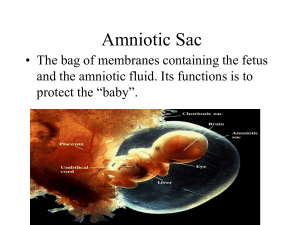
Contents - TMA Department Sites
advertisement

№ Hours amount CONTENT OF PRACTICAL /SEMINAR OCCUPATION Names those and their maintenance on sections Obstetrics 1. 6 Organisation and work structure of obstetrical-gynecologic permanent establishment. Principles of safe maternity. Modern perceptions of prevention of intrahospital infection. Clinic anatomy of female genital organs. Maternal passages, fruit as the object of labors. 2. 6 Basis of perinatal help. Survey methods of pregnant. Diagnostics of early and late pregnancies. Operating principles of family polyclinic, organisation of medical help pregnant in city and in the rural areas. State estimation of fetals. Role of family polyclinic in prevention of obstetric complications. Preparation for partner labors. Maternity school. 3. 6 Labors. Labors periods. Partner labors. Maintaining of партограммы. Active maintaining of placental stage. State estimating of newborn on Apgar scale. Labors Биомеханизм when front kind of position of vertex. Pretreatment of newborn. 4. 6 Physiology postpartum period. Physiology infancy.10 principles of breast feeding. Joint residence of mother and child. Care for mammary glands. 5. 5, 5 Breech labors. Labors Biomechanism. Lovett reception, reception of Maurice-Smellie-Veit 6. 5, 5 Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Etiology, classification, clinic, treatment. 7. 5, 5 8. 6 9. 6 Hypertensive condition during pregnancy. Preeclampsia, diagnostics, treatment, tactics. Course of pregnancy, parturitions and puerperal period when renal diseases and anaemia. Asymptomatic bacteriuria Role factor rhesus in obstetric. Rh haemolytic disease of fruit and newborn. Inogenous jaundice, diagnostics and treatment. 1 10. 11. 6 Pre-term deliveries. Use of токолитиков. Antenatal application of corticosteroids. Pregnancy prolongation. Labors induction when prolonged pregnancy. 5, 5 Fetoplacental deficiency, delay syndrome of foetal development, urgent present states and problems of fruit. 12. 6 Vaginal bleedings in late pregnancies: placental presentation and Premature detachment of normally situated placenta. 13. 6 Vaginal bleedings after delivery parturition: anomalies fastening placenta, hypotonia and metratonia, cervical ruptures and perineal, parts delay of afterbirth. Diagnostics, tactics, preventive measures. Hemorrhagic shock. Internal combustion engine syndrome. 14. 6 Unsatisfactory advancement of labors. Passive and active phases of labors. Classification. Etiology, clinic and diagnostics of distinctive types of anomalies of birth activity. Obstetric tactics and prevention. Stimulation of labor by the oxytocin upon recommendations of WHO. 15. 6 Contracted pelvis, etiology, kind of, classification, diagnostics. Disparity of fetal head and mother Taz. Shoulders dystocia. Causes of origin and clinical symptoms functionally contracted pelvis. Complications for mother and fruit, their prevention. 16. 5, 5 Wrong position and fetal presentation, causes, diagnostics, tactics. 17. 5, 5 Vaginal perinatal hemorrhages: uterine rupture. Classification, etiology and pathogenesis, clinic, diagnostics, therapy principles, prevention. 18. 5, 5 19. 6 Delivery operations:, the obstetrical forceps, the fruit of vacuum extraction Caesarean section. Urgent present states and problems of newborn. Intensive care of newborn. Fetal infections of fruit. Concept about TORCH-инфекциях. Ways of fetal infection. Diagnostics, treatment, obstetric tactics. 2 20. 6 HIV-infection transmission from mother to fruit. Prevention integration of cession HIV from mother to child in effective perinatal departure. The election of mode of delivery (elective Caesarean section ), the safe practices maintaining labors. Safe practice baby feeding. Prevention of postpartum complications. HIV in workplace. 21 6 Pathology of postpartum period. Secondary postpartum hemorrhage, thromboembolism. Breast problems. Postpartum depression. 22 5, 5 Infections in the postnatal period. Current concepts. Classification, ways of spread of infection. Modern perceptions of contagious matters. Diagnostics. Therapy principles. Prevention. Groups substandard risk, prevention on an outpatient basis. Gynecology 1. 4, 5 Anamnesis role. Survey methods of gynecological sick. Scheme of case. Supervision of sick. 2. 4, 5 Normal menstrual cycle and its regulation. Violation of menstrual function. Amenorrhea. Hypomenstrual syndrome. 3. 4, 5 Dysfunctional uterines bleeding. 4. 4, 5 Bleeding in I pregnancy half. Abortions. 5. 4, 5 Ectopic pregnancy, cholecystic sideslip, chorionepithelioma. 6. 4, 5 Inflammatory diseases of female genital organs of nonspecific and specific etiology. 7. 4, 5 Uterine myoma. Endometriosis. 8. 4, 5 Benign and malignant ovarian tumors. 9. 4, 5 Wrong positions and developmental anomaly of female genital organs. 10. 4, 5 Background and pre-cancer disease. Neck cancer and uterine body. 11. 4, 5 Sterile marriage. Contraception problems. Intermediate control. 3 4 № lecture subjects Hours amount 1. CONTENT OF LECTURE COURSE 1 2h 2 2h 3 4 2h 5 6 2h 2h 2h 7 2h 8 9 10 2ч 2h 11 12 2h 13 14 15 16 2h 2h 2ч 2h 2h 2h 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 2h 2h 2h 2h 2h 2h 2h Subject name of desk study Obstetric Conception. Stages of intrauterine foetal development. Critical terms of development. Structure and placenta function. Influence of harmful factors and medicines on fruit. Physiological change in the body of pregnant. Normal labors. Offensive causes and regulation of birth activity. Clinic and periods mechanism of labors. Pregnancy toxicosis. Etiology, classification. Early toxicosis. Hypertensive condition during pregnancy. Classification, clinic, complications, treatment. Pregnancy and births when anaemia and renal disease. Fetoplacental system and its of functional state. Fetoplacental deficiency, The syndrome of developmental delay fruit (SDDF) Etiology. Diagnostics, prevention. Rh factor in obstetric. Immunoincompatible pregnancy: on rhesus antigen and abo systems. rh haemolytic disease of fruit. Spontaneous abortion and pregnancy prolongation Anomalies of birth activity. Bleedings in II pregnancy half. The premature detachment is normal disposed placenta. Placental presentation. Bleeding in последовом and fourth stage of labor. Hemorrhagic shock. Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome BLOOD. Contracted pelvis in modern obstetric. Obstetric traumatism. Uterine rupture. Infantile asphyxia. Delivery traumatism. Intensive care of newborn. Purulent septic diseases of postpartum period. Etiology, spreading ways. Classification. Groups substandard risk, prevention on an outpatient basis. Obstetric peritonitis. Sepsis. Gynecology Item gynecology. Normal menstrual cycle and its regulation. Propaedeutics of gynecological diseases. Violation of menstrual cycle. Classification. Amenorrhea. Dysfunctional uterines bleeding. Inflammatory diseases of female genital organs. Bleeding in I pregnancy half. Ectopic pregnancy. Good tumor of uteruses. Ovarian tumor. 5 8. 9. Background and pre-cancer neck disease and uterine body. Neck cancer and uterine body. 2 h Sterile marriage. 2h Topic: Organization and structure of obstetrics and gynecologyhospital. The principles of safe motherhood. Modern views on the prevention of nosocomial infection. Clinical anatomy of the female genital organs. The birth canal, the fetus as the object of delivery 1st place of employment, equipment - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the audience; Fake-pelvic fetal doll, the female pelvis: Pelvic-trainer: a simulator of birth; -Standard models of pregnancy; -Classical models of delivery; -Dummy "ZOE"; -Sets of slides on the topics of discipline; Methods work in small groups: a method of the incident, the "round table" to solve problems, "a handle on the middle of the table", "swarm", etc.; -Training and practical skills to control the system OSKE (objective structured clinical examination). -Video, TV, TV; -PC (Pentium-III); -Slide set with typical states on ultrasound scanning of pregnant and gynecological patients; Kit video blogs "VJOG" (USA), covering the modern-dos tizheniya in diagnosis and treatment of obstetric and gynecological conditions; 6 Kit videos and films with a typical demonstration of obstetrical and gynecological operations and manipulations. -Educational computer programs; -Training and testing multimediasistemy; -Use e-mail and INTERNET; -Simulation games and case studies; -Movie "The principles of epidemiological compliance regime in the maternity hospital"; -Slides (structure midwifery complex anatomy of the female genital organs); Kit test tasks. -List of office obstetrical hospital; Structure work in a hospital obstetrical units (the functional significance of each branch); Illustrations of the anatomy of the female genital organs (ligamentous apparatus and pelvic floor muscles, blood supply, innervation, etc.); -A schematic representation of the pelvic planes, indicating oblique, direct and cross dimensions; -Size head and torso of the fetus; -Image of a lumbosacral diamond in a woman with normal size of the pelvis. Center for training in practical skills Offices and laboratories, maternity complex 6.Content of classes 6.1. Theoretical part The subject of Obstetrics and Gynecology Gynaecology - the science of the woman of the female body. The name comes from combining the Greek words: gyne-woman, logos-science. Gynecology consists of two major parts: Obstetrics and Gynecology, actually. 7 Obstetrics (from the French word - assaucher man to give birth, childbirth.) Survey the state of the female body during conception, pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. Gynecology in the narrow sense of exploring female sexual apparatus, its physiology and pathology outside of pregnancy.The main task of obstetrics - is preventing the transition of physiological state in pregnancy pathology. Type of obstetrical and gynecological institutions, their main tasks.The organization of obstetrical hospital. Ca-nitarno and epidemiological regime in maternity hospitals (maternity complex structure, especially the work). Sanitary-educational work.Familiarity with the work of departments. The organization of specialized units for treating pregnant women with various diseases, perinatal centers for nursing preterm infants regional maternity hospitals, specialized sanatoriums and rest homes for pregnant women, strengthening of health education and health education of the population in the area of maternal and child health, the organization of rural health units disease prevention among adolescents, the girls prepare for family life and many other reproductive health problems. The structure of the maternity facilities and organization of work in their strictlystructed on the same principle in accordance with international standards on the basis of the order of 500 Ministry of Health of Uzbekistan. As part of maternity complex has the following structural divisions: hospital, medical - diagnostic unit and Administrative - Economic part. Maternity Hospital in its structure is: • Receiving - Inspection Division; • department of pathology of pregnancy (30-35% of the total number of obstetric beds); • I obstetrical department (25-30% of the total number of obstetric beds); • II obstetrical department (25-30% of the total number of obstetric co-ek); • emergency department and intensive care during pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum women; • intensive care and neonatal intensive care; • gynecological department (15-20% of the total number of beds midwifery complex); 8 • sterilization and laboratory departments. Receiving - Inspection Division is composed of the receiving part, the observation and bathing and delousing establishment. Here, an obstetrician or midwife collects medical history, conducting physical examination. Assesses the state of pregnancy, measures body temperature, examination of the skin, throat, soschityvaet pulse, blood pressure in both hands and get acquainted with an exchange card pregnant. Department of Pathology of pregnancy are intended to provide adequate medical care for pregnant women, as attendants, and with extragenital pathology. Obstetrical department I and II are identical and are designed for delivery of adoption of the reference and the postpartum period. In the emergency department and intensive care during pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum and intensive care units and neonatal intensive care is emergency care and intensive care. Gynecology department are intended to provide of a qualified medical care for pregnant until 20 weeks. pregnant and nonpregnant women with inflammatory diseases of genital organs, infertility, etc. Strict adherence to all rules of asepsis and antisepsis is critical in obstetric practice. The program "Safe Motherhood" The initiative "Safe Motherhood" was launched in 1987 This international programs aimed at health professionals who deliver health care to women during pregnancy, childbirth and post-ro-Dov. This initiative was undertaken in order to promote the efforts of the medical community to reduce maternal mortality by half to 2000 It was decided to continue this initiative, but under a different name - "Ensuring safe motherhood," because there was no indicators that are planned in the program. Safe motherhood means not only prevention of illness and death, it also involves the care of mother and child. This concept includes physical, mental and social wellbeing of women before delivery, during and after birth, which should ensure a healthy birth and childhood, which is consistent with the Constitution of WHO (1948), which defines health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity " The principles of "Safe Motherhood" 9 Provide antenatal care to every pregnant woman is the primary responsibility of the family, which lives in this woman. A woman needs the support of his family and the community during pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and during lactation, especially if it has problems. To provide such care families need information, skills and motivation to ensure the implementation and maintenance of any new practice. This approach is also needed in the social and financial support from the community. Moreover, it needs support from the health care system by the Organization of appropriate, sensitive and friendly services that are provided to full service of maternal and perinatal care, taking into consideration the physical, emotional and psychosocial needs of women and newborns, but. Targeted interventions for maternal and child Health workers can anticipate, avoid or solve many non-expected and sometimes dangerous problems that can occur during labor, thus reducing the maternal mortality rate to very low levels.However, health workers also need the support that can be achieved only in the hospital when they see-dyat that their knowledge and the equipment available is not enough to deal with complications during childbirth. All women need care in primary care and specialized care is needed only in selected cases. At the same time, these two types of care (primary and specialized care) must work together, while providing effective integrated services. In many countries, postpartum care is provided even less likely than care during childbirth. This is an extremely important area where there are many opportunities for improvement. MODERN CONCEPTS OF PREVENTION Nosocomial infections Nosocomial infections can also be classified as endemic or epidemic. More common endemic infection. For epidemic outbreaks of infection are characterized, which are defined as an unusual increase in the incidence of infection. Nosocomial infections are spread all over the world, as in developed countries and in countries with limited resources.Infection in hospitals - this is one of the main causes of mortality and increased morbidity in patients who are in hospital. This is a serious problem, both for patients and health-care system as a whole. Nosocomial infections: sources and transmission The bacteria that cause nosocomial infections can be transmitted in various ways: 1. Permanent or transit flora of patients (endogenous infection).Bacteria present in the normal flora to cause infection, because beyond their natural habitat (eg, urinary tract infections), as a result of tissue damage (wound), or the wrong antibiotic, provoking an overgrowth of bacteria. For example, Gram-negative bacteria from the digestive 10 tract frequently cause infections of surgical wounds after surgical operations performed on the abdomen, urinary tract infection or a cat-terizirovannyh patients. 2. Flora received from another patient or healthcare worker (exogenous crossinfection). The bacteria are transmitted from patient to patient: • Through direct contact (hands, spraying saliva or other bodily fluids) • Respiratory infections (drops of moisture or dust carrying bacteria from an infected patient), • A health care workers infected protsessse patient care (hands, nose, throat, and clothing), which are temporary or permanent vehicle of infection, later transferring bacteria to other patients in direct contact with care • In subjects infected patients (including equipment tion), the hands of staff, visitors or other objects in the surrounding medium (ie water, other liquids or foods). 3. Flora received from the environment of medical institutions (endemic or epidemic heteroinfection environment). Several types of micro-organisms survive well in an environment of medical institutions: • In the water, wet places, sometimes on the sterile products or disinfectants (Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Mycobacterium) • The linen, equipment and care. Proper cleaning is usually limits the risk of bacterial survival, because for the life of the majority of microorganisms need moisture or high temperature, and nutrients of matter • In the food • In the fine dust and droplets of sputum, released during the speech, and cough (if the size of bacteria is less than 10 μm in diameter, it is kept in the air for several hours and can enter the respiratory tract, like fine dust) Nosocomial infections: sources and transmission • People are the main source, the main carrier and the recipient of microorganisms, become a new source of infection. Nosocomial infections: prevention Prevention of nosocomial infections requires an integrated program and its monitoring, including the following key components: 11 • Limiting the transmission of microorganisms from patient to patient in their care: - Wash hands and use gloves; - Compliance with the rules of asepsis; - Insulation measures; - Sterilization and disinfection; - Laundry • Control of infection in the environment • Protecting patients: rational use of antimicrobial drugs, nutrition, vaccination Nosocomial infections: prevention For infection control responsibility of all health workers - doctors, nurses, therapists, pharmacists, technical personnel and other-nal Hand hygiene: the importance of All bacteria, which can be found on the hands can be divided into two categories: transient and resident. The resident flora, that which inhabits the deeper layers of skin are more difficult to remove. In addition, there is less likelihood that the resident flora (eg, staphylococcal infection and coryneform bacteria) lead to the emergence of nosocomial infections. Transient flora, one that inhabits the upper layers of the skin easier to remove by routine handwashing. Health workers often acquire it during direct contact with patients or contaminated surfaces in the immediate vicinity of the patient. The hands of medical personnel is a major component in the transmission of nosocomial infections. Transmission of nosocomial infections can be minimized by adhering to proper hand hygiene. Handwashing Technique Hands should be disinfected before direct contact with the patient and after any activity or contact that can infect the hands, including after gloves are removed. At the same time, detergents and alcohol based gels are a practical alternative to soap and water, alcohol itself is not the cleanser. Dirty or potentially Conti12 nirovannye microorganisms hands must be washed thoroughly with soap and warm water, then wipe dry. Preparation of the hands increases the effectiveness of disinfection. Inadequate drying can lead to reinfection of hands that have just been washed. Wet the surface more effectively contribute to the transfer of microorganisms than dry, in addition, if you do not wipe your hands dry, the skin is more susceptible to damage. For drying hands should use disposable paper towels are high quality. Towels should be near the wash basins in wall containers. Restricting visits by relatives The effectiveness of the practice of limiting visits not dokazana.Mnogie Me-health facilities justify the prohibition or restriction of visits to the possibility of infection, despite the fact that research in parallel and retrospective control groups showed no adverse effect on the level of visits to bacterial contamination of newborns. Masks and hats From wearing hats and masks should be discarded, and the aprons and gowns but Sitonly for those who do not want to soil their own clothes in contact with the child. Medical personnel should use special medical or sterile gowns, when vozhmozhno release blood or other body fluids, as well as in the case of invasive procedures or manipulations • Protection of patient, medical staff wearing masks in an operating room, in contact with patients with depressed immunity tetom, with procedures related to the penetration into the body cavity. In these cases, enough to use a surgical mask. • Protection of medical staff: health workers should wear masks during contact with patients with sexually transmitted through airborne droplets, or during bronchoscopy, or similar examinations. In this case, high-performance mask. • Patients with infections transmitted by airborne droplets, must wear a surgical mask while being outside of prison. Ultraviolet radiation As an additional measure of air purification, ultraviolet radiation (UVB) is effective in reducing the transmission of airborne bacterial and viral infections in hospitals (wards and corridors), military barracks, school buildings, but it has little inactivating effect on fungal spores. Health care facilities use UV lamps of two types - with directional and omnidirectional radiation. 13 Regular maintenance of the UV radiation is very important.Typically, this service is to purify lamp from dust and replace the old bulbs as needed. UV tubes should be changed and cleaned according to manufacturer's instructions. Staff of health facilities using the system of UV disinfection of premises, must be trained on the following issues: 1. basic principles of operation of UV systems (mechanism and limitations). 2. potential danger of excessive UV exposure. 3. potential sensitivity associated with certain medical conditions or use of certain medications. 4. the importance of maintenance and record keeping. Patients and visitors to medical facilities that use UV system should be informed about the purpose of their use and warn of potential hazards and safety precautions. The use of disinfectants. The effectiveness of routine use of disinfectants is not proven. Proved that the bacterial contamination of the floor surface back to its original level within 2 hours after washing, regardless of whether it was carried out with or without a disinfectant. Instead of spraying disinfectants recommended for use carefully washing and mechanical cleaning. The structure of the female pelvis. Sex and age differences of the pelvis. Taz obstetric point of view (the size of the planes, the inclination). External genitalia, the structure, function. Internal sex organs (uterus, tubes, ovaries), the structure and function.Topography of the pelvic organs of a woman. Muscles, ligaments, tissue, peritoneum, blood, lymphatic system, the innervation of reproductive organs. Female reproductive system consists of the internal reproductive organs located in the pelvic cavity, and external genital organs outside the bone of the pelvis. The internal genital organs include: the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes and vagina. External genitalia include: pubis, large and small labia, clitoris and vaginal vestibule. Vagina - vagina, colpos, tubular, muscular - elastic body is folding, its walls formed ¬ form a vaulting - front, rear, left, right.Uterus - uterus is pear-shaped, consists of three parts (body, neck, neck), weight 50-100,0 length 8 cm, and has three layers: mucous - endometrium, a muscular - myometrium, serous - perimetrium.On 14 both sides of the uterus are the fallopian tubes (tubae uterinae). Ovaries - ovaria paired female sexuality as ¬ iron, measuring 4X2X2 cm, weight: 6-8 g, consists of cortical (located follicles) and medullary layers. II. Pelvis - pelvis bone channel, sealed joints ¬ E, which are located within sex and neighbor ¬ tion in their bodies. Pelvis in obstetrics is very important, because it is the birth canal and by not moving fruit ¬ mu. The pelvis consists of four bones: two unnamed, sacrum and coccyx. Hip bone is made up of three bones: the iliac (os ileum), sedation lischnoy (os ischii), pubic (os pubis), which are connected in vertlozhnoy depression (acetabulum). Ilium is the upper section of an unnamed braid ¬ T - ends crest iliac bone (crista iliaca). It is front and rear ends with two vystu ¬ Memo - peredneverhnyaya iliac spine-spina iliaca nor superior, anteroinferior - spina itlaca anrerior posterior, iliac spine caudineural-spina iliaca inferior superior iliac spine and lowback - spina iliaca posterior inferior. Ha inner surface of the iliac bone, the transition to the wing body relies pectiniform races ¬ ledge, arcuate, bezy ¬ myannaya line - llnia innominata, idushaya to the sacrum and the upper edge of the pubic arch. Ischium has a body that forms the acetabulum and the two branches: the upper and lower, the upper branch goes from the body downward and ending point of buttock - tuber ischii. On the back bone of the lower branch of a ledge - spina ischii, the lower branch is a forward and upward and connects with the lower branch of the pubic bone. Pubic bone, is triangular in shape ¬ th and consists of a body and two branches: upper and lower. The body is part of the acetabulum, wind ¬ integer connected to each other pubic symphysis joints (symphisis). Sacrum consists of 5-6 vertebrae, joined together into one. The front surface is concave, convex rear. At the junction of I and V sacral vertebra is formed ledge - sacral promontory (promontorium). Verhushka connected to the coccyx by moving the joint. The pelvis of the male female differences has the depth, subtlety, eat-bone. The pelvis is important in the delivery and is wired the way in which childbirth is moving fetus. Distinguish big and small basin boundaries between them is in front - the upper edge of the symphysis, laterally - unnamed line promontorium. Big basin is bordered in front - the abdominal wall, behind-the spine, the sides of the wings flank bone .. The dimensions of a large basin. 15 1.distantio spinarum 25-26 cm distance between distant points of the spina iliaca anterior superior. 2.distantio cristarum 28 - 29 cm, long-term point of crests iliac bone. 3. distant about trochanterica - 31 -32 cm distant points trochanter major. 4. Conjugata externa 20-21 cm from the top corner of the lumbar and upper diamondnot the outside edge of the symphysis. 5. Conjugata lateralis - Conjugate lateral - from the spina iliaca anterior superior to the spina iliaca posterior superior - the same side - is 14 - 15 cm 6. Conjugata obliqva - from the spina iliaca anterior superior to the spina iliaca posterior superior - the opposite side is 17 - 18 cm In the pelvis are 4 planes. 1. The plane of the entrance to the pelvis. Border: front - the upper edge of the symphysis of articulated ¬, laterally linea innominata, rear - Cape - promontorium. Dimensions: direct conjugates called true-conjugata vera - the distance from the edge of the pubic arch verhnevnutrennego to Cape = 11 cm, cross - distant points linea innominata 13 cm, oblique right and left are equal to 12 cm, the distance from the sacroiliac joint to povzdoshnolonnogo hill. 2. The plane of the widest part. Border: front - mid symphysis pubis, rear joint of the 2nd and 3rd sacral vertebrae, laterally inner plate ¬ ka - fossa acetabu-lum Dimensions: straight from the mid symphysis pubis to the junction of the 2nd and 3rd sacral vertebra - 12.5 cm, cross ¬ nye distant centers of the acetabulum -12.5 cm 3. The plane of the narrow part. Border: front - the edge of the pubic arch, laterally - Seats awn-GOVERNMENTAL bones behind - sacrococcygeal joint. Dimensions: straight - from the bottom of the pubic arch to the sacrococcygeal junction - 11.5 cm cross-distant point of the inner surface of her buttocks ¬ Bug-ditch tuber ischia - 11,0 cm 16 4. The plane out of the pelvis. Border: front - the edge of pubic ¬ articulated, rear - the coccyx, laterally - Seats ¬ nye mounds. Dimensions: straight from the bottom of the symphysis to the coccyx ver ¬ hushki -9.5 cm cross - long-term point of buttocks - 11 cm in carrying the line through the centers of all sizes direct wire axis formed by the pelvis, having the shape of a fishing hook. In a study of women should perform the following measurements: 1. Large size of the pelvis. 2. Sizes yield the pelvis. 3. The circumference of the wrist joint - ¬ Index Over loveva 14 - 16 cm 4. The height of the womb = 4 - 5 cm 5. Diagonal conjugates = 13 cm 6. Outdoor konyogaty = 20 - 21 cm 7. Rhombus of Michaelis - longitudinal size-11cm, cross-10 ,5-11 cm 8. Pubic angle - is 90 - 100 °. 9. The circumference of the pelvis = 80 - 90 cm 10. The inclination of the pelvis - the ratio of the plane of the WMO ¬ yes in a small basin above the horizontal. The pelvic floor. Output from the bone of the pelvis is closed tight muscle-fascial plate Coy, called the pelvic floor. The system of muscles and the fascia is called the diaphragma pelvis. Anterior aperture is fixed to the pubic bone, posterior to the coccyx with the lig.sacrotuberosita, on each side, to the fascia obturatoria. The pelvic floor consists of three layers. 1. The outer layer of the following muscles. a) m. sphincter ani externus b) m. bulbocaver nosus (constrictor cunni) a) m transversus perinei superficialis d) m. ischio - cavernosus 17 2. Layer forming the pelvic diaphragm, consists mainly of fascial tissue, which signed a thicker m. transversus perinei profundus 3. The deep muscle layer, which closes Snee ¬ sy pelvis. This m.levator ani, consisting of m. pubococcygeus, so ileiococcygeus, so ischiococcygeus. The edges that pubococcugens both sides grip the rectum and form hiatus genitalia, rectum through which passes in front than the vagina and urinary ¬ emissive channel.During childbirth the pelvic floor is undergoing great changes, and participates in izg ¬ nanii fruit, forming a channel, sometimes damaged. Fetus as the object of delivery In a study of the fetus as an object of births in the first place should pay attention to his head, as most major part, on the seams and springs for their role in childbirth. You should know the basic concepts of acoustic ¬ sherskie: chlenoraspolozhenie, position, appearance, presenting part, wired point insertion. The head of the mature fruit consists of a 2-hour unequal ¬ Tay - cranial and facial. The skull is formed from the forehead ¬ GOVERNMENTAL - os frontalis, parietal-os parietalis, temporal-os temporalis and neck - os occipitalis bones, which are interconnected by means of sutures and fontanelles. On the head are the following joints: the frontal suture-sutura frontalis ME-forward to the frontal bone, sagittal or sagittal-sutura sagitalis-between parietal bones, coronal sutura coronaria between the parietal and frontal bones; lyambdovidny (sutura lambdoi-dea) - between the parietal and occipital bones. Springs at the head of the following: a) a large fontanel - fonticulus major is between the backs of the frontal and anterior parts of both parietal bones, is a connective tissue plate diamond shape. b) a small fontanel - fonticulus minor is triangular in shape, located between the rear parts both the parietal and occipital bones. Springs connect the sagittal suture. a) lateral fontanelles-fonticulus lateralia Sutures and fontanelles at birth and move for ¬ go at each other, cowering in the same direction, increasing in another, which is called the configuration ¬ her. As it 18 detects the position of the head doctor in the pelvis and follows the mechanism of labor. On the head distinguish the following dimensions and the corresponding circle. 1.Pryamoy-d. frontoocclpitalls: from the nose to the outermost point of the occiput-12 cm, circumference 34 cm-circumferentia frontooccipitalis. 2. Large oblique - d. mentooccipitalis - from chin to neck circumference, 13 cm - circ. mentooccipltalis - 42 cm 3. Small scythe - d. suboccipito-bregmaticus of suboccipital fossa to the middle of the large fontanel-9, 5 cm, circle-circ. suboccipito-bregmaticus - 32 cm 4. Vertical - d. sublingva bregmaticus from the mid ¬ HN large fontanel to suboccipital bone = 9.5 cm, the circumference of circ.sublingva-bregmaticus 32 - 33 cm 5. Large cross - d. biparietalis distant point of the parietal protuberances = 9.5 cm 6. Small cross - d. bifemporalis between temples = 8 cm To determine the transverse size of the fruit of the shoulder girdle = 12 cm, circle 3536 cm, cross-time measures yagodichek ¬ - 9-9.5 cm, circumference 27-18 cm, measure the growth of the newborn, an average of 50-53 cm, weight - an average of 3500.0. DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY. DETERMINATION OF PREGNANCY The diagnosis of pregnancy is certain, if the examination determines the fruit, heart rate and stirring of the fetus on ultrasound - the ovum. These reliable signs of pregnancy do not appear at the beginning of it, and at later stages (V-VI per month). In early pregnancy diagnosis established on the basis of suspected and probable grounds. Suspected (doubtful), signs of pregnancy . To include the alleged grounds of common manifestations of the changes associated with pregnancy: - Changes in appetite (an aversion to meat, fish, etc.), a whim (the attraction to spicy dishes, to unusual substances - chalk, clay, etc.), nausea and vomiting in the morning; - Change the olfactory sensations (an aversion to spirits, tobacco smoke, etc.); - Changes in the nervous system, irritability, drowsiness, mood instability, etc.; - Skin pigmentation on the face, the white line of the stomach, nipples and areola. Probable signs of pregnancy 19 This group of symptoms include changes in menstrual function and changes in sexual organs: - Cessation of menstruation; - The appearance of colostrum milk in the nipple opening moves when pressing on the breast; - Cyanosis (cyanosis) of the vaginal mucosa and cervix; - Change the size, shape and consistency of the uterus; - Laboratory tests (determination of chorionic hormone in urine and blood). Credible evidence - Identify parts of the fetal abdominal palpation women (Leopold techniques). - Identification of fetal movements during palpation: a feeling of fetal movement during palpation or ultrasound. - Listening to fetal heart tones. Pregnancy diagnosis is confirmed by auscultation of fetal heart tones with a frequency of 120 / 140 min. Heart rate can be determined with 5-7 weeks with the help of instrumental methods: ECG, phonocardiography, cardiotocography, ultrasound, and from 17-19 weeks - auscultation. Identify the likely signs of pregnancy produced by: - Survey; - Palpation of breast and squeezing colostrum; - Examination of the vulva and the vagina; - Research by mirrors; - Vaginal and two-handed examination of abdominal-vaginal women. Delay of menstruation is an important feature, especially in women with regular cycles. The value of this symptom is increased when it is combined with breast engorgement and the appearance of colostrum in them, with the appearance of cyanosis vagina and especially the vaginal part of cervix, with the change of the magnitude and consistency of the uterus. With the onset of pregnancy as it progresses the size of the uterus change. Changing the shape of the uterus is determined by two-handed (bimanual) examination. Uterus in nonpregnant women is pear-shaped, somewhat compacted in the anteroposterior 20 size. With the onset of pregnancy, the uterus changes shape. With 5-6 weeks of the uterus becomes globular shape. Starting from 7-8 weeks, the uterus becomes asymmetric, may bulge one of the corners. By about 10 weeks the uterus again becomes spherical, and by the end of pregnancy becomes ovoidnuyu form. Of pregnancy indicate the following features: The increase in the uterus. The increase in the uterus markedly at 5-6 weeks of gestation, the uterus is first increases in the anteroposterior direction (becomes spherical), and later increased its transverse size. The greater the duration of pregnancy, the more the increase in the uterus. By the end of the month II of pregnancy the uterus grows to the size of a goose egg in the late months of pregnancy III uterine fundus at the level of the symphysis or slightly above it. Sign-Gegara Horwitz. The consistency of the pregnant uterus is soft, with pronounced softening is particularly strong in the area of the isthmus. Fingers of both hands with two-handed study found in the neck with almost no resistance. This feature is very characteristic of early pregnancy. Sign Snegireva. For pregnancy is characterized by mild variability of the consistency of the uterus. Softened pregnant uterus during the two-handed investigations under the influence of mechanical stimulation and reduced plotneet in size. After the cessation of stimulation of the uterus again becomes soft consistency. Sign Piskacheka. In the early stages of pregnancy often occurs asymmetry of the uterus, depending on the dome-shaped protrusion of the right or left corner of it with 7-8 weeks. Protrusion corresponds to the site of implantation of fetal eggs. With the growth of gestational sac protrusion gradually disappears (to 10 weeks). Gubarev Gaus and drew attention to the easy mobility of the cervix in early pregnancy. Easy displaceability cervix associated with a significant softening of the isthmus. Guenther sign. In the early stages of pregnancy there is reinforced anterior bend of the uterus, resulting from the strong softening of the isthmus, as well as crestthickening (bulge) on the front surface of the uterus in the midline. This thickening is not always determined. Thus, the diagnosis of pregnancy set on the basis of clinical examination. However, in some cases, the diagnosis of pregnancy or difficulty with the differential diagnosis 21 of laboratory diagnostic methods used. Diagnosis of early pregnancy is based on determining a woman's body fluids of substances that are specific to pregnancy. Modern methods of diagnosis of pregnancy is divided into biological, immunological, echographic (ultrasound), and others. Both biological and immunological methods are based on the determination in biological material (usually in the urine) horiogonadotropina (HCG) - a hormone secreted by the chorion. Horiogonadotropin (hCG) in their chemical nature close to lyutropinu pituitary (LH), a glycoprotein with a relative molecular mass of 37 900. The hormone is composed of two peptide chains (a and b-subunits), one of which (a) the same for all glycoproteins - CG, lyutropina (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and thyrotropin (TSH), and another - b-specific to each of them. b-subunit of hCG with a relative molecular mass of 23 000 has a specific hormonal activity. HCG synthesis begins with the first days of pregnancy and continues until birth with a maximum production at 60-70 days after implantation. Then its level is reduced and remains stable until delivery. Currently, the diagnosis of early pregnancy, immunological methods. Immunological methods are based on the precipitation reaction with rabbit antiserum to either fix complement or to the suppression of the haemagglutinin. The most widely used method for suppressing the haemagglutinin developed simultaneously in two laboratories in 1960, Z. S w ierczynska, E. Samochowiec (Poland) and L. Wide, C. Gemzell (Sweden). The method is based on inhibition of agglutination between the "charged" HGH red blood cells (antigen) antiserum to HCG (which contains specific antibodies) and extended in the urine. When the antiserum (antibody) was added erythrocytes, "charged" hCG (antigen) and the urine of pregnant, then present it binds to the hCG antiserum, and red blood cells do not undergo agglutination and settle to the bottom of the vial. If added to the urine non-pregnant women, does not contain HGH, there is agglutination, and red blood cells are distributed evenly in the ampoule. To perform the diagnostic content of the reaction vial was dissolved in 0.4 ml of the supplied to a set of phosphate buffer and using the supplied capillary add two drops of fresh morning urine filtered. Contents of the vial is stirred and the vial is placed at room temperature. After 2 hours reaction into account: even distribution of red blood cells in the vial indicates the absence of pregnancy, settling them down in the form of rings or buttons - the presence of pregnancy. Radioimmunoassay method is 10 times more sensitive immunoassay. The most common method of double antibodies, based on the precipitin antibodies to the hormone. Radioimmunoassay for determination of HCG is best to use quick sets, manufactured by different companies. Application of radioimmunological methods 22 makes it possible within 5-7 days after implantation of fetal eggs to determine the level of hCG which is equal to 0,12-0,50 IU / liter. Latest radioimmunoassay methods for determining the b-subunit of hCG in the molecule can determine its level equal to 3.0 IU / liter. Time of detection is 1.5-2.5 min. ELISA rapid methods of determining the HCG or b-hCG in the urine can diagnose pregnancy within 1-2 weeks after nidatsii ovum. There is a test system for rapid determination of the presence or absence of pregnancy, which can be used by women themselves. Other research methods The study of basal body temperature based on the effects of progesterone on the heat regulating center, located in the hypothalamus (hyperthermic effect). The first 3 months of pregnancy, basal temperature, measured in the morning on an empty stomach in bed with the same thermometer - above 37 ° C. Investigation of the properties of cervical mucus is also based on the effects of progesterone on the physico-chemical properties of mucus. During pregnancy, starting from very early periods, there is no symptom of "pupil", as the diameter of the cervical canal of less than 0.2 cm in air drying of secretions from the cervical canal there are no large crystals. Diagnosis of uterine pregnancy by ultrasound as early as possible 4-5 weeks (from the first day of last menstrual period!). In this case the thickness of the endometrium define fertilized egg in the form of a rounded education of low echogenicity with an inner diameter of 0.3-0.5 cm in the I trimester growth rate of the weekly average ovum size is approximately 0.7 cm, and 10 weeks, it fills the entire uterine cavity. By 7 weeks of pregnancy, most pregnant women in the study of oral ovum can identify an embryo as a separate entity length of 1 cm in these terms, the embryo is already possible visualization of the heart - the site with a rhythmic oscillation of low amplitude and mild physical activity. When the biometrics in the I trimester of major importance for the establishment of pregnancy is the