvania State University, 2012. Print 4 D. Spurlock. Determination of Water Hardness by Complexometric Titration. Indiana University Southeast, 2012. Web. 12 Nov. 2012. <http://homepages.ius.edu/DSPURLOC/c121/week13.htm > 1 Almarzooqi 3 removed by filtration. Another softening technique is the ion exchange method. This method exchanges monovalent cations like Na+ and H+ with the Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions.1 Water hardness can be measured by using two different techniques, EDTA and AA (Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy). Both methods of calculating water hardness were used in the lab to verify the hardness of the water sample. Getting two different sources of evidence provides stronger evidence for the hardness of the water calculated and eliminates sources of error that can influence the results. AA is used to detect the presence of metals in a solution by projecting monochromatic light through the water. The atoms in the water absorb the energy from the light, and the change in Energy (ΔE) is measured by the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer at the known specific wavelengths.1 For the Mg2+ ions, the absorbance was measured at the wavelength 422.7 nm and Ca2+ ions were measured at the wavelength 202.5 nm. The amount of absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions, and using the BeerLambert law, the concentration can be calculated. The Beer-Lambert Law addresses the linear relationship between absorbance and the concentration of metal ions in the solution, described the by the equation ℷ = 𝑎𝑏𝑐 where ‘a’ is the constant molar absorbance, ‘b’ is the path length of light taken, and ‘c’ is the absorbance, which is proportional to the concentration.5 A graph of Absorbance vs. Concentration can be graphed to provide a line-of-best-fit equation for each metal ion. The other technique in determining the hardness of water is EDTA titration. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is used with eriochrome black (EBT) to detect Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions. 5 Beer-Lambert Law. The University of Adelaide: Department of Chemistry. Web. 11 Nov. 2012. <http://www.chemistry.adelaide.edu.au/external/soc-> Almarzooqi 4 The chemical reaction is: HD2= + Mg2+ + Ca2+ Blue - Red + H+ + Ca2+ CaEDTA + MgEDTA + HD2Immediately Eventually Blue The indicator is added and if no Mg2+ is in the sample of water, then the color of the solution will be blue both at the start and end of the reaction. If there is Mg2+ in the sample, then it will react to turn the sample a purple color. The CaEDTA is formed immediately once the EDTA is added, and once all of the Ca2+ has reacted, the EDTA bonds with the Mg2+ ions. As the MgEDTA chelate is formed, the solution begins to turn blue as the Mg2+ is taken out of solution. The number of drops it takes in the titration for the solution to turn blue again is used in the equation MEDTAVEDTA= MCa2+VCa2+, where the volume is the number of drops and molarity is the concentration of the Ca2+ ions. From the molarity, the hardness in parts per million (ppm) is calculated to give the hardness of the sample of water.1 Both EDTA and AA provide the hardness of water, but they each do so using different chemistry tools and techniques. AA measures the change in energy of the water sample once a light is shined through it, and the absorbance value measured is proportional to the concentration of metal ions. The EDTA titration involves the reaction of the water sample with the EDTA and by using the number of drops of EDTA used for the solution to turn blue again, the concentration of the Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions can be calculated. Using the two differing techniques gives two separate numerical values for the hardness of water, which should be close in value. The difference can be attributed to the error involved in each technique influencing the values. Almarzooqi 5 The water samples for the lab include Dasani, Aquafina, Evian, and tap water from Stephen Hall. The Dasani, Aquafina, and Evian were bought from McLanahan’s, which is located on College Ave. These samples were used because the lab was focused on the differences in the hardness of waters amongst various commercial brands of water. The tap water from Stephen Hall comes from the Pennsylvania water supply, which does not soften the water to modify the water quality. The hardness of