Functional Groups (2)
advertisement

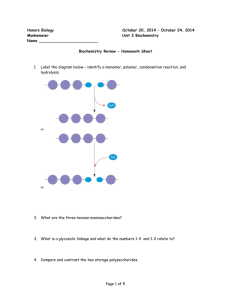
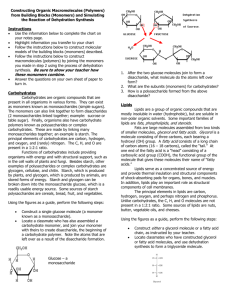
Functional Groups We were looking at molecules. Functional group is a sub part to a molecule (that might not contain whole molecules) such as OH. Hydroxyl group (OH) is bound to something else. Water is a polar molecule. H becomes + and oxygen becomes negative. It’s a polar molecule. Carbonyl group has two subgroups. High-energy bond that can be broken down to release energy. Ketone (Asotone are ketone) – middle of the carbon bond Aldehydes – end of the carbon bond Carboxyl group is when hydroxyl + carbonyl come together. Their properties are both hydroxyl and carbonyl. That makes acid. NH2 is used in amino g Amino group – monomers of proteins. Amino acid has carboxyl in one end and amino group in another end. They’re part base and acid. Sulfhydryl (SH) – when you have two sulfhydryl, it forms a bridge. They make a disulfhyde bridge. A and B comes together and they form a bridge. They do cross linking such as hair together. Phosphate (P) – 4 oxygen (one has 2 bonds, 3 more has 1). Transferring energy/Releases energy especially in contact with water. Example: Glycerol. POH^4Methyl group – methylation or demethylation (taking away). Biological marker (mark molecules so cell can know if that molecule is already used or not. that they already transcribe), 3 hydrogen stuck to a carbon with an R. It also helps identify male and female sex hormones. How to build macromolecules Carbohydrates – made of monomers of saccharides, which are stuck together by glycosidic linkage. Proteins – made of monomers of amino acids, which are stuck together by peptide bonds Nucleic acid – phosphodiesther bonds Lipids (Fats) – fatty acid chains Glycerol molecule with hydrocarbon tail = fatty carbon chain Glycerol molecule has phosphate in order to transfer energy Dehydration reaction is used to stick hydrocarbon chain with glycerol molecule. Triacylglycerol has 3. Saturated fat means it can’t take any more bonds (nothing, but single bonds) and unsaturated is more flexible. Trans fats are the worst type of fats because it can’t really break up. Phospholipids have 2 fatty acid chains). It makes the cell membrane or lipid bi. Head = hydrophilic, tail = hydrophobic. Polar is attracted to polar. Steroids are a type of fats that deliver messages. Cholesterol has bad and good and they’re types of steroids. To join monomers together, you need to dehydrate of the monomers to make up polymers. Water is important because it helps building up or breaks up bonds (hydrolysis). Dehydration is also called condensation. Then, covalent bond occur. OH-()-H H-()-OH -> H20 comes out -> OH–()---()-H Glycosidic linkage is 1 to 4 prime or 4 to 1 prime. The difference between starch and cellulose. Starch is the main food source. Starch has 1 to 4 prime (Amylase to digest), while cellulose has 4 to 1. Alphaglucose joins 1 to 4 = starch Betaglucose join 4 to 1 = cellulose Steroids are a type of fat Chitin can be digested (can be found in fungi and arthropods) LDL – low-density lipids HDL – high-density lipids Come up plan for enzymes (which area do you like to look at, researching experiments before we do it) - Temperature (which is good for catalase that does well) Temperature and looking for range - PH (what’s the appropriate range accurately) - Substrate concentration (changing the hydrogen prioxide) - Enzyme concentration - Salinity (how much salt)