definition of the average internal diameter of the ovum and the coccyx, the size of the parietal (CTD) of the embryo, whose values are strictly correlated with a pregnancy. The most informative method of ultrasound examination in early-stage pregnancy is a transvaginal scan, transabdominal scan is used only when the bladder filling to create a "acoustic window". DETERMINATION OF PREGNANCY AND BIRTH DATE 23 Definition of pregnancy produced on the basis of anamnestic data (delayed menstruation, date of the first stirring of the fetus), according to physical examination (the magnitude of the uterus, the size of the fetus), and according to additional research methods (ultrasonography). Gestational age and date of birth is determined by: - By date of last menstrual period. From the first day of last menstrual period is counted the number of days (weeks) at the time of the survey pregnant. To determine the date of delivery to the first day of last menstrual period added 280 days (10 lunar months), or use a formula Naegeli, from the date of last menstrual period began consuming 3 months and add 7 days. This method can not be used in women with irregular cycles. - According to ovulation. If, by virtue of certain circumstances a woman can set a date for the alleged pregnancy (rare sex, the operation of in vitro fertilization (IVF), insemination with donor sperm), then the pregnancy is counted from the date of conception, pre-adding 2 weeks, and date of birth defined, measured from the date of the proposed 38 weeks of ovulation, or using the following formula: from the date of ovulation rob 3 months 7 days. - On first appearance. If the registration of mandatory pregnancy pregnant time of the study is a vaginal examination, which with a certain accuracy can determine the gestational age (see table). - For the first perturbations. Definition of pregnancy on the date of first stirring of the fetus may in the second half. On the average, primiparous women feel stir the fruit, ranging from 20 weeks, and multiparous - with 18 weeks of pregnancy. - According to the ultrasound. The accuracy of gestational age by ultrasound is quite high, especially in the I trimester of pregnancy. In II and III trimester of pregnancy error in the determination by this method is increased because of the constitutional features of the fetus or pregnancy complications (small for gestational, diabetic fetopatiya etc.), so the value is a dynamic ultrasound monitoring of the fruit. - The prenatal leave. According to Russian legislation with 30 weeks of pregnancy, a woman has the right to pre-natal leave. For a quick calculation of the duration of pregnancy and childbirth produce special obstetric calendars. Objective definition of pregnancy in the I trimester bimanual examination is possible with women, because the uterus during this time frame is located in the pelvis. With 24 16 weeks uterus bottom probes above the vagina and the pregnancy is judged by the height of standing on the bottom of the uterus pubic joint is measured by a tape. The magnitude of the uterus and its bottom elevation of standing in various stages of pregnancy Gestational age, weeks Evidence - 4 The uterus is the size of a hen's egg - 8 The uterus is the size of a goose egg - 12 The uterus is the size of a man's fist, the bottom of the top edge of the womb - 16 Bottom of the uterus midway between the navel and vagina (6 cm above the heart) 20 Uterus stretches the stomach, her bottom at a distance of 11-12 cm above the vagina, there are fetal movement, heart rate auscultated - 24 Bottom of the uterus at the navel, 22-24 cm above the vagina - 28 Uterine fundus 4 cm above the navel, 25-28 cm above the vagina - 32 Bottom of the uterus midway between the umbilicus and xiphoid process, 30-32 cm above the vagina, abdominal circumference at the navel of 80-85 cm, somewhat flattened belly, straight head size 9-10 cm - 36 The bottom of the uterus in costal arches, at the level of the xiphoid process, abdominal circumference 90 cm and the navel is smoothed, straight head size 10-12 cm - 40 Bottom of the uterus falls in the middle between the navel and the xiphoid process, 32 cm above the vagina, abdominal circumference 96-98 cm, belly jutting, head straight size 11/12 cm primiparous head pressed against the entrance to the pelvis, in multiparous - mobile For recognition of pregnancy known, a correct measurement of the height of standing on the bottom of the uterus and vagina of the abdomen. Measuring the height of standing above the vagina uterus produce a tape or tazomerom, while the woman lies on her back, legs straight, the bladder emptied before the test. Measure the distance between the upper edge of the symphysis and the most prominent point of the uterus. In the second half of pregnancy produced abdominometry a tape that is 25 placed upon the front of the level of the navel, behind - in the middle of the lumbar region. Measuring the length of fetus contributes additional data to determine the gestational age. Precise measurement of the unborn baby is difficult, and the data obtained in this way are merely indicative. Measurement is carried out with tazomera. The woman lies on her back, the bladder must be emptied prior to measurement. Feeling the abdominal wall through the fruit, one-button of tazomera set at the lower pole of the head, the other - on the bottom of the uterus, where most are the buttocks of the fetus. VV Sutugin found that the distance from the lower pole of the head to the pelvic end of exactly half the length of the fetus (from head to toe). Therefore, the value obtained when measuring the distance from the lower pole of the head to the buttocks, multiplied by two. From this number subtract 3-5 cm depending on the thickness of the abdominal wall. Having determined the length of the fetus, divide that number by 5 and get the gestational age in months. When pregnant women are admitted, their BP, heart and respiratory rates, temperature, and weight are recorded, and presence or absence of edema is noted. A urine specimen is collected for protein and glucose analysis, and blood is drawn for a CBC and blood typing. A physical examination is done. While examining the abdomen, the clinician estimates size, position, and presentation of the fetus, using Leopold's maneuvers (see Fig. 1: Normal Pregnancy, Labor, and Delivery: Leopold maneuver. ). The clinician notes the presence and rate of fetal heart sounds, as well as location for auscultation. Preliminary estimates of the strength, frequency, and duration of contractions are also recorded. A helpful mnemonic device for evaluation is the 3 Ps: powers (contraction strength, frequency, and duration), passage (pelvic measurements), and passenger (eg, fetal size, position, heart rate pattern). Leopold maneuver. (A) The uterine fundus is palpated to determine which fetal part occupies the fundus. (B) Each side of the maternal abdomen is palpated to determine which side is fetal spine and which is the extremities. (C) The area above the symphysis pubis is palpated to locate the fetal presenting part and thus determine how far the fetus has descended and whether the fetus is engaged. (D) One hand applies pressure on the fundus while the index finger and thumb of the other hand palpate the presenting part to confirm presentation and engagement. 26 27 Topic: Physiological puerperal period. The neonatal period. EVALUATION OF newborn on Apgar score. PRIMARY TOILET of newborn. PRINCIPLES OF BREASTFEEDING. JOINT STAY OF MOTHER AND CHILD. 1. venue for the classes - Obstetrics and Gynecology Department, a lecture room; - Fake-pelvic, female pelvis, doll of a fetus; -Sets of slides on the topics of discipline; - Methods of working in small groups: a method of the incident, of the "round table"; of solving problems, "a pen in the middle of the table", "swarm", etc.; -Training and monitoring system for the practical skills OSCE (objective structured clinical examination). - televideo unit, TV; -PC (Pentium-III); -Slide set with typical states on ultrasound scanning of pregnant and gynecological patients; - the complete set of video journals "VJOG" (USA), covering recent advances in diagnosis and treatment of Obstetrics and Gynecologyical disorders; - the complete sets of videos and films with a typical demonstration of obstetrical and gynecological operations and manipulations; - educational films; - Educational computer programs; - drill-and-practice program; 28 - Use e-mail and INTERNET; - business game and situational tasks; - Center for training in practical skills; - Offices and laboratories of the maternity complex; - Delivery room; - the complete set of tests; - Phantom with a doll; - Post-natal wards; - Contours of the uterus at different periods of the postpartum period; - Video: "a child – a person number one" -Test items I, II, III and IV levels of complexity; - Step instructions for research: a general examination of puerpera, assessment of breast and lactation, determine the condition of the uterus, the nature of lochia, primary processing of the newborn; - Slide “Apgar score”; - Slide “Silverman score”; - Diagram depicting the contours of the uterus at different periods of puerperal period; - Slide showing the changes of lochia in different puerperal period. 2.Working hours of the classes Number of hours-5 3. Objective point -To examine changes in the cardiovascular, endocrine, excretory systems, the genitals and breasts in parturients during the postpartum period; -To examine the clinical management of physiological post-natal period; - Demonstrate methods of puerperant (general examination, the state of the mammary glands, the rate of involution of the uterus); 29 - To discuss the diagnostic criteria for the general state of the newborn on Apgar and Silverman scores; - To discuss the principles of breastfeeding; - Compare the results with postpartum rooming-in in the course of postnatal stay in the division; - To acquaint with the structure and principles of postnatal department. Tasks The student should know: -Changes in the cardiovascular, endocrine, excretory system, in the genital organs and mammary glands in parturients during the postpartum period; -Features of the course and conduct of postpartum period; -Sanitary measures in the postpartum period; -Basic principles of breastfeeding. The student should be able to: To conduct a differential diagnosis of the physiological and complicated course of postpartum period, to examine the puerperant correctly (general examination, the state of the mammary glands), to determine the rate of involution of the uterus, to define a character of lochia, according to objective and additional methods of examination (ultrasound, blood tests, urine tests, swabs on the vaginal flora ) to assess the current postpartum period. 4.Motivation Postpartum or puerperal, is called the period during which in the body of parturients is reversed (involution) of the organs and systems, which are subjected to changes due to pregnancy, childbirth. During this period the woman is at risk of infectious diseases, septic diseases. The main objective of puerperal period is the prevention of these diseases in mothers and newborns. Postnatal period coincides with the beginning of the formation of new family ties. Illness of the mother or baby may disrupt this process. 5.Inside and outside subject communication 30 Teaching this topic is based on the knowledge bases of students of anatomy, topographical anatomy, histology, normal and pathological physiology, endocrinology and microbiology .. Acquired during the course knowledge will be used during the passage of endocrinology, internal medicine, surgery, pathological obstetrics, gynecology, health, neonatology and paediatrics. 6.The content of the classes 6.1. A Theoretical part I. Changes in women after childbirth. A. Reproductive organs and mammary glands 1. Uterus.2. Neck of uterus. 3. Vagina. 4. Ovaries. 5. Mammary glands. B. Other organs: 1. Urinary tract. 2. Cardiovascular System. 3. Digestive System. II. Postpartum regimen management. A. Early postpartum. B. Late postpartum period: 1. General care. 2. Laboratory studies 3. Daily physical examination: a) Uterus, b) Abdomen, с) lochia, d) perineum, e) urinary bladder, f) The mammary gland, g) lungs, h) extremities. III. Neonatology. 1. The basic principles of aiding to newborns in a delivery room. 2. Assessment physical development of newborns. technology. 3. up-to-date perinatal 4. Paraphysiological state of newborns. Postpartum (puerperal) period is the period beginning after the birth of the placenta and continuing 6-8 weeks. During this time there is regression of (involution) of all organs and systems that have undergone a change due to pregnancy and childbirth. The exceptions are the mammary glands, which functions increase in the postpartum period. Uterus. Immediately after the birth of placenta the uterus begins to shrink and a few minutes later acquires a rounded shape. Its wall becomes dense, gaping vessels of placental site are compressed. Bottom of the uterus is located at or just below the navel. 2 weeks after birth the uterus is already within the pelvis. Its size has continued to shrink, and four weeks after birth correspond to the size of non-pregnant uterus. Within a few days after birth the surface layer of decidua is rejected and isolated as 31 lochia. Regeneration of the endometrium is due to epithelial glands. The walls of the uterus, with the exception of placental site, epithelization lasts for 7-10 days, the endometrium of normal thickness reaches 2-3 weeks after birth. Placental site epithelization is much slower due to endometrial covering neighboring areas by the end of 6 weeks after birth. Delayed epithelialization placental site may be the cause of uterine bleeding in the late postpartum period. The most pronounced changes occur in the involutional genitals, especially in the uterus. Rate of involutional changes is expressed in the first 12.8 days. Nearest 2-4 hours after delivery, especially emphasized and designated as early postpartum period. After this time, starting late postpartum uterus period. After birth of the placenta uterus is greatly reduced in size due to a sharp reduction in its muscles. Its body is almost spherical form, retains a greater mobility by lowering the tone of the stretched ligaments. The cervix is as the thin-walled sac with wide-gaping maw with the outer edges of the torn and hanging in the vagina. Cervical canal passes freely hand into the uterus. The whole inner surface of the uterus is an extensive wound surface with the most severe destructive changes in the placental site. The lumina of the vessels in the placental site is compressed by reducing the muscles of the uterus, they form clots, which helps stop bleeding after childbirth. The next days the involution of the uterus is very fast. Every day the height of standing of uterine fundus is reduced by an average of 2 cm. It is necessary to consider that the rate of involution are dependent on the parity of birth, degree of stretching during pregnancy (large fetus, polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancy), breastfeeding in the first hours postpartum, the functions neighboring organs. Due to compression of the blood and lymph vessels, obliterating some of them are obliterated. The cytoplasm of the muscle cell undergoes fatty degeneration, and then fatty degeneration. The reverse also occurs in the development of intramuscular connective tissue. A significant portion of vascular obliteration and transformed into connective tissue strands. The healing process inside the uterus begins from decay and rejection of fragments of spongy layer of decidua, blood clots, thrombi. During the first 3-4 days the uterine cavity is sterile. This contributes to phagocytosis and extracellular proteolysis. Decaying particles decidua, blood clots and other tissue elements are rejected are lochia. Epithelization of the inner surface of the uterus occurs in parallel with rejection decidua and ends with the 10 day postpartum period (except the placental site). Fully endometrium restored in 6-8 weeks after birth. Neutral tone ligament of the uterus is restored by the end of 3 weeks. 2. Cervix. After 2-3 days after birth the tone of the cervix is reduced, internal mouth is exposed at 2-3 cm. By the end of the first week after birth the cervix is completely formed. 32 The involution of the cervix occurs more slowly. Before other parts the inner mouth is contracted and formed. This is due to the reduction of the circular muscle fibers. After 3 days inner jaws miss one finger. Formation of the cervical canal ends by the 10 day. By this time, the inner mouth completely closes. Outer jaws closes at the end of the 3rd week and takes the form of a slit. 3. Vagina. Within three weeks after giving birth vaginal walls are puffy, its light a little bit expanded. Edema completely disappeared by the end of the postpartum period. 4. Ovaries. For most women menstruation absent during the whole period of breastfeeding. In the absence of lactation, ovulation occurs on average at 10 weeks after the birth and menarche - the 12th. Menstruation may appear on the 7-9th week after birth, in such cases, the first menstrual cycle is usually anovulatory. In the ovaries during the postpartum period ends regression of the corpus luteum and begins to grow follicles. Due to the evolution of large amounts of prolactin in lactating women menstruation is absent for a few months or a total time of breastfeeding. In non-breastfeeding women menstruation is restored within 6-8 weeks after birth. First period after birth, usually occurs on a background of anovulatory cycle: follicle grows, matures, but ovulation does not occur, the corpus luteum and endometrium aren’t formed. Endometrium do not have processes of proliferation. Because of follicle atresia and the fall in titre of estrogenic hormones rejection occurs in the endometrium - menstruation. In the future ovulatory cycles are restored. In some women, ovulation and pregnancy are possible in the first months after birth, even against the background of breast-feeding. 5. Mammary glands. Pregnant women under the influence of estrogen, progesterone, cortisol, prolactin, placental lactogen and insulin is a rapid development of glandular structures of mammary glands. During pregnancy, lactation suppresses by steroid hormones, synthesized by the placenta. After delivery, their rates are falling quickly and on a background of high levels of prolactin, lactation begins. Initially, the breasts secrete colostrum, which is different from the milk higher in protein and immunoglobulin. The function of mammary glands after birth reaches its highest development. During pregnancy, under the action of estrogens are formed milk ducts under the influence of progesterone is the proliferation of glandular tissue. Under the influence of prolactin is enhanced blood flow to the mammary glands, and increased secretion of milk, leading to breast engorgement, the most pronounced at 3-4 days postpartum. Milk secretion is the result of complex reflex and hormonal influences, and is regulated by the nervous system and lactogenic (prolactin) hormones of the adenohypophysis. The 33 stimulating effect of hormones have thyroid and adrenal glands, as well as a reflex effect in the act of sucking. On the first day postpartum mammary glands secrete colostrum. Colostrum is a thick yellow liquid with an alkaline reaction. It contains galactoblast, white blood cells, milk balls, epithelial cells of glandular vesicles and ducts. Colostrum is richer than mature milk proteins, fats, minerals. Protein amino acid composition of colostrum in an intermediate position between the protein fractions of human milk and blood serum, which obviously makes it easier to adapt the organism to the newborn during the transition from placental nutrition to feed breast milk. Colostrum is greater than in mature breast milk, protein, binds iron (lactoferrin), which is required for the formation of blood newborn. There are high in immunoglobulins, hormones (particularly corticosteroids), and enzymes. This is important because in the first days of life newborn functions of several organs and systems have immature immune and is in its infancy. Transitional milk, which is formed on the 3-4th days, on the 2-3rd week becomes a permanent structure and is called mature milk. B. Other organs. 1. Urinary tract. The bladder is often injured during birth, hereupon in the early postpartum period, it may be cystic overdistension and urinary retention. This increases the risk of urinary tract infections. Postpartum atony of the bladder increases with conduction anesthesia. Renal blood flow, GFR, and reabsorption of electrolytes, amino acids and glucose in the tubules are returned to baseline in 6 weeks after birth. Expansion of the renal pelvis, calyces and ureters may remain for several months. 2. Cardiovascular system. If delivery is in vaginal birth vaginal blood loss typically less than 500 ml, and for caesarean section - 1000 ml. Despite of blood the loss after childbirth increases the stroke volume of the heart (because of placental blood flow off, the return of extravascular fluid into the bloodstream and increases venous return). Due to the fact that heart rate decreases, cardiac output remains unchanged or slightly increased. 2 weeks after delivery cardiac output returns to normal. 3. Digestive system. The synthesis of proteins in the liver increases in pregnant women under the influence of estrogen, which is manifested by increased levels of serum proteins. 3 weeks after birth it returns to normal. The first 2-4 hours after a normal delivery a puerpera is in the delivery room. An obstetrician takes care of the overall state of the woman in childbirth, her heart rate, blood pressure, monitors the status of the uterus constantly: determines the texture, the height of the bottom of standing, watching the degree of blood loss. In the early 34 postpartum period he inspects the soft birth canal, if there is an indication for the inspection. Also he inspects the external genitalia and perineum, the vagina and the lower third of the vagina. Inspection of the cervix and upper vagina make by means of mirrors. All of the detected gaps are sewn up. In assessing the blood loss during childbirth take into account the amount of blood released in the sequence and the immediate postpartum period. The average blood loss was 250 ml and the maximum physiological - not more than 0.5% of woman’s body weight in childbirth. Keeping the postpartum period. A. Early postpartum period. After 2-4 hours puerperant on a gurney carrying to a physiologic postnatal ward. The processes occurring in the body of the puerperant after uncomplicated childbirth are physiological and should be considered a healthy woman. It is necessary to consider several characteristics of a post-partum period associated with lactation, the presence of wound surface on the site of placental site, reduced the protective forces of the mother. Therefore, in addition to medical supervision, for the puerperant is necessary to create a special regime with strict observance of the rules of aseptic and antiseptic. In the postpartum unit must strictly observe the principle of cyclic filling chambers. This principle consists in the fact that in one chamber is placed parturients who gave birth during the same day. Compliance of cycling is facilitated by small wards (for 2-3 persons), as well as the accuracy of profiling, that is , separation chambers parturients who for health reasons have to stay in a nursing home for a longer period than healthy woman in childbirth. It is necessary to follow the child-friendly principles, that is rooming-in. Such rooming-in significantly reduced incidence of disease of women in the postpartum period and the incidence of children. His mother is actively involved in caring for a newborn baby, which limits the child's contact with the personnel department of obstetric and creates favorable conditions for colonization of the infant microflora mothers, reduces the possibility of infecting the newborn hospital strains of opportunistic microorganisms. In this regimen immediately after birth a newborn baby in good condition can be attached to the mother's breast. The first toilet of newborn and care for him in the first days is carried out by a nurse of exercise room and a mother. The nurse teaches the processing of the skin sequence preparation and mucous membranes of the child (eyes, nasal passages, cleaning the), teaches the use of sterile material and disinfectants. Examination of the umbilical cord and umbilical stump wounds carries a pediatrician. At present accepted active management of the postpartum period, consisting of early rising, which improves blood circulation, speed up the process of involution of the reproductive system, normalizing the function of the bladder and intestines. Every 35 day obstetrician and midwife take care of puerperant. Body temperature is measured twice a day. Particular attention is paid to the nature of the pulse, measure blood pressure. The condition of the breast, shape, condition of nipples, the presence of scratches and cracks (after nursing) are assessed. Determine the height of standing uterus, its width, texture, presence of pain. Standing height of uterine fundus was measured in centimeters relative to lonnomu articulation. During the first 10 10 days it falls at average to 2 cm per day. They assess the nature and quantity of lochia, observe the general condition of delivered and appreciate the consistency, size and tenderness of the uterus, as well as character of discharge from the genital tract. It is better that the child was with his mother from the very first days of life. B. Late puerperal period 1. General duty nursing. Every 4 hours define the basic physiological characteristics of puerperant, observe urine output, assess the nature and tone of uterine secretions from the genital tract. They explain how to care for the external genitalia and perineum, trained in breastfeeding and childcare, if necessary - pick analgesics. 2. Laboratory research. In the first days after birth common blood test with a leukogram testing is performed. If necessary, determine the blood group and Rhfactor. Women with Rh-negative blood test the blood on anti-Rh antibody. To identify parturients to be vaccinated they are determined on antibody titers to rubella virus (if the study was not performed earlier). 3. Daily physician check-up. a. Uterus. About velocities of the inverse change the uterus judge on height of the standing of its bottom and consistence. Normally soon after childbirth uterus gains the thick consistency, its bottom is situated below umbilicus. The slow reduction of the uterus can be accompanied the significant bleeding, sometimes blood agglomerates in her(its) cavities. After caesarean section a big attention is paid on painfulness during palpation – early symptom of endometritis. b. The Abdomen. Beside postoperative patients is payed attention on ballooned abdomen and presence of the peristalsis. In the first day after operation peristalsis is weakened or is absent. On 2-nd-3-d day it is restored, and the gases begin to leave. The Ballooned abdomen, gases retention, absence of the peristalsis point on paresis of the bowels. This can result from long surgical interference or early sign of the infectious complications. Some authors advise to begin receiving the fluid food after appearance intestine noises, other - only after gases leaving. If the fluid food receiving does not cause the nausea or vomiting, the woman could be kept on usual mode of the alimentation. 36 c. Lochias. Pay attention to amount, colour and scent of the discharge. In the first several day after childbirth Lochia is mainly presented in blood clot and scrap of necrosial, decidual tunic. The Amount of the discharge usually such, as during menstruations. After several day the amount of blood in uterine discharge decreases, nature of the separations becomes bloody - serosus. Through several weeks the discharge become scanty and else more bright. The Unpleasant scent of lochias points on infection. d. Perineum. During the check-up exclude hematoma, inflammation and ruption of perineum. Care includes washing the external genital organs with medicine by weak disinfecting solution and warm sitting baths. During the ruptures of III-IV degree is prescribed the softening purgative, for example Dufalac. The parturient is discharged home only after normalizations of the stool. At haemorrhoid after prolonged second period of childbirh quite often appears the exacerbation. For treatment of haemorrhoid use the unguent and candles with Hydrocortison, cotton wool tampones, ed by juice Hamamelis virgin, and warm sitting baths. E . The Urinary bladder. In consequence of trauma in labor or epidural anaesthesia can develop the atony of urinary bladder. The Urine is released with the catheter. If it is required to repeat catheterization, install the Foley catheter for one day. During the expressed periurethral edema or ruptureraphy in the field of external opening of urethra for prevention of urinary retention it is possible to install the Foley catheter immediately. f. The Mammary glands. Pay attention to the mammary glands and check, if there no sign of the inflammation. It Is Greeted only breast feeding. In obstetric institutions it is necessary to introduce and support 10 principles of breast feeding. Conduct the lessons, inform, explain among younger, average, senior medical personnel, among doctors, as well as amongst pregnant. If woman doesn’t want to have breast feeding, for suppression of the lactations of the mammary glands usually make tight bandage or prescribe Bromocriptinum, 2,5 mg per os 2 times in day during 14 days. After stopping the medicine recurrent lactation is possible. For her(its) removal Bromocriptinum is prescribed else for 7 days. The side effects of the medicine are orthostatic hypothony, sickness, vomiting, nausea, in rare cases develops insult. g. Lungs. Pneumonia can appear after caesarean section. The Preventive maintenance includes the respiratory atheletics. h. The extremities. In afterbirth period the risk of the deep veins thrombosis and thrombophlebitis is increased. 37 Neonatology is a section of pediatrics, exploring physiological particularities and disease of one month old children. The Development of neonatological help on modern stage is characterized by creation specialized services for family, pregnant mothers, newborn, infant and children of the early age, united into perinathal centers. The Stages of medical help to newborn are provided by work of obstetric and pediatric services. Since moment of the birth and bandaging of the umbilical cord stops only one, umbilical relationship between mother and child, begins neonatal period, which lasts 28 days. It is divided into early (first 168 hours of life) and late neonatal period. The Functional condition of child at the first minute and hours of life is characterized by reaction of adaptation to new condition. Adaptative particularities of the functional systems of the fetus and newborn depend on mother’s organism, current of pregnancy and labor. The Generic act is a significant pressure on fetus. Three periods of labor differ from each other. Retraction activity of the uterus is accompanied with the change of the metabolic processes in parturient and fetus. Each reduction of the uterus brings to reduction of uterine-placentary blood flow. At the first period of labor in the pause between bearing- down pressure in cavities of the uterus is 8-10 mms. On height of the birth pain is 20-50 mms. In the second period of labor the pressure can increase to 70 mms. Blood flow in uterus stops, blood pool is formed, it provides nutrition to fetus during birth labor. The Organism of parturient helps the fetus to cope with generic stress and adapt by the help of increasing of cortysol production above the level of cortysol bond possibilities of the plasma that promotes transition of certain cortysol concentrations to fetus. The Period of newborn, or neonatal period, begins since the moment of childbirth, the first breath and bandaging of the umbilical cord. The First minute and days of life are characterized by reaction of adaptation to new condition of surrounding area. Time of umbilical cords bandaging is not indifferent for child. Because of additional placentary volume of blood occurs adaptation of pulmonary and heart system, and increase the ferric volume in organism. Bandage of umbilical cords and shutdown of placentary blood flow due to realignment of child’s blood flow: increasing of the pressure in big circle of blood. With beginning of the independent breathing blood flow through lungs increases in 5-10 times in contrast with intrauterine period. Accordingly increases the return of blood into left atrium, where, either as in aorta, increases the pressure. The High pressure in left half of heart promotes closing the 38 damper of oval window (for several hours). Closing arterial (Botallo’s duct) duct occurs in consequence of narrowing of his(its) bright spot. Bypass of blood from left to right (from aorta into pulmonary artery) can be saved before 4 days of life and clinically reveal itself by noise. The lungs of fetus are filled by liquid, which is prodused by the cells of respiratory epithelium. Since the moment of the generic activity development begins preparation to straightenning of lungs: occurs mechanical pressurement of thorax and displacing of fetal liquids. Under the influence of the first breath and reflex reduction of the respiratory muscles (in greater degree of the diaphragm) negative pressure s in thorax, promoting breathing the atmospheric air in respiratory ways. A vascular component has big importance in mechanism of the lung straightening. Filling pulmonary vessels by blood brings to slow expansion of the small branches of pulmonary artery and ends to 4-5 days of life. Surfaktant system, making bronchial epithelium, changes in them power of the surrface pull during breath in and out. At the first week of the life newborn’s frequency of the breathing varies from 30 to 60 at minute and depends on functional condition of organs and systems and particularities of the metabolism. At the first week of the life physiological acydosis and reduction of the tension of the oxygen in blood is revealled, changes the amount of the glucose and lipoproteins. As sources of energy in this moment are used high concentrations non-etherified fat acids. The Metabolic processes in fatty tissue run actively. CARDINAL PRINCIPLE of the RENDERING HELP to NEWBORN in PUERPERAL COMMON-ROOM Immediately after birth of the head necessary to draw off from mouth cavity and nose by the help of catheter, united with vacuum instrument or sterile ballon, masses, consisting of juxta-fetus water, mucos and blood. The Child is put on warm pallet, coated with two sterile diapers, located near to mother . Than is made: the repeated aspiration from cavityof mouth and nose; the preventive maintenance of blenorrea; the primary bandaging of the umbilical cord; show the child to mother ; value the condition on scale Apgar for the first minute. 39 Undertaking the secondary processing the umbilical cord and secondary preventive maintenance of blenorrhea realize in specially conducted place for newborn children in sterile robe and preparing in the rules of the asepsis and antisepsis. The Staple on umbilical remainder is not done, but change the ligature at condition: thick and juicy umbilical cord, rh-negative blood mother, newborn in heavy condition. Conduct primary processing skin cover, measurement of the length, circumferences of the head, and circumferences of thorax. The Primary estimation of the functional condition of newborn is conducted on scale of the Virginia Apgar (USA), offered in 1953. In Russia is accepted two times estimation on scale Apgar: on 1 and 5 minutes after birth of all newborn pregnancy regardless of period and masses of the body at birth. The Leading indexes of vital activity are: heartbeat, breathing, muscular tone, reflex activity and color of skin cover, which value 0, 1, 2 balls. Healthy newborn has an estimation of 8-10 balls. Clinical symptoms, specified in scale Apgar hang from many factor, from degree of maturity first of all, metabolic change and gravity to asphyxias. Maturity of newborn defines on the basis of clinical, functional and biochemical parameters. At each age period, as from zygotes, particularities to adapting the fetus, newborn and infant correspond to his calendar age with ambience in the aggregate, surrounding him(it) and interacting with him. The Condition of the central nervous system is an informative feature of maturity. At study child value the pose, position, spontaneous moving of the person, emotional reactions, innate unconditional reflexes. On clinical sign maturity newborn define by means of merit tables on amount ball to each sign. ESTIMATION of the PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT of NEWBORN For estimation of the physical development of newborn usually use statistic depending on age or percentiles merit tables. The Parameters of the physical development of newborn, located in interval M ± 2s (s - an average square-law deflection) or R10 - R90 pertain to normal physical factor for given age. The Parameters of the physical development newborn hang from parameter and age of his(its) parents, particularities of the feeding, conditions of life and serial number of women pregnancy. Proportions of the physique and feeding newborn are very important. Newborn, delivered at term - a child, been born at period of pregnancy 37-42 weeks. Head forms 1/4 parts of the body. The determination has Special importance to circumferences of the head at birth (and in speaker) of the mass of the body, but in the same way her(its) forms. To variant of the normal form refer following: 40 dolichocephalism - extending in front- back direction, brachiocephal - in transverse, and tower skull. The Bones of the skull soft, can lay on each other by sagittal and coronary sutures. The Particularities are shown in table of maturity. Born prematurely newborn - a child, which was born at period below 37 weeks of pregnancy. Been born alive at period 22 - 28 weeks and survived at the first 168 hours of life. To normal parameter of the development at periods 28-37 weeks refer the children with mass of the body from 1000,0 before 2500,0, length 38-47 sm, circumference of the head 26-34 sm and circumference of the thorax 24-33 sm. The Mass of the body cannot be a main criterion of premature. Exists the notion "low mass of the body at birth" are children with mass less 2500,0 at birth, which were born upon the terms. To postmature newborn refer the children, been born after 294 days or 42 weeks. The frequency of the birth of these children is from 8 before 12%. Are observed the clinical signs of trophic breaches: reduction turgor of the skin, thickness of subdermal-fatty layer, desquamation, dryness and scaling of the skin, absence of lubrificant, thick bones of the skull, quite often with closed sutures. At collation of age and factors of the physical development select the following groups: newborn with large mass of the body, which above average to given period on 2s or 90 percentiles and more; with normal physical development for given age; with low mass of the body to age or with delay development. The following types of RID are met: immaturity or "small for date", dysplastic or asymmetric and late type or intrauteral hypotrophy. The combinations of the different types of RID can be met in one child. Pathogenesis of the development delays is multiform. MODERN PERINATAL TECHNOLOGIES (physiological adaptation and shaping of newborn health) Physiological, biological and psychological relationships between mother and child is not broken before 1,5 years of his(its) afternatal development. Physiological shaping of newborn adaptation reactions and the following development of infant is possible only at condition of joint stay of mother and child in puerperal permanent establishment. The Constant contact of mother and child, which begins from births: after primary cutting off umbilical remainder. The Child is put on belly of mother 41 and put to mammal glands. On shaping of defensive power of the child’s organism extremely negative affects washing the mammary glands with disinfecting fluids or water with soap. On areola of nipple is discharged out enormous amount of biologically active and defensive factors (lysocyme, Ig, bifidobacteriums and etc), which required for physiological shaping of local and the general immune system, microbiocenosis and digestive function. The Early discharge from puerperal department (for 3-4 days)is possible at condition of the surgical cutting off umbilical remainder (after 12 hours of life). Till 3 day of staying puerperal house exists the raised colonization their hospital strains of bacteria, possessing high resistance to antibiotics and disinfecting facility, virulent and toxic. To 6 days practically all mothers and children are colonized. Paraphysiological conditions of newborn: " initial decrease of the mass of the body, not exceeding 6-8% from mass of the body at birth; " expansion of the sweat glands; "toxic erythema”; " sexual crease”; " physiological hyperbilirubinemia; In all other cases of the change the functional newborn condition is related with factors of the risk from mother’s and fetus side. Marked improvement in maternal and perinatal outcome for pregnancies complicated by renal disease has occurred during the past 40 to 50 years. An understanding of the disease processes and improvements in obstetric care, with more successful and earlier intervention, have led to the improved outcomes. Renal disorders in pregnancy can range from asymptomatic bacteriuria to end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis, all being influenced by the physiologic changes of pregnancy. Women who have mild to moderate renal disease or a renal transplant are now challenging obstetricians and nephrologists with pregnancy. Thus, these physicians must understand renal diseases and their effect on pregnancy, and vice versa. This chapter reviews the physiology of renal changes during pregnancy and provides a summary of renal disorders. RENAL CHANGES IN PREGNANCY Anatomic changes involving the urinary tract begin in the first trimester of pregnancy and can persist up to 16 weeks postpartum. These changes include dilatation of the 42 renal calyces, pelves, and ureters, as well as reduced ureteral peristaltic activity. Their precise etiology is unknown but can be attributed to a combination of mechanical and hormonal factors.1 Dilatation of the ureter is usually more prominent on the right secondary to dextrorotation of the gravid uterus. In addition, there is reduced ureteral peristalsis and a greater volume of residual urine compared with the nonpregnant state. These factors predispose to urinary stasis and to an increased risk of infection. Much of the data relating to the effect of pregnancy on renal hemodynamics are derived from small studies in which measurements show considerable individual variation. Autoregulation maintains renal blood flow at a relatively constant level despite wide variations in perfusion pressure (mean renal artery pressure). Renal blood flow is usually assessed by p-aminohippurate clearance, which measures effective renal plasma flow (ERPF). The ERPF significantly increases during pregnancy. It reaches a peak increment in midtrimester of 50% to 85% and then shows a small decline during the third trimester that is unrelated to posture. The ERPF and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in pregnancy are markedly affected