water in State College is 120-190 mg/l, which is classified as hard.2 The Dasani water, as indicated by the ingredients on the bottle, contains magnesium sulfate and calcium carbonate, so the water is expected to be hard.6 The rankings of hardness from hardest to the softest water were expected to be Tap water, Dasani, Aquafina, and Evian. Due to the higher cost and reputation of Evian water, it was hypothesized that it would be the softest water, containing the least amount of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions. Aquafina water was expected to fall between Evian and Dasani. Procedure The procedure for the “Chemistry of Natural Waters” experiment was taken from the PSU Chemtrek, written by Stephen Thompson, on pages 10-15 to 10-22.1 The four water samples were obtained from McLanahan’s store and Stephen Hall on the University Park campus in State College. Each group member conducted the experiment using similar tests for each individual water sample in order to determine the hardness of each water sample. The hardness of the water was first calculated using the AA technique. Since the Dasani water contained no suspended particles, it did not need to be filtered through in order to remove any possible particles. The Atomic Absorption 6 Purified Water. Dasani. Web. 8 Nov. 2012. <http://www.dasani.com> Almarzooqi 6 Spectrometer calculated the absorbance for the Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions by placing a tube into the water sample. The graphs of light absorbance vs. metal ion concentration were then made and the values were converted to their “equivalent concentration of CaCO3”1 using the calculations provided in Section G.1 The sum of the hardness of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions is the total hardness value and was compared to the EDTA titration value calculated. The EDTA titration was used on each water sample in order to determine the hardness of each sample. Using a 1x12 well strip, one drop of EBT indicator, NH3/NH4CI/MgEDTA buffer, and the water sample were added to each well strip. A titration was then done by adding 1 drop of the 2 x 10-4 M EDTA to the first well, 2 drops to the second, 3 to the third, and so on. The first blue well represents the point where excess EDTA exists, and is defined at the end point where all of the Mg2+ ions have bonded with EDTA to form a chelate. Using the equation MEDTAVEDTA= MCa2+VCa2+, the concentration of both Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions can be calculated. The Dasani water sample had an EBT buffer mixture colored blue, which means that the water sample was extremely soft and contained little to no Mg2+ ions. Deviating from the directions given in the PSU Chemtrek, the Dasani water needed to be concentrated in the experiment so that the presence of Mg2+ ions could be detected. Therefore, a titration was done in which 10 drops of the water sample was added instead of 1 drop. The Evian water sample tested by lab member Taylor Blackford needed to be diluted in a 1:1 ratio due to the hardness of the water sample indicated by the red color when the Ca2+ was added.7 Total Dissolved Solutes (TDS) was examined for the water samples by placing a drop of the water sample onto Aluminum foil and onto a hot plate. A drop of distilled 7 Blackford, Taylor, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 31-36. Almarzooqi 7 water and 1.0 x 10 -3 M Ca2+. The remaining residue after the water evaporated was examined. The hardness of the water was also determined by EDTA titration after a softening agent was added to the water sample. Since the Dasani water was determined to be extremely soft, instead of adding the softening agent to the Dasani water sample, a 1 x 10-3 M Ca2= sample was used. A 1 cm height was measured with the 1 x 10-3 M Ca2+ solution and 20 mg of the commercial softening agent was added; an EDTA titration similar to the titration conducted previously was done. The final step in determining water hardness included examining the ion exchange of the divalent cation described in the Introduction. The pH of the water sample was taken to indicate whether the water is soft or hard; soft water is classified as acidic and hard water is basic.8 Results Table 1: AA Standard Obtained by Brown for Ca2+ ions9 Ca2+ concentration (ppm) Absorbance value (at 422.7 Check Standard (ppm) nm) 0.00 - - 1.000 0.01082 1.27 5.00 0.0531 5.09 10.00 0.10000 9.81 25.0 0.23103 24.08 50.0 0.43298 50.45 Water pH Water Hardness. Serenity Water Gardens. Web. 8 Nov. 2012. <http://serenitywatergardens.com> 9 Brown. AA Standards. 