by posture, being maximal when the pregnant woman lies on her side.2 Normal pregnancy is associated with plasma volume expansion and an increase in the GFR of 40% to 65% (measured by inulin clearance) and a decrease in GFR of approximately 15% to 20% late in the third trimester.1,3 The mechanisms responsible for the increase in GFR, plasma volume, and renal plasma flow rate are unknown. Nitric oxide, endothelin, and relaxin may play a role in renal vasodilation in human pregnancy.1 Changes in renal anatomy, hemodynamics, and tubular function are listed TESTS OF RENAL FUNCTION AND DISEASE IN PREGNANCY Tests of renal function in pregnancy must be interpreted in relation to the changes in plasma volume, glomerular filtration, and tubular reabsorption that normally occur with advancing gestation. Many of the commonly used tests of function yield lower results in pregnancy than in the nonpregnant state. Consequently, values that may be regarded as normal in the nonpregnant state may well indicate renal dysfunction in pregnancy. Uric acid, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine levels are crude indices of renal function. In pregnancy, plasma uric acid usually decreases by 25% beginning in the first trimester and increases during the third trimester. Upper normal limits of plasma uric acid levels are 5 to 5.5 mg/dL in pregnancy.4 Levels are influenced by race, multiple gestation, and time of day sampled, with higher levels in the morning. An indicator of renal filtration, the BUN normally decreases from nonpregnant levels of 12 mg/dL (4.3 mmol/L) to 9 mg/dL (3.2 mmol/L), and plasma creatinine levels 43 decline from a nonpregnant mean value of 0.7 mg/dL (62 mmol/L) to 0.5 mg/dL (44 mmol/L).1 If the plasma creatinine level exceeds 0.80 mg/dL (80 mmol/L) or the BUN is greater than 14 mg/dL at any stage in pregnancy, renal dysfunction should be suspected and more detailed investigation should be performed. The kidney and liver affect serum urea levels. The liver synthesizes urea, which is influenced by protein intake, metabolism, and hepatic function. Urea reabsorption is by the kidneys and varies with hydration. Therefore, it is possible for renal function to be normal in the presence of an abnormal BUN or abnormal in the presence of a normal BUN. In addition, renal function must decline by at least 50% before either the BUN or the creatinine level becomes abnormal, where clinical signs of renal insufficiency become apparent (Figs. 1 and 2). Fig. 1. Relation between plasma level of urea nitrogen and rate of glomerular filtration. A similar relationship exists for serum creatinine. Fig. 2. Relation between functioning renal tissue and clinical signs of renal failure. The 24-hour creatinine clearance is the best clinical measurement of GFR. By week 8 of pregnancy, the creatinine clearance rate normally increases by 45% and remains elevated during the second trimester. In the final weeks of pregnancy, creatinine clearance usually declines to near nonpregnant levels. Error in the measurement of creatinine clearance in a pregnant woman can occur; the most common type of error is an incomplete 24-hour urine collection. Accurate timed urine collection is particularly difficult in pregnancy because significant volumes of urine may remain in the dilated collecting system. To avoid this error, patients should be well hydrated and should rest on their left side for 1 hour before starting and completing the 24-hour urine collection.1 In addition, the secretory component of creatinine excretion increases in moderate renal failure, and creatinine clearance rates tend to overestimate GFR. Despite these problems, creatinine clearance still remains the most useful measure of GFR in clinical practice. Urinalysis is essentially unchanged during pregnancy. However, many variables can affect the results. Normal kidneys should be able to concentrate urine to a specific gravity of 1.026 or more and to dilute urine to a value less than 1.005. In pregnancy, posture affects urine concentration and specific gravity. Urine tends to be more dilute after a left lateral position is maintained compared with an upright position.2 The urine must be at room temperature for the dipsticks to be reliable. Dipsticks exposed to air will give false-positive results for glucose and false-negative results for blood.5 Observational error and training also affect the sensitivity of predicting proteinuria by dipstick.6 Saudan and colleagues7 showed that the use of an automated urinalysis 44 device for the detection of proteinuria reduced the false-positive rate. Proteinuria diagnosed on dipstick should be confirmed with a 24-hour urine. The method of collection is very important when collecting a urine specimen. It is difficult for the woman to obtain a satisfactory clean voided specimen by herself, especially when she is far along in pregnancy. In addition, the specimen must be collected before the pelvic examination; it may be collected by the examiner while the patient is in the dorsal lithotomy position. The diagnosis of renal disease in pregnancy should begin by taking a careful history and performing a thorough physical examination. Particular attention should be directed toward any history of renal disorders, proteinuria, hypertension, collagen vascular diseases, or glycosuria affecting either the patient or close relatives. Physical examination includes inspection of the optic fundi. Signs of uremia are usually a late feature in the natural progression of renal disease and indicate significant dysfunction. Laboratory investigation begins with urinalysis of protein, glucose, ketones, specific gravity, and sediment. Glucosuria is usually detected with a glucose oxidaseimpregnated dipstick. In pregnancy, the most common reasons for persistent glucose in the urine are physiologic glucosuria of pregnancy and diabetes. However, the possibility of primary renal disease with renal glucosuria should be considered. Conventional screening for proteinuria uses a dipstick that is sensitive to albumin. Five percent of healthy adults exhibit postural proteinuria, a benign condition; this can be ruled out by comparing protein levels in the first voided urine with a specimen obtained after the woman was upright for several hours. False-positive results for protein can be due to concentrated urine, many white blood cells in the urine, or vaginal secretions with epithelial cells. Fever, stress, and exercise can also cause transient proteinuria. Proteinuria in pregnancy should be evaluated using a 24-hour urine collection and should not be considered pathologic until it exceeds 300 to 500 mg in 24 hours.1 Higby and coworkers8 showed that the upper limit of normal was 260 mg for urinary protein and 29 mg for albumin in a 24-hour period. Both increased after 20 weeks' gestation. Studies have shown that a 2-hour or 12-hour collection of urine correlates with creatinine clearance and protein measured in a 24-hour specimen.9,10 Evans and associates9 calculated total protein using a protein/creatinine ratio in the 2-hour group and compared the results with the 24-hour urine (1840.8 ± 786 and 1944 ± 1060 mg [mean ± SE], respectively, r2 = 0.95, p < 0.0001). The nephritic syndrome is characterized by greater than 3 to 3.5 g/24 hours. In assessing the significance of proteinuria in pregnancy, the clinician should remember that increasing protein 45 excretion with advancing gestation associated with known renal disease does not necessarily indicate significant progression of the disease. Examination of urinary sediment requires a fresh specimen, ideally the first voided morning specimen. The presence of cells within a cast indicates that the cells came from the renal parenchyma. As a general guide, leukocyte casts are associated with infections or inflammatory processes, erythrocyte casts with glomerular disease, and fatty casts with nephrosis. In addition, pyuria is a common finding in renal disease. White blood cells, casts, and pyuria may be present as reaction inflammation of the glomeruli or kidney substance. Pyuria in the absence of casts may be due to infection anywhere in the genitourinary tract. Finally, the nephritic syndrome is characterized by the presence of doubly refractile fat bodies (Maltese crosses), which are visible only under polarized light. The role of renal biopsy in pregnancy is controversial. It is potentially dangerous, especially in the presence of hypertension. Further, it has been argued that the histologic changes of glomerular disease may be obscured by the changes from pregnancy itself. In the largest study of pregnant women, Packham and Fairley11 reported on 111 renal biopsies and concluded that renal biopsy in the first two trimesters of pregnancy did not appear to be associated with an increased rate of complications, and in most women it provides a positive diagnosis for undiagnosed hematuria and proteinuria. However, Kullner and coworkers12 reported 4 hematomas in 15 antepartum biopsies and 3 hematomas in 3 postpartum biopsies; 2 of these patients required transfusion. The occurrence of complications is similar to the major complication rate of 2.4% reported by Gonzales and associates13 in 1005 biopsies in the general population. Perirenal hematomas, perirenal abscess, and sepsis were considered major complications Lindheimer and associates14 reviewed the role of renal biopsy in pregnancy and believed that biopsy should be performed only if it would change management and should be postponed until after delivery. Postpartum renal biopsy may be useful in determining the prognosis for patients with hypertension in pregnancy. In a study of 20 postpartum renal biopsies, Gaber and Spargo15 could distinguish between patients with glomerular endotheliosis, a reversible lesion with no long-term sequelae, and focal glomerulosclerosis, which is not reversible and indicates underlying hypertensive disease with nephrosclerosis. It is possible to categorize almost all renal problems in pregnancy using the information gained from a detailed history, urinalysis, BUN, creatinine level, and creatinine clearance. In certain patients, renal ultrasound may provide useful additional information, particularly if renal calculi or a tumor is suspected, but may be limited secondary to the pregnancy. Renal radiographs are rarely indicated in 46 pregnancy and pose a radiation hazard to the fetus. If they are necessary, limiting the number of films will minimize the risk to the fetus. Computed tomography scans may aid in the diagnosis of nephritic abscesses, and magnetic resonance imaging may be helpful to rule out tumor. Radiation exposure to the fetus should not exceed 5 rads. Cystoscopy can be performed for the usual indications. ACUTE RENAL INSUFFICIENCY With the legalization of abortions and the use of antibiotics, the incidence of acute renal failure (ARF) in pregnancy has markedly decreased in developed countries secondary to a decrease in the incidence of septic abortions. A further decrease is due to improvements in prenatal care, quick recognition of the condition, and initiation of treatment of abruptio placentae and preeclampsia. In industrialized countries, the rate of ARF is less than 0.004%.16 Preeclampsia, hemorrhage, and abortions account for 95% of the obstetric causes of ARF.17 Grunfeld and Pertuiset16 reviewed 57 patients presenting over a 22-year period. The most common precipitating factor was hemorrhage, which included 13 cases of abruptio placentae. Severe preeclampsia or eclampsia accounted for 12 cases, and infection was the cause in 8 patients. The overall maternal mortality rate was 14%, and the incidence of bilateral renal cortical necrosis was 33%. Defined as a sudden decrease in renal function that results in retention of nitrogenous wastes, ARF can be classified as prerenal, intrinsic, or postrenal. The causes of ARF are listed in Table 2. Prerenal conditions are the most common causes of ARF and usually result from inadequate perfusion of the kidneys. Obstetric complications of ARF include hemorrhage from placenta previa, abruptio placentae, and uterine atony (Table 3). ARF from renal hypoperfusion is usually reversible within 24 to 36 hours with volume replacement and correction of the underlying cause.18 Without prompt treatment, acute tubular necrosis (ATN) may develop. Most of the deaths from ARF in pregnancy are due to the underlying disease rather than the renal failure itself. ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSIS Vascular hyperactivity with preferential cortical ischemia, diminished glomerular permeability, intraluminal obstruction, back leak of luminal contents across damaged tubular epithelium, and abnormalities in prostaglandin metabolism all have been demonstrated in ATN.19 However, the mechanism precipitating renal shutdown is unknown. In ATN, the BUN and creatinine levels rise steadily for 2 to 10 days and then plateau. There follows a recovery phase characterized by a marked diuresis; in most patients, normal renal function resumes. Only about 50% of patients with ATN become oliguric, and in these patients proteinuria is rarely more than 1 g per day. The 47 death rate ranges from 20% to 60%; sepsis and hemorrhage are the major causes of death. In addition, ATN can occur for the same reasons in the gravida as it occurs in the nonpregnant patient. The management of ATN has been well described by Brenner and Lazarus.20 The first step is to identify and treat the underlying disease process, with the aim of preventing progression to parenchymal renal disease. It is important to distinguish between extrarenal azotemia and acute parenchymal renal failure. The former may result from congestive heart failure, hypovolemia, infection, trauma, hemorrhage, and urinary tract obstruction. Analysis of serum and urine samples may prove helpful if the diagnosis is not clear. The urine sodium concentration exceeds 25 mEq/L and urine sediment contains brownish pigmented casts and an increased number of tubular cells. In ARF, volume correction should always precede the use of diuretics, with the exception of mannitol, which is a volume expander and an osmotic diuretic. Mannitol may reduce swelling of the endothelial cells and thus improve renal blood flow. If the patient is volume expanded and not hypotensive, then mannitol is contraindicated and furosemide is the diuretic of choice. During the oliguric phase, fluids should be restricted to avoid hypertension and pulmonary edema. Life-threatening hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and acidosis may develop rapidly; thus, electrolyte and acid-base status must be carefully monitored. Acute hyperkalemia (potassium level more than 6 mEq/L) may be treated with sodium bicarbonate, insulin and glucose, ion exchange resins, or calcium gluconate. Dialysis is often the treatment of choice. During the diuretic phase of ATN, patients are at risk for electrolyte imbalance and hypovolemia. ARF may be complicated by neurologic signs such as progressive lethargy, hyperreflexia, clonus, and a positive Babinski's sign. These signs disappear as renal function improves. Bacterial infection is a major risk and must be aggressively treated. Adequate nutritional status is important to combat infection, replace lost protein, and facilitate recovery of renal function. Standard recommendations include restriction of protein, sodium, and potassium; however, dietary requirements vary from patient to patient and according to the level of renal function. One of the benefits of dialysis is that it allows a more flexible diet. ACUTE CORTICAL NECROSIS Excluding death, the most serious complication of ARF is bilateral renal cortical necrosis (BRCN). The condition is characterized by the death of renal cortical tissue with sparing of the medulla. Its pathophysiology is uncertain. Lindheimer and colleagues21 suggested that endothelial damage by endotoxin is followed by the 48 formation of thrombi. The incidence of BRCN is probably underestimated because patchy cortical necrosis with partial or almost complete recovery or renal function may be overlooked if a patient survives and the appropriate investigations are not undertaken. Abruptio placentae is the most common pregnancy complication associated with BRCN, whereas the incidence is relatively low in patients with severe preeclampsia. BRCN should be strongly suspected if ARF develops before 30 weeks of gestation and is associated with prolonged anuria or oliguria (of more than 10 days' duration). Anuria or oliguria is the rule, and urine is usually blood-stained. Renal biopsy or selective arteriography can be used to confirm the diagnosis and distinguish between extensive and patchy cortical necrosis. Most patients with BRCN progress to chronic renal failure; before the availability of renal dialysis, the condition was usually fatal. Some patients with this disease have a slow recovery in renal function for up to 3 years after the onset and can achieve a satisfactory lifestyle without dialysis.22 PREECLAMPSIA Preeclampsia is a syndrome characterized by hypertension and proteinuria. The disease process starts far before the appearance of any clinical signs or symptoms. Its etiology is unknown but is thought to be due to endothelial damage. A multisystem disorder, preeclampsia has multiple effects on the kidney. It is a frequent cause of proteinuria in pregnancy. Endotheliosis, swollen intracapillary endothelial cells in the glomeruli, is the hallmark lesion of preeclampsia in the kidney. In addition, preeclampsia may cause focal glomerular sclerosis. An increase in renal vascular resistance causes a reduction of renal blood flow. Therefore, GFR, ERPF, and the filtration fraction decrease in preeclampsia. The exact etiology for the decline in renal function is unknown. After delivery, the functional decrements usually reverse quickly but can progress to ATN if treatment is not initiated at an appropriate time. Pregnancy outcomes complicated by preeclampsia and ARF are associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality. Sibai and colleagues18 reported outcomes in 31 pregnancies in 30 patients with renal failure; 18 women had preeclampsia and 12 had superimposed preeclampsia with existing hypertension, renal disease, or both. All the women in the preeclampsia-only group developed ARF 1 to 5 days postpartum, whereas seven women in the other group developed ARF postpartum. Overall, gestational age at delivery was less than 30 weeks in 37.5% of the pregnancies and 21 to 36 weeks in 47%. All 18 patients in the preeclampsia-only group had ATN, and 9 required dialysis. All patients had normal renal function within 8 weeks of follow-up. Two patients in this group died at 8 to 9 weeks postpartum after the ATN resolved. Autopsy results showed no residual renal disease. In the other group, 11 patients 49 survived and 9 of these patients required dialysis. Before delivery, seven of the nine had abnormal renal function. One patient who had glomerulosclerosis and ARF died 3 days after termination of her pregnancy at 16 weeks' gestation. The association of HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome complicated by acute renal failure does not significantly increase maternal morbidity or mortality rates. Selcuk and colleagues23 described 39 cases of pregnancy-related ARF. Fourteen (36%) of the patients had HELLP syndrome and 12 of the 14 required dialysis. Fourteen of the other patients without HELLP syndrome also required dialysis. Recovery rate, maternal death rate, and fetal death rate were similar in both groups. Another study compared adverse perinatal outcome in women with HELLP syndrome (n = 32) with women with severe preeclampsia without HELLP syndrome (n = 32) at less than 28.0 week's gestation.24 There were no significant differences between the groups with respect to ARF. There were no maternal deaths. An additional study revealed that subsequent pregnancies in patients who have had prior pregnancies complicated by ARF and HELLP syndrome tend to have favorable outcomes and long-term prognosis.24 In conclusion, ARF is infrequent in well-managed patients with severe preeclampsia. Maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity rates increase with the association of ARF in these patients. Early identification and proper management of ARF in patients without associated medical or obstetric complications does not result in residual renal damage. CHRONIC RENAL INSUFFICIENCY Chronic renal failure is defined as a reduction of renal mass and loss of renal reserve from an insult to the kidney. Initially, surviving nephrons hypertrophy in number and function. This initial adaptation predisposes the remaining nephrons to sclerosis and unrelenting destruction, which can eventually lead to end-stage renal disease. Chronic renal failure has multiple etiologies; diabetes and hypertension have replaced glomerulonephritis as a major etiology. Renal insufficiency is classified as mild, moderate, or severe. Patients with mild disease have a serum creatinine level of 1.4 mg/dL or less, or 125 umole/L or less, and no hypertension. Those with moderate renal insufficiency have a serum creatinine level of 1.5 to 2.5 mg/dL, or 125 to 250 umole/L, and those with severe disease have a creatinine level of 2.5 mg/dL or more, or 250 umole/L or more.25,26 Maternal and perinatal outcomes are usually not affected with mild renal insufficiency. Likewise, the effects of pregnancy do not worsen renal function when mildly impaired.27 50 Early studies have reported a significant deterioration of renal function in pregnant patients with moderate renal insufficiency.28,29. However, more recent studies have shown less deterioration.27,28,29,30,31,32 The largest study comprised 82 pregnancies in 67 women with primary renal disease and a serum creatinine level of more than 1.4 mg/dL.27 The underlying disorder was glomerulonephritis in 51% of the women and chronic tubulointerstitial disease in the remaining. Of these women, 72% had moderate renal insufficiency (serum creatinine level 1.4 to 2.4 mg/dL) and 18% had severe (2.5 mg/dL or more). In this study, end-stage renal disease was defined as a serum creatinine level of more than 6.0 mg/dL, and a change in renal function was defined as a 25% change in the equation 1/serum creatinine, which linearly correlates with GFR. Overall, the total rate of decline in renal function was 43%; renal function declined in 11 women during pregnancy and in 16 after delivery. Women with hypertension at the first prenatal visit had a significantly lower mean 1/Scr but not a decreased GFR in the third trimester compared with those who were normotensive. In contrast, women who developed hypertension in the third trimester had a decreased 1/Scr and GFR compared with women without hypertension. By 6 months postpartum, hypertension was no longer associated with a decline in the mean 1/Scr or in GFR.27 During pregnancy, a total of 43% of women experienced a decrease in the GFR, of these, 23% had a decline between delivery and 6 weeks postpartum, and the remaining 57% remained stable. At 6 month postpartum, 31% of the women experienced a pregnancy-related decline that persisted, 10% had a decline between 6 weeks postpartum and 6 months, 8% experienced a pregnancy-related decline but recovered, and the remaining 51% continued to be stable. Overall, the fetal survival rate was 93%, and 59% delivered prematurely. The rates of preterm delivery and intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) for women with severe renal disease were 73% and 57%, respectively; the rates for women with moderate disease were 55% and 31%, respectively. The fetal survival rate in women with severe renal disease was 100%, and the outcome of pregnancy was not correlated with the presence of high-grade proteinuria. Women with hypertension and renal disease at the first prenatal visit were not at increased risk for preterm delivery, IUGR, or reduced fetal survival. However, hypertension in the third trimester was associated only with an increase in the rate of IUGR.27 END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE Women with end-stage renal disease rarely become pregnant secondary to infrequent and irregular menstrual cycles, anovulation, and hormonal abnormalities. The frequency of conception has been reported to range from 0.3% to 2.2% per year; the rate of conception in patients undergoing hemodialysis is about twice that of patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.33 Some conception rates may be incorrect as a result 51 of biased data collection of surveys from dialysis centers. In addition, pregnancies may go unrecognized: early spontaneous abortion may be mistaken for heavy menses in women with end-stage renal disease with irregular menstruation. Okundaye and colleagues33 reported the largest registry of pregnant patients with end-stage renal disease. In 930 dialysis centers, 344 pregnancies occurred in 318 women. Limitations to this report are biased reporting, exclusion of 60% of the dialysis centers, and incomplete information. In these 318 women, 58 were started on dialysis after conception and 209 conceived while undergoing dialysis. The outcome in women who conceived before dialysis was better than in those who conceived after beginning dialysis. Seventy-three percent of women who started on dialysis after conception had surviving infants, compared with 40.2% of women who were receiving dialysis when they conceived. Overall, out of the 320 pregnancies, there were 42% surviving neonates, 6% stillborn infants, and 7.5% neonatal deaths. Spontaneous abortions occurred in 32%; of these, 38% occurred in the second trimester. The remaining 10.8% elected therapeutic abortion. The authors also concluded that a lower frequency of prematurity and low birthweight was associated with conception before dialysis. There was no statistical significance between the fetal survival rate and causes of renal failure. In addition, women who had fewer years of dialysis before conceiving tended to have a better outcome compared with those with more years of dialysis. Lastly, there was no statistical difference in infant survival or mean gestational age of live-born infants among women with different frequencies of dialysis. However, women who received more than 20 hours of dialysis per week had better infant survival rates and less prematurity than those receiving less than 20 hours per week.32 The pregnancy rate for women receiving dialysis ranges from 23% to 73.3%.32,33 Nakabayashi and co-workers34 reported 15 pregnancies in women receiving chronic hemodialysis from 1985 to 1997. Of these, 4 infants died shortly after birth from prematurity and the other 11 showed normal development at 1 year of age. One infant was diagnosed with retrolental fibroplasias of prematurity. There were no congenital anomalies. All showed signs of preterm labor and most were born prematurely, with the mean gestation age at delivery in the 11 surviving neonates of 33.0 ± 4.7 weeks (range 23 to 38 weeks). Survival of the neonate was associated with years of dialysis. Neonates who died of prematurity were born to women who had been receiving dialysis for more than 9 years, and the remaining who survived were born to women who had been receiving dialysis for less than 6 years.33 Dialysis management in a pregnant patient differs slightly from that in a nonpregnant one. The hours and frequency of dialysis are increased by 50% to maintain a BUN of 52 less than 80 mg/dL, with the ideal range 50 to 60 mg/dL.26 BUN levels of more than 80 mg/dL are associated with an increased risk for fetal demise. During dialysis, it is important to avoid hypotension and rapid fluctuations in intravascular volume. Anemia is common in patients receiving dialysis and is exacerbated by pregnancy.35 Approximately 35% of patients need to be transfused before or at delivery. Giving packed red blood cells during dialysis prevents volume overload and aggravation of hypertension. Erythropoietin has been shown to be effective in treating anemia in pregnancy. In addition, patients receiving dialysis need a diet consisting of 70 g protein, 1500 mg calcium, 50 mmol potassium, and 80 mmol sodium, with supplements of dialyzable vitamins.35 Counseling of dialysis-dependent patients embarking on pregnancy should emphasize the poor fetal prognosis. Further, patients should be aware that they will have to contend with a high risk of pregnancy complications and an increased frequency and duration of dialysis. PREGNANCY AFTER RENAL TRANSPLANT Chronic renal failure is often accompanied by amenorrhea, but fertility returns rapidly after transplantation. During the past decade there has been a steady increase in the number of pregnancies after renal transplantation. Davison and Milne36 reviewed pregnancies in transplant patients. Fewer than 40% of conceptions did not continue beyond the first trimester; of the remainder, 94% were successful. In most patients, renal function improved during pregnancy, but in 15% there was a deterioration that could persist after delivery. The incidence of graft rejection appears to be no greater than in the nonpregnant population. Preeclampsia was the most common complication, affecting 30% of pregnancies.36 In transplant recipients, changes in urinary protein excretion, plasma uric acid, platelet count, or liver function tests seem to be less useful as markers of preeclampsia than in the normal population. Infection is an important consideration in any patient receiving immunosuppressive drugs. Aseptic technique should be used for even minor surgery and steroid therapy augmented. A transplanted kidney rarely obstructs labor, and delivery by cesarean section is required only for obstetric reasons. In utero exposure to high-dose steroid and immunosuppressive agents does not seem to be associated with an increased incidence of congenital anomalies in the offspring of pregnant women with a renal transplant. Current data suggest that steroids and immunosuppressive agents (prednisone, cyclosporin A, and azathioprine) at the doses used to prevent graft rejection in transplant recipients are well tolerated by the fetus. In theory, these drugs could cause fetal growth retardation, adrenal and bone marrow suppression, and immunosuppression predisposing to intrauterine infection. However, 53 more than 50% of live-born infants had no neonatal problems. Davison and Milne36 reported a 45% to 60% preterm delivery rate and an incidence of small-forgestational-age infants of greater than 20%. Long-term studies are required to determine whether there may be other effects, particularly an increase in the incidence of malignancies or abnormalities in the subsequent generation. Before any woman with a renal transplant embarks on a pregnancy, an obstetrician and nephrologist should counsel her. Lindheimer and colleagues37 proposed guidelines for transplant patients before pregnancy. At least 2 years should have elapsed since the transplant, and the woman should be in good health without severe hypertension, severe renal insufficiency, or persistent proteinuria. In addition, she should be receiving maintenance doses of immunosuppressive therapy. Pregnancy appears to have no effect on graft function or survival; however, an important concern is that a mother may not survive long after the pregnancy. Current data suggest that 10% of mothers die within 7 years of pregnancy. Eighty percent and 50% of recipients of kidneys from living donors and from cadavers, respectively, are alive 5 years after the transplant. If renal function is normal 2 years after transplantation, then the survival rate exceeds 80%.36 GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Acute glomerulonephritis (the acute nephritic syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt appearance of red blood cells and red blood cell casts in the urine. Renal function is usually impaired, with sodium and water retention leading to edema and hypertension. The BUN and creatinine levels rise, and creatinine clearance declines. Proteinuria is common but is normally less than 3.5 g per 24 hours. Renal diseases presenting as acute glomerulonephritis include poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, lupus glomerulonephritis, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, and Goodpasture's syndrome. Laboratory investigations may help to distinguish the different causes and should include urine microscopy, creatinine clearance, 24-hour urinary protein collection, serum IgA and complement determinations, streptozyme assay and antistreptolysin 0 titers, and evaluation of antinuclear antibody.38 Management problems include control of hypertension, electrolyte balance, and edema. Uremia may not respond to conservative measures and may require renal dialysis. Chronic glomerulonephritis implies progressive loss of renal function, proteinuria, and diminishing renal size caused by primary or secondary glomerular disease that has failed to resolve or respond to treatment. End-stage renal failure eventually ensues, requiring hemodialysis. Jungers and associates39 observed 171 pregnancies in women with biopsy-proven primary chronic glomerulonephritis and concluded that 54 pregnancy did not adversely affect the course of renal disease in patients who had normal renal function before pregnancy. POSTSTREPTOCOCCAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is very uncommon in pregnancy. The diagnosis usually depends on a history of streptococcal infection within the previous weeks and an elevated antistreptolysin titer. Fetal loss is almost invariable. Renal function returns to normal after delivery. Patients who have a history of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis and whose renal function has returned to normal are not at risk of fetal loss or preeclampsia.40 MESANGIAL IgA NEPHROPATHY In most countries, mesangial IgA nephropathy is the most common type of glomerulonephritis, and yet there are surprisingly few accounts of pregnancy and IgA nephropathy. Kincaid-Smith and Fairley41 summarized the outcome of 102 pregnancies in 65 patients with mesangial IgA nephropathy. The outcome in individual patients with IgA nephropathy may vary from no change in renal function or biopsy features during 25 years to a fulminating progression to end-stage renal failure in a matter of 2 months. It is therefore difficult to be certain whether renal function that deteriorates during pregnancy was precipitated by the pregnancy or was the natural course of the disease. The prognosis for fetal outcome is generally good in patients with normal renal function and without pre-existing or early developing hypertension.41 FOCAL AND SEGMENTAL HYALINOSIS AND SCLEROSIS Jungers and colleagues42 studied 10 pregnancies in six patients with focal and segmental hyalinosis and sclerosis and found a high rate of fetal complications with one abortion, four preterm deliveries (including one stillbirth), and two neonates with severe growth retardation. Proteinuria recurred or increased in four pregnancies. None of the patients studied were in renal failure at conception, and none progressed to failure during pregnancy. Similar findings were reported by Kincaid-Smith and Fairley.41 Again it is difficult to determine the effect of pregnancy on the course of this condition, but most reports suggest an adverse effect,40 particularly if renal failure and hypertension are present at conception.42,43,44 REFLUX NEPHROPATHY Kincaid-Smith and Fairley41 analyzed data from 345 pregnancies complicated by reflux nephropathy and examined the effect of renal function on outcome. Abnormal renal function, defined as a serum creatinine level greater than 1.25 mg/dL, was 55 associated with significantly higher rate of fetal loss and a greater chance of preeclampsia and a decline in renal function. They also observed a marked and rapid decline in renal function in every patient with a serum creatinine level greater than 2.3 mg/dL. Proteinuria proved to be a good indicator of prognosis because it reflected the development of progressive secondary glomerular lesion. Abe and colleagues45 retrospectively studied the influence of antecedent renal disease on pregnancy in 72 women with primary glomerular disease. The incidence of normal delivery and live births was highest in cases of membranous glomerulonephritis. There was no difference in the fetal outcome for IgA nephropathy and non-IgA proliferative glomerulonephritis. Outcome was unfavorable in cases associated with hypertension (more than 140/90 mm Hg) or impaired renal function (glomerular filtration rate less than 70 mL per minute) or when biopsy specimens showed arteriosclerosis or cortical tubulointerstitial changes. Although renal function deteriorated in 11 patients, the authors could not be certain whether this had been precipitated by the pregnancy. They concluded that a combination of clinical and histologic parameters should be used to assess the prognosis for pregnancy in women with primary glomerular disease. INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS Interstitial nephritis implies primary damage to the tubulointerstitial system of the kidneys with secondary glomerular damage. The acute form usually presents with rapid deterioration in renal function, especially if caused by a drug or an infectious agent. Chronic interstitial disease may occur as a consequence of any disorder that produces chronic damage to the renal interstitium—for example, chronic hypertension, diabetes mellitus, chronic pyelonephritis, and drug abuse, particularly a combination of phenacetin and aspirin. Hematuria and proteinuria are not characteristic of chronic interstitial nephritis, and the condition is typically insidious in onset and progression. It is often associated with an inability to concentrate urine. Pregnancy outcome is less than optimal. The fetal loss rate is particularly high (10% perinatal mortality) if interstitial nephritis is complicated by hypertension or preeclampsia. COLLAGEN VASCULAR DISEASES The collagen vascular diseases are systemic disorders of unknown cause characterized by multiorgan inflammation and unpredictable remissions and exacerbations. Chronic inflammatory changes are usually found in the microvasculature, although larger vessels may also be involved. Renal involvement is generally an unfavorable prognostic sign. 56 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Investigation has predominantly focused on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which is by far the most common collagen vascular disorder encountered in obstetric practice. The condition is associated with overproduction of circulating autoantibodies to a wide variety of antigens, particularly nuclear antigens. The autoantibodies may damage tissue directly or indirectly by forming antigen-antibody immune complexes, as in lupus glomerulonephritis. Bobrie and colleagues46 reviewed 213 pregnancies (73 women) associated with lupus nephritis. Renal biopsy was performed in 66 women, showing proliferative glomerulonephritis in 48. After exclusion of therapeutic abortions (24/213), the overall percentage of live births was 87%. Fetal loss was higher if the onset of SLE occurred during pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period. Fetal prognosis when pregnancy occurs after the onset of SLE depends not only on the disease activity but also on other factors such as the presence of nephrotic syndrome, hypertension, or impaired renal function.47 The fetal mortality rate appears to be independent of the presence or absence of lupus anticoagulant.48 The latter is closely associated with anticardiolipin antibodies. A high anticardiolipin level has been reported to be a sensitive predictor of fetal growth retardation or intrauterine fetal death in pregnant patients with SLE.49 Although most offspring of patients with lupus are normal, it has been known for many years that some neonates have transient skin rashes and positive results of antinuclear antibody tests. A neonatal lupus syndrome has been described,50 the predominant features of which are discoid skin rashes, congenital heart block, and antinuclear antibodies in maternal and neonatal serum. The cutaneous manifestations usually resolve within 3 months. Congenital heart block may occur in isolation or may be associated with other congenital cardiac anomalies or with skin rashes. The heart block is caused by fibrosis of the conducting system and is permanent. There is a close correlation between isolated congenital heart block and the presence of maternal antibody to soluble tissue ribonucleoprotein antigens anti-Ro (SS-A). The activity status at conception provides no guide to the course of lupus nephropathy. This is particularly true in patients with a history of a severe form of lupus nephritis.51 Proteinuria may increase during pregnancy, and the serum creatinine level may either rise or not fall normally. Exacerbations of lupus nephropathy are usually moderate and can easily be controlled by steroid therapy. However, the course of maternal lupus nephritis is especially poor when SLE presents during pregnancy.46,51,52 SLE with superimposed preeclampsia may present with signs and symptoms indistinguishable from a flare-up of lupus nephritis. Antibody 57 assays may help to differentiate these conditions. Rising titers of anti-DNA antibodies or falling levels of complement C3 or C4 are compatible with an exacerbation of SLE.53,54 Patients with SLE in pregnancy should receive steroid therapy if clinical or immunologic signs or symptoms of disease activity develop. Hypertension should be treated with antihypertensive agents. Bobrie and colleagues46 favor routine administration of steroids postpartum to prevent a flare-up. In the past, lupus nephritis was one of the most common reasons for recommending therapeutic abortion in SLE. This procedure was not always followed by a remission and sometimes resulted in significant maternal morbidity and even death. Therapeutic abortion is now rarely indicated. A favorable fetal outcome may be anticipated even in the presence of severe lupus nephritis, provided the disease is stable and in remission and renal function and blood pressure are normal at conception. Fetal wastage is higher when the disease is active. There is no evidence to suggest that pregnancy has an adverse effect on SLE, and most exacerbations of lupus nephropathy during pregnancy represent the effect of hypertension or superimposed preeclampsia. Even in the presence of nephrotic syndrome during pregnancy, fetal and maternal outcome may be good if hypertension and renal insufficiency are not severe. The successful management of a pregnancy complicated by lupus nephritis requires close cooperation between obstetrician, nephrologist, and rheumatologist. THE RHESUS FACTOR IN OBSTETRICS The frequent fears, anxieties and miseries of families suffering from Rhesus incompatibility may possibly become a thing of the past in the light of recent experimental results obtained by teams of investigators at Liverpool and Baltimore, and their claims to having perfected a method of preventing iso-immunization of Rhesus-negative pregnant women. It is felt, in view of these promising achievements,that a survey of the present state of our knowledge of the Rhesus bloodgroup factor and its complexities should be of help and benefit. Historical Aspects'" It was in 1939 that a case was reported by Levine and Stetson of a woman in her second pregnancy who was delivered of an 8-month stillborn foetus. At that time this was a not uncommon outcome of a pregnancy, and it might well have passed unnoticed but for the fact that the delivery was followed by a postpartum haemorrhage for which the patient received 500 ml. of her husband's blood, which was known to be of the same ABO bloodgroup system as her own. (The ABO system had been discovered by Landsteiner in 1900.) The mother developed a severe haemolytic reaction to the transfusion, from which she fortunately recovered. The 58 blood specimens were subsequently retested and were found to be incompatible. A new blood-group system had been discovered, to which no name was given. In the following year Landsteiner and Wiener conducted their famous experiments by which blood from the Macaca rhesus monkey was injected into rabbits and guinea-pigs. They then made the very surprising discovery that the resulting antibodies not only agglutinated the red cells of the monkey but also those of 85% of the White people tested in New York. The new agglutinating factor thus discovered was named the Rhesus (Rh) factor. Persons possessing the factor were called Rh-positive, and those lacking it Rhnegative. It was soon realized that the Rh factor was identical with the 'new' group that Levine and Stetson had described a year before. In 1941 Levine et al. demonstrated that Rh incompatibility between mother and baby was the cause of the long-recognized clinical entity of erythroblastosis foetalis,nowadays preferably referred to as 'haemolytic disease of the newborn'. The great advances in our knowledge of this subject are a tribute to the excellent teamwork between immuno-haematologist, obstetrician, and paediatrician. The Rhesus Blood-group System'" The Rh system is made up of 3 pairs of allelomorphic genes that are closely linked together on the chromosomes. These genes are known as D and d, C and c, E and e. A fourth gene (and possibly a fifth) has been described (F).