14 Oct. 2012. 11:30 pm. 8 Almarzooqi 8 Table 2: AA Standards Obtained by Brown for Mg2+ ions Mg2+ concentration (ppm) Absorbance Value (at 202.5 Check Standard (ppm) nm) 0.00 - - 1.000 0.01517 1.48 5.00 0.08718 5.62 10.00 0.18376 10.53 25.0 0.39579 24.72 30.0 0.48868 29.02 Figure 1: Light Absorbance vs. Mg2+ Ion Concentration at 202.5 nm Light Absorbance vs. Metal Ions [Mg2+] 0.6 Absorbance 0.5 0.4 y = 0.0159x + 0.0083 R² = 0.9972 0.3 Concentration 0.2 Linear (Concentration ) 0.1 0 0 10 20 30 Concentration (ppm) 40 Almarzooqi 9 Figure 2: Light Absorbance vs. Ca2+ Ion Concentration at 422.7 nm Light Absorbance vs. Metal Ions [Ca2+] 0.5 0.45 Absorbance 0.4 y = 0.0085x + 0.01 R² = 0.9987 0.35 0.3 0.25 Series1 0.2 Linear (Series1) 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 10 20 30 40 Concentration (ppm) 50 60 Absorbance Unit ppm Ca2+ -0.0004 0.00 ppm hardness (CaCO3) 0.00 Mg2+ 0.0621 3.38 13.9 3.38 13.9 Total Hardness Table 3: AA hardness for Dasani Water Sample ppm hardness was calculated for AA by using the equations given by the trend lines for each graph. Calculations: For Ca2+ ion hardness, the equation in Figure 2 y= 0.0085x+0.01 was used where y= the absorbance unit given by the AA for the metal ion. y= 0.0085x + 0.01 -0.0004= 0.0085x + 0.01 Almarzooqi 10 -0.0104= 0.0085x x= -1.22 ppm The concentration of the Ca2+ ions cannot be negative, so the concentration is assumed to be 0 ppm. Similar calculations were used to calculate the ppm for Mg2+ ions. The ppm then needs to be converted to its “equivalent concentration of CaCO3”, which measures true hardness of the water sample.1 Using the molar mass of Mg2+, this can be done. 2+ 𝑔 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑜3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑔 24.3 𝑀𝑔2+ 𝑚𝑜𝑙 100.0 3.38 ppm Mg x = 13.9 ppm CaCO3 Table 4: EDTA Titration for Dasani Water Sample Drops of EDTA ppm hardness Water Sample 6 12 Softened Water 3 .6 The EDTA titration conducted on the water sample was amplified by a factor of ten since the water sample was extremely soft. The Softening Agent was added to 1 X 10^-3 M CaCl2 since the Dasani water was extremely soft. In order to convert the drops of EDTA to ppm we use the equation MEDTAVEDTA= MwaterVwater in order to find the concentration of the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions in the sample. Since the volume units are on both sides of the equation, the units cancel out and do not matter. Therefore, the number of drops can be used as the volume. MEDTAVEDTA= MwaterVwater (2 x 10-4 M) (6 drops) = (Mwater)(10 drops) Mwater= 1.2 x 10-4 Almarzooqi 11 The concentration of the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions needs to be converted to CaCO3 because numerous cations can contribute to the concentration calculated by EDTA titration. By using the molar mass of CaCO3 the conversion can be made. 1.2 𝑥 10−4 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 𝐿 𝑥 100.0 𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑥 1000 𝑚𝑔 𝑔 = 12 𝑝𝑝𝑚 The same calculations must be done for the EDTA titration used for the water sample after the water has been softened. Since the water sample was extremely soft and needed to be amplified by a factor of ten, conducting EDTA titration on the Dasani water sample after the softening agent was added would produce poor results. Instead, CaCl2 was used. Concentration can also be expressed in grains/gallon by using the conversion between Molarity= moles/liter to grains/gallon. 1 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛 𝐶𝑜𝐶𝑂3 64.7 𝑚𝑔 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 = = 17.1 𝑝𝑝𝑚 𝑔𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑛 3.780 𝐿 The EDTA titration calculated is converted to ppm hardness, which is ppm 𝐶𝑜𝐶𝑂3 12 𝑝𝑝𝑚 𝑥 1 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛/𝑔𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑛 = .702 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛/𝑔𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑛 17.1 𝑝𝑝𝑚 Group member data was exchanged, and calculations similar to the calculations shown above were performed. Group Water Sample Data Notations: 1. Samar Almarzooqi- Dasani sample10 2. Taylor Blackford: Evian sample7 3. Mariam Ahmad- Aquafina sample11 4. Laura Bleiel- Tap water (Stephen Hall)12 10 11 Almarzooqi, Samar, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 45-50. Ahmad, Mariam, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 30-36. Almarzooqi 12 Table 5: AA Water Results for All Samples Water Sample Absorbance Units ppm hardness 1. Dasani10 Ca2+ -0.0004 0.00 2+ Mg 0.0621 12.00 Total Hardness: 12.00 2. Evian7 Ca2+ .3002 84.70 Mg2+ .2456 61.55 Total Hardness: 146.25 3. Aquafina11 Ca2+ -0.0031 0.00 2+ Mg 0.0790 18.3 Total Hardness: 18.3 4. Tap Water12 Ca2+ .2647 149.82 2+ Mg .2778 139.50 Total Hardness: 289.32 Table 6: EDTA Water Results for All Water Samples Water Sample 1. Dasani10 Water Sample Softened Water Sample 2. Evian7 Water Sample Softened Water Sample 3. Aquafina11 Water Sample Softened Water Sample 4. Tap Water12 Water Sample Softened Water Sample 12 Drops EDTA ppm (CaCO3) grains/gallon 6 3 12 .6 .702 .0351 10 7 40 28 2.34 1.61 11 3 22 .6 1.23 .0351 7 5 280 200 16.37 11.70 Bleiel, Laura, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 41-47. Almarzooqi 13 Table 7: Additional Data for Comparing Water Hardness Between Water Samples Water Sample 1. Dasani 2. Evian 3. Aquafina 4. Tap Water Distilled Water 1 x 10-4 M Ca2+ Total Dissolved Solute (TDS) Faint white ring Visible white circles Faint white ring Prominent white residue left after evaporation No residue Prominent White residue pH of sample pH of resin sample 6 3 8 3 6 3 Basic Acidic - - Discussion The hypothesis for the water hardness amongst the commercial water products Evian, Dasani, and Aquafina, along with tap water from Stephen Hall, was that the order of water hardness from hardest to softest water would be: Tap water from Stephen Hall, Aquafina, Dasani, and Evian. From the results obtained through EDTA titration and AA from the differing water samples, the hypothesis was rejected. Both tests support the water hardness rankings in the water samples to be Tap water, Evian, Aquafina, and Dasani in order from hardest to softest water. From EDTA titration, the total hardness for the tap water was 289.32 ppm hardness from AA and 280 ppm from EDTA titration11, which is higher than the State College water hardness range of 120-190 ppm hardness recorded by the State College Burough Water Authority.2 The large difference in water hardness value between the value of State College water compared to the dormitory water (Stephen Hall) can be due to the accumulation of metal ions that can occur as the water Almarzooqi 14 travels through the pipes in order to reach the dormitories. Since scale, the formation of CaCO3 deposit, occurs in pipes when hard water is heated, the pipes in State College could have the metal ions that cause water hardness, like Ca2+ and Mg2+ions, already present. When the water runs through the pipes, it can pick up more metal ions, causing it to have a higher concentration of metal ions. The Evian water had the second highest ppm hardness value, 146.25 ppm from AA and 40 ppm from EDTA titration, which was not expected.7 Since Evian is often thought of as the most expensive and high quality water, it was hypothesized that it would have the softest water value. The hardness of the Evian can be explained when taking into account that Evian water is taken from springs.13 Spring water is water accumulated from underground sources in which the water interacts with the soil and rocks.14 The rocks and soil contain metal ions like Mg2+ and minerals like Ca2+, which can account for the hardness in the Evian water sample. As the water runs over the rocks and is held beneath the soil, the concentration of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions would increase, making the water hard. Both Dasani and Aquafina are purified water brands, which explains why they have the lowest water hardness results from AA and EDTA titration. Purified water can come from any source, but the water goes through a series of processes like distillation, reverse osmosis, and deionization in order to remove all impurities in it.15 The AA Evian Natural Spring Water-Annual Water Quality Report. Evian. NSF International, 2012 Web. 10 Nov. 2012. <http://www.evian.com> 14 The Water Cycle: Springs. United State Geological Survey. U.S Department of Interior, 2012. Web. 10 Nov. 2012. <http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/watercyclesprings.html> 15 Stout, John. Purified Water vs. Spring Water. The Phantom Writers. The Defined Writers, 2012. Web. 10 Nov. 2012. 