* The D antigen is th~ antigen that was originally described and the one commonly referred to when discus sing the Rh system. It is the gene that is responsible for well over 90% of all the dangers associated with the Rh bloodgroups. Rh-positive persons are either homozygous (DD) or heterozygous (Dd). The Rhnegative are always dd. The Rh antigen is well developed before birth. In 1942 Bornstein and Israel demonstrated the D antigen in the red cells of 5 foetuses between 17 and 42 mm. in length. In 1955 Chown examined a 6-weeks embryo (32 mm.) and found the Rh factor in the cord blood; he also obtained a positive direct Coombs test from the sensitized cells. This means that even an early embryo may sensitize a pregnant woman. Racial differences are found in various blood-group systems. The same applies to the Rh group. In most European countries about 15% of people are Rhnegative, but a very low incidence is found in some countries in the East, such as China and Java. In South Africa the frequencies vary with race, being highest among the Whites. In the Cape Town area, according to M. C. Botha,' the following 59 frequencies of Rh-negative people obtain among the various racial groups: nonJewish White population 16%; Jewish White population 12%; Cape Coloured population under 5/'0' with a fairly similar incidence in the Bantu group. The Rhesus Antibodies Antibodies to the Rh antigen are formed by the mother as a response to foetal Rh-positive cells that enter the maternal circulation. The antibodies produced cross back in turn to the foetal side and when present in sufficient amounts will destroy the foetal red blood-cells. At the initial sensitization the antibody concentration is usually not high enough to affect the foetus. It has been repeatedly demonstrated that these 'foetal haemorrhages' into the maternal circulation do in fact occur. Finn et al.' (1961) examined maternal blood-smears and demonstrated the presence of foetal cells in many of the specimens. They also found that there was a significant association between 'large' foetal bleeds (i.e. over 5 ml.) and antibody formation, and suggest that the placental barrier is probably the most important factor in protecting against Rh sensitization, always provided that foetal bleeding is necessary for maternal sensitization. Brown' (1963) examined postpartum blood- mears of 165 mothers within 24 hours after delivery and succeeded in demonstrating foetal cells in 83 cases (50%). Most cases of foetal haemorrhage occur during labour. It has been shown that minute amounts of foetal blood, of the order of 0•03 - 0•07 m!., can suffice for maternal ensitization.' In the absence of previous transfusion with Rh-positive blood, sensitization in the first pregnancy is virtually unknown. Types of Rhesus Antibodies Two different and quite distinct types of antibodies are formed against the Rh factor. These are (1) the 'complete' or saline antibodies, also known as agglutinin, and (2) the 'incomplete' or albumin antibodies. The complete or saline antibodies are the antibodies probably formed in the early stages of sensitization. They are detected by their ability to agglutinate Rh-positive cells suspended in a saline medium. Saline antibodies do not cross the placenta and are therefore not responsible for causing haemolytic disease of the newborn. The incomplete or albumin antibodies develop at a later stage of sensitization. They have no naked-eye or rillcroscopical effects on Rh-positive cells suspended in saline. It can, however, be demonstrated by various tests that an interaction has occurred between them, and these cells, when 'coated' by incomplete antibodies, will no longer react with saline antibodies. On the other hand, the incomplete 60 antibodies will react with and agglutinate Rhpositive cells when suspended in an alburilln (i.e. protein) medium. The incomplete antibodies, as opposed to the saline type, are able to cross the placental barrier and are therefore responsible for producing haemolytic disease of the newborn. Incidence of Sensitization Although many Rh-incompatible matings occur, most escape sensitization. The total incidence of haemolytic disease of the newborn is estimated at I: 200 pregnancies.7 Hartmann8 (1949) analysed 25,340 blood samples and found 3,309 pairs at risk, of which, however, only 175, i.e. 1: 19, developed antibodies. Stratton8 (1953) analysed 13,300 Rh-negative mothers and calculated the incidence of haemolytic disease in the baby as 1: 23 (565 cases). Morley et al: (1961) gives an incidence of 1: 25. This means that a 96% reassurance can be given to parents. ZoutendyklO (1963) makes the interesting observation that, although in South Africa the incidence of sensitization is roughly equal in Whites and Bantu, a significant percentage of Bantu remain below the critical level, put at 1 : 16 to 1: 32. Botha3 (1963) recently reported the following figures as the incidence of anti-D antibody formation among all pregnant women examined in the Cape Town area, viz.:Whites 1: 178, Cape Coloured 1: 434, and Bantu 1: 417. He also reported that the incidence per 100 Rh-negative women was 3•5% in Whites, and 4•8% in Bantu and Coloured. Protection by ABO-Incompatibility In 1943, soon after the discovery of the Rh system,Levine drew attention to the fact that the parents of children with haemolytic disease of the newborn, due to the Rh factor, were more often ABO-compatible than a control series of parents. Several series have since been published to substantiate this finding, as shown in the following table from Van Loghem and Spaander" (reported by Race and Sanger'): THE ABO RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HUSBANDS AND WIVES IN FAMILIES WITH HAEMOLYTIC DISEASE OF THE NEWBORN DUE The mechanism of this protection can possibly be explained as follows: Anti-A and anti-B agglutinins are naturally-occurring antibodies and are therefore present from birth. They will immediately destroy foetal red cells carrying the incompatible ABO group if they enter the maternal circulation before they have a chance to act as a simultaneous Rh antigen. 61 Another possible explanation is that ABO-incompatible foetuses may be eliminated so early in pregnancy that they cannot act as a Rh antigen. In a South African series of White cases recently published by Zoutendyk'O it was found that in cases of haemolytic disease of the newborn with parents compatible in the ABO system the exchange transfusion rate varied from 91-1 to 94•2%, as opposed to a rate of 5•8 8•9% (differences according to various blood-groups) in such babies where the parents were incompatible for the ABO blood-groups. Not only does ABO incompatibility decrease the frequency of sensitization but it also reduces the severity of the affected case. Possible Mechanisms in Rhesus Iso-immunization Although it has now been generally accepted that foetal haemorrhages across the placenta do occur, it still remains a matter of speculation how and under what circumstances these bleeds take place. Knox et al." state that in cases of Rh immunization there has been a higher incidence of obstetric procedures likely to disturb the choriodecidual space and thus favour leakage of foetal red cells into the maternal circulation. These procedures include external version, surgical induction, caesarean section, Crede's expression of the placenta, and manual removal of the placenta. These authors" also found that there was a statistically significant higher incidence of preeclamptic toxaerilla in Rh-sensitized patients than in a control series (33% vs 5%). 'The risk of sensitization rises with increasing severity of the toxaemia.' It is interesting to observe that, despite the constant selection against the heterozygote exerted in the past by haemolytic disease of the newborn, no appreciable change in proportion between the frequency of Rh-positive and Rh-negative cases could be demonstrated. A possible explanation was offered in 1949 by Glass, who, after an analysis of the records in Baltimore, concluded that Rhnegative sensitized families averaged a higher number of pregnancies than either Rh-positive or Rh-negative nonsensitized controls. It would appear that a higher perinatal mortality had acted as a stimulus in these families to overcompensate by having a larger number of children. Antibody Titres The level of antibodies in the mother is expressed by the antibody titre. The mother's serum is mixed with red cells suspended in several media, including a saline solution and a bovine albumin solution. The titres of both the complete and incomplete antibodies are determined. The antibody titre is taken early in pregnancy and again later on. When no antibodies are found at the initial examination a single repeat test 62 between the 34th and 36th weeks of pregnancy is usually sufficient. More frequent readings are necessary when antibodies are present. If antibodies are found early in pregnancy, previous sensitization must be postulated.The antibody titre is of great help in assessing the individual case and in predicting the likely outcome of the pregnancy. A few points of importance must be mentioned at this stage: 1. The mere presence of antibodies in a patient with a negative history is of greater importance than the actual antibody level, because the present foetus, if Rhpositive,will be suffering from haemolytic disease. 2. For subsequent pregnancies a rise in titre has more significance than the actual level of antibodies. 3. A severely affected infant can be found without any increase in titre, or with a relatively low level of antibodies. 4. A Rh-negative foetus in a previously sensitized patient can be found associated with either a fall or, even,a rise in titre. Keeping all these points in mind, it can still be said that a definite correlation exists between the antibody titre and the severity of the disease' process in the infant. For example, Jacobs13 has never had a fatal case with an antibody titre of 1: 8 or less. Coplerud" quotes no loss of babies with a titre less than 1: 4, and a 70% mortality at levels of 1: 256 or higher. Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn The essential underlying pathology of this condition is an excessive haemolysis of foetal red cells before, at, or shortly after birth as a result of iso-immunization of the mother. (Iso-immunization is the production of immune antibodies in an individual in response to the injection of an antigen from another member of the same species.) Immunization may be the result of an incompatible blood transfusion or of a previous sensitizing pregnancy. The D antigen and the ABO system are the responsible. bloodgroups in 98% of all cases of haemolytic disease of the newborn. The remaining cases are caused by the less frequent and not so well-known blood-groups. As stated above, only about 4% of Rh-incompatible matings are at risk. The typical course of the disease is that of one or two normal infants followed by successively more severely affected siblings. This is not always the case, however. Tovey and Valaes" (1959) analysed 200 first-affected babies and concluded that dangerously high titres (1: 40 or more) were reached in 28•5% of cases, with a perinatal mortality in this group of 63 31•6%. This shows that even a first-affected pregnancy sometimes ends in a dead baby. In general it can be said that if the first sibling is mildly affected the chances are that the following babies will also be only mildly affected. Once a stillbirth has occurred a repeat stillbirth may be expected in 80% of cases delivered at term. The risk increases to 90% with two previous sWlbirths.• One factor of importance in the prognosis of the Rh baby has not been mentioned so far. This is the genotype of the father. If the father is heterozygous for the D factor there is a 50% chance that the foetus will be Rhnegative and therefore not at risk of developing haemolytic disease of the newborn. From the foregoing discussion it will have become clear that the three main points in the management and prognosis of a Rh-sensitized pregnancy are: 1. The previous obstetrical history as well as the history of possible previous transfusions. 2. The antibody titre, and 3. The genotype of the father. Additional factors of importance are: 4. Racial differences. Zoutendyk'• has found that Rhsensitized pregnancies in the Bantu are often of a milder type than in Europeans. 5. Sexual differences. Males are more commonly affected than females; a mortality ratio of 2: 1 has been quoted." Male foetuses are also more frequently eliminated in early pregnancy than female foetuses. In view of the highly successful treatment of the liveborn affected baby with exchange tran fusions, the prevention of intra-uterine foetal death and tillbirth remains the outstanding problem in haemolytic disease of the newborn. Premature induction of labour, however, can never provide the complete solution, for intra-uterine foetal death may occur as early as the 18th week of pregnancy." With exchange transfusions Walker" (1958) obtained a 97% survival rate in 822 liveborn babies treated in the Newcastle hospitals between 1952 and 1957. Zoutendyk'•(1963) reports a drop in mortality since the introduction of exchange 64 transfusions from an estimated 25% to less than 5%. The actual prevention of isoimmunization in the mother is the logical next step in the fight for the eradication of this disease. Treatment of the Rhesus Iso-immunized Patient The following factors, some of which are discussed above, are of importance to the obstetrician in deciding on the management of a patient sensitized to the Rh factor: 1. The past history. 2. The antibody titre and the husband's genotype. 3. Regular antenatal visits. Throughout the antenatal period a close watch must be kept for the development of pre-eclamptic toxaemia and hydramnios. Should either of these complications develop, earlier termination is indicated. Another ominous sign is a slowing of foetal movements. 4. A straight X-ray of the abdomen. Thi should be done in all cases before induction of labour. It will help to diagnose a hydrops foetalis, and is also of value in assessing the approximate maturity of the foetus. 5. Induction of labour and amniocentesis. These la t two factors will be discussed in greater detail, in particular premature induction, because this remains, for the time being, the best contribution the obstetrician can offer in reducing the perinatal mortality of infants suffering from haemolytic disease of the newborn. Induction of Labour and A mniocelltesis The practice of premature termination of pregnancy by induction of labour is based on the fact that most of the damage to the foetus is done during the last month of gestation. Over the past 10 years there has been virtual uniformity of opinion on the necessity and value of premature induction, but the actual indications and timing vary with different authors. A useful new tool in the hands of the obstetrician is the analy is of liquor amnii obtained by amniocentesis. Amniocentesis is considered the only reliable method at present available of diagnosing the Rh-negative foetus in utero in a previously sensitized mother. Moreover, it gives a more accurate picture of the progress of the disease than blood tests can do. MacBeth and Robertson18 (1961) were able to give a very accurate prognosis with this method. Walker'• (1957) claimed a 95% accuracy of prediction in 101 cases tested before the 35th week of pregnancy. Amniocentesis should be performed before the 35th week; it is of no great advantage, and often difficult to do, 65 before the 30th week. The bilirubin disappears from the liquor after the 35th week and falsely low levels are then sometimes obtained. The decision when to induce labour will therefore depend on various factors, viz.: on the past history, on the antibody titre, on the foetal maturity, and on the appearance of the liquor; as well as on the presence or absence of hydramnios or pre-eclamptic toxaemia, and on the history concerning decreasing foetal movements. Each case will have to be assessed and managed on its own merits. It is generally agreed that no case should be allowed to go postmature. Induction of labour 7 - 10 days before term is recommended in a first-affected pregnancy or in a subsequently affected pregnancy if no exchange transfusion had been required in the first one. In cases where an exchange transfusion had been required in the preceding pregnancy, and in all cases with a prevIOUS history of a stillbirth or a neonatal death as the result of Rh sensitization, induction of labour should be performed at the 37th week of pregnancy, or even earlier under adverse conditions like very high titres, preeclamptic toxaemia., or hydramnios. It should always be done not less than one week before the time at which the previous stillbirth took place. Should induction of labour be necessary as early as the 35th week, an elective caesarean section may be indicated. Tovey and Valaes's (1959) induce first-affected pregnancies only when the titre is 1: 40 or higher; otherwise they are allowed to go to term. In a subsequently affected pregnancy premature induction of labour is practiced when there has been a rise in titre as compared with the preceding pregnancy. If the father is homozygous Dpositive and the titre is I: 40 or more, induction is recommended at 35 weeks, because stillbirths usually occur before the 37th week. Method of induction. A surgical induction of labour, with or without 'pitocin', is the method of choice in the vast majority of cases. Townsend et al.'" (1961) report on 228 successful inductions out of 23 I cases, more than half of which were performed before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Where induction fails, a caesarean section will have to be done. An elective caesarean section may occasionally be indicated. The Erythroblastotic Neonate As a direct result of the more frequent use of premature induction, the doctor is faced with a steadily increasing number of liveborn ba.bies suffering from haemolytic 66 disease of the newborn. The baby can be affected in one of three distinct clinical entities, viz.: (1) haemolytic anaemia of the newborn, (2) icterus gravis neonatorum, and (3) hydrops foetalis (usually a stillbirth). Smith" states that, if untreated, 5 - 15/,,0 of liveborn infants with haemolytic disease of the newborn will develop kernicterus. Of these cases, 70% will probably die in the first week of life and the rema.ining 30% will develop central nervous complications later on in life. This last group of patients constitutes about 10% of all cases of cerebral palsy. The Early Management of the Baby As soon as the mother goes into labour the pathologist and paediatrician must be notified. At delivery early clamping of the cord is essential in order to prevent overloading of the infant's circulation; cardiac failure is one of the main causes of perinatal death. Samples of cord blood must be collected for the following tests that are necessary for the proper assessment of the baby's condition: 1. ABO blood-grouping and determination of the Rh factor (heavy coating with incomplete antibodies sometimes gives a false negative Rh result). 2. Direct Coombs test. A positive result means that the baby's cells are sensitized. 3. Cord-serum bilirubin. Ordinarily a value of less than 3 mg./100 mI. would not be considered as an indication for exchange transfusion. This of course refers to the indirect bilirubin level. A high direct bilirubin level is no indication for exchange transfusion. 4. Cord-blood haemoglobin. The average normal cord haemoglobin is 16•6-+-1•5 G./IOO rnI. A heel-prick haemoglobin is generally 1 G./IOO rnI. higher than a simultaneous cord-haemoglobin reading. 5. Peripheral blood smear. This must be examined for the presence of normoblasts and other early cells. 6. Reticulocyte count. It should be remembered that one may find a raised reticulocyte count in combination with a normal haemoglobin reading. A repeat reticulocyte count is of value in such cases. Exchange Transfusion In this paper only the main indications will be given, without any detailed discussion. The aims in exchangetransfusing a baby are the treatment or prevention of cardiac failure and/or hyperbilirubinaemia, as well as the control of anaemia. A simple blood transfusion for the correction of anaemia may be necessary 67 later on instead of, or in addition to, exchange transfusion, because antibodies sometimes remain in the foetal circulation for 4 – 8 weeks after birth. The following, singly or in combination, are indications for an exchange transfusion: 1. Clinical evidence of severe disease. 2. Abnormal laboratory findings, such as the following:cord-blood haemoglobin below 14 G./100 m!. (or heel haemoglobin below 15 G.); cord-serum bilirubin above 3 - 4 mg. per 100 rnI.; strong direct positive Coombs test; high reticulocyte count and the presence of premature red cells in the peripheral blood. 3. Miscellaneous factors such as the following: a high antenatal antibody titre (1: 64 or more); a previous stillbirth or neonatal death caused by haemolytic disease; prematurity or male sex in the infant. Recent Developments in the Study of the Rhesus Factor In 1963 two teams of investigators, from Liverpool and Baltimore," published a paper that may have farreaching future effects on the control of haemolytic disease of the newborn. Experimental studies on the prevention of Rh haemolytic disease were first reported in 1961 by Finn et al.: who analysed 85 families with Rh-negative mothers and Rhpositive fathers to whom 4 or more children without evidence of sensitization had been born. They found that the parents were ABO-incompatible in 42•9% of these families, as compared with 22% in families with children suffering from Rh haemolytic disease. The protection afforded against Rh sensitization by co-existent ABO incompatibility is discussed above. The Liverpool workers (Finn et aJ.4) felt that in the same way as crossed-over foetal cells are eliminated by the naturallyoccurring antiA and anti-B antibodies in the mother, so it should theoretically be possible to destroy the invading Rh-positive cells by giving anti-D antibodies to a postpartum woman. Because most 'foetal bleeds' occur during labour it should be possible to prevent maternal sensitization by injecting anti-D antibodies immediately after labour. The problem of antepartum 'foetal bleeds' could obviously not be solved in this way. In the initial experiments Rh-positive (ABO-compatible) cells were injected into Rhnegative volunteers, followed by an infusion of plasma containing a high titre of 'complete' antibodies. The results were most discouraging, for it was found that antibody formation was in fact enhanced by this procedure. In subsequent tests incomplete instead of complete antibodies were infused; much better results were 68 obtained in this way, but it was found that even small amounts of saline antibodies when mixed with the incomplete variety were capable of reducing its effectiveness in preventing antibody formation in the tested person. It was realized that the higher in titre the incompatible antibodies were, and the freer of saline antibodies, the better the protective results would be. Lately a concentrated gamma-globulin preparation containing only anti-D ~ntibodies has been tested, with very good results. At the time of the publication of the paper" no tests had yet been done on pregnant women. The experiments now in progress should be carefully watched and followed, both by the medical and lay world,in the hope and expectation that a major breakthrough in the important subject of. the Rh factor may be achieved in the not distant future. SUMMARY A D co CLUSIONS A review of the history and the present state of knowledge of the Rhesus factor, mainly as it affects the obstetrician,is presented. The importance is discus ed of the various factors es ential in assessing the individual case, including the past obstetrical history of the patient, and the value and the limitations of the antibody titre and the paternal genotype. The place of premature induction of labour as the obstetrician's main contribution to the management of the Rhesus-sensitized case is described, and stress i laid on the marked improvement in foetal survival rates over the last decade as a result of this policy. The uJtimate aim remains the prevention of sensitization, and recent research carried out, and early encouraging results obtained, are described. I wish to express my gratitude to Prof. James T. Louw for continuous encouragement and stimulation in the prepation of this paper; and also to Dr. M. C. BOlha, Pathologlstm-Charge, Cape Provincial Blood Transfusion Services, for advice and helpful criticism and for allowing access to his records. REFERE 'CES I. Boorman. K. E. and Oodd, B. E. (1961): All Introduction to Bloodgroup Serology, 2nd ed., Pp. 66 - 67. London: Churchill. 2. Race, R. R. and Sanger. R. (1962): Bloodgronps in Man, 4th ed. pp. 69 135 and 154. Oxford: Blackwell. 3. Botha, M. C. (1963): Proceedings 0/ the Blood TrallS/usion Con. ference. Durban (in the press). 4. Finn, R.. Clarke, C. A., Oonohoe, W. T. A.. McConnell. R. B.. Sheppard, P. M., Lehane, D. and Kulke, W. (1961): Brit. Med. J .. I, 14 6. 5. Brown, E. S. (1963): Ibid., I, 1000. 6. Smith. C. H. (960): Blood Diseases 0/ In/ancy and Childhood, p. 100. St. LoUIs: C. V. Mosby. 7. Donald, 1. (1960): Practical ObStetric Problems, 2nd ed., p. 681. London: L1oyd-Luke. 8. (a) Hartmann, O. (1949): Op. cit.,' p. 387. (b) Stratum, F. (1953): Ibid., p. 387. 9. Morley, W., Anderson, D. G. and Forsythe, W. R. (1961): Obstet. and Gynec., 18, 294. 10. Zoutendyk, A. (1963): S. Afr. Med. 1.. 37, 428. Second Half of Pregnancy: Common conditions of minor bleeding include an inflamed cervix or growths on the cervix. Late bleeding may pose a threat to the health of the woman or the fetus. Contact your health care provider if you experience any type of bleeding in the second or third trimester of your pregnancy. Placental Abruption: Vaginal bleeding may be caused by the placenta detaching from the uterine wall before or during labor. Only 1% of pregnant women have this problem, and it usually occurs during the last 12 weeks of pregnancy. Signs of Placental Abruption: • Bleeding 70 • Stomach pain Women who are at higher risks for this condition include: • Having already had children • Are age 35 or older • Have had abruption before • Have sickle cell anemia • High blood pressure • Trauma or injuries to the stomach • Cocaine use Placenta Previa: Placenta previa occurs when the placenta lies low in the uterus partly or completely covering the cervix. It is serious and requires immediate care. It occurs in 1 in 200 pregnancies. Bleeding usually occurs without pain. Women who are at higher risks for this condition include: • Having already had children • Previous cesarean birth • Other surgery on the uterus • Carrying twins or triplets Preterm Labor: Vaginal bleeding may be a sign of labor. Up to a few weeks before labor begins, the mucus plug may pass. This is normally made up of a small amount of mucus and blood. If it occurs earlier, you could be entering preterm labor and should see your physician immediately. Signs of Preterm Labor include these symptoms that occur before the 37th week of pregnancy: • Vaginal discharge (watery, mucus, or bloody) • Pelvic or lower abdominal pressure • Low, dull backache 71 • Stomach cramps, with or without diarrhea • Regular contractions or uterine tightening Placenta praevia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search Placenta previa Classification and external resources Diagram showing placenta praevia. Placenta praevia (placenta previa AE) is an obstetric complication in which the placenta is attached to the uterine wall close to or covering the cervix.[1] It can sometimes occur in the later part of the first trimester, but usually during the second or third. It is a leading cause of antepartum haemorrhage (vaginal bleeding). It affects approximately 0.5% of all labours. It is hypothesized[who?] to be related to abnormal vascularisation of the endometrium caused by scarring or atrophy from previous trauma, surgery, or infection. In the last trimester of pregnancy the isthmus of the uterus unfolds and forms the lower segment. In a normal pregnancy the placenta does not overlie it, so there is no bleeding. If the placenta does overlie the lower segment, it may shear off and a small section may bleed. Women with placenta previa often present with painless, bright red vaginal bleeding. This bleeding often starts mildly and may increase as the area of placental separation increases. Praevia should be suspected if there is bleeding after 24 weeks of gestation. Abdominal examination usually finds the uterus non-tender and relaxed. Leopold's Maneuvers may find the fetus in an oblique or breech position or lying transverse as a result of the abnormal position of the placenta. Praevia can be confirmed with an ultrasound.[2] In parts of the world where ultrasound is unavailable, it is not uncommon to confirm the diagnosis with an examination in the surgical theatre. The proper timing of an examination in theatre is important. If the woman is not bleeding severely she can be managed non-operatively until the 36th week. By this time the baby's chance of survival is as good as at full term. Placenta previa is classified according to the placement of the placenta: 72 • Type I or low lying: The placenta encroaches the lower segment of the uterus but does not infringe on the cervical os. • Type II or marginal: The placenta touches, but does not cover, the top of the cervix. • Type III or partial: The placenta partially covers the top of the cervix • Type IV or complete: The placenta completely covers the top of the cervix Contents • 1 Risk factors • 2 Intervention • 3 References • 4 External links Risk factors The following have been identified as risk factors[citation needed] for placenta praevia: • Previous placenta previa, caesarean delivery,[3] or D&C e.g. used for incomplete or missed miscarriage, abortion, to treat or investigate heavy bleeding or other diagnostic purposes. • Women who have had previous pregnancies, especially a large number of closely spaced pregnancies, are at higher risk. • Women who are younger than 20 are at higher risk and women older than 30 are at increasing risk as they get older. • Women with a large placentae from twins or erythroblastosis are at higher risk. • Race is a controversial risk factor, with some studies finding that people from Asia and Africa are at higher risk and others finding no difference. Contracted Pelvis _____________________________________ Definition Anatomical definition: It is a pelvis in which one or more of its diameters is reduced below the normal by one or more centimeters. 73 Obstetric definition: It is a pelvis in which one or more of its diameters is reduced so that it interferes with the normal mechanism of labour. Factors influencing the size and shape of the pelvis • Developmental factor: hereditary or congenital. • Racial factor. • Nutritional factor: malnutrition results in small pelvis. • Sexual factor: as excessive androgen may produce android pelvis. • Metabolic factor: as rickets and osteomalacia. • Trauma, diseases or tumours of the bony pelvis, legs or spines. Aetiology of Contracted Pelvis Causes in the pelvis • Developmental (congenital): o Small gynaecoid pelvis (generally contracted pelvis). o Small android pelvis. o Small anthropoid pelvis. o Small platypelloid pelvis (simple flat pelvis). o Naegele’s pelvis: absence of one sacral ala. o Robert’s pelvis: absence of both sacral alae. o High assimilation pelvis: The sacrum is composed of 6 vertebrae. o Low assimilation pelvis: The sacrum is composed of 4 vertebrae. o Split pelvis: splitted symphysis pubis. • Metabolic: o Rickets. o Osteomalacia (triradiate pelvic brim). • Traumatic: as fractures. • Neoplastic: as osteoma. 74 Causes in the spine • Lumbar kyphosis. • Lumbar scoliosis. • Spondylolisthesis: The 5th lumbar vertebra with the above vertebral column is pushed forward while the promontory is pushed backwards and the tip of the sacrum is pushed forwards leading to outlet contraction. Causes in the lower limbs • Dislocation of one or both femurs. • Atrophy of one or both lower limbs. N.B. oblique or asymmetric pelvis: one oblique diameter is obviously shorter than the other. This can be found in: • Naegele’s pelvis. • Scoliotic pelvis. • Diseases, fracture or tumours affecting one side. Diagnosis of Contracted Pelvis History • Rickets: is expected if there is a history of delayed walking and dentition. • Trauma or diseases: of the pelvis, spines or lower limbs. • Bad obstetric history: e.g. prolonged labour ended by; o difficult forceps, o caesarean section or o still birth. Examination • General examination: o Gait: abnormal gait suggesting abnormalities in the pelvis, spines or lower limbs. o Stature: women with less than 150 cm height usually have contracted pelvis. 75 o Spines and lower limbs: may have a disease or lesion. o Manifestations of rickets as: square head, rosary beads in the costal ridges. pigeon chest, Harrison’s sulcus and bow legs. o Dystocia dystrophia syndrome: the woman is short, stocky, subfertile, has android pelvis and masculine hair distribution, with history of delayed menarche. o This woman is more exposed to occipito-posterior position and dystocia. • Abdominal examination: o Nonengagement of the head: in the last 3-4 weeks in primigravida. o Pendulous abdomen: in a primigravida. o Malpresentations: are more common. Pelvimetry It is assessment of the pelvic diameters and capacity done at 38-39 weeks. It includes: • Clinical pelvimetry: o Internal pelvimetry for: inlet, cavity, and outlet. 76 o External pelvimetry for: inlet and outlet. • Imaging pelvimetry: o X-ray. o Computerised tomography (CT). o Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) . Internal pelvimetry (is done through vaginal examination) • The inlet: o Palpation of the forepelvis (pelvic brim): The index and middle fingers are moved along the pelvic brim. Note whether it is round or angulated, causing the fingers to dip into a V-shaped depression behind the symphysis. o Diagonal conjugate: Try to palpate the sacral promontory to measure the diagonal conjugate. Normally, it is 12.5 cm and cannot be reached. If it is felt the pelvis is considered contracted and the true conjugate can be calculated by subtracting 1.5 cm from the diagonal conjugate .This assessment is not done if the head is engaged. • The cavity: o Height, thickness and inclination of the symphysis. o Shape and inclination of the sacrum. o Side walls: To determine whether it is straight, convergent or divergent starting from the pelvic brim down to the base of ischial spines in the direction of the base of the ischial tuberosity. Then relation between the index and middle finger of the base of ischial spines and the thumb of the other hand on the ischial tuberosity is detected. If the thumb is medial the side wall is convergent and if lateral it is divergent. o Ischial spines: 77 Whether it is blunt (difficult to identify at all), prominent (easily felt but not large) or very prominent (large and encroaching on the mid-plane). The ischial spines can be located by following the sacrospinous ligament to its lateral end. o Interspinous diameter: By using the 2 examining fingers, if both spines can be touched simultaneously, the interspinous diameter is £ 9.5 cm i.e. inadequate for an averagesized baby. o Sacrosciatic notch: If the sacrospinous ligament is two and half fingers, the sacrosciatic notch is considered adequate. • The outlet: o Subpubic angle: Normally, it admits 2 fingers. o Bituberous diameter: Normally, it admits the closed fist of the hand (4 knuckle). o Mobility of the coccyx. by pressing firmly on it while an external hand on it can determine its mobility. o Anteroposterior diameter of the outlet: from the tip of the sacrum to the inferior edge of the symphysis. FINDINGS INDICATING ADEQUATE PELVIS: Data Finding Forepelvis (pelvic brim) Diagonal conjugate Symphysis Sacrum Side walls 78 Ischial spines Interspinous diameter Sacrosciatic notch Subpubic angle Bituberous diameter Coccyx Anterposterior diameter of outlet Round. ³ 11.5 cm. Average thickness, parallel to sacrum. Hollow, average inclination. Straight. Blunt. ³ 10.0 cm. 2.5 -3 finger - breadths. 2finger - breadths. 4 knuckles (> 8.0 cm). Mobile. ³ 11.0 cm. External pelvimetry It is of little value as it measures diameters of the false pelvis. Thom’s, Jarcho’s or crossing pelvimeter can be used for external pelvimetry. • Interspinous diameter (25cm): between the anterior superior iliac spines. • Intercrestal diameter (28 cm): between the most far points on the outer borders of the iliac crests. • External conjugate (20 cm). • Bituberous diameter: can be measured by pelvimeter. 79 In rickets, the interspinous equals or even exceeds the intercrestal diameter. Radiological pelvimetry It is indicated mainly in borderline pelvic contraction. • Lateral view: The patient stands with the X-ray tube on one side and the film cassette on the opposite side. o It is the most important view as it shows the anteroposterior diameters of the pelvis, angle of inclination of the brim, width of sacrosciatic notch, curvature of the sacrum and cephalo-pelvic relationship. • Inlet view: The patient sits on the film cassette and leans backwards so that the plane of the pelvic brim becomes parallel to the film. • Outlet view: The patient sits on the film cassette and leans forwards. N.B. The measurements can be identified by using a graduated scale or Thom’s perforated grid, in which the perforations are 1cm apart, while taking the X-ray film.The picture of the scale or grid on the X-ray film allows the measurement. Cephalometry • Ultrasonography: is the safe accurate and easy method and can detect: o The biparietal diameter (BPD). o The occipito-frontal diameter. o The circumference of the head. • Radiology (X-ray): is difficult to interpret. Cephalopelvic disproportion tests These are done to detect contracted inlet if the head is not engaged in the last 3-4 weeks in a primigravida. • (1) Pinard’s method: o The patient evacuates her bladder and rectum. o The patient is placed in semi-sitting position to bring the foetal axis perpendicular to the brim. o The left hand pushes the head downwards and backwards into the pelvis while the fingers of the right hand are put on the symphysis to detect disproportion. 80 • (2) Muller - Kerr’s method: o It is more valuable in detection of the degree of disproportion. o The patient evacuates her bladder and rectum. o The patient is placed in the dorsal position. o The left hand pushes the head into the pelvis and vaginal examination is done by the right hand while its thumb is placed over the symphysis to detect disproportion. Degrees of Disproportion • Minor disproportion: o The anterior surface of the head is in line with the posterior surface of the symphysis. During labour the head is engaged due to moulding and vaginal delivery can be achieved. • Moderate disproportion (1st degree disproportion): o The anterior surface of the head is in line with the anterior surface of the symphysis. Vaginal delivery may or may not occur. • Marked disproportion (2nd degree disproportion): o The head overrides the anterior surface of the symphysis. Vaginal delivery cannot occur. Degrees of Contracted Pelvis • Minor degree: The true conjugate is 9-10 cm. It corresponds to minor disproportion. • Moderate degree: The true conjugate is 8-9 cm. It corresponds to moderate disproportion. • Severe degree: The true conjugate is 6-8 cm. It corresponds to marked disproportion. • Extreme degree: The true conjugate is less than 6 cm. Vaginal delivery is impossible even after craniotomy as the bimastoid diameter (7.5 cm) is not crushed. Mechanism of Labour in Contracted Pelvis The Flat Rachitic Pelvis 81 Characters: • Inlet: reduced antero-posterior diameter. • The pelvic inclination: is exaggerated due to increased lumbar lordosis. • The sacrum has the following characters: o - The promontory is pushed forwards so the tip is pushed backwards. o - Diminished or obliterated concavity. o - Bent at the middle may be present. • The outlet has the following characters: o Increased antero-posterior diameter. o Increased bituberous diameter. • The interspinous equal the intercrestal diameter. Mechanism of labour: • Engagement: with the sagittal suture in the transverse diameter. • Asynclitism with anterior parietal bone presentation so that the shorter subparietal supraparietal diameter (9cm) is passed instead of the biparietal (9.5cm) in the narrow true conjugate. • Lateral displacement of the head so that the bitemporal diameter is passed through the narrow true conjugate . • Deflexion of the head as the descent of the occiput is resisted by the lateral pelvic wall . • Correction of the asynclitism and deflexion with further descent of the head. • Rotation of the occiput 2/8 circle anteriorly and the head is delivered easily due to wide outlet. Simple Flat Pelvis Characters: • Reduced antero-posterior diameters of the inlet, cavity and outlet. • No rachitic manifestations. 