13 Almarzooqi 15 resulted in a water hardness value of 18.3 ppm hardness for Aquafina and 12.00 ppm for Dasani. The EDTA titration resulted in a water hardness value of 22 ppm hardness for Aquafina and 12 ppm hardness for Dasani. 9,10 These two water samples are the softest water samples observed in the lab, meaning that they have little to no concentrations of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions. The expected results from the hypothesis do not support the evidence for the Dasani and Aquafina water sample hardness values calculated by both AA and EDTA titration. It was expected that Aquafina would have a higher hardness value compared to Dasani since the ingredients in Dasani indicate that there is MgSO4 and CaCO3.6 Both the AA and EDTA titration water hardness results show that Aquafina has a higher water hardness value than Dasani. The reasons why there could be a difference in metal ion concentrations between two purified water brands can be due to differing purifying techniques used by commercial companies. Aquafina is slightly harder than Dasani (18.3 ppm – 12.00 ppm = 6.3 ppm greater), so the purifying process for the water does not remove as much of the impurities as the purifying process of Dasani does. The Total Dissolved Solutes (TDS) and the pH of both the water and resin samples in Table 7 also provide further evidence to support the hardness values from EDTA titration and AA from all water samples. The tap water from Stephen Hall was originally very basic, and the pH of the resin was acidic. Soft water is acidic and hard water is basic.16 The pH shows that the tap water is hard, as seen by the AA and EDTA titration results, which showed that the tap water from Stephen Hall has the hardest water. The Evian water sample had a pH of 8, which indicates that is basic, therefore hard.7 The pH for both the Dasani and Aquafina water samples were the same, pH 6.9,10 A pH of 6 is 16 Water pH and Water Hardness. Serenity Water Gardnes. 2010. Web. 10 Nov. 2012 Almarzooqi 16 acidic, which is proof of the softness of the two brands. The pH values were the same, which means that the concentration of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions in the two water brands is very similar. The differences between the hardness values given by EDTA titration and AA results are not very large, and they can be explained by human error in the lab procedure and the overall error in the Absorption Spectrophotometer provided by the Check Standards.9 The differences between EDTA titration and AA for the hardness values is the biggest for the Evian sample where the EDTA titration produced a value of 40.0 ppm and the AA produced a 146.25 ppm hardness value. The 106.25 ppm hardness value (146.25 ppm-40.0 ppm) is very large and occurs as a result of the error associated with each technique for determining water hardness. The other water samples yielded smaller differences between EDTA titration and AA water hardness values, yet there was still a difference. The EDTA titration was all done by hand, so there is a lot of room for human error in counting the number of drops and the possibility of contaminating a water sample. Contamination and human error can have big effects, which can account for the difference between the two water hardness values. AA also has error in the concentrations that are actually used for each metal ion. The Check Standard column in Tables 1 and 2 show that for each concentration measured, the actual check standard was greater. For example, for Ca2+ ions, the concentration calculated to be 25.0 M was actually 24.08 M.9 Also, the R2 values on the graphs for Ca2+ and Mg2+ are .9987 and .9782 respectively, meaning that for Ca2+ concentration, 99.87% of the absorbance units calculated are accounted for by the concentrations according to the trend line. Even though the Atomic Absorbance Spectrophotometer is a piece of expensive equipment, it Almarzooqi 17 is not perfect in its calculations. The human and machinery error accounts for the differences between the EDTA titration and AA water hardness values. The AA technique is the more precise of the two for determining water hardness because the AA can produce a value to 4 significant figures, compared to the 2 significant figures EDTA titration water hardness values have. AA is also done by an expensive machine, which is programmed to detect the presence of Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions, so the numbers are more accurate. EDTA detects the presence of all cations, not only the Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions AA detects. EDTA titration is done by hand, which is susceptible to contamination. The EDTA titration is also not very accurate since the concentration of hardness is determined when the color change to blue is noticed, not known absolutely. Being off by even 1 well count (1 drop), can change the water hardness by as much as 20 ppm.10 Therefore, AA is the better of the two techniques and even though there is error in the concentrations and the check standards, the differences are very small that they do not affect the ppm hardness greatly. The AA also produces an equation for each metal ion that allows other absorbance values to be calculated since solving for one variable using the equations is possible. AA is also much easier to do, and multiple water samples can be done in a shorter amount of time, so it is more time efficient than EDTA. The water softening technique resulted in water samples with lower ppm hardness values, which is shown in Table 6. The Dasani water hardness decreased from 12 ppm to .6 ppm after the water softening technique was conducted.10 The pH of the resin in Table 7 also show that all water samples had a final pH of 3, which is indicative of soft water.7,10,11,12 Industries and households can therefore use water softening agents to decrease the concentrations of Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions in their water supply. Almarzooqi 18 Conclusion The EDTA and AA techniques showed that the order of water sample from highest to lowers water hardness in ppm hardness is Tap Water (Stephen Hall), Evian, Aquafina, and Dasani, which rejected the hypothesis that Evian would have the softest water. Water hardness is a problem in industries and can be easily solved by water softening techniques that remove the Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions that lead to the buildup of the deposit that blocks pipes and causes energy inefficiencies in heating. Spring water is harder than purified water due to the minerals and metal ions present in the soil and rocks the water runs over. State College water is hard, and the values obtained in the lab for dormitory water had a higher water hardness than that recorded for the range of State College water. Water hardness, while not harmful to people, can lead to problems that need to be solved by water softening techniques. These techniques are often used by industries and households to soften the water by removing the Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions causing the water hardness and leading to the energy inefficiencies and pipe blockage. References Thompson, Stephen. PSU CHEMTREK: Small-Scale Experiments for General Chemistry. New Jersey: Hayden McNeil, 2012. Print 2 FAQ. SCBWA: State College Borough Water Authority. Web. 11 Nov. 2012. <http://www.scbwa.org/pages/faq> 3 Robillard, Sharpe, and Swistock. Water Softening. The Pennsylvania State University, 2012. Print 4 D. Spurlock. Determination of Water Hardness by Complexometric Titration. Indiana University Southeast, 3 April, 2012. Web. 12 Nov. 2012. <http://homepages.ius.edu/DSPURLOC/c121/week13.htm > 5 Beer-Lambert Law. The University of Adelaide: Department of Chemistry. Web. 11 Almarzooqi 19 Nov. 2012. <http://www.chemistry.adelaide.edu.au/external/soc-> 6 Purified Water. Dasani. Web. 8 Nov. 2012. <http://www.dasani.com> 7 Blackford, Taylor, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 31-36. 8 Water pH Water Hardness. Serenity Water Gardens. Web. 8 Nov. 2012. http://serenitywatergardens.com 9 Brown. AA Standards. 14 Oct. 2012. 11:30 pm. 10 Almarzooqi, Samar, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 45-50. 11 Ahmad, Mariam, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 30-36. 12 Bleiel, Laura, Chem 111 Laboratory Notebook, pp. 41-47. 13 Evian Natural Spring Water-Annual Water Quality Report. Evian. NSF International, 2012 Web. 10 Nov. 2012. 14 The Water Cycle: Springs. United State Geological Survey. U.S Department of Interior, 2012. Web. 10 Nov. 2012. <<http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/watercyclesprings.html> 15 Stout, John. Purified Water vs. Spring Water. The Phantom Writers. The Defined Writers, 2012. Web. 10 Nov. 2012. 16 Water pH and Water Hardness. Serenity Water Gardens. 2010. Web. 10 Nov. 2012