82 Mechanism of labour: The process passes as flat rachitic pelvis till the mid cavity where internal rotation and further descent cannot occur due to persistence of flattening of the pelvis and contracted outlet. So deep transverse arrest is common and vaginal delivery is obstructed. Contracted Outlet (Funnel Pelvis) Characters: • The pelvic capacity is diminished from the inlet to the outlet. • Subpubic angle is acute. • Convergent side walls. • Bituberous diameter is 8 cm or less. Causes: • Android pelvis. • Anthropoid pelvis. • Osteomalacia. • High assimilation pelvis. • Spondylolisthesis. • Oblique pelvis. • 20% of generally contracted pelvis. Mechanism of labour: • Normal descent and engagement as the pelvic inlet is normal. • Extreme flexion and moulding of the head at the level of the jutting ischial spines. • Because of the narrow subpubic angle, the head is pushed backwards with more liability to perineal tears. • In case of occipito-posterior, the funnel pelvis interferes with long anterior rotation so persistent occipito-posterior and deep transverse arrest are common. The 83 face to pubis position is more favourable as it brings the short bitemporal diameter in the narrow subpubic angle. Management: It depends on Thom’s dictum: • If the sum of bituberous + posterior sagittal is >15 cm and bituberous diameter is >8cm: vaginal delivery is allowed with episiotomy and low forceps. • If the Thom’s dictum is <15 cm or the bituberous diameter is <8cm: caesarean section is performed. • Symphysiotomy: may be done in distant areas with no facilities for C.S. and the foetus is living. Management of Contracted Pelvis It depends mainly on the degree of disproportion. • Minor disproportion (minor degree of contracted pelvis): vaginal delivery. • Moderate disproportion (moderate degree of contracted pelvis): trial labour, if failed ® caesarean section. • Marked disproportion (severe or extreme degree of contracted pelvis): caesarean section. Trial of Labour It is a clinical test for the factors that cannot be determined before start of labour as: • Efficiency of uterine contractions. • Moulding of the head. • Yielding of the pelvis and soft tissues. Procedure: • Trial is carried out in a hospital where facilities for C.S is available. • Adequate analgesia. • Nothing by mouth. • Avoid premature rupture of membranes by: o rest in bed, 84 o avoid high enema, o minimise vaginal examinations. • The patient is left for 2 hours in the 2nd stage with good uterine contractions under close supervision to the mother and foetus. Suitable cases for trial of labour: • Young primigravida of good health. • Moderate disproportion. • Vertex presentation. • No outlet contractions. • Average sized baby. Termination of trial of labour: • Vaginal delivery: o either spontaneously or by forceps if the head is engaged. • Caesarean section if: o failed trial of labour i.e. the head did not engage or o complications occur during trial as foetal distress or prolapsed pulsating cord before full cervical dilatation. Indications of caesarean section in contracted pelvis • Moderate disproportion if trial of labour is contraindicated or failed. • Marked disproportion. • Extreme disproportion whether the foetus is living or dead. • Contracted outlet. • Contracted pelvis with other indications as; o elderly primigravida, o malpresentations, or o placenta praevia. 85 Complications of Contracted Pelvis • Maternal: o During pregnancy: Incarcerated retroverted gravid uterus. Malpresentations. Pendulous abdomen. Nonengagement. Pyelonephritis especially in high assimilation pelvis due to more compression of the ureter. o During labour: Inertia, slow cervical dilatation and prolonged labour. Premature rupture of membranes and cord prolapse. Obstructed labour and rupture uterus. Necrotic genito-urinary fistula. Injury to pelvic joints or nerves from difficult forceps delivery. Postpartum haemorrhage. • Foetal: o Intracranial haemorrhage. o Asphyxia. o Fracture skull. o Nerve injuries. o Intra-amniotic infection. Links • Dystocia : Guidelines, reviews • Labor, delivery : Guidelines, reviews Transverse Lie, or baby lying sideways 86 “Transverse Lie” means a sideways position. The baby has his head to one of his mother’s sides and the bottom across her abdomen at her other side. The word transverse is also used in phrases describing two of the normal head down positions. Left occiput transverse (the ideal starting position) and right occiput transverse. These head down babies facing the mother's hip. The side of the mother’s body that the back of the baby’s head is on is indicated by the first word, left or right. The baby faces the opposite hip. To see several different fetal positions go to Belly Mapping. Look at the end of the article for emailed advice. Here are some images to help you understand the lie of a baby in relation to the pelvis. Left: The baby on the left is in the ideal start position - left occiput transverse. The head is transverse but the head is down. This baby is in a vertical lie, meaning the baby lies up and down. One end or the other points towards the pelvis. Right: The baby on the right is lying sideways in the womb - transverse lie. In a Transverse Lie the baby's head is on one of the mother’s sides and the baby's bottom is on the other side. For instance, one mom with a transverse baby will have the head on her left side and the baby's bottom on her right. The hands and feet may be kicking and waving towards her cervix (in the lower part of the uterus) when the baby's belly is down. Another transverse baby may have the head on her mother's right and kick upwards or towards the front. What’s the problem with a transverse lie? The baby who is lying sideways cannot be born vaginally. The baby has to get vertical to fit through the pelvis. A breech or vertex (head down) baby can usually fit. The baby in a transverse lie can not fit. Labor contractions cannot bring this baby through the pelvis. Perhaps the arm or umbilical cord would come through the pelvis. Or the shoulder might block the opening. We can try to help this baby move to a head down, or cephalic, position so that a cesarean can be avoided. When is transverse lie a problem? It is normal for a baby to be transverse in the first and second trimester. We hope that the baby is in a vertical position between 26 and 31 weeks gestation. The breech position is considered normal when found between 26 and 31 weeks gestation. Most babies are head down by 28-30 weeks gestation; a few babies wait to settle head down until 31-34 weeks. And only a few babies who aren't head down after 36 weeks 87 can get there on their own. After 30 weeks, it may be good to do some exercises to help your baby get head down. Late in pregnancy it is more difficult to help the side ways baby to become head down. When the baby has been transverse in the last trimester, the womb becomes shaped for a transverse baby. Conversely, the baby will stay transverse when the pelvic inlet (brim) is not symmetrical or the lower uterine segment (the lower part of the womb where the head would normally settle) is not symmetrical. Crossing our legs, holding toddlers on our favorite hip, a fall, etc. can put a twist in the lower uterine segment. Gravity helps, but there is less room to navigate the womb. First time mothers and women with tight, sturdy musculature, spasming ligaments or tight fascia can do exercises or have body work or both to loosen these soft tissues and allow more fetal movement. Women who have birthed before, and who have loose soft tissues (this includes a few first time mothers, but mostly experienced mothers) may actually need to prop their wombs and abdomens up to let the baby get head down! After 32-34 weeks, I am quite concerned to find a transverse baby – except when the baby was breech recently and is now in a leisurely process of flipping to head down. The breech to head down process shouldn't take more than 3 days (when it doesn't happen instantly). Breech lie or transverse lie? The transverse lie position is sometimes loosely called breech. This seems more common among ultrasound technicians. Midwives and doctors do not use these terms interchangeably. They are not the same. The breech baby lies vertically, the transverse lie baby lies horizontally. The breech baby has an easier time getting head down than the baby who has been transverse into the third trimester. An interesting point is that a breech baby may move to the transverse lie for a couple days before finishing the flip to head down. If your transverse baby was just recently breech wait a couple days before worrying, and keep up the techniques you are using to help baby into a head down position. A confusing variation: One woman had weak uterine ligaments. She was a strong woman, athletic. Perhaps the jolting stops of sports effected her uterine ligaments in this way. Her first baby was head down, but with her little bottom resting on her mother's right hip. The baby was folded over at her waist in this way for the entire third trimester. I wondered how it would effect birth. I suggested a pregnancy belt but 88 the mother wasn't concerned. Her labor advanced beautifully and the baby came down through the pelvis perfectly. I was happy to see how well birth works in a fetal position variation that I had never noted before in a first time mother. The baby had seemed somewhat in a transverse lie, but since the head was in the pelvis, wasn't. The mother used active labor positions and free movement, instinctively moving with her labor and the baby came down well. Techniques to correct a transverse lie when the belly seems tight Things you can do yourself: • Use the Inversion off the couch, as shown in the video, for 30 seconds, 2-3 x a day, • Do the Breech Tilt for 5-10 minutes, 2-3 times a day. (Dr. Carol Phillips says the ironing board technique is not as effective as the forward leaning inversion.) • Stand on your head in a pool of warm water, such as a backyard swimming pool or a therapeutic pool at a hospital or rehabilitation center. Some hotels will let you join a swimmer’s club. When you are using an inversion by laying on your back, the Breech Tilt, you can place a very cold item, like frozen veggies wrapped in a thin dish towel (don't freeze your skin!) on your abdomen in the place that is BEHIND and ABOVE the baby's head. At the same time, place a very warm item, like a toasty rice sock, BELOW and IN FRONT OF baby's face. We are hoping that the baby moves towards the warmth.So the warmth must also be between the baby's face and the pubic bone. The warm object can be right over the pubic bone if the baby's head is down by the hip socket, almost to the brim. This is a helpful addition to other techniques and is not likely to work just by itself. Inversions are recommended unless your bodyworker or care giver says specifically that you have medical reasons not to do an inversion. Adjust the placement of the warm and cold items according to your individual situation. For instance, you might know from an ultrasound where the placenta is. Putting warm or cold items on top of the placenta may not be effective. Don't worry if you don't know where your placenta is. From a comment on the Forward-leaning inversion video on Gail's blog post: Thank you SO much for posting this! for the past couple i've been alot of pain but i didn't know that all the pain was coming from my son being transverse. i knew he was lying like that but i never knew it could cause all the pain it was causing. i was even sent to L&D to see if i was in preterm labor. at my follow-up OB appt she told 89 me that if he didn't move that A.) i'd be in pain until i went into labor and B.) it'd be a mandatory c-section. i'm only 36 weeks along and was missing tons of work along with sleep and just turning into a nasty woman to be around in general. after leaving the OB's office and learning that this was the reason for all my pain, i texted my doula who told me to look up your website. after learning that our son was in a "transverse lying position" i found the video of the lady doing the modified headstand off the couch and decided to try it off a bed. i was able to hold the pose for (30) seconds but i didn't think anything had happened. my hubby checked the babies position and sure enough he was in the perfect occipital posterior position! it's been over (4) days now and he hasn't moved back so i'm praying we are safe. Inversion is an excellent thing to do, but may not be enough on its own. If using the inversion doesn't work after 3-4 days, when you are 32 or more weeks pregnant, then I would suggest getting professional body work. See more about this lower down in this article, and see more fun things to help baby flip head down under the Breech category. Release your psoas muscles. You can help by taking brisk walks. Swing the weight of your legs from the thigh. Each day, lay on the floor on your back for no more than ten minutes with your ankles resting on a chair. Your knees are bent to a 90-degree angle. Breath slow and deep from your belly. See your belly rise and fall like a sleeping toddler. There are several yoga extensions of the legs that help. Massaging your own psoas is quite effective. Also, a myofascial massage person, or a chiropractor who includes hands on massage, pressure point release, etc. can accelerate your psoas release with their skills. Wear a pregnancy belt to actually give a slight pressure that may relax the abdomen. The "slope" of the abdomen with a belt, supports the baby dropping down into the pelvic brim. These techniques will relax your psoas muscles over time. If the womb seems tight around the baby (chronically, not just during Braxton-Hicks contractions) in pregnancy, then professional help is needed. Techniques to correct a Transverse Lie when the belly seems loose 90 For women who have given birth before, and a very few first time moms, the trouble may not be with tightness, but rather with looseness. The techniques then have to adapt to the mother. The idea is that once the baby is head down, support the abdomen with a pregnancy belt and perhaps a rolled hand towel so that the baby stays head down and in a vertical lie. A manual version may also be successful in helping baby get head down. The looser the mama, the more likely the success. Anterior placenta may be a reason not to do a manual version. Using a pregnancy belt for transverse lie When the lower abdomen is loose, as with a pendulous uterus, add a pregnancy belt to create an improved slope to the lower uterine segment. A pregnancy belt helps the uterine ligaments hold the uterus upright so the baby can get into an upright position. For the mom with loose ligaments, I would suggest wearing a pregnancy belt in the fifth month through to labor, and for very loose moms with a pendulous womb, then wearing the belt through pushing the baby out is safest. Professional help for a Transverse Lie Bodywork can correct the length of the uterine ligaments so that they are all symmetrical. Chiropractic adjustments align the pelvic bones so the joints are symmetrical and this, in turn, helps the uterine ligaments become symmetrical. Doing both the bony adjustments and the soft tissue work is the most time efficient and successful, if the mother’s Inversions don’t work in 3-4 days. Some chiropractors and craniosacral therapists know how to do myofascial release of the round and broad ligaments. Certainly, a myofascial massage worker can do this. Maya abdominal massage is another excellent choice for symmetry. Acupuncture, effective for fetal positioning, especially when done by an experienced professional. Moxibustion, heating the acupuncture points with a stick of mugwort incense, can be done at home inexpensively. Best results from 20 minutes a day during the 34 and 35th week. Chiropractic, neck and pelvis, including SI, Symphysis Pubis, Webster and other areas as individually needed. 91 Myofascial, buckled sacral release and diaphragmatic release Homeopathy, Pulsatilla or other remedies can help with malposition. See a professional for best results. This work is specifically for you pelvis, neck and soft tissues (sacral fascia, round and broad ligaments of the uterus, cervical ligaments and sacrotuberous ligament). Remember the time to hire bodywork for transverse babies would be between 32 weeks and birth. The sooner the better! Begin at or after the middle of the seventh month. If you want to try things at home in weeks 32 to 34 that seems reasonable, though if baby is big, and/or mom is tight I would start getting professional help earlier. Starting in mid pregnancy isn't too early. Moxibustion is so helpful in weeks 34-35 and beyond, but particularly these two weeks are more successful to get baby head down. Use in addition to other methods of helping baby get head down. Add myofascial release to the Chiropractor's adjustments. Ask the chiropractor to add Websters to both sides in one visit, if they would please. Craniosacral work can make chiropractic more effective and visa versa. Head stands in a warm pool of water. Hanging from a yoga sling (1 minute) or inversion table (1 minute). Learn to release your psoas. CoreAwareness.com with Liz Koch. A tight psoas my hold the baby's head back above the brim to the side. Talking to your baby, too. Whether out loud or by journaling. See what you can learn about your self this way, too. If your daughter has been transverse all along do everything you can, all of the above you can. If she was breech last week and transverse this week, she is likely to get head down with less to do. But it sounds like she's been transverse a while. Very often this is from a soft tissue issue in the lower uterine segment which can be caused by torsion in the pelvis and the surround soft tissues (ligaments, fascia, muscles etc.) Addressing these issues will likely allow the baby to move into a head down position. Exceptions, if the placenta is below the baby covering the access to the cervical area. An unusual uterine shape, a partial septum or a fibroid blocks the baby's attempts to get head down. Ultrasound would reveal something as obvious as these. Ultrasound is 92 unlikely to reveal a twist in the lower segment of the uterus which is one of the soft tissue issues I mean. Please let me know if any of these or another suggestion helps you. I will hope for the best and expect the best for you and your baby, - Gail" How many times do you need to do the inversion? How quick can baby get head down again? You see the range of success in the comments to the Feb. 9th 2007 blog post from one inversion, to three, to several. It doesn’t always work, but it seems to work often. I’d add what else can I do? Professional help: Myofascial release, chiropractic, and craniosacral therapy along with your acupuncture may increase chances of success. I can’t promise, of course. But these are efficient ways to address the cause. Self help: Begin with the Rebozo sifting, go to the forward-leaning inversion and follow it with the breech tilt using hot and cold pacs. Then I’d add a pelvic floor release. How often does a baby go transverse at the end of pregnancy? It is uncommon. Still you are likely to get the baby head down even in three days with several short, forward-leaning inversions and addressing the soft tissue cause, assuming that something was, or became, twisted near your cervix or brim. A twist in the cervical ligaments will twist the lower uterine segment where the baby would like to put his or her head. Depending on the amount of twist the baby may back up and go transverse or breech. This is fixable with the right body work for you. Be kind to yourself as you try to take on this challenge. You are doing the best you can with a suddenly complex situation. Keep breathing and talking to your baby. Together you will find your way to the other side of the transverse lie. I'd also ask a woman who is scheduled before 41 weeks for a cesarean for a transverse lie or breech presentation: Is convenience the most important thing to schedule your baby's birth around? If not, you might ask for a postponement. You'd be taking additional responsibility for your birth. But this is something to research adn to discuss with your doctor. Obstetric anal sphincter injury 93 The conventional definitions of the 4 grades of perineal laceration in the US have been supplemented by more recent modifications included in a recent British Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) guideline (TABLE 1).3 The definition of third-degree laceration now reflects the various degrees of anal sphincter injury that may occur: partial (3a), full-thickness (3b), external anal sphincter injury, with or without injury to the internal anal sphincter (3c). The incidence of clinical third- and fourth-degree lacerations varies widely; it is reported at between 0.5% and 3.0% in Europe and between 5.85% and 8.9% in the US.2,4-6 A landmark British paper from 1993 revealed that though only 3% had a clinical third- or fourth-degree perineal laceration, 35% of primiparous women (none of whom had any defect before delivery) had ultrasound evidence of varying degrees of anal sphincter defect at 6 weeks postpartum that persisted at 6 months.2 However, only about a third of these women had symptoms of bowel disturbance during the time of study. FAST TRACK Instrument delivery increased risk of anal injury 2- to 7-fold; vacuum-assisted delivery should be used when circumstances allow These findings are supported by a meta-analysis in which 70% of women with a documented obstetric anal sphincter injury were asymptomatic.7 This meta-analysis concluded that clinical or occult obstetric anal sphincter injury occurs in 27% of primigravid women, and in 8.5% of multiparous women. The long-term significance of occult obstetric anal sphincter injury and any relationship with geriatric fecal incontinence is unknown, although 71% of a sample of women with late-onset fecal incontinence were found to have ultrasound evidence of an anal sphincter defect thought to have occurred at a previous vaginal delivery.8 A recent English study9 reveals that when women were carefully re-examined after delivery by a skilled obstetrician looking specifically at the anal sphincter, the prevalence of clinically diagnosed third-degree lacerations rose sharply from the 11% initially diagnosed by the delivering physician or midwife to 24.5%. A subsequent endoanal ultrasound detected only an additional 1.2% (3 injuries, 2 of which were in the internal anal sphincter and therefore clinically undetectable). This strongly suggests that the vast majority of obstetric anal sphincter injuries can be detected clinically by a careful exam and that, when this is done, true occult injuries will be a rare finding. Classification of perineal injury INJURY DEFINITION 94 First degree Injury confined to vaginal mucosa Second degree sphincter Injury of vaginal mucosa and perineal muscles, but not the anal Third degree Injury to the perineum involving the anal sphincter complex (external and internal) 3a <50% of external sphincter thickness is torn 3b >50% of external sphincter thickness is torn 3c Internal sphincter is torn Fourth degree epithelium Injury to external and internal sphincter and rectal mucosa/anal Mechanisms of injury Maintenance of fecal continence involves the coordinated action of several anatomical and physiological elements (FIGURE 1).10 An intact, innervated anal sphincter complex (both external and internal) is necessary. The sphincter complex can be damaged during childbirth in 3 ways. Direct mechanical injury. Direct external or internal anal sphincter muscle disruption can occur, as with a clinically obvious third- or fourth-degree perineal laceration or an occult injury subsequently noted on ultrasound. Neurologic injury. Neuropathy of the pudendal nerve may result from forceps delivery or persistent nerve compression from the fetal head.14 Traction neuropathy may also occur with fetal macrosomia and with prolonged pushing during Stage 2 in successive pregnancies, or with prolonged stretching of the nerve due to persistent poor postpartum pelvic floor tone. Injured nerves often undergo demyelination but usually recover with time. Combined mechanical and neurologic trauma. Isolated neurologic injury, as described above, is believed to be rare. Neuropathy more commonly accompanies mechanical damage.15 Who is at risk? Several risk factors are unavoidable. One of these is primiparity, a consistently reported independent variable also associated with other risk factors for obstetric anal sphincter injury, such as instrument delivery (TABLE 2). 95 TABLE 2 Major risk factors for obstetric anal sphincter injuryRISK FACTOR ODDS RATIO Nulliparity (primigravidity) 3–4 Inherent predisposition: Short perineal body 8 Instrumental delivery, overall 3 Forceps-assisted delivery 3–7 Vacuum-assisted delivery 3 Forceps vs vacuum 2.88* Forceps with midline episiotomy 25 Prolonged second stage of labor (>1 hour) 1.5–4 Epidural analgesia 1.5–3 Intrapartum infant factors: Birthweight over 4 kg 2 Persistent occipitoposterior position 2–3 Episiotomy, mediolateral1.4 Episiotomy, midline 3–5 Previous anal sphincter tear 4 Preventing obstetric anal sphincter injury Sphincter injury can occur even when obstetrical management is optimal. Although evidence from RCT data is often lacking, sufficient observational and retrospective data support the following recommendations to reduce the likelihood of injury. Choose vacuum delivery before forceps Any form of instrument delivery increases the risk of obstetric anal sphincter injury and altered fecal continence by between 2- and 7-fold.2,16,24 An RCT found clinical third-degree tears in 16% of women with forceps-assisted deliveries, compared with 7% of vacuum-assisted deliveries; the authors concluded that, when circumstances allow, vacuum delivery should be attempted first (acknowledging however that 23% 96 of vacuum deliveries failed and proceeded to a forceps extraction, a sequence associated with increased injury).17 A meta-analysis confirmed that vacuum extraction is preferred when instrumental delivery is necessary (SOR: A). When midline episiotomy was performed during instrument delivery, the risk of obstetric anal sphincter injury approximately doubled again, such that, in one study, forceps delivery with episiotomy caused a 25-fold increase in obstetric anal sphincter injury. Any steps that may safely reduce the need for instrument delivery should be supported. Toward this end, the Canadian Clinical Practices Obstetrics committee has recommended evidence-based labor interventions such as one-to-one support in labor, the increased use of a partogram in labor and appropriate oxytocin use, all in an effort to reduce needs for operative interventions. Episiotomy was long promoted as a means of preserving the integrity of the perineal musculature and of avoiding damage to the anal sphincter, and it has been practiced routinely by some.27 Strong evidence now indicates that routine episiotomy (midline or mediolateral) is unhelpful and should be abandoned. Observational evidence overwhelmingly shows that midline episiotomy is strongly associated with obstetric anal sphincter injury.19,22,23,30,31 One of the few RCTs comparing midline with mediolateral episiotomy, although flawed in its design, noted that a clinical third-degree laceration occurred as an extension of episiotomy in 11.6% of midline incisions compared with just 2% of mediolateral cuts. Another RCT, designed to examine routine versus restrictive episiotomy, noted that all but 1 (98%) of the 47 third- or fourth-degree lacerations in a group of 700 women followed midline episiotomy.29 A retrospective database analysis noted a 6-fold higher risk of third-degree perineal lacerations for women undergoing midline episiotomy compared with mediolateral incision.23 Elsewhere, midline episiotomy was associated with a 5-fold increase in symptoms of fecal incontinence at 3 months postpartum when compared with women with an intact perineum. Even when midline episiotomies do not extend into clinical third-degree lacerations, the incidence of resultant postpartum fecal incontinence triples when compared with spontaneous second-degree perineal lacerations.30 The authors postulate that a perineum cut by midline episiotomy allows for more direct contact to occur between the fetal hard parts and the anal sphincter complex during delivery, thereby increasing occult obstetric anal sphincter injury. Observational data conflict as to whether mediolateral episiotomy contributes to, or protects against, obstetric anal sphincter injury—although the burden of evidence favors it as a risk factor that should be 97 avoided when possible.16,23,33 An angle of mediolateral incision cut closer to 45 degrees from the midline has been associated with less obstetric anal sphincter injury than incisions cut at closer angles to the midline. Repairing sphincter injury Detecting injury in labor: With any severe perineal laceration, closely inspect the external and, if exposed, internal anal sphincter and perform a rectal exam, particularly for women with numerous risk factors (although no good evidence supports the role of the rectal exam in diagnosing obstetric anal sphincter injury). Colorectal surgeons have advocated the use of a muscle stimulator to assist in identifying the ends of the external sphincter, but this has not become common practice. Immediate vs delayed repair: It is standard practice to repair a damaged anal sphincter immediately or soon after delivery. However, given that a repair should be well done, and since a short delay does not appear to adversely affect healing, be prepared to wait for assistance for up to 24 hours rather than risk a suboptimal repair. Analgesia and setting Adequate analgesia is an essential element in a good repair. Complete relaxation of the anesthetized anal sphincter complex facilitates bringing torn ends of the sphincter together without tension.39 Though theoretically this can be attained with local anesthetic infiltration, RCOG recommends that regional or general anesthesia be considered to provide complete analgesia.37 It is further recommended that repair of the anal sphincter occur in an operating room, given the degree of contamination present in the labor room after delivery and the devastating effects of an infected repair (SOR: C).40 FAST TRACK Strong evidence shows that routine episiotomy should be abandoned; midline episiotomy is strongly linked with anal sphincter injury Repair technique There are 2 commonly used methods of external anal sphincter repair: one, the traditionally taught end-to-end approximation of the cut ends, and the other, overlapping the cut ends of the external sphincter and suturing through the overlapped portions (FIGURE 2).36 Though an RCT from 2000 noted no significant 98 difference in outcomes between these methods,41 other authors have suggested that an overlapping technique is preferred, and it remains the method most often used by colorectal surgeons in elective, secondary anal sphincter repairs. A Cochrane review of which technique is better has been registered in the Clinical Trials Database. General agreement is that closure using interrupted sutures of a monofilament material, such as 2-0 polydioxanone sulfate (PDS), is the preferred closure method for the external sphincter (SOR: C).36,40 It is recommended that a damaged internal sphincter be repaired with a running continuous suture of a material such as 2-0 polyglactin 910 (Vicryl) (SOR: C). ILLUSTRATION BY RICH LaROCCO: Immediately after repair, consider giving patients laxatives and broad-spectrum antibiotics, and possibly refer for physical therapy Use a stool softener It had long been thought that constipation following obstetric anal sphincter injury allowed the sphincter to heal more effectively. However, new evidence from RCTs shows that using a laxative instead of a constipating regimen is more helpful in the immediate postpartum phase.43 Toward this end, use a stool softener, such as lactulose, for 3 to 10 days postpartum for women with obstetric anal sphincter injury. Should you prescribe an antibiotic? Given the devastating effects of post-repair infection, most authorities consider it prudent to prescribe a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics, possibly including metronidazole (SOR: C)37,40 A Cochrane review is registered to further examine this issue. A separate Cochrane review of the use of antibiotics for instrument vaginal delivery concluded that quality data were insufficient to make any recommendations Obstetric fistula Obstetric fistula (or vaginal fistula) is a severe medical condition in which a fistula (hole) develops between either the rectum and vagina (see rectovaginal fistula) or between the bladder and vagina (see vesicovaginal fistula) after severe or failed childbirth, when adequate medical care is not available[citation needed].Contents [hide] Symptoms and signs The resulting disorders typically include incontinence, severe infections and ulcerations of the vaginal tract, and often paralysis caused by nerve damage[citation 99 needed]. Sufferers from this disorder are usually also subject to severe social stigma due to odor, perceptions of uncleanliness, a mistaken assumption of venereal disease and, in some cases, the inability to have children[citation needed]. Causes The fistula usually develops when a prolonged labor presses the unborn child so tightly in the birth canal that blood flow is cut off to the surrounding tissues, which necrotise and eventually rot away. More rarely, the injury can be caused by female genital cutting, poorly performed abortions, or pelvic fractures[citation needed]. Other potential direct causes for the development of obstetric fistula are sexual abuse and rape, especially within conflict/post-conflict areas, other surgical trauma, gynecological cancers or other related radiotherapy treatment and, perhaps the most important, limited or no access to obstetrical care or emergency services[citation needed]. Distal causes that can lead to the development of obstetric fistula concern issues of poverty, lack of education, early marriage and childbirth, the role and status of women in developing countries, and harmful traditional practices and sexual violence. Poverty, early marriage, and lack of education place women in positions of severe disadvantage and do not enable them to be advocates for their own health and wellbeing. Yet another causal factor is that of logistical access to health care clinics[citation needed]. Many women who suffer from this condition are living in very rural areas and, therefore, access to emergency services often requires some form of travel. The availability of transportation, cost of transportation and road construction can all play a crucial role in the ability of pregnant women to access emergency obstetrical services[citation needed]. The availability and access to medical facilities that have a trained staff and specialized surgical equipment needed for cesarean births is also very limited in certain parts of the world. In many instances, women do not consider their local hospitals and clinics to be places where they could ever seek such care and therefore do not go when there is an obstetrical emergency[citation needed]. Risk factors Primary risk factors are early or closely-spaced pregnancies and lack of access to emergency obstetric care; a 1993 study[citation needed] in Nigeria found that 55 percent of the victims were under 19 years of age, and 94 percent gave birth at home or in poorly equipped local clinics. When available at all, cesarean sections and other 100 medical interventions are usually not performed until after tissue damage has already been done. Early marriage, domestic violence, female genital mutilation, malnutrition which is linked to under-development of the female body, and lack of education/illiteracy also put women at great risk for developing obstetric fistula[citation needed]. Lack of personal knowledge about and experience with childbirth may also put a woman at risk to developing obstetric fistula, especially for women who have previously experienced limited complications with past vaginal births. Women giving birth for the first time and with no real knowledge regarding childbirth may not recognize an emergency situation/complication and therefore not seek out help. Countries that suffer from poverty, civil and political unrest or conflict, and other dangerous public health issues such as malaria, HIV/AIDS, and tuberculosis often suffer from a severe burden and breakdown within the healthcare system. This breakdown puts many people at risk, specifically women. Many hospitals within these conditions suffer from shortages of staff, supplies, and other forms of necessary medical technology that would be necessary to perform reconstructive obstetric fistula repair. Prevention Prevention comes in the form of access to obstetrical care, support from trained health care professionals throughout pregnancy, providing access to family planning, promoting the practice of spacing between births, and supporting women in education and postponing early marriage. Fistula prevention also involves many strategies to educate local communities about the cultural, social, and physiological factors that condition and contribute to the risk for fistula. One of these strategies involve organizing community-level awareness campaigns to educate women about prevention methods such as proper hygiene and care during pregnancy and labour[citation needed]. Prevention of prolonged obstructed labour and fistula should preferably begin as early as possible in each female’s life. For example, improved nutrition and outreach programs to raise awareness about the nutritional needs of female children to prevent malnutrition as well as improve the physical maturity of young mothers, are important fistula prevention strategies. It is also important to ensure access to timely and safe delivery during childbirth; measures include availability and provision of emergency obstetric care as well as quick and safe caesarean sections for women in obstructed labour. Midwives located in the local communities where fistula is prevalent can also contribute to promoting health practices that help prevent future development of obstetric fistulas. Promoting education for girls is also a key factor to preventing fistula in the long term. 101 There are currently several organizations that have developed effective fistula prevention strategies. One of them is the Tanzanian Midwives Association, which works to prevent fistula by improving clinical health care for women and delaying early marriages and childbearing years, as well as help the local communities advocate the rights of females.[1] Treatment Treatment is available through reconstructive surgery[citation needed]. This surgery for uncomplicated cases has a 90% success rate, and success rates for more complicated cases are estimated to be 60% successful[citation needed]. The cost for this procedure, which includes the actual surgery, post-operative care and rehabilitation support, is estimated to be US$300 – $450. Successful surgery enables women to live normal lives and have more children, but it is recommended to have a cesarean section to prevent the fistula from recurring. Post operative care is vitally important to prevent infection. Some women are not candidates for this surgery, but can seek out alternative treatment called a urostomy and a bag for the collection of urine is worn on a daily basis. Challenges with regards to treatment include the very high number of women needing reconstructive surgery, access to facilities and trained surgeons, and the cost of treatment. For many women, even $300 US dollars is simply an impossible price and they cannot afford the surgery. The largest challenge that stands between women and fistula treatment is information. Most women have no idea that treatment is available. Because this is a condition of shame and embarrassment, most women hide themselves and their condition and suffer in silence with no relief. Catheterization Fistula cases can also be treated through urethral catheterisation if identified early enough. The Foley catheter is recommended because it has a balloon to hold it in place. The indwelling Foley catheter drains urine from the bladder. This decompresses the bladder wall so that the wounded edges come together and stay together giving it a greater chance of closing naturally, at least in the smaller fistulas. According to data collected by Dr Kees Waaldijk, Director of the Nigeria National Fistula Programme, out of a case series of 4424 patients with obstetric fistula who were treated within 75 days post partum, 37% (1579 patients) are cured completely with the use of a Foley catheter without the need of surgery. Even without preselecting the least complicated obstetric fistula cases, the systematic use of a Foley 102 catheter by midwives after the onset of urinary incontinence could cure over 25% of all new fistula cases each year without the need for surgery. Prognosis If left untreated, ulcerations and infections can persist as well as kidney disease and kidney failure leading to death[citation needed]. Urinal and fecal leaking are the major physical side effects and because many women suffering from obstetric fistula do not want to leak, they will limit their intake of water and other liquids. This can lead to a very dangerous case of dehydration. Nerve damage to the legs is also noted as a medical side effect[citation needed]. In some cases, many women struggle to walk from this nerve damage and need physical therapy following the treatment of the fistula. Most women living with obstetric fistula also struggle with depression, abandonment by their partners, families and communities, and live in isolation because of the constant leaking and odor. Many women report feelings of humiliation, pain, loneliness, shame and mourning for the loss of their lives and the child they lost during delivery[citation needed]. Because of the constant leaking and smell, many women are isolated from food preparation and prayer ceremonies because they are thought to be constantly unclean. Suicide and attempted suicide are also common amongst women with this condition[citation needed]. Social isolation, increased poverty and decreased employment opportunities due to this condition force many women to turn to commercial sex work and begging[citation needed]. Epidemiology According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 50,000 to 100,000 women develop obstetric fistulas each year and over two million women currently live with obstetric fistula.[2] The WHO claims that fistula was largely eradicated in developed countries in the late 19th century; it still affects two to three million women in developing countries. History Obstetric fistula was very common throughout the entire world but virtually disappeared within Europe and North America due to improvements in obstetrical care[citation needed]. The surgery to cure it was developed by J. Marion Sims. To this day, the prevalence of obstetrical fistula is much lower in places that discourage early marriage, encourage and provide education of women, and grant women access to family planning and skilled medical teams to assist during childbirth. This 103 condition is still very prevalent in the developing world, especially in parts of Africa and much of South Asia (Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Nepal). Society and culture During most of the 20th century obstetric fistula was largely missing from the international global health agenda. This is reflected by the fact that obstetric fistula was not included as a topic at the landmark United Nations 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD)[citation needed]. The 194 page report from the ICPD does not include any reference to obstetric fistula. However, since 2003 obstetric fistula has been gaining awareness amongst the general public and has received critical attention from UNFPA, who have organized a global campaign to "End Fistula"[citation needed]. New York Times columnist Nicholas Kristof, a Pulitzer-prize winning writer, wrote several columns in 2003, 2005 and 2006[citation needed] focusing on fistula and particularly treatment provided by Catherine Hamlin at the Fistula Hospital in Ethiopia. Increased public awareness and corresponding political pressure have helped fund the UNFPA's Campaign to End Fistula, and helped motivate the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) to dramatically increase funding for the prevention and treatment of obstetric fistula. Caesarean section A Caesarean section, (also C-section, Caesarian section, Cesarean section, Caesar, etc.) is a surgical procedure in which one or more incisions are made through a mother's abdomen (laparotomy) and uterus (hysterotomy) to deliver one or more babies, or, rarely, to remove a dead fetus. A late-term abortion using Caesarean section procedures is termed a hysterotomy abortion and is very rarely performed. The first modern Caesarean section was performed by German gynecologist Ferdinand Adolf Kehrer in 1881. A Caesarean section is usually performed when a vaginal delivery would put the baby's or mother's life or health at risk, although in recent times it has been also performed upon request for childbirths that could otherwise have been natural.[1][2][3] In recent years the rate has risen to a record level of 46% in China and to levels of 25% and above in many Asian and European countries, Latin America, and the USA. Etymology The Roman Lex Regia, (later the Lex Caesarea) of Numa Pompilius (715-673 BC), required that the child of a mother dead in childbirth be cut from her womb. This 104 seems to have begun as a religious requirement that mothers not be buried pregnant, and to have evolved into a way of saving the fetus, with Roman practice requiring a living mother be in her 10th month of pregnancy before the procedure was resorted to, reflecting the knowledge that she could not survive the delivery. Rumours that the term refers to the birth of the Roman emperor Julius Caesar are false; although Caesarean sections were performed in Roman times, no classical source records a mother surviving such a delivery,[5][8] – the earliest recorded survival dates to 1500 AD[9] – and Caesar's mother Aurelia Cotta lived to serve him as an advisor in his adulthood. The term has also been explained as deriving from the verb caedo, 'to cut', with children delivered this way referred to as caesones. Pliny the Elder refers to a certain Julius Caesar (not the emperor, but a remote ancestor) as ab utero caeso, "cut from the womb", a godly attribute comparable to rumors about the birth of Alexander the Great.[10] This and Caesar's name may have led to a false etymological connection with the ancient monarch. Some link with Julius Caesar, or with Roman Emperors generally, exists in other languages as well. For example, the modern German, Danish, Dutch and Hungarian terms are respectively Kaiserschnitt, kejsersnit, keizersnede, and császármetszés (literally: "Emperor's cut").The German term has also been imported into Japanese ( 帝王切開 teiõsekkai) and Korean (제왕 절개 jewang jeolgae), both literally meaning "emperor incision." Similar in Western Slavic (Polish) cięcie cesarskie, (Czech) císařský řez and (Slovak) císarský rez (literally "imperial cut"), whereas the South Slavic term is (Slovenian) cárski réz, which literally means tzar cut. The Russian term kesarevo secheniye (Кесарево сечение késarevo sečénije) literally means Caesar's section. The Arabic term ( ق ي صري ة دةو الwilaada qaySaríyya) also means pertaining to Caesar or literally Caesarean. The Hebrew term ( קיסרי ניתוחnitúakh Keisári) translates literally as Caesarean Surgery. In Romania and Portugal it is usually called cesariana, meaning from (or related to) Caesar. According to Shahnameh ancient Persian book, the hero Rostam was the first person who was born with this method and term ( ر س تم ي نهrostamineh) is corresponded to Caesarean. Finally, the Roman praenomen (given name) Caeso was said to be given to children who were born via c-section. While this was probably just folk etymology made popular by Pliny the Elder, it was well known by the time the term came into common use. History 105 Successful Caesarean section performed by indigenous healers in Kahura, Uganda. As observed by R. W. Felkin in 1879. Bindusara (Born c. 320 BC, ruled: 298 - c.272 BC) , the second Mauryan emperor of India after Chandragupta Maurya the Great, is said to be first child born by surgery. His mother, wife of Chandragupta Maurya, accidentally consumed poison and died when she was close to delivering him. Chanakya, the Chandragupta's teacher and advisor, made up his mind that the baby should survive. He cut open the belly of the queen and took out the baby, thus saving the baby's life. Pliny the Elder theorized that Julius Caesar's name came from an ancestor who was born by Caesarean section, but the truth of this is debated (see the article on the Etymology of the name of Julius Caesar). The Ancient Roman Caesarean section was first performed to remove a baby from the womb of a mother who died during childbirth. Caesar's mother, Aurelia, lived through childbirth and successfully gave birth to her son, ruling out the possibility that the Roman Dictator and General was born by Caesarean section. The Catalan saint Raymond Nonnatus (1204–1240), received his surname—from the Latin non natus ("not born")—because he was born by Caesarean section. His mother died while giving birth to him. In 1316 the future Robert II of Scotland was delivered by Caesarean section—his mother, Marjorie Bruce, died. This may have been the inspiration for Macduff in Shakespeare's play Macbeth". (see below). Caesarean section usually resulted in the death of the mother; the first recorded incidence of a woman surviving a Caesarean section was in the 1580s, in Siegershausen, Switzerland: Jakob Nufer, a pig gelder, is supposed to have performed the operation on his wife after a prolonged labour.[14] However, there is some basis for supposing that women regularly survived the operation in Roman times. [15] For most of the time since the sixteenth century, the procedure had a high mortality rate. However, it was long considered an extreme measure, performed only when the mother was already dead or considered to be beyond help. In Great Britain and Ireland the mortality rate in 1865 was 85%. Key steps in reducing mortality were: Introduction of the transverse incision technique to minimize bleeding by Ferdinand Adolf Kehrer in 1881. This is thought to be first modern CS performed. The introduction of uterine suturing by Max Sänger in 1882. Extraperitoneal CS and then moving to low transverse incision (Krönig, 1912).[clarification needed] 106 Anesthesia advances. Blood transfusion. Antibiotics. European travelers in the Great Lakes region of Africa during the 19th century observed Caesarean sections being performed on a regular basis. The expectant mother was normally anesthetized with alcohol, and herbal mixtures were used to encourage healing. From the well-developed nature of the procedures employed, European observers concluded that they had been employed for some time. The first successful Caesarean section to be performed in America took place in what was formerly Mason County Virginia (now Mason County West Virginia) in 1794. The procedure was performed by Dr. Jesse Bennett on his wife Elizabeth. An early account of Caesarean section in Iran is mentioned in the book of Shahnameh, written around 1000 AD, and relates to the birth of Rostam, the national legendary hero of Iran. Types There are several types of Caesarean section (CS). An important distinction lies in the type of incision (longitudinal or latitudinal) made on the uterus, apart from the incision on the skin. The classical Caesarean section involves a midline longitudinal incision which allows a larger space to deliver the baby. However, it is rarely performed today as it is more prone to complications. The lower uterine segment section is the procedure most commonly used today; it involves a transverse cut just above the edge of the bladder and results in less blood loss and is easier to repair. An emergency Caesarean section is a Caesarean performed once labour has commenced. A crash Caesarean section is a Caesarean performed in an obstetric emergency, where complications of pregnancy onset suddenly during the process of labour, and swift action is required to prevent the deaths of mother, child(ren) or both. A Caesarean hysterectomy consists of a Caesarean section followed by the removal of the uterus. This may be done in cases of intractable bleeding or when the placenta cannot be separated from the uterus. 107 Traditionally other forms of Caesarean section have been used, such as extraperitoneal Caesarean section or Porro Caesarean section. A repeat Caesarean section is done when a patient had a previous Caesarean section. Typically it is performed through the old scar. In many hospitals, especially in Argentina, the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Australia, and New Zealand the mother's birth partner is encouraged to attend the surgery to support the mother and share the experience. The anaesthetist will usually lower the drape temporarily as the child is delivered so the parents can see their newborn. Indications Caesarean section is recommended when vaginal delivery might pose a risk to the mother or baby. Not all of the listed conditions represent a mandatory indication, and in many cases the obstetrician must use discretion to decide whether a Caesarean is necessary. Some indications for Caesarean delivery are: Complications of labor and factors impeding vaginal delivery such as prolonged labor or a failure to progress (dystocia) fetal distress cord prolapse uterine rupture increased blood pressure (hypertension) in the mother or baby after amniotic rupture increased heart rate (tachycardia) in the mother or baby after amniotic rupture placental problems (placenta praevia, placental abruption or placenta accreta) abnormal presentation (breech or transverse positions) failed labor induction failed instrumental delivery (by forceps or ventouse. Sometimes a 'trial of forceps/ventouse' is tried out - This means a forceps/ventouse delivery is attempted, and if the forceps/ventouse delivery is unsuccessful, it will be switched to a Caesarean section. overly large baby (macrosomia) 108 umbilical cord abnormalities (vasa previa, multi-lobate including bi-lobate and succenturiate-lobed placentas, velamentous insertion) contracted pelvis Other complications of pregnancy, preexisting conditions and concomitant disease such as pre-eclampsia hypertension multiple births precious (High Risk) Fetus HIV infection of the mother Sexually transmitted infections such as genital herpes (which can be passed on to the baby if the baby is born vaginally, but can usually be treated in with medication and do not require a Caesarean section) previous Caesarean section (though this is controversial – see discussion below) prior problems with the healing of the perineum (from previous childbirth or Crohn's Disease) Bi-corniute uterus Risks Risks for the mother: The mortality rate for both Caesarian sections and vaginal birth, in the Western world, continues to drop steadily. In 2000, the mortality rate for Caesareans in the United States were 20 per 1,000,000.[23] The UK National Health Service gives the risk of death for the mother as three times that of a vaginal birth.[24] However, it is misleading to directly compare the mortality rates of vaginal and Caesarean deliveries. Women with severe medical conditions, or higher-risk pregnancies, often require a Caesarean section which can distort the mortality figures. Risks for the child: This list is currently incomplete and should not be taken as comprehensive or reflective of current research. It covers some of the most commonly discussed risks to the child posed by the procedure itself rather than the medical indications that may 109 call for it. Some risks are rare, and as with most medical procedures the likelihood of any risk is highly dependent on individual factors such as whether other pregnancy complications exist, whether the operation is planned or done as an emergency measure, and how and where it is performed. Lower apgar scores/ neonatal depression: babies may experience a period of inactivity or sluggishness after delivery, possibly due to an adverse reaction to the anesthesia given to the mother Potential for infant injury: it is possible though very rare for surgical tools used for the uterine incision to injure the infant. Wet lung: retention of fluid in the lungs can occur if not expelled by the pressure of contractions during labor Potential for early delivery and complications: Pre-term delivery is possible if due date calculation is inaccurate. One study found an increased risk of complications if a repeat elective Caesarean section is performed even a few days before the recommended 39 weeks. Higher infant mortality risk: in c-sections which are performed with no indicated risk (singleton at full term in a head-down position), the risk of death in the first 28 days of life has been cited as 1.77 per 1,000 live births among women who had c-sections, compared to 0.62 per 1,000 for women who delivered vaginally Risks for both mother and child Due to extended hospital stays, both the mother and child are at risk for developing a hospital-borne infection Studies have shown that mothers who have their babies delivered by Caesarean take longer to first interact with their child when compared with mothers who had their babies vaginally. Incidence The World Health Organization recommends the rate of Caesarean sections between 10% and 15% of all births in developed countries. However, in 2004, the Caesarean rate was about 20% in the United Kingdom, while the Canadian rate was 22.5% in 2001-2002 In Italy the incidence of Caesarean sections is particularly high, although it varies from region to region. In Campania, 60% of 2008 births reportedly occurred via 110 Caesarean sections. In the Rome region, the mean incidence is around 44%, but can reach as high as 85% in some private clinics. In the United States the Caesarean rate has risen 48% since 1996,eaching a level of 31.8% in 2007.[36] A 2008 report found that fully one-third of babies born in Massachusetts in 2006 were delivered by Caesarean section. In response, the state's Secretary of Health and Human Services, Dr. Judy Ann Bigby, announced the formation of a panel to investigate the reasons for the increase and the implications for public policy. In Brazil's public health network, the rate reaches 35%, while in private hospitals the rate approaches 80%.[citation needed] China has been cited as having the highest rates of C-sections in the world at 46% as of 2008 Studies have shown that continuity of care with a known carer may significantly decrease the rate of Caesarean delivery[39] but there is also research that appears to show that there is no significant difference in Caesarean rates when comparing midwife continuity care to conventional fragmented care. Analyzing the rise in Caesarean section rates The US National Institutes of Health says that rises in rates of Caesarean sections are not, in isolation, a cause for concern, but may reflect changing reproductive patterns: The World Health Organization has determined an “ideal rate” of all cesarean deliveries (such as 15 percent) for a population. One surgeon's opinion is that there is no consistency in this ideal rate, and artifcial declarations of an ideal rate should be discouraged. Goals for achieving an optimal cesarean delivery rate should be based on maximizing the best possible maternal and neonatal outcomes, taking into account available medical and health resources and maternal preferences. This opinion is based on the idea that if left unchallenged, optimal cesarean delivery rates will vary over time and across different populations according to individual and societal circumstances. There has been a rapid growth in the number of c-sections performed. For example, there has been a fourfold increase from 1971 to 1991. (From 4.2 c-sections per 100 births). This may be accredited to the improved technology in detecting pre-birth distress. Malpractice has been looked into because of the rapid increase in c-sections. Some argue that the higher costs of c-section births compared to regular births make physicians quicker to recommend a c-section. Usually, if a doctor makes a 111 recommendation people are quick to take it to heart and act upon it. The effect of relative c-section price on c-section usage should be examined. However, some commentators are concerned by the rise and have noted several evidence-based studies. Louise Silverton, deputy general-secretary of the Royal College of Midwives, says that not only has society’s tolerance for pain and illness been “significantly reduced”, but also that women are scared of pain and think that if they have a Caesarean there will be less, if any, pain. It is the opinion of Silverton and the Royal College of Midwives that “women have lost their confidence in their ability to give birth." Silverton's analysis is controversial among some surgeons. Dr Maggie Blott, a consultant obstetrician at University College Hospital, London and then a Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) spokeswoman on Caesareans (and Vice President of the RCOG), responded: 'There isn't any evidence to support Louise Silverton's view that increasingly pain-averse women are pushing up the Caesarean rate. There's an undercurrent that Caesarean sections are a bad thing, but they can be life-saving. A previously unexplored hypothesis for the increasing section rate is the evolution of birth weight and maternal pelvis size. It is proposed that since the advent of successful Caesarean birth over the last 150 years, mothers with a small pelvis and babies with a large birth weight have survived and contributed to these traits increasing in the population. Such a hypothesis is based upon the idea that even without fears of malpractice, without maternal obesity and diabetes, and without other widely quoted factors, the C-section rate would continue to rise simply due to slow changes in population genetics. Elective Caesarean sections Main article: Elective caesarean section This section may stray from the topic of the article into the topic of another article, Elective_caesarean_section. Please help improve this section or discuss this issue on the talk page. (January 2011) Caesarean sections are in some cases performed for reasons other than medical necessity. Reasons for elective Caesareans vary, with a key distinction being between hospital or doctor-centric reasons and mother-centric reasons. Critics of doctorordered Caesareans worry that Caesareans are in some cases performed because they are profitable for the hospital, because a quick Caesarean is more convenient for an obstetrician than a lengthy vaginal birth, or because it is easier to perform surgery at a scheduled time than to respond to nature's schedule and deliver a baby at an hour that is not predetermined.[45] Another reason for doctors to recommend C-section is 112 money. In China, doctors are compensated based on the monetary value of medical treatments offered. As a result, doctors have an incentive to persuade mothers to choosing the more expensive C-section. In this context, it is worth remembering that many studies have shown that operations performed out-of-hours tend to have more complications (both surgical and anaesthetic).[46] For this reason if a Caesarean is anticipated to be likely to be needed for a woman, it may be preferable to perform this electively (or pre-emptively) during daylight operating hours, rather than wait for it to become an emergency with the increased risk of surgical and anaesthetic complications that can follow from emergency surgery. Another contributing factor for doctor-ordered procedures may be fear of medical malpractice lawsuits. Italian gynaecologyst Enrico Zupi, whose clinic in Rome Mater Dai was under media attention for carrying a record of caesarian sections (90% over total birth), explained: “We shouldn't be blamed. Our approach must be understood. We doctors are often sued for events and complications that cannot be classified as malpractice. So we turn to defensive medicine. We will keep acting this way as long as medical mistakes are not depenalized. We are not martyrs. So if a pregnant woman is facing an even minimum risk, we suggest she gets a C-section " Studies of United States women have indicated that married white women giving birth in private hospitals are more likely to have a Caesarean section than poorer women even though they are less likely to have complications that may lead to a Caesarean section being required. The women in these studies have indicated that their preference for Caesarean section is more likely to be partly due to considerations of pain and vaginal tone. In contrast to this, a recent study in the British Medical Journal retrospectively analysed a large number of Caesarean sections in England and stratified them by social class. Their finding was that Caesarean sections are not more likely in women of higher social class than in women in other classes. Some have suggested that due to the comparative risks of Caesarean section with an uncomplicated vaginal delivery, patients should be discouraged or forbidden from choosing it. Some 42% of obstetricians believe the media and women are responsible for the rising Caesarean section rates. Some studies, however, conclude that relatively few women wish to be delivered by Caesarean section. Anaesthesia Both general and regional anaesthesia (spinal, epidural or combined spinal and epidural anaesthesia) are acceptable for use during Caesarean section. Regional 113 anaesthesia is preferred as it allows the mother to be awake and interact immediately with her baby. Other advantages of regional anesthesia include the absence of typical risks of general anesthesia: pulmonary aspiration (which has a relatively high incidence in patients undergoing anesthesia in late pregnancy) of gastric contents and Oesophageal intubation. Regional anaesthesia is used in 95% of deliveries, with spinal and combined spinal and epidural anaesthesia being the most commonly used regional techniques in scheduled Caesarean section.[54] Regional anaesthesia during Caesarean section is different to the analgesia (pain relief) used in labor and vaginal delivery. The pain that is experienced because of surgery is greater than that of labor and therefore requires a more intense nerve block. The dermatomal level of anesthesia required for Caesarean delivery is also higher than that required for labor analgesia. General anesthesia may be necessary because of specific risks to mother or child. Patients with heavy, uncontrolled bleeding may not tolerate the hemodynamic effects of regional anesthesia. General anesthesia is also preferred in very urgent cases, such as severe fetal distress, when there is no time to perform a regional anesthesia. Vaginal birth after Caesarean Main article: Vaginal birth after caesarean While vaginal birth after Caesarean (VBAC) are not uncommon today, their numbers are shrinking. The medical practice until the late 1970s was "once a Caesarean, always a Caesarean" but a consumer-driven movement supporting VBAC changed the medical practice. Rates of VBAC in the 80s and early 90s soared, but more recently the rates of VBAC have dramatically dropped owing to medico-legal restrictions. In the past, Caesarean sections used a vertical incision which cut the uterine muscle fibres in an up and down direction (a classical Caesarean). Modern Caesareans typically involve a horizontal incision along the muscle fibres in the lower portion of the uterus (hence the term lower uterine segment Caesarean section, LUSCS/LSCS). The uterus then better maintains its integrity and can tolerate the strong contractions of future childbirth. Cosmetically the scar for modern Caesareans is below the "bikini line". Obstetricians and other caregivers differ on the relative merits of vaginal and Caesarean section following a Caesarean delivery; some still recommend a Caesarean routinely, others do not. In the US, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) modified the guidelines on vaginal birth after previous 114 Caesarean delivery in 1999 and again in 2004. This modification to the guideline included the addition of the following recommendation: Because uterine rupture may be catastrophic, VBAC should be attempted in institutions equipped to respond to emergencies with physicians immediately available to provide emergency care. This recommendation has, in some cases, had a major impact on the availability of VBACs to birthing mothers in the US. For example, a study of the change in frequency of VBAC deliveries in California after the change in guidelines, published in 2006, found that the VBAC rate fell to 13.5% after the change, compared with 24% VBAC rate before the change.[58] The new recommendation has been interpreted by many hospitals as indicating that a full surgical team must be standing by to perform a Caesarean section for the full duration of a VBAC woman's labor. Hospitals that prohibit VBACs entirely are said to have a 'VBAC ban'. In these situations, birthing mothers are forced to choose between having a repeat Caesarean section, finding an alternate hospital in which to deliver their baby or attempting delivery outside the hospital setting. Intrauterine hypoxia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Intrauterine hypoxia (IH, and birth asphyxia) occur when the fetus is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen. IH is used to describe inadequate oxygen availability during the gestation period, birth asphyxia (also referred to as perinatal asphyxia or Asphyxia neonatorum ) can result from inadequate supply of oxygen immediately prior to, during or just after delivery. There is considerable controversy over the diagnosis of birth asphyxia due to medicolegal reasons.[1][2] Because of its lack of precision, the term is eschewed in modern obstetrics.[3] IH may be due to a variety of reasons such as cord prolapse, cord occlusion, placental infarction and maternal smoking. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) may cause or be the result of hypoxia. Birth asphyxia may result due to prolonged labor, breech delivery in full-term infants; placental abruption, and maternal sedation in premature infants. Oxygen deprivation is the most common cause of perinatal brain injury.[4] Intrauterine hypoxia and birth asphyxia can cause hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy which is cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) from inadequate oxygen. This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the fetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary or as a 115 contributing risk factor in numerous neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as epilepsy, ADHD, eating disorders and cerebral palsy. " The problem of perinatal brain injury, in terms of the costs to society and to the affected individuals and their families, is extraordinary." (Yafeng Dong, PhD)[5][6][7][8][9][10] Contents [hide] • 1 Cause • 2 Epidemiology • 3 Financial Costs o 3.1 Medicolegal • 4 References • 5 External links [edit] Cause There are various causes for intrauterine hypoxia (IH). The most preventable cause is maternal smoking. Cigarette smoking by expectant mothers has been shown to have a wide variety of deleterious effects on the developing fetus. Among the negative effects are carbon monoxide induced tissue hypoxia and placental insufficiency which causes a reduction in blood flow from the uterus to the placenta thereby reducing the availability of oxygenated blood to the fetus. Placental insufficiency as a result of smoking has been shown to have a causal effect in the development of preeclampsia. While some previous studies have suggested that carbon monoxide from cigarette smoke may have a protective effect against preeclampsia, a recent study conducted by the Genetics of Pre-Eclampsia Consortium (GOPEC) in the United Kingdom found that smokers were five times more likely to develop preeclampsia.[11] Nicotine alone has been shown to be a teratogen which affects the autonomic nervous system, leading to increased susceptibility to hypoxia-induced brain damage. Maternal smoking, a preventable cause of intrauterine hypoxia. [12][13][14][15][16][17] Maternal anemia in which smoking has also been implicated is another factor associated with IH/BA. Smoking by expectant mothers causes a decrease in maternal nucleated red blood cells (NRBC), thereby reducing the amount of red blood cells available for oxygen transport.[18][19][20] 116 The perinatal brain injury occurring as a result of birth asphyxia, manifesting with-in 48 hours of birth, is a form of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Treatment of infants suffering birth asphyxia by lowering the core body temperature is now known to be an effective therapy to reduce mortality and improve neurological outcome in survivors, and hypothermia therapy for neonatal encephalopathy begun within 6 hours of birth significantly increases the chance of normal survival in affected infants. [edit] Epidemiology Disability-adjusted life year for birth asphyxia and birth trauma per 100,000 inhabitants in 2002 In the United States intrauterine hypoxia and birth asphyxia was listed as the tenth leading cause of neonatal death. Sudden infant death syndrome in which fetal hypoxia has been shown to be a key factor is the third leading cause of death. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that globally, between four and nine million newborns suffer birth asphyxia each year. Leading to an estimated 1.2 million deaths and about the same number of infants who develop severe disability. WHO estimates for global neonatal deaths caused by birth asphyxia are 29%.[21][22] Financial Costs Intrauterine hypoxia or birth asphyxia IH/BA was the ninth most expensive medical condition treated in U.S. hospitals by average hospital cost and resultant hospital charge.[23] IH/BA is also a causitive factor in cardiac and circulatory birth defects the sixth most expensive condition, as well as premature birth and low birth weight the second most expensive and it is one of the contributing factors to infant respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) also known as hyaline membrane disease, the most expensive medical condition to treat and the number one cause of infant mortality.[24][25][26] Meconium aspiration syndrome From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search Meconium aspiration syndrome Classification and external resources Micrograph of fetal membranes with meconium-laden macrophages, a finding that may accompany meconium aspiration. H&E stain. 117 Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS, alternatively "Neonatal aspiration of meconium") is a medical condition affecting newborn infants. It occurs when meconium is present in their lungs during or before delivery. Meconium is the first stool of an infant, composed of materials ingested during the time the infant spends in the uterus. Meconium is normally stored in the infant's intestines until after birth, but sometimes (often in response to fetal distress) it is expelled into the amniotic fluid prior to birth, or during labor. If the baby then inhales the contaminated fluid, respiratory problems may occur. Contents • 1 Classification / Definitions • 2 Signs and symptoms • 3 Causes • 4 Pathophysiology and Mechanism • 5 Diagnosis • 6 Prevention and Screening • 7 Treatment • 8 Prognosis • 9 Epidemiology • 10 History • 11 Research directions • 12 See also • 13 References • 14 External links Classification / Definitions Signs and symptoms The most obvious sign that meconium has been passed during or before labor is the greenish or yellowish appearance of the amniotic fluid. The infant's skin, umbilical cord, or nailbeds may be stained green if the meconium was passed a considerable 118 amount of time before birth. These symptoms alone do not necessarily indicate that the baby has inhaled in the fluid by gasping in utero or after birth. After birth, rapid or labored breathing, cyanosis, slow heartbeat, a barrel-shaped chest or low Apgar score are all signs of the syndrome. Inhalation can be confirmed by one or more tests such as using a stethoscope to listen for abnormal lung sounds (diffuse crackles and rhonchi), performing blood gas tests to confirm a severe loss of lung function, and using chest X-rays to look for patchy or streaked areas on the lungs. Infants who have inhaled meconium may develop respiratory distress syndrome often requiring ventilatory support. Complications of MAS include pneumothorax and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Causes Fetal distress during labor causes intestinal contractions, as well relaxation of the anal sphincter, which allows meconium to pass into the amniotic fluid and contaminate the amniotic fluid. Meconium passage into the amniotic fluid occurs in about 5-20 percent of all births and more common in overdue births. Of the cases where meconium is found in the amniotic fluid, meconium aspiration syndrome develops less than 5 percent of the time.[1] Amniotic fluid is normally clear, but becomes greenish if it is tinted with meconium. Pathophysiology and Mechanism The pathophysiology of MAS is due to a combination of primary surfactant deficiency and surfactant inactivation as a result of plasma proteins leaking into the airways from areas of epithelial disruption and injury.[2] The leading three causes of MAS are 1. Due to physiologic maturational event,[3] 2. A response to acute hypoxic events,[3] and 3. A response to chronic intrauterine hypoxia.[3] If an infant inhales this mixture before, during, or after birth, it may be sucked deep into the lungs. Three main problems occur if this happens: • the material may block the airways • efficiency of gas exchange in the lungs is lowered • the meconium-tainted fluid is irritating, inflaming airways (pneumonitis) and possibly leading to chemical pneumonia. 119 These can lead to possibly fatal or long term health problems for the infant.[3] Diagnosis This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. Treatment Amnioinfusion, a method of thinning thick meconium that has passed into the amniotic fluid through pumping of sterile fluid into the amniotic fluid, has not shown a benefit in treating MAS .[5][6] Until recently it had been recommended that the throat and nose of the baby be suctioned by the delivery attendant as soon as the head is delivered. However, new studies have shown that this is not useful and the revised Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines published by the American Academy of Pediatrics no longer recommend it.[citation needed] When meconium staining of the amniotic fluid is present and the baby is born depressed, it is recommended by the guidelines that an individual trained in neonatal intubation use a laryngoscope and endotracheal tube to suction meconium from below the vocal cords.[citation needed] If the condition worsens to a point where treatments are not affecting the newborn as they should, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) can be necessary to keep the infant alive.[7] HIV-infection transmission From mother to child Etiology, epidemiology and HIV-infection diagnostics The situation at peace with HIV-infection, may be defined as pandemic and to put in line with two world wars, as in respect of a number of carried away lives, and on damage at, which the it inflicts society. On WHO figure, on 2002. The amount HIV infected peoples in the world achieved 42 million the man. Only during this past year became infected HIV - 5 million. The man and 3, 1 million - died from AIDS. Daily in the world infected roughly 16000 men. The peoples mortality of young age from AIDS occupies the first place among all reasons for mortality rate of this age bracket of population. 48% victims AIDS made up woman, every fifth deceased from this disease - the child. 120 Most first cases of new infection were registered by the centre on control over diseases US (CDC ) in 1981 among young homosexual, casual the carinii pneumonia or the Kaposhi sarcoma. At most of them was found ton - the cell immunodeficiency, caused by the hIV - HIV. First the HIV-infection was described in its final stage, received later the name <the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome> (AIDS ). The presupposition about infectious ens morbi was expressed already in June 1982. In future it turned out that the cases AIDS have been found at drug user, drug injectors intravenously, prostitutes; peoples, haemophiliac and receiving the replacement therapy by preparations, received from donors blood; faces, received the transfusion of donor blood; childrens, born from mothers from some of risk group; sexual partners, AIDS patients. Etiology Due to of changeability can arise strains, differing on many characteristics, including on stability and susceptibility to different AntiRetroviral agents. Cause of development of AIDS, largely, is more pathogenic and contagious HIV1. In 1986 French scientists in western regions of Africa pathogenic for man the retrovirus was found, which caused t-lymphocytes defeat. Has been requested to call its HIV -2. It has been found that it is independent virus, causing the AIDS. It, largely, Is discovered at countries inhabitants of West Africa, is less pathogenic and under contagious. Subject to structure of individual fragment of env gene now separate "the subtypes" of virus, designated capitals of roman alphabet А-Н, about and so on . Subtypes HIV with unequal frequency separate in the different period of time on different territories (to Ukraines and Eastern Europe - but in, with; in Russia - but in, with, D, G, H ). In different the population groups, stricken HIV, may predominate the different subtypes of virus: and - among faces, user injection drugs, in - when homo- and heterosexual contacts ). Obvious connection certain subtype with clinical symptoms disease or variant its current while is elusive The hIV (HIV ) regard to lentiviruses subfamily ( word ribbon means slowed down, long-term ) retroviruses families. Salient characteristics of retroviruses are the unique structure of genom and the ferment presence - reverse transcriptase (the RNAdependent DNA-polymerase ). The attendance of reverse transcriptase or reverse 121 transcriptase in virus structure provides the back orientation of stream of genetic information: not from DNA to rna, but on the contrary, from rna to DNA. Virus structure When high-resolution electron microscopy microscop has the икозаедрическую structure, keeps 72 external convexities (the glycoprotein thorns ). The convexities consist of several basic proteins, coating the HIV1 - gp120, gp41, GP160. The virus core was formed from several proteins, one of them - p24. gp120 the glycoprotein HIV1 has the affinity with surface proteins of t-lymphocytes most and macrophages Introduction phases HIV in the cell HIV - obligate intracell micro-organism. Tentatively it's proven that the introduced in the bloodstream the alive culture HIV, not being able to penetrate in cells, dies for 15 minute. Its the replication (reproduction ) occurs proper interior of host cells. The process this begins by <recognition> virion (extracellular form of virus ) the target cells and the ingresses into her. Target cell marker, which permits virion <to enquire> and to find such cell, is located on its surface the receptor СD4+. The reproduction HIV is bound only with certain cells. It is assumed that the virus can actively penetrate in cells, at the surface of which is the receptor СD4+, with which the it взаимодействует. This receptor carry largely the cells, circulating in blood, lymphomas and tissue liquid, and also associated with nonspecific elements of nerve tissue. However reliable methods the fact of active reproduction HIV was found only in lymphocytes and some cells of macrophagal-monocytar number of, that provides evidence about mandatory participation of these cells in development of infectious process. The complete viral life cycle is realized fairly rapidly, all for 1-2 day; per day forms up to 1 milliards of viral particles, these is why for the long period in the body may accumulate the substantial quantity of mutant variants HIV. Hitting in the body, the virus very quickly is multiplied in cells of mononuclear system of peripheral blood. Arises the viremia. The due to the fact that the surface proteins of viruses and host cell complementar, the viruses attack cell-host and phagocyted by it. The t helpers, Monocytes /Macrophages and the microglia cells of cell, having the affinity of cell receptors to HIV1, are called <CD4+>. The antigen of gp120 account for interaction between virus and cell-host. 122 After fastening to CD4+ the molecule of gp120 transfers to, bringing about enzymatic the reaction, which <opens> certain the site of gp41, required for virus infiltration in the cell. p41 call <receptor protein>. Reverse transcription and viral replication Following virus introduction in the cell occurs the penetration it in cytoplasm of host cell. The virus produces DNA, employing as of gauge own rna accompanied by duplication in the double-stranded structure. The reverse transcriptase is those by the ferment, which gives retroviruses the unique chance to synthesize DNA, employing rna as sample. To DNA is transported in nucleus and is integrated in chromosomal DNA (the provirus ). The virus becomes by the cellular element and will remain by it up to cell death. In future occurs the virus infiltration from cell in the cell forming of многоядерного cell syncytium Virus stability in the environment. In environment, when drying of lymphoid cells, infected with HIV the viral activity vanishes during several days. When drying of cell-free fluid with the addition of human plasma the virus dies at a temperature of 23-27 degrees through 7 days. In liquid medium at a temperature of 23-27 degrees the virus keeps the activity within 15 day, when 36-37 degrees - 11 days. In blood, intended for transfusion, the virus experiences years, and in frozen sera its the activity remains up to 10 years. Heating to 56° causes its the inactivation through 30 mine, up to 70° - through 10 mine; when boiling the virus dies through 1-2 minute. Usual dips, such as 3% the solution of hydrogen peroxide, 5%раствор of lysol, 0, 2% sodium hypochlorite, 1% the solution of gluteraldehyde, 70% the ethanol, the ester, the acetone, destroy the virus in environment. Equally, HIV is resistant to action of ultra-violet rays and ionizing radiation, remains in dry kind of 4-6 days at a temperature of 220С. Epidemiology The HIV-infection, with epidemiologic view, enters the category of grave infection and it is considered by the антропонозным disease. Source of infection are the medium of hIV. The carriage of virus may last from 3 months up to 10 years and more. In the body infected man HIV is found in the most in blood, cerebrospinal fluid, lymphoid tissue, brain, sperm, vaginal секрете, catamenial blood, грудном milk, and in smaller concentrations - in lacrimal fluid, saliva, секрете sweat glands. On degree of infective risk the biological fluids are being distributed by the as follows: most the great danger has HIV infected the blood (for contamination fairly 0, 1мл of infected 123 blood ), - the sperm, the vaginal secret, the cerebrospinal fluid further go. Such biological fluids, as the perspiration, the saliva, the urine, the lacrimal fluid, and also the fecals keep so few virus, that contamination from them is not likely. Transmission mechanism Transmission mechanism of HIV-infection - contact. The HIV-infection is transmitted by the natural and artificial ways. By this time it's been proven the existence three of transduction pathways of hIV: 1. When sexual contacts - naturally 2. Vertical - from mother to fruit or child - naturally 3. Parenteral - when blood transfusion from HIV infected face, use of blood components, when tissue transplantation or bodies, and also when cooperative use of one and the same syringes and needles for injections without preliminary sterilization - artificial way. Gender route of infection is realized when hetero- (the man and woman ) and homo(man, having the sex with men ) sexual contacts. Vertical way - cession from HIV infected mother to fruit during pregnancy, labors and child when feeding by the грудным milk. Is realized as by means of transplacental transfer (during pregnancy ), and intrapartum mechanism (during labors ), and also postnatally - during breast feeding. Parenteral way - when blood transfusion and its components, transplantation of organs and tissues, in result of exploitation infected needles, syringes, non axenic medical instruments. The parenteral way infecting is realized also among consumers of injection drugs, the drug injectors intravenously. Cession factors in this case can be as not aseptic common syringes and the needles, and itself drug, in which blood with the objective it < cleaning> is added to. The possibility of virus transmission in Bytom through the infected razor sets, and other колюще-режущие items was not ruled out. When domestic contacts the virus can be transferred also through items of personal sanitation, contaminated with blood remainders (the tooth brush, the blades for shaving, sharp and the acute cutting devices when procedures with integrity violation of dermal covers, the manicure, the pedicure ). In the same time contamination it is impossible through common crockery; when sailing in the basin, use by the toilet facility etc.. 124 The virus transmission of HIV-infection through bites of bloodsucking insects (louse, flea, the gnats ) is not evidenced. The cession probability of HIV-infection high when oneshot contact with non axenic multitime tools for manipulations. Recipient contamination when transfusion HIV infected blood is 90 %. ion when transfusion HIV - infected blood is 90 %.When sexual contact cession probability HIV are significantly lower. Infecting in medical institutions it is possible when transfusion contaminated with blood, its preparations, repeated usage contaminated with blood of medical instruments (syringes, intravascular катетеров, gynecological mirrors, hog, endoscopes, surgical and other implements ), not past corresponding the handling. With the objective of warning of intrahospital cession of HIV-infection of it is necessary each referred for medical help to consider, as potential bearer of hIV. To use syringes, the needles, the systems, the instrument of nonreusable. Strictly abide by rules of disinfecting, pre-sterilized cleaning and sterilization of medical and laboratory instrument of multitime the use. When rendering of all types of medical help they is necessary strictly to observe the precautionary measures. Each medical worker ЛПУ when delivery of health care sick has to remember about danger of infection by HIV. in each branch office of permanent establishment the medical instruments must обеззараживаться, be held the cleaning before sterilization. The medical workers must abide by the rule of disinfecting and sterilization, in order not to get infected virus. In workplace of medical workers must be extract from directive documents, leads, methodological manuals Ministry of Health of Republic of Uzbekistan. when conducting the medical the manipulation in order to avoid contamination by the HIV-infection it is necessary the exercise caution, all manipulation should be held obligatory in rubber gloves, special protective clothing (the bathrobe, the mask 4-5 layer, when appropriate the goggles ). Acute cutting and the piercing instruments to the extent possible use are smaller than. For the prevention hit blood of sick on the skin, the mucosa and damaged area they is necessary to observe following regulations: Damaged area of personnel skin (the scratches, the cracks, the cuts, the abrasions ) to close band-aid; To put on goggles, the mask, if the blood spraying or liquid the internal environments, and also when manipulations with blood samples and sera is supposed; Up to dispatch in lab the blood samples and liquid the internal environments must be placed in containers or in Bixa with dependable caps. 125 HIV induced immunopathogenesis Driving link of immunodeficiency pathogenesis when HIV-infection is t helpers defeat, which serve by the key link in circuit and humoral, and cellular immune response. In immunodeficiency pathogenesis it is possible schematic to select two stage: 1. The phased quantity reducing of CD4+ of cells - corresponds clinically latent disease stage; 2. The catastrophic quantity reducing of CD4+ of cells - corresponds clinically expressed illness stage. The transition to quick disease progression link with the fall of cytolytic activity of CD8+ of cells - t suppressors About HIV-infection прогрессировании judge by number change of lymphocytes CД4 and viral the burden (hv ). When HIV actively are multiplied, it infects and kills lymphocytes CД4, which Play the crucial role defence of organism from infections. On the activity of HIVinfection judge by number lowering of lymphocytes СД4. Viral burden is virus concentration in blood. Its it is possible to measure in blood sample by means of polymerase chain reaction to the ribonucleic acid HIV (PCR on rna HIV ). The viral burden achieve very high level shortly after infection by HIV. with the advent of antibodies to HIV it drop sharply, however in several year, when the lymphocytes number CD4+ decreases, it again grow. Higher viral burden, higher are cession risk HIV. The lymphocytes number of CD4+, and the viral burden serve by findings HIVinfection progression. Less cell number CD4+ in the body those is heavier than stage HIV infection. The high level hv is marked when primary infecting and when advanced stage HIV infection, when the lymphocytes number CD4+ is reduced. When primary infecting HIV, when in the body the antibodies to virus are lacking, the infection fast extends in the body, reaching ceiling level of number hv. this period is called by the acute retroviral syndrome. Within this period Attu in blood may not emerge, but the man is source of infection <the window period>. 126 Through 2-6 weeks after infecting in the body are starting to crop up antibodies to HIV and their availability becomes eventual to define serological methods. Usually, through 3 months at most infected it can be determined antibody to HIV. further the level of viral burden is reduced. The cells level CD4+ is stabilising, - the organism elaborates larger amount of lymphocytes in exchanges destroyed by the virus. This period may last years - the stage of asymptomatic current. The stage of development of AIDS comes, the when viral burden start growing, and the cell number CD4+ is reduced. Seroconversion - penetration HIV in the body, antibody production. The asymptomatic stage - the symptom absence of HIV-infection, the immune system hinders the virus duplication. May appear as generalizated by the lymphadenopathy. The symptomatic stage - appear the clinical symptoms of HIV-infection, some oppression of immune system. Most frequently this occurs by the weight loss; easy by the leather damages and mucous; shingle; recurrent by the upper respiratory tract infections; diarrhoea of agnogenic by the duration more 1 month; fever of agnogenic (constant or recurrent ) duration more 1 month; candidiasis of mouth cavity; hairy leucoplakia of mouth; heavy bacterial infections (for example pneumonia, purulent myositis ). AIDS - the terminal illness stage, is characterized by the disease developing HIV related study. Clinic HIV-infection is cureless, long-time elapsing disease. Executed supporting the antiretroviral therapy and treatment of opportunistic infections extends and improves the living standard of sick. The clinic course of the disease in childrens and adults have its features . The period of acute the HIV-infection (primary infecting HIV ) may be asymptomatic, roughly at 50% sick the acute mononucleossimilar syndrome is developing, which is going on 2 up to 6 weeks. Consecutive the acute infection is characterized viral replication, as evidenced by the high level виремии and p24 антигенемии. After 2nd up to 8th week, the level виремии decreases greatly. Although some the effectiveness of primary immune answer to introduction HIV, it is not able to discharge unconditionally the organism from virus. 127 In the latent period usually not is seen signs of a disease, except for lymphadenopathy. In practice all lymphoid system is going to be vast in scope reservoir of actively replicated viruses, in spite of a low level виремии. The discrepancy interlevel the virus replication in peripheral blood and lymphoid tissue are taking place. Disease progression, the distribution HIV in lymphoid tissue cause the violation its structure. This stage is characterized by the immunity activating. The chronical activating of T-cell link of immunity, including CD4+ cells, creates the favourable conditions for virus replication. Gradually occurs the level reduction of CD4+ of T cells and the increase in the number of CD8+ of T cells. CD8+ T cells - t suppressors faction - cytotoxic lymphocytes, bearing on its membrane receptor of CD8+. Usually CD4+ the cells is 65% t-lymphocytes of peripheral blood, CD8+ of cell - remaining 35%. Normal correlation from 1, 8 up to 2, 2. This correlation is reduced or becomes back in the patient the HIV-infection. Symptomatic stage. The when absolute amount of CD4+ of t-lymphocytes is reduced lower 500, minimum the violation of immune response clinically demonstrate, that occurs by cutaneus infections, caused by herpes zoster, oral or vaginal candidiasis, allergic cutaneous reactions. Disease progression from acute infection up to AIDS may continue more than 1 year up to 15 years. With quantity reducing of CD4+ of cells immunological "the control" of HIV-infection becomes less effective, increases the viruses amount, that in turn, the level of CD4+, that, ultimately still reduces, the immune answer to the opportunistic infections makes impossible. In terminal disease stage the amount of CD8+ also is reduced, after leaving the organism without each defense against uncontrollable viral replication. Almost at all HIV - positive peoples since the clinical symptoms of HIVinfection and in the long run, AIDS - its the late stage are developing. As progression HIV-infection the lymphocytes number СД4+ continues come to down, and the susceptibility to opportunistic infections grow. The opportunistic infections are prompted by the harmless for normal man by micro-organisms, which is able to provoke the disease only against immunodeficiency. For example among HIV infected prevail the carinii pneumonia. Deployed the HIV-infection stage is characterized by opportunistic infections easy, brain, eyes and other bodies. At the stage AIDS the carinii pneumonia, the cytomegalovirus infection, the toxoplasmosis, the candidiasis, the cryptosporidiosis, the histoplasmosis, other 128 parasitic, viral and fungus infections, and also some kinds of malignant neoplasms, for instance the Kaposi sarcoma often are developing. Besides immune system, HIV the cells of brain, intestine and heart directly hits. Clinically this may appear as disturbance of function bodies data. These conditions are developing when high viral burden, i. e. when late the illness stages. One of frequent symptoms - the fatigue, which can be connected with defeat of cardiac muscle. The violation intestinal absorption leads to depletion and cachexia, what can contribute to accession of enteroinfections. The lowering of cognitive human abilities with HIV/AID in their turn can be connected with brain damage. АRV Therapy Facilitates number conservation of lymphocytes CD4+ and cutback of viral the burden, increases the duration of asymptomatic stage of HIVinfection and finally, offensive AIDS moves aside. Now the preparations are lacking, which could fully to remove HIV from organism, but the drugs - the antiretroviral therapy (automatic excitation control ) lifetime and the chronic administration of which are available, permits to suppress the virus duplication in the body to a level, allowing to keep the immune system and to delay the development of AIDS over the long term (no data on duration bounds of this period ). Method of laboratory diagnosis 1 The immunoenzyme analysis (IEA) 2. The express (quick ) the tests 3.The immunoblotting (the western blot ) 4. Polymerase chain reaction method (PCR ). Risk groups on HIV - infecting among pregnant • Faces, user drugs intravenously now or previously. • The faces, having the sexual contacts with partners, which used or make use drugs intravenously, with HIV infected, and also with blood recipients and bodies (without examination ). • Blood recipients and bodies. • Woman, which was being conducted the artificial insemination (without donors examination 129 • Face, having the clinical features AIDS-related complex. • Pregnant with associated diseases, passed by the genital tract (sexually transmitted disease ). • Woman, having HIV infected childrens. • Pregnant, having the professional contacts stained with blood. • Woman, having several sex partners. The frequency of virus transmission from HIV infected mother to fruit is 21 up to 40% in the absence of treatment and от1 up to 10-12% when care delivery. Ways of virus transmission It's been proven the cession possibility HIV from mother to fruit through the following routes: • Transplacentary; • Blood-borne; • Rising through amniotic sacs or amniotic fluids; • Iatrogenic way when diagnostic invasion manipulations; • When pectoral feeding. The vertical transmission HIV can come about: • During pregnancy, in any trimester of pregnancy, • During delivery parturition • When грудном feeding. The frequency of perinatal transmission HIV is introduced on scheme. 60% - cession during labors 20% - during pregnancy 20% when грудном feeding Risk factors of perinatal transmission HIV: Mother 130 • Condition of mother's health • Drug use • Alcohol abuse • Nutrition full value condition • Low level витаминаА • Absence of antiretroviral therapy • Presence sexually transmitted diseases Breast feeding - 12-20% 002 breast feedingObstetric factors • Placenta condition • Anhydrous period more 4 hours • Bleeding in labors • Хорионамнионит • Pre-term deliveries • Invasion monitoring (precarious vaginal inspections and so on ) • Amniotomy, episiotomy • Obstetrical forceps, vacuum extractor • The mode of delivery (Caesarean section ) Virological (when ВИЧ-2 transmission - 1% ) Fruit • Prematurity • Skin integrity and mucous • Condition of digestive tract • Ripeness of immune system Risk of perinatal the infecting is going up, if: 131 • Amount of viral copies> 10 000 in 1 microliter • Amount of CD 4+ <500-600 in 1 microliter • Changing of the correlation of CD 4+/CD 8+ <1, 5 (rate 2: 1 ) • Presence sexually transmitted diseases, TORCH - infections at mother ( Cervical-Vaginal infection ) • ChorionAmnionitis • Placental deficiency • Inflammatory change in placenta • Anhydrous period more 4 hours • Duration of act of delivery • Application of invasion monitoring • Amniotomy, episiotomy • Breast feeding • Vaginal Mechanism of perinatal cession The precision mechanism of perinatal cession remains non-elucidated. It is known, that if the virus transmission occurs in first trimester, the pregnancy ends by the abortion. The virus transmission in more the late pregnancies is more amenable to therapies by антиретровирусными preparations, which passes through placenta. The risk infecting is going up shortly before labors and during labors - 60%, that is important when assigning the preventive therapy. Aftermaths of antenatal HIV-infection: when intrauterine infecting reliably more often is registered Delay of intrauterine foetal development ( DIFD ), conditioned by the violation of фетоплацентарного blood circulation Flow peculiarities of pregnancy and births at HIV infected of женщи • Increase in the number of pre-term deliveries, • Premature rupture of amniotic fluid sac, 132 • Birth premature and immature childrens Application of antiretroviral preparations during pregnancy: • The decision concerning treatment during pregnancy must be taken most woman after condition discussion its health and therapy advantages for fruit • The woman, within first trimester of pregnancy may delay launched care deliveries after 10-12 week of intrauterine growth, because in period of organogenesis the embryo is most susceptible to teratogenic drug actions Infecting when грудном feeding: • The breast milk may be the source several infections, including the cytomegalovirus, the HIV-infection and other. • HIV was drawn from pectoral the milk HIV infected women. The nucleic acids of virus have been identified by the method in cells and extracellular educations, containing both in colostrum, and late milk. • In грудном milk HIV infected the specific antibodies to HIV (IgA, IgM ) were found, when these antibodies still was not determined in blood sera. • By the most effective ways to avoid contamination through breast milk is of abandon it. • Data approach is recommended in the U. S. and elsewhere, where the risk of disease of child when artificial feeding relatively low. • Artificial feeding reduces the transmission risk of HIV-infection and other infectious diseases. • The possibility of thermal processing of pectoral the milk is дискутабельным • Infecting through breast feeding is important problem, because more 20% cases of perinatal contamination are linked to this transduction pathway of HIV-infection Rejection of breast feeding: • In many developing countries the substandard risk of infectious diseases and heavier run of the disease among those childrens is marked, who does not вскармливается breast. When artificial feeding in 1, 5 - 5 times grows the mortality. This is why the rejection of breast feeding, as the method of preventing not is very popular. But most important of negative risk of breast feeding when HIV-infection is HIV-infection. 133 • Infecting HIV through breast milk - the significant route of infection, and this is why to solve this problem is needed the preclusive strategics. Assumed the transmission mechanism of HIV-infection during labors: • Direct contact between skin and mucosa of baby and шеечно-влагалищными secrets of mother. • Virus absorption of these secrets. • Rising infecting of amniotic fluid. • In gestation period can come about four the multiple growth of level HIV in шеечно-влагалищных secrets. Higher the coefficient infecting baby, born first their twins, it is possible, is explained more protracted exposure to infected secrets. • Evidently, the length of labor has no such importances, as the duration violation of fetal membranes. • In a variety of examining the long-run disturbance of fetal membranes associate with risk increase of cession, and it's proven that the anhydrous period above 4 hours increases the risk infecting almost twice, regardless of finite mode of delivery Choice of tactics of родоразрещения when HIV-infection The rational generation of delivery parturition tactics together based on antiretroviral therapy may essentially reduce the level of vertical transmission HIV. • Planned Caesarean section together with antiretroviral therapy provides the additional protection. • In womens, receiving in gestation period the long-term course of antiretroviral treatment, which was held planned Caesarean section, the cession HIV from mother to child made up less 1%, when natural maternal passage Tactics of natural maternal passage for HIV infected • Should avoid long-term anhydrous period, because the cession HIV from mother to child grows when anhydrous period more 4 hours 2 time. • Shouldn't complications. prosecute amniotomy, if the labors are leaking without • Should avoid any procedures, in which the dermal covers break down or the contact possibility of fruit with maternal blood (invasion monitoring ) is going up. 134 • Shouldn't prosecute the episiotomy or the perineotomy, the as routine technique. • To avoid superposition of obstetrical forceps, vacuum extractor • Not desirably carry to out the inducing delivery and birthincrease. • To carry out the sanitation of maternal passages over all act of delivery (2% chlorhexidine solution each 2 hours ). • Newborn of desirably to wash in disinfecting or soap solution, to avoid skin lesions and mucous. • To carry out on акушерским indications or elective in planned procedure until starts of birth activity and membranes break, weighing risks to mothers, the presence of available treatments, the condition of mother's health and the forecast for Caesarean section fruit Conducting feature of hemostatic Caesarean section • Caesarean section was conducted on 38 weeks of gestation up to breaking of the water and launched birth activity. • Preferably carry to out the longitudinal slit frontal abdominal wall. • To use the clamps for vessels. • The cut on uterus to generate scissors, in order not to mar amniotic envelope. • Up to fruit extraction is superimposed on the continuous suture on cut on uterus - the hemostatic suture. • After placing a suture, the surgeon changes glove and coats the wound by sterile gauze napkins. • Is produced the puncture and exhausting of amniotic fluid - the child is being born by the dry Recommendations for level reduction of vertical transmission HIV • For level reduction of vertical transmission HIV high-active antiretroviral combined therapy is recommended. • The viral burden must be determined throughout the whole pregnancy. 135 • Prior (elective ) Caesarean section reduces the level of vertical transmission in womens, which did not get antiretroviral therapy and the viral burden of which was not determined • When viral burden more 1000 копий/мл it is possible commend to select prior Caesarean section. • When low viral burden, less 1000 advantages копий/мл Caesarean section is not evidenced. • The role Caesarean section in lowering of vertical transmission HIV is not evidenced, if it is performed with labors beginning or after breaking of the water. • They is necessary to inform women concerning choice of method of delivery parturition, as regarding of risk, connected with оперецией, and method predominances for preservation of health Caesarean section of child Possible strategy for risk decrease of perinatal transmission HIV • Confidential counselling and voluntary test on HIV. • Alternative feeding of newborn • Antiretroviral therapy. • Additive of vitamin A • Treatment of anemia at HIV of positive pregnant of destination track of irons doping and folic acid • Diagnostics and treatment sexually transmitted disease. • Washing of parturient canal during labors and delivery • The delivery parturition by the operation way Caesarean section. • Use of non-invasive methods акушерской help. • Other medical services for pregnant womens: opportune diagnostics of complications of such as eclampsia, bleedings, anaemia; immunization against tetanus; infection preventing during delivery parturition and after births of children at mother and newborn; safe delivery parturition • Provision of services of family-planning, reproductive election. • Lifestyle change (rejection of drugs, smoking, taking alcohol 136 In increasing numbers of women, living with HIV/AID, want to keep the pregnancy and to give the life healthy child; free from HIV-infection. However, unless to undertake no actions, the cession risk HIV from child mother (proton magnetic resonance ) in childrens, being on artificial feeding, is 15-30%; breast feeding raises the risk up to 20-45% (1 ). The child may get infected HIV during pregnancy, during labors and when nursing. Today there are the efficient methods ППМР. Where these methods are available and shall be used, the frequency proton magnetic resonance manages to create reduce to 1-2% (1-3). To these methods belong: • The antiretroviral prevention (АРВ-профилактика ), which is held at mother during pregnancy and births, and also at child in the first week of life; • Obstetric interference, including planned Caesarean section (PKC ); • Rejection of breast feeding (4-6 ). The basic task - to seek build-down frequency proton magnetic resonances as in all European region WHO, especially in those countries, where the HIV-infection epidemics is growing at expense of consumption of injection drugs, and the health service system is weakened due to transitional period in the economy. The high coverage by the antenatal care, the presence well-developed infrastructure of healthcare, the high literacy rate, relatively low the infections abundance and the availability of effective measures on ППМР lend this region the auspicious opportunity in order to exterminate the infant HIV-infection and to become example for entire world. WHO popularizes the overarching strategy of HIV-infection prevention at babies and little kids, composed of four directions: • Primary prevention of HIV-infection; • Warning нежелательной pregnancy at HIV infected of женщин1 • Cession prevention HIV from child mother; • Treatment provision, help and support HIV infected mothers and their families. This protocol concerns third component of strategics - cession prevention HIV from mothers their childrens. It corresponds regional purpose on HIV-infection prevention at babies in Europe: to seek to 2010 frequency reductions of HIV-infection at babies to a level less 1 case per 100 000 liveborn and HIV-infection frequencies at babies, born from HIV infected mothers, to a level lower 2%. 137 The European purpose corresponds global purpose, delivered on special UN General Session on HIV/AID in 2001 - to cut to 2010. Quota HIV infected babies on 50%. The data minute adapted for Republic of Uzbekistan on the basis of European minute and is basic document for Cession preventions HIV from child mother(CPCM) Fever During and After Childbirth Objectives: - Discuss best practices for management of infection during and after childbirth. - Describe strategies for prevention of infection - Distinguish between prophylactic and therapeutic use of antibiotics Fever During Pregnancy and Labor: Differential Diagnosis - Cystitis - Acute pyelonephritis - Septic abortion - Amnionitis - Pneumonia - Malaria - Typhoid - Hepatitis Acute Pyelonephritis Treat, because of risks of preterm labor, sepsis Easy to treat Inexpensive Management of Acute Pyelonephritis: - Check urine culture and sensitivity and give appropriate antibiotic - If no culture available, give IV antibiotics until woman is fever-free for 48 hours: Ampicillin every 6 hours + gentamicin daily 138 - Ensure adequate hydration by mouth or IV - Give paracetamol by mouth for pain and to lower temperature Acute Pyelonephritis: Subsequent Prophylaxis Recurrence of acute pyelonephritis in the same gestation is reported to be 10–18%. Suppressive therapy: 2,7% will get another urinary tract infection. No suppressive therapy: 20–30% will get another urinary tract infection. To prevent further infections, give antibiotics once daily at bedtime for remainder of pregnancy and 2 weeks postpartum: Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole Amoxicillin Septic Abortion Cause of 12.9% of maternal deaths. Postabortion care has had tremendous impact on reducing mortality, particularly with use of manual vacuum aspiration. Management of Septic Abortion Begin antibiotics as soon as possible before evacuation: Ampicillin every 6 hours PLUS gentamicin daily PLUS metronidazole every 8 hours Continue until fever-free for 48 hours Manual vacuum aspiration Amnionitis Prompt intrapartum initiation (rather than delay until after delivery) of broad spectrum antibiotics results in: Less newborn bacteremia Less newborn pneumonia Reduced maternal febrile morbidity Shorter duration of hospitalization 139 Treatment initiated intrapartum will not mask newborn infection Management of Amnionitis Ampicillin and gentamicin: Broad coverage for wide variety of organisms Crosses placenta and achieves adequate concentrations in the fetus Excellent activity against group B streptococci and E. coli – major causes of newborn sepsis No detectable teratogenesis from parenteral gentamicin, streptomycin, tobramycin or oral neomycin Give combination of antibiotics until delivery: Ampicillin every 6 hours PLUS gentamicin daily If cervix is favorable, induce labor with oxytocin If cervix is unfavorable, ripen with prostaglandins and infuse oxytocin or deliver by cesarean section If woman delivers vaginally, discontinue antibiotics postpartum If woman has cesarean section: Continue above antibiotics Add metronidazole every 8 hours Continue until fever-free for 48 hours. Fever after Childbirth: Differential Diagnosis Metritis Pelvic abscess Peritonitis Breast engorgement Mastitis 140 Breast abscess Wound abscess, wound seroma or wound hematoma Wound cellulitis Cystitis Acute pyelonephritis Deep vein thrombosis Pneumonia Atelectasis Uncomplicated malaria Severe/complicated malaria Typhoid Hepatitis Obstetric and Medical Factors Affecting Postpartum Sepsis - Intervention during labor and delivery - Dangerous infections following prolonged and obstructed labor - Thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, coagulopathy and septic shock may complicate the infection - Remember that clostridium infections may be difficult to detect and occur where contamination with earth. Health Service Factors Affecting Postpartum Sepsis Majority of deaths occur between first and second week of puerperium and are linked to medical and midwifery/nursing staff factors: Inadequate: – monitoring of temperature – bacteriological investigations – treatment with antibiotics or operative intervention 141 Lack of: – asepsis and antisepsis – blood for transfusion – appropriate drugs Fever After Childbirth (general management): -Encourage bedrest -Ensure adequate hydration by mouth or IV -Decrease temperature -If shock suspected, begin treatment immediately Management of Metritis Start antibiotics: Ampicillin every 6 hours Gentamicin every 24 hours Metronidazole every 8 hours Assess if retained placental fragments. All the while: Give fluids Transfuse fluids Give pain medication Continue close monitoring Watch for shock Watch for development of abscess Antibiotics for Metritis: Intravenousus antibiotics: Ampicillin every 6 hours 142 Gentamicin every 24 hours Metronidazole every 8 hours Continue until fever-free for 48 hours Septic Shock Intravenousus antibiotics for sick patients Antibiotics for Gram + (penicillin, ampicillin) Gram - (gentamicin), and Anaerobes (metronidazole) Adequate doses of antibiotics are necessary Aggressive fluid resuscitation (2–3 liters to start) Look for abscess, peritonitis or other condition requiring surgery Intravenousus antibiotics may be necessary for longer if bacteremia Prevention Strategies Infection prevention practices for every delivery: Minimum manipulation High-level disinfected or sterile gloves for examination Avoid unnecessary procedures (e.g., episiotomy) Three Cleans: Clean hands Clean surface Clean blade Plus: Clean tie Clean perineum 143 Clean nails Many causes of fever during and after childbirth. Therapeutic antibiotics ONLY if disease is diagnosed. Duration or treatment dependent on disease, whether or not cesarean section has occurred or presence of bacteremia. Septic Shock Hypotension and decreased tissue perfusion resulting from the body's response to various byproducts of infection is termed septic shock. In obstetrics and gynecology, septic shock is one of the more frightening, but thankfully rare, sequelae of the various infectious complications of pregnancy, gynecologic surgery, or pelvic inflam¬matory disease. Perhaps 8 to 10% of infected ob-gyn patients are bacteremic, and at most 12% of these experience shock. The relative youth and health of these patients result in a fatality rate of at most 3%, compared to upward of 81% in some popula¬tions of nonobstetric patients.40 Diagnosis By definition septic shock entails a sepsis-mediated decrease in tissue perfusion, leading to deficient oxygen and nutrition supply to tissues. If left unchecked, shock ultimately causes serious impairment of cellular function and death. Even though a decrease in blood pressure is usually perceived as fairly essential for the condition, in the earliest stage, so-called warm shock, hypotension may be subtle or absent. The patient will have an elevated temperature with warm extremities, low systemic vascu¬lar resistance, tachycardia, and leukocytosis and may otherwise appear to be obviously infected, often precipitating a "fever work-up" and initiation of antibiotics. Ancillary laboratory findings, including transient hyperglycemia, thrombocytopenia, and other evidence of coagulopathy, may be present if investigated. However, the physician may overlook low blood pressure, merely assuming that the patient's condition represents a "normal" infection. Therefore misdiagnosis in the warm shock stage may be quite dangerous. Subsequently, endogenous catecholamine release produces marked vasoconstriction, which reduces peripheral tissue perfusion, and cellular hypoxia, resulting in cool extremities, high systemic resistance, cyanosis, and oliguria, the so-called cold shock. Hypoxia at the cellular level leads to lactic acidosis from anaerobic me¬tabolism. If significant myocardial depression leads to cardiovascular collapse, in the face of hypotension and hypoxia, the stage of irreversible shock is diagnosed. The diagnosis of septic shock is therefore based upon the demonstration of in¬fection of some source, coupled with clinical hypotension or other findings noted earlier. 144 Besides clinical examination, including vital signs, diagnostic evaluation should include bacterial cultures of appropriate sources as well as complete blood count (including platelets and WBC differential), clotting studies, general chemis¬tries, and urinalysis. If pulmonary infection (or pulmonary decompensation) is sus¬pected, chest roentgenography is in order. The clinician must be aware of other disorders that may give similar clinical symptomatology, including hemorrhagic (hypovolemic) shock, pulmonary embolus, amniotic fluid embolus, diabetic ketoac-idosis, cardiac tamponade, and such rarities in the ob-gyn patient as acute aortic dissection.42 Pathophysiology Septic shock is the most common form of distributive shock, wherein aberrant blood flow distribution is the initial physiologic defect (the other two types of shock being cardiogenic and hypovolemic). It should be noted that in general, after an hour or more of clinical shock, a patient will exhibit all three types of shock, because of the interaction of reflex vasoconstriction, vascular permeability, and hypoxic cardiac dysfunction that result no matter what the initial type of insult was. Septic shock is commonly caused by gram-negative bacilli, though infection by gram positives, fungi, rickettsiae, and viruses may precipitate shock as well. Bacterial products, including endotoxin and exotoxin, provoke activation of macrophages, the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways, the fibrinolytic pathway, and the direct and properdin complement pathways. The subsequent release of diverse me¬diators of these various and complex pathways (eg, histamine, bradykinin, kallikrein, hydrogen peroxide, and superoxide free radicals) causes increased capillary permeability, vasodilation (initially), and endothelial damage. Intravascular volume is lost to the extracellular space, which, coupled with vasodilation, results in hypo¬tension. Decreased blood pressure, in turn, causes a reflex increase in cardiac out¬put and heart rate. If this hypotension is unrelieved, the sympathetic nervous system becomes activated, causing marked and generalized vasoconstriction and ultimately tissue hypoperfusion (which may be made worse by the local effects of epithelial damage). Finally, lengthy tissue hypoxia has long been recognized to cause a shift to anaerobic metabolism and subsequent lactic (metabolic) acidosis. The sequelae of metabolic acidosis include relaxation of arteriolar smooth mus¬cle and constriction of venule walls, leading to pooling of blood in the capillary beds. This causes more loss of fluid into the extravascular space and further decrease in circulating volume, and hence continued hypotension and decreased cardiac out¬put. Added to this cycle of decreasing perfusion is the impairment of myocardial function by endogenous opioids (ie, endorphins) and by myocardial depressant fac¬tor. 145 Ultimately, failure of tissue oxygenation and nutrition leads to generalized tis¬sue death, as the patient succumbs. Septic shock in the pregnant patient appears to be more severe than in the nonpregnant individual. Studies in animal models indicate that less endotoxin, in cases of induced gram-negative shock, is required to induce shock and organ necrosis in gravid animals. Effects are much more pronounced near term, and metabolic aci¬dosis is much worse in pregnant animals compared to nonpregnant controls. Sur¬prisingly, the fetus is more resistant than the mother, at least to the effects of endo¬toxin. It appears that adverse effects on the baby are predicated upon the mother's condition, rather than on any direct effects of the offending toxins. Outcome and Sequelae It may seem superfluous to speak of sequelae of septic shock, which is itself consid¬ered a sequel to serious infectious conditions. However, aside from the possibility of death due to prolonged hypotension and acidosis, the patient in various stages of septic shock runs the risk of end-organ damage and dysfunction. As tissue hypoxia and physiologic failure affect the various systems, individual organ function may continue to be suboptimal, even if the shock itself resolves. In particular, shock may incite acute renal failure, adult respiratory distress syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation, myocardial ischemia/infarction, and gastrointestinal hemor¬rhage. Perhaps the most troublesome of these is adult respiratory distress syndrome, which is a common cause of death in septic shock patients. Finally, it must be re¬membered that patients who do not expire from sepsis itself are at risk of complica¬tions of therapy, such as anesthetic effects, pulmonary collapse or hemorrhage from invasive monitoring, infectious sequelae of blood component transfusion, and the like. Fetal sequelae of septic shock will be more indirect, since, as noted earlier, the fetus seems more resistant to the effects of endotoxin. However, maternal hypoten¬sion and vasoconstriction will cause detrimental changes to uterine perfusion, re¬sulting in both decreased oxygen transfer to the fetus and increased uterine activity. Therefore while she is aggressively managed for hypotension and other manifesta¬tions of shock, the pregnant woman with sepsis must be observed judiciously for signs both of premature labor, to ensure that prematurity does not complicate the situation, and of fetal distress brought on by maternal hemodynamic instability. Management 146 The treatment of septic shock consists of four basic components: hemodynamic sta¬bilization, with improvement of functional intravascular volume; maintenance of an adequate airway, including endotracheal intubation, if necessary; identification of the specific focus of infection and its extirpation, if possible; and initiation of appro¬priate antibiotics.43'46 It should be appreciated that the urgency of the situation com¬pels the physician to perform the specific tasks necessary for these four goals simul¬taneously, in concert with support personnel such as nursing, anesthesia, laboratory, blood bank, and others (Table 8-3). Volume replacement is the first and most im¬portant therapeutic strategy in the treatment of septic shock. Patients will have ei¬ther absolute or relative hypovolemia, depending upon the degree of vasodilation and third-spacing of fluid. With judicious use of the SwanGanz or other pulmo¬nary artery catheter, isotonic crystalloid (eg, normal saline, lactated Ringer's solu¬tion) may be given freely as pulmonary capillary wedge pressures (PCWP) are mon¬itored. If the PCWP increases by more than 7 mmHg, fluid administration may be curtailed to avoid pulmonary edema; if it does not rise by at least 3 mmHg, then more volume is administered (the so-called 7-3 rule). It is important to emphasize the utility of the PCWP, especially in the obstetric patient. Use of the traditional central venous pressure has been demonstrated to be inadequate in the estimation of pulmonary pressure dynamics. TABLE 8-3 Protocol for Management in Cases of Septic Shock Diagnosis Physical examination (including vital signs) Insertion of triple lumen pulmonary artery flotation catheter Maternal complete blood count and coagulation profile General chemistry panel Amniotic fluid or endometrial culture, if available Blood culture Catheterized urine for culture and analysis Culture of other operative site, if available Fetal monitoring, if appropriate 147 Management Large-bore venous access and arterial catheter Indwelling urinary bladder catheter Fluid replacement (crystalloid) Serial blood gas and central pressure monitoring Antibiotic therapy (after cultures taken) Pressor agents, as necessary (dopamine) Electrolyte replacement Acidosis correction (with sodium bicarbonate) Correction of clinically significant coagulopathy or anemia with appropriate blood component replacement Surgical removal of infected focus, as soon as the patient is adequately resuscitated (including evacuation of uterus in cases of septic abortion or retained products of conception) Fetal monitoring, if appropriate Narcotic antagonists (naloxone) Especially in cases of warm shock, fluid administration (along with appropriate antibiotic therapy or removal of the infected focus) may be all that is necessary for resuscitation of the patient. However, if the patient is refractory, especially if signifi¬cant sympathetic-mediated vasoconstriction is thought to be present, dopamine hydrochloride may be used to improve cardiovascular parameters. Dopamine has dose-dependent alpha- and beta-adrenergic activity, such that at low doses it increases myocardial contractility and heart rate and causes vasodilation of renal, cor¬onary, cerebral, and splanchnic vessels by its beta-adrenergic effects. There is also vasoconstriction in skeletal muscle, in effect shunting blood to more important organs. Initial doses of 2 to 5 Hg/kg per minute are titrated upward until blood pressure, cardiac output, and other hemodynamic parameters are stabilized. Ad¬ministration should not exceed 15 to 20 (J-g/kg per minute, as this allows alphaadrenergic predominance and vasoconstrictive reduction in tissue perfusion. It should 148 be noted that dopamine administration during pregnancy decreases uterine blood flow, at least in the animal model. Oxygen supplementation should be initiated immediately. Nasal prongs or mask may be utilized initially, including the continuous positive airway pressure mask. At the first sign of respiratory decompensation, however, intubation and mechanical ventilation should be instituted. Serial arterial blood gas measurements should doc¬ument the patient's oxygenation status, as well as evidence of carbon dioxide reten¬tion and acidosis. As mentioned earlier, attention to the PCWP will aid in the pre¬vention of pulmonary edema due to overhydration. Treatment of the infection itself is centered about the administration of antibiot¬ics and the removal, if possible, of the focus of infection. Initial antibiotic therapy should consist of a combination of antibiotics that covers most bacteria anticipated in the infectious process. Combinations that include a penicillin (penicillin G, am-picillin), an aminoglycoside (gentamicin, tobramycin), and a specifically anti-anaerobic antibiotic (clindamycin, metronidazole) are appropriate as empiric ther¬apy in cases of septic shock. If Staphylococcus aureus is suspected, as in the case of purulent wound infection, vancomycin may be substituted for the penicillin if meth-icillin resistance is significantly prevalent in the community. However, although an¬tibiotics are absolutely essential in the management of these patients, removal of the septic focus is extremely desirable, if at all possible. This may entail evacuation of the uterus in cases of septic abortion, delivery in cases of chorioamnionitis, hysterec¬tomy in cases of abscess after cesarean section, "total pelvic sweep" in instances of ruptured tubo-ovarian abscess, debridement of necrotic tissue resulting from necro-tizing fasciitis, or drainage of pus in cases of postoperative wound abscess. Occa¬sionally, the practitioner will balk at such an undertaking in the severely ill patient, with the protest, "She's too sick to take to surgery!" Often, however, the patient's condition will only deteriorate until surgery is accomplished, leading to the saga¬cious reply, "She's too sick not to take to surgery!" Another measure historically utilized in the therapy of septic shock is the use of corticosteroids, which presumably enhance cardiac function by several mechanisms, dilate cerebral and visceral vasculature, and prevent third-spacing of fluid by various actions. However, clinical studies have not convincingly proven any positive effect of steroids on survival in severe, late shock, though they may be helpful in some patients early in the illness.54 There has also been some interest in the use of opiate antagonists in shock patients. Compounds such as naloxone are thought to exert some benefit through the blockade of naturally occurring endorphins, which medi¬ate some of the deleterious effects of the condition. However, even though positive results have 149 been achieved in animal models, insufficient work has been done in humans to make opiate antagonists a standard of therapy in the treatment of septic shock. Pyoinflammatory postpartum illness The purpose of classes: to explore the etiology and pathogenesis of septic process, classification of post-natal illness, factors contributing to the development of postpartum infectious diseases during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period, clinical course, teach students methods of diagnosis, principles of treatment of postpartum purulent-inflammatory diseases and their prevention. Postpartum infectious diseases - diseases observed in parturients directly related to pregnancy and childbirth and due to bacterial infection. Infectious diseases identified in the postpartum period, but the pathogenesis is not related to pregnancy and childbirth (influenza, dizentireya, etc.), a group of postpartum illness is not expected. Etiology and pathogenesis Pyoinflammatory diseases continue to be one of their pressing problems of modern obstetrics. The introduction of obstetric practice over half a century ago, antibiotics contributed to a sharp reduction in the frequency of postpartum infectious diseases. However, in the last decade all over the world celebrate the growth of post-natal infections. The frequency of postpartum infectious diseases varies due to the lack of standardized criteria, ranging from 2% to 10%. Several infectious complications occur more frequently after caesarean section. From septic obstetric complications worldwide die every year about 150 thousand women. Septic complications in the postpartum period, as the cause of maternal mortality continue to keep the sad leadership, taking 1-2 places, sharing it with obstetric hemorrhage. This is facilitated by a number of factors that make up the features of modern medicine. Change contingent pregnancy and childbirth, many of whom are women with severe extragenital pathology, with induced pregnancy, with hormonal and surgical correction nedonashivaniya pregnancy, etc. This is also due to the changing nature of the microflora. In connection with a broad and not always sufficiently justified the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, as well as means of disinfection emerged strains of bacteria that possess multiple resistance to antimicrobials and disinfectants. There was a selection from the disappearance of the weaker, less resistant to adverse conditions and the accumulation of microorganisms in clinical antibiotic species and strains. Negative role in the prevention of postpartum infectious diseases played a creation of large obstetric hospital stay with separate mother and child. When the concentration of large contingents of pregnancy, childbirth and newborns under one roof ", because of their physiological characteristics very prone 150 to infection, the risk of infectious diseases increases dramatically. One of the factors contributing to the increase in infectious complications in obstetric practice is the widespread use of invasive diagnostic methods (fetoskopiya, amniocentesis, kordotsentez, direct fetal electrocardiogram, intrauterine tokografiya), implementation of the operational benefits in pregnant women (surgical correction of isthmic-cervical insufficiency with recurrent pregnancy loss ). The factors of nonspecific protection of the human body from microbial invasion include its own bacterial and viral "envelope". Currently, about 400 species of bacteria and 150 viruses can be identified by someone with no signs of illness. The bacterial flora of different parts of the body prevents the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms. Any invasion of healthy epithelium is almost always preceded by a change in the microflora. As infectious diseases of female genital tract, and diseases, sexually transmitted diseases, accompanied by changes in vaginal ecology. Genital tract can be represented as a collection of microscopic cells of different types, each of which represents a habitat or ecological niche inhabited by several species of microorganisms. Each ecological niche characterized by its own, slightly different from the others, the population of microorganisms. Although microorganisms are well adapted to changing environmental conditions, the latter have on them, both quantitative and qualitative impact. In the genital tract of women similar phenomena observed during menstruation, pregnancy, postpartum, postabortion, and menopause. On the micro-organisms that live in the vagina, is mentioned in the second half of last century. In domestic literature, the first message of the study on microflora of the vagina was made by Professor D. O. Ott in 1886. In 1887 he was offered a theory of self-purification of the vagina. This theory is based on the fact that located in the vagina of healthy women vaginal wand produces lactic acid. Formation of lactic acid comes from the glycogen contained in the cells of the mucous membrane of the vagina. The resulting lactic acid provides unfavorable conditions for the existence of coccal flora. Reducing the acidity of the vagina and the concentration of lactobacilli leads to increased growth of opportunistic microorganisms. In healthy non-pregnant women of reproductive age found 109 anaerobic and aerobic 108 colony-forming units (CFU) per 1 ml of vaginal contents. Rank sequence of bacterial species is as follows: anaerobic, lactobacilli, peptokokki, bacteroids, epidermialnye Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, eubacteria. Among aerobes predominate lactobacilli, diphtheroids, staphylococci, streptococci, among anaerobes - peptostreptokokki, bifidobacteria, bacteroids. During pregnancy, hormonal changes in the epithelium of the vagina and cervix associated with progressive decrease in pH value of vaginal content that promotes the 151 growth of normal vaginal flora - Lactobacillus, as well as estrogenic activity promotes the growth of vaginal epithelial cells and accumulation of glycogen in them. Glycogen is a substrate for the metabolism of lactobacilli, leading to the formation of lactic acid. Lactic acid provides an acid reaction in vaginal contents (pH 3,8-4,4), necessary for the growth of lactobacilli. Lactobacilli are a factor in this nonspecific protection. In healthy pregnant women compared with non-pregnant ones there is a 10-fold increase in the allocation of lactobacilli and reduce bacterial colonization of the cervix with increasing gestational age. These changes lead to the fact that the child is born in a medium containing microorganisms with low virulence. In the postpartum period have shown substantial increase in the membership of most groups of bacteria, including bacteroids, E. coli, Streptococcus group B and D. Potentially all these species may be a cause of postpartum infection. The relative constancy of the vaginal microflora provide a set of homeostatic mechanisms. In turn vaginal microflora is one of the links of the mechanism regulating the homeostasis of the vagina by suppressing pathogenic micro-organisms. Obviously, damage to any of the components of this multicomponent system, caused by endo-and exogenous factors that lead to imbalances in the system and serves as a prerequisite for the development of infectious disease by autozarazheniya. The mechanism of development of diseases of the urogenital tract is in violation of the balance of micro-organism, which leads to suppression of lactobacilli, and in some cases disappearance and, accordingly, to the activation of pathogenic microflora. Actively developing, pathogenic microflora can achieve a sufficiently high concentration and serve as a hotbed of post-natal infection. Decisive role in the occurrence of infection in the postpartum period are state macroorganism, virulence of the microbial agent and the massiveness of infection. Imbalance in the system of "micro-organism" of the organism may be due to various reasons. Outside of pregnancy predisposing factors of postpartum infectious diseases are: endogenous extragenital foci of infection in the nasopharynx, oral cavity, renal pelves; extragenital non-communicable diseases (diabetes, lipid metabolism). During pregnancy, the breach contributed to physiological disorders of the immune system pregnant. By the end of pregnancy in women mark a significant change in the content in the blood serum of individual classes of immunoglobulins (G, A, M), reducing the absolute number of T-and B-lymphocytes (secondary physiological 152 immunodeficiency). Against this background, a rather fragile ecosystem of the vagina, resulting in the development of bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women. Bacterial vaginosis - vaginal ecosystem pathology is caused by increased growth mainly obligate-anaerobic bacteria. Bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women is on average 14-20%. In 60% of parturients with postoperative endometritis identified the same microorganisms from the vagina and from the uterus. In bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women is several times increased risk of wound infection. Reasons for changing the composition of vaginal flora in pregnant women may be: unreasonable and / or inconsistent antibacterial treatment, as well as the use of surface disinfectants in healthy pregnant women. Predispose to the development of an infectious process, many pregnancy complications: anemia, OPG-gestosis, placenta previa, pyelonephritis. Mentioned above, invasive methods of investigation of fetal, surgical correction of isthmiccervical insufficiency increase the risk of postpartum infection. At birth there are additional factors contributing to the development of postpartum infectious diseases. First of all, with a discharge of mucus plug, which is a mechanical and immunological barrier (secretory lgA) for microorganisms, lost one of the physiological barriers anticontagious female genital tract. Amniorrhea raises the pH (reduce acidity) of vaginal contents, and a study of vaginal contents after the outpouring of water revealed an important fact - the complete absence of secretory immunoglobulin A. The reason for this phenomenon, a purely mechanical removal belkovosoderzhaschih substrates from the surface of the mucous membranes of the birth canal, drastically reduces the local secretory protection . Found that 6 hours after amniorrhea there was not a barrier antiinfectious female genital tract, and the degree of contamination and the nature of the microflora depend on the duration of anhydrous interval. Against this background, greatly increase the risk of postpartum infectious complications in preterm water, prolonged labor, early amniotomy unreasonable, repeated vaginal studies, invasive methods of investigation of fetal status in labor, violation of sanitary-epidemiological profile. Clinical manifestation of the rising infection in childbirth is chorioamnionitis. In mothers, against the background of long waterless period or childbirth, worse general condition, temperature rises, there is a fever, the pulse becomes more frequent, amniotic fluid becomes turbid with a smell, sometimes appear puruloid selection changes the blood picture. Even with 12-hour interval anhydrous, 50% of women giving birth developed chorioamnionitis, and 24 hours later, this percentage is close to 100%. Approximately 20% of parturients undergoing chorioamnionitis at birth, develops postpartum endomyometritis and other forms of puerperalnyh diseases. Predispose to the 153 development of postpartum infectious complications of obstetric surgery, birth trauma, bleeding. In the postpartum period in the genital tract parturients not a single antiinfectious barrier. The inner surface of the postpartum uterus represents a wound surface, and the contents of the uterus (blood clots, epithelial cells, sites decidua) is a favorable environment for microbial growth. Uterine cavity easily infected by the ascent of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic flora of the vagina. As mentioned above, some parturients postpartum infection is a continuation of chorioamnionitis. Postnatal infection - mostly wound. Most of the wounds, which serves a gateway to infection, formed the primary focus. In post-natal infection of such a lesion in most cases is localized in the uterus. Further development of the infectious process due to the balance of the system "organism-microbe, and is directly dependent on the virulence of the microflora and the massiveness of infection of the uterus with one hand and the state of the protective forces of organism-partum with the other. Protective factor against the spread of bacterial agents from the uterus in the postpartum period is the formation of the placental site of leukocyte "Shaft." Perhaps perineal infection, vagina, cervix, especially if they remain unrecognized and not sewn. Of infection in the postpartum period contribute: subinvolyutsiya uterus, the delay part of the follow, inflammatory diseases of genital organs in history, the presence of extragenital foci of bacterial infection, anemia, endocrine diseases, violation of sanitary-epidemiological profile. Pathogens of purulent-inflammatory diseases may be pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Among the most frequent pathogens - gonococcus, chlamydia, mycoplasmas, Trichomonas. Opportunistic microorganisms inhabit the human body, being a factor of nonspecific immune defense. However, in certain circumstances they can become agents of puerperal infection. Etiologic structure of pyo-inflammatory diseases in obstetrics was robust. Great importance has antibacterial therapy: influenced by antibiotic-sensitive species are giving way to his stable. Thus, before the opening of antibiotics most formidable agent of postpartum diseases was hemolytic streptococcus. Once in obstetric practice have begun to use antibiotics, sensitive to them gave way to streptococcus staphylococcus, easier to form stable forms of these drugs. With 70 years in medical practice using a broad spectrum antibiotic to which staphylococci sensitive. In this regard, they are to some extent lost its importance in infectious pathology, and their place was taken by gram-negative bacteria and anaerobes asporogenous, more resistant to these antibiotics. 154 As agents of puerperal infections can be aerobes: enterococci, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, group B streptococci, staphylococci. Often flora is represented anaerobes: bacteroids, fuzobakterii, peptokokki, peptostreptokokki. In modern obstetrics has increased the role of Chlamydia, mycoplasma infection, fungi. The nature of the pathogen determines the clinical course of postpartum infection. Anaerobic Gram-negative cocci not seem to be very virulent. Anaerobic gramnegative rods contribute to the development of severe infection. The most common cause of obstetric septicemia is E. coli. Staphylococcus aureus causing wound infection and puerperal mastitis. Unlike some other infectious diseases caused by parasite detection, different clinical forms?? postnatal infections may be caused by various microorganisms. At present, the etiology of postpartum infections leading role played by microbial associations (80%), with a more pathogenic properties than monoculture because of the virulence of microorganisms can grow in the associations of several species in the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thus asporogenous anaerobic bacteria in association with aerobic species cause the development of severe forms of puerperal endometritis. PATHWAYS In 9 out of 10 cases of postpartum infection such as the route of infection does not exist, because there is an activation own conditionally pathogenic flora (autozarazhenie). In other cases, the infection takes place outside hospital strains resistant in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. It should also provide a relatively new way of infection - intraamnialny associated with the introduction of invasive obstetric practice research methods (amniocentesis, fetoskopiya, kordotsentez). Pathways In the case of massive infection with highly virulent microflora and / or significant reduction of the protective forces partum infection of primary focus extends beyond it. Excrete following pathways of infection of primary focus: hematogenous, lymphogenous by extension, perineural. CLASSIFICATION Classification of postpartum infectious diseases is certain difficulties in connection with a variety of pathogens, the diversity and dynamism of their clinical manifestations, as well as the lack of standardized criteria and terminology. The classification can be based on anatomical-topographical, clinical, bacteriological principles or their combination. 155 Currently, widespread classification of postpartum infectious diseases SazonovaBartels. According to this classification, various forms of puerperal infection treated as separate stages of a single dynamically flowing infectious process. First phase - an infection limited to the tribal area of wounds: postpartum endometritis, postpartum ulcer (on the perineum, the wall of the vagina, cervix). Phase - the infection has spread beyond the tribal wounds, but remained localized within the pelvis: Metro, parametrit, salpingooophoritis, pelvioperitonit limited thrombophlebitis (metrotromboflebit, pelvic vein thrombophlebitis). Stage -infection has gone beyond the limits of the pelvis and has a tendency to generalization: diffuse peritonitis, septic shock, anaerobic gas infection, progressive thrombophlebitis. Fourth stage - a generalized disease: sepsis (septicemia, pyosepticemia). CLINIC The clinical picture of postpartum infectious diseases is very variable, due to polietiologichnostyu postpartum infection stages and various means of dissemination, of non-uniform response of the organism parturients. When the diversity of the clinical course of both localized and generalized forms of postnatal diseases there are some characteristic symptoms: fever, chills, tachycardia, sweating, insomnia, headache, euphoria, reduction or loss of appetite, dizuricheskie and dyspeptic phenomena, reduction in blood pressure (in septic shock, sepsis). Local symptoms are: abdominal pain, delay or lohy abundant puruloid lohii in an unpleasant odor, subinvolyutsiya uterus, suppuration of wounds (perineum, vagina, anterior abdominal wall after cesarean section). At present, the widespread use of antibiotics in connection with the change in the nature and properties of the main pathogens of clinical picture of postpartum infectious diseases has undergone some changes. PASSING deleted, subclinical forms, which are characterized by a discrepancy between the condition of patients, clinical manifestations and severity of the disease, slow the development of the pathological process, not the severity of clinical symptoms. FIRST STAGE Postnatal ulcer occurs after injury of the skin, mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix as a result of operational delivery through the vaginal, prolonged confinement large fruit. Prevailing local symptoms: pain, burning, congestion, swelling of tissues, purulent discharge, the wound bleeds easily. In large areas of destruction, and inadequate treatment can occur generalization of infection. 156 Fester stitches in the crotch include in the same group of diseases. In these cases, remove the stitches and heal the wound on the principles of purulent surgery: lavage, drainage, use nekroliticheskih enzymes, adsorbents. After cleaning the wound impose secondary sutures. Postoperative wound infection after cesarean section is characterized by general and local manifestations, changes in the blood. When postoperative wound festering seams must be removed to ensure that the outflow of wound, purulent cavity drain. In auditing the wounds should be deleted eventeratsiyu, which first emerged is a sign of peritonitis after cesarean section and necessitating hysterectomy with uterine tubes. Postpartum endometritis is one of the most common complications of the postpartum period and 40-50% of all complications. Most of endometritis is a result of chorioamnionitis. One-third of parturients with postpartum endometritis were diagnosed during pregnancy bacterial vaginosis. There are four forms of puerperal endometritis (classical, abortifacient, and subclinical endometritis after cesarean section). Classical form of endometritis occurs for 1-5 days. The body temperature rises to 3839? Since, there is tachycardia 80-100 bpm. minute. Depression of the general condition, chills, flushing and dryness of the skin, topically - subinvolyutsiyu and soreness of the body of the uterus, with the smell of pus discharge. Changed the clinical picture of blood: leukocytosis 10-15 * 109 / l with neutrophilic shift to the left, an ESR of 45 mm / h. Abortive form appears for 2-4 days, however, with the start of adequate treatment for symptoms disappear. Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension, Pre-eclampsia, Eclampsia. Objectives: 1) Tactics for diagnosing and managing hypertension, pre-eclampsia and eclampsia 2) Describe strategies for controlling hypertension 3) Describe strategies for preventing and treating convulsions in pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Classifications: Chronic hypertension 157 Pregnancy-induced hypertension: - Pregnancy-induced hypertension without proteinuria - Mild pre-eclampsia - Severe pre-eclampsia - Eclampsia Etiology of Pre-eclampsia/Eclampsia: • Imbalance in prostaglandin metabolism: Prostacyclin production and Thromboxane A2 not primary etiology • Generalized arteriolar constriction with increased sensitivity to pressors • Failure of 2nd wave of trophoblastic invasion into spiral arteries of the uterus • Failure of C-V adaptation to normal preganancy • Decreased cardiac output and plasma volume Pregnancy-induced hypertension: woman over 20 weeks gestation with diastolic blood pressure > 90 mm Hg without proteinuria. Mild pre-eclampsia: -Two readings of diastolic blood pressure 90-110 mm Hg 4 hours apart after 20 weeks gestation; - Proteinuria more 1 gr/l; - No other signs/symptoms of severe pre-eclampsia. Severe pre-eclampsia: - Diastolic blood pressure > 110 mm Hg; - Proteinuria > 3 gr/l; - Other signs and symptoms sometimes present: Epigastric tenderness Headache Visual changes 158 Hyperreflexia Pulmonary edema Oliguria Eclampsia: - Convulsions occurring after 20 weeks gestation in a woman without a previously known seizure disorder - A small proportion of women with eclampsia have normal blood pressure Predicting pre-eclampsia using Risk Factors: Objective: To determine if risk factors for pre-eclampsia could be used to predict who develops it. Results: Those women who developed gestational hypertension at an earlier gestational age were more likely to progress to pre-eclampsia. Approximately 15–25% of women initially diagnosed with gestational hypertension will develop pre-eclampsia It is difficult to predict who will develop pre-eclampsia. Strategies for Preventing Eclampsia. Antenatal care and recognition of hypertension. Identification and treatment of pre-eclampsia by skilled attendant. Timely delivery. 3,4% of women with severe pre-eclampsia will have a convulsion. Eclampsia is significant cause of in-hospital maternal death. Predicting Eclampsia Study: Cannot use 2nd trimester mean arterial pressure or diastolic pressure to predict eclampsia. Eclampsia is abrupt in onset, without warning signs in about 20% of women. Management of Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension • Manage as outpatient • Monitor BP, urine for protein and fetal condition weekly 159 • If BP increases manage as mild pre-eclampsia • If signs of severe IUGR or fetal compromise admit for assesment and possible delivery • Counsel re warning signals for pre-eclampsia/eclampsia • If patient remains stable- allow normal labor and delivery Management of Mild Preeclampsia (<37 wks) • All patients receive maternal and fetal evaluation at diagnosis • If outpatient follow-up twice weekly • If feasible fetal evaluation weekly • DO NOT give anti-convulsants, anti-hypertensives, sedatives, tranquilizers, or diuretics • No salt restriction, no restriction in activity • If blood plessure normalizes or stabilizes-send home with precautions, review twice weekly • If an arrest of development of a fetal noted consider delivery • If proteinuria worsens manage as severe preeclampsia Management of Mild Preeclampsia (>37 wks) • Signs of fetal compromise-asses cervix and deliver • Cervix favorable-rupture membranes and induce with oxytocin or Pgs • Cervix unfavorable-ripen cervix with Pgs or Foley catheter and induce or deliver by C-section Management of Severe Pre-eclampsia • All patients with severe pre-eclampsia must be managed actively • Don’t rely on absence of symptoms and signs (blurred vision, hyperrelexia, edema, epigastric pain) to delay delivery. Expectant management is NOT recommended Initial Assessment and Management of Eclampsia ♦ Shout for help - mobilize personnel 160 ♦ Rapidly evaluate breathing and state of consciousness ♦ Check airway, blood pressure and pulse ♦ Position on left side ♦ Protect from injury but do not restrain ♦ Start intravenozus infusion with large bore needle (16-gauge) ♦ Give oxygen at 4 L/minute DO NOT LEAVE THE WOMAN UNATTENDED Antihypertensive Drugs Principles: - Initiate antihypertensives if diastolic blood pressure > 110 mm Hg - Maintain diastolic blood pressure 90-100 mm Hg to prevent cerebral hemorrhage Management During a Convulsion ♦ Give magnesium sulfate ♦ Gather emergency equipment (O2, mask, etc) ♦ Position on left side ♦ Protect from injury but do not restrain ♦ DO NOT LEAVE THE WOMAN UNATTENDED Anticonvulsive Drugs: Magnesium sulfate, Diazepam, Phenytoin Post-convulsion management Prevent further convulsions Control blood pressure Prepare for delivery (if undelivered) Magnesium Sulfate Use magnesium sulfate in - Women with eclampsia 161 - Women with severe pre-eclampsia necessitating delivery Start magnesium sulfate when decision for delivery is made Continue therapy until 24 hours after delivery or the last convulsion, whichever occurs last. Introduction of magnesium sulfate: Loading doze: 16 ml 25% magnesium sulfate give slowly intravenozus, then enter intramuscularly on 20 ml in each buttock. Supporting doze: 10 ml 25% magnesium sulfate introduce in each buttock each 4 hours. Overdose magnesium sulfate Symptoms: Loss of reflexes, flushing, somnolence, slurred speech, muscular paralysis, respiratory difficulty (16 breaths/minute or more), cardiac arrest, decrease diurezis (30ml/hour). Management • introduce DC MgSO4 • Calcium gluconate 1gm (10 ml 10%) intravenozus • Assist ventilation Intubate if needed Subject: Anamnesis role. Survey methods of gynecological sick. Scheme of case. Supervision of sick. I. Methods of examination of gynecological sick 162 Gynecology - (gуne - woman, logos - exercise ) science of woman. Starting to examining gynecological sick, is needed first of all to collect the anamnesis, for correctly collected the anamnesis clears up the cause of contraction of a disease. The anamnesis is going after complaints clearing: A ) chief complaint B ) additional complaint Suffered disease: A ) infectious diseases: (scarlatina, hepatit and so on ) B ) somatic C ) operation Catamenial and reproductive functions, contraception character: A ) menarche, formation (6-12 month ), B ) character мensis, abundance, debility. Date of last menstruation, time Become sexually active C ) number and outcome of all pregnancies D ) VMA, application of oral contraceptive. Gynecological diseases and operation on genital organs. Pathologic secretion: бели, precipitations neck, vaginal. Function neighbouring bodies. A ) long-time current chronical inflammatory processes, recurrences, Aggravations, therapy, effect. B ) violation of menstrual cycle: DUB (dysfunctional uterine bleeding), myoma adenomatosis and so on. C ) husband disease (partner ). Family history. Cession of disposition to diseases hereditably, presence of similar pathology at close and relatives. 163 Way of life, nutrition. Pernicious habit, work condition and Bytom. Anamnesis morbi II. inspection of sick On Brey, 1978. Obesity when has developed? Topobiological of evaluation: body length, body mass Body mass (kg ) IBM= --------------------(Body length, m)2 Rate IBM (Index of body mass ) = 20-26 IBM = 26-30 - tendency to obesity IBM more 30 - risk of development of metabolic abnormalities IBM more 40 - high risk of metabolic abnormalities Body type, types: Female Men's: and ) men's; b ) virile Eunuchoidial - the body length, the feets length are increased. Men's and virile - hyperandrogenism consequence as a child. Eunuchoidial - shortage of hormonal function of Ovaries. 2. Phenotypic evaluation. Dysplasia presence and dismofgy, characteristics for different clinical forms developmental disorder of genital glands. 3. Body hair character and condition of dermal covers Body hair character: on female or men's type, its redundancy Its emergence up to or after menarche, skin condition - increased the greasiness, presence acnes, increased the porosity - faces, back. Hirsutism degree (increased Body hair ) by the scale of Baron (1974 ). 164 I Art. - mean - pilosis of abdominal line, pilosis of labrum, pilosis of About teat cup liner fields II Art. - average - 1, 2, 3 + chin pilosis, inner surfaces of the thigh III Art. - strong - 1, 2, 3, 4. % + breast pilosis, backs, buttocks, shoulders. 4. Mammary glands - part of reproductive system, гормонально- dependable body target for action sex hormones, prolactin and other hormones (thyroid, adrenal glands). At 40% gynecological sick different the St. Agatha's disease are available. Inspection at the position (palpation ): standing, lying, size - hypoplasia, hypotrophy Trophic changes on the skin. Absence separated from nipples or presence: colour, consistency, character (pus, blood dopant - cancer, transparent or greenish - cysts, milk - galactorrhea, amenorrhea). 5. Inspection of external and internal genital organs A ) hypoplasia presence of low and major lips - pallor, dryness of vaginal mucosa gipoestrogeniya Juiciness, vulva cyanotic, plentiful transparent secretion of cervical mucilage. Hypoplasia of minor lips, head increase of clitori, increase of S between clitori foundation and external urethral opening (more 2 melanoma associated antigens ), hypertrichiasis B ) double touch, research at mirrors. III. special methods of examination TFD (tests of functional diagnostics ): Symptom “pupil” (estrogens production by ovaries ) when normal menstrual cycle - it is only in 1 cycle stage, when anovulatory cycle - long-term. Symptom tension cervical mucilage (Mach at a point of ovulation = 10-12 melanoma associated antigen ) Cytologic examination separated vagina (4 cell types ). It is based on cyclic changes of vaginal epithelium. There are 4 reactions of vaginal of smears: 1 reaction - atrophic smear: basal and parabasal cells, expressed the estrogens deficit; 2 reactions - intermediate, basal and parabasal cells - mean estrogenic saturation; 165 3 reactions - intermediate and cells of surface layer - moderate estrogenic saturation; 4 reactions - cursory big squamous cells with pyknotic nucleus are dominated by - the great estrogenic saturation. On cell counting of vaginal epithelium the test of karyopyknotic index is based: relation of cursory squamous cells with pyknotic nucleus to everything else. In rate during cycle it range from 20% at the beginning and at the end of up to 70-80% in the middle of cycle. 1 phase of menstrual cycle - 25-30%, ovulation - 60-80%, 2 phases (middle ) 25-30%. Basal temperature one from fancy pastry of functional diagnostics Histological examination of the endometrium (2-3 days before the mensis in sohranennomm.ts.), And anovulation - from the time of bleeding. Tissue biopsy and cytologic examinations Biopsy - in vivo taking of needed fabric for microscopic examination: A) incisional, or excision - excision of chip of tissue. B ) aiming - material fence under control by means of coleitis- or hysteroscope. C ) puncture - the material receive by means of puncture. Importance - detection of precancers and cancers ш/м, disease of lower genital organs, vagina. The material receive by the excision way of site of uterine cervix by the scalpel, the haemostasis - placing a suture. Cytologic diagnosis: A) smear - imprints B ) punctate from pathologic hotbeds Method: is competent at, highly informative, permits to discriminate tumour defeat on most elemental its stages. Character of pathological process (signs ): Morphologic feature of cells Quantitative relationship of individual cell groups Location cosmic ray. elements in preparation 166 1. Uterine cervix: A) ektotserviks Б ) cervical canal 2. Endometrium - aspiration of the uterus. Aspirate taken at 25-26 days of the Mc or no earlier than 25-30 days if premenopausal (no regular cycle) A) dry aspiration B) The jet irrigation (0,9% NaCI + 10% sodium citrate) (10:1). Detection in the aspirate histological study of actively proliferating cells in the endometrial glandular complex-like structures - cytological sign of endometrial hyperplasia. Determination of hormones and their metabolites Diagnostic value of a definition: testosterone its predecessors - the DEA and 17-OH - (17-hydroxy-progesterone) gonadotrophins - LH, FSH, PRL ovarian hormones and adrenal (Estradiol, progesterone, cortisol). Functional Tests Purpose: 1. Clarification of the functional state of different parts of the system of reproduction 2. Identification of reserve capacity of the adrenal, ovary, endometrium. F) Test with progestins Objective: To determine the degree of deficiency, to determine the reactivity of the endometrium Progesterone 1% - 1 ml / m 6 days Norkolut 5 mg for 8 days. 167 The sample is positive if, after the withdrawal of the drug after 3-5 days indicated menstrualnopodobnoe reaction. Indicates a moderate deficiency. Sample with E and F (estrogen-progestin) Purpose: 1. Eliminate the disease or injury endometrium - the uterine form of amenorrhea. Determine the degree of estrogen deficiency. Mikrofollin 0.1 mg (2 tablets of 0.05 mg) of 8-10 days, then - norkolut 5 mg of 5-7 days. 2-4 days – menstrual similar bleeding. A negative result indicates a profound organic changes of the endometrium - uterine form of amenorrhea. - A sample to establish the source of hyperandrogenism in women with clinical signs of virilization. The source of androgens in women are the adrenal glands and ovaries (virilizing ovarian tumors). Dexamethasone test - based on the features of glucocorticoid to suppress ACTH release, which inhibits the formation and isolation of adrenal androgens. A) Small Dexamethasone sample: 0.5 mg hormone every 6 hours for 3 days (2 mg / day). Two days before drug administration and the day after the cancellation are determined DHEA and 17-OH progesterone in blood and 17-KS in urine. The sample "+" - if content is reduced steroids for more than 50-75%. Means - a source of adrenal adrogenov. Decrease to less than 50-25% - ovarian source. At negative sample - Big deksamestazonovaya sample: 2 mg h / r 6:00 (8 mg / day) 3 days. A negative result - the presence of virilizing adrenal tumors, because androgen production tumor is autonomous and independent of ACTH. Functional tests to determine the level of violations of GHS test with clomiphene (antiestrogenic action). Indications: diseases, accompanied by xp. anovulation, oligo-amenorrhea. From the 5th to the 9th day of the withdrawal bleed bleeding to 100 mg per day (2 tablets of 50 mg). 168 Operation: Blockade of estrogen receptors in the pituitary area of the hypothalamus. Strengthening the secretion of gonadotrophin - releasing - hormone. Release of gonadotropins FSH and LH. Stimulation of the synthesis of steroids in the ovarian follicle ripening. Control samples: Determination content gonadotropins and estradiol in the blood (before and 5-6 days after admission). Increased gonadotropin indicate persistent pituitary reserves - the answer to the pituitary response lyuliberin. Increasing numbers of estradiol before ovulation indicates a potential activity of the ovary: gonadotrophic responsive to stimulation. In general, positive test indicates that the stored function YY and ovary. Negative test, including monophasic and T0 and the absence of MP bleeding (25-30 days after receiving clomiphene) indicates: Impaired function of the hypothalamus (not released GnRH) Violation of the functional ability of the pituitary gland to release gonadotropins. Test with lyuliberinom (with a negative test with clomiphene) - 100 mcg synthetic analogue of GnRH - a /. Prior to the introduction and after 15.30, 60 and 120 min after administration of a permanent catheter is blood sampling for the determination of LH The sample "+" if the 60 min of LH increases to ovulatory numbers - means that the pituitary function is preserved, and the hypothalamus - is broken. Test with gonadotropins Uses: A) suspected primary ovarian failure. Used pergonal - menopausal gonadotropin cheklovechesky / m 2 amp. (150 IU) for 5-7 days. Control: estradiol levels before and after injection. The sample "+" if the estradiol levels increased by 3-5 times, the data dynamic ultrasound: the presence of follicles D at least 18 mm. Neg. sample - a primary ovarian deficiency. 5.Instrumentalnye methods: Endoscopic methods: 169 A) Colposcopy - examination of the vulva, vagina vaginal part of cervix. site selection for biopsy. Type: Simple Premium - inspection after processing w / m 3% solution of acetic acid rum (there are 4 min: Intermittent edema of the epithelium, mucosal swelling spinous layer, reducing the subepithelial blood vessels, reducing blood supply). after treatment with 3% p-rum Lugol iodine stain glycogen in the cells of healthy epithelium in a dark brown color. Pathologically altered cells in various dysplasias are poor in glycogen. Yodnegativnye sites. Chromocolposcopy (modification extended) Inspection w / m after painting various dyes (methyl violet, hematoxylin, etc.) Informative method for diagnosis: pre-cancerous and cancerous diseases w / m, endometriosis, w / m, polyps, endocervisits Hysteroscopy - Identification / m pathology A) gas (check the cut in carbon dioxide) B) liquid (different solutions: poly-reopoligljukin, isotonic NaCI p-ry). The advantage over the gas GS is that there is no danger of gas embolism in i / m manipulations: control over the quality of diagnostic curettage, removal of a polyp, myoma node untwisting, etc. Uses: Uterine bleeding, conditioned i/ m pathology: submucous fibroids with the location site, polyps, adenomyosis, endometrial cancer, the presence of foreign bodies (fragments of the Navy), continued bleeding after dilatation and curettage treatment, monitoring treatment of endometrial hyperplastic processes, infertility in cases of suspected i/ m adhesions, malformations of the uterus. Contraindications: acute diseases of the genital organs, the presence of vaginal smears of trichomonads, yeast fungus, a large number of white blood cells, common diseases - acute thrombophlebitis, pyelonephritis, pneumonia, flu, sore throat 170 serious condition women for diseases of cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys. Laparoscopy: against pneumo-peritoneum inspection is conducted when injected into the abdominal cavity - CO2 or air: A) Pelvic B) the abdominal cavity. Uses: Clarification of the Fallopian tubes and identify the level of occlusion (chromopertubatsiya), clarifying the diagnosis of SSC, clarifying the nature of the anomalies of the uterus, the elucidation of the causes of pelvic pain, clarify the causes of infertility (with proven ovulatory cycles and fallopian tubes). A) execution of small conservative surgery: coagulation endometriosis, polycystic ovarian resection or electrocoagulation, adhesiolysis for chronic salpingatah without obstructions of pipes. B) Endoscopic surgery: removal of tubes, ovarian cysts, conservative myomectomy, uterine amputation. B) Emergency laparoscopy: differential diagnosis between acute appendicitis and right-adnexitis, suspected rupture or microperforation piosalpinksa, diff. between diagnosis and adnexitises prrgressiruyuschey ectopic pregnancy, ovarian apoplexy. Ultrasound diagnostics. Based on the fact that different tissues have different ehoplotnost and variously absorb ultrasonic waves. In pathological processes, the thickness of the structure and consistency of the tissue change, change, and the acoustic properties of tissues. In two ways: transabdominal and transvaginal through the abdominal wall during bladder filling: a) displaced from pelvic bowel loops b) Comparison with the differentiation of solid and liquid tumors. No filling of the bladder. Particularly promising in the diagnosis of early uterine and ectopic pregnancies, SSC and ovarian tumors. Normal size uterus ovaries on ultrasound: 171 Dl. - 6,7 (5,5-8,3 cm) Length - 2.9 + 0.2 Width - 5,1 (4,6-6,2 cm) Width - 2.8 + 0.4 Anterolateral Anterolateral Rear size - 3.6 (2,8-4,2) Rear size - 1.9 + 0.5 The average size of the follicle at the time of ovulation = 2.1 mm M-ECHO represents the thickness of the endometrium: a phase = 8-10 mm, Phase 2 12-13 mm Radiographic methods: HSG (hysterosalpingography) - Indications: Diagnosis of fallopian tubes. Identification of anatomical changes in the walls of the uterus: Endometriosis, uterine submucous, polyps, endometrial hyperplastic processes in the endometrium Held in the 1st phase of the menstrual cycle - 5-7 days. Contrast agents: verotrast, urotrast, verografin. First - 5 ml in the uterine cavity, then 5-7 ml of contrast to the fallopian tubes, the picture is recorded the passage of contrast medium through fallopian tubes. 2. R-graphy skull. Study the dynamics of the neuro-endocrine syndromes. We investigate the ephippium - bone bed pituitary tumors for diagnosis A) aimed shot sella B) the total craniography 3. Computed tomography 4. Medical and genetic research: Uses: 1. The absence or delay of sexual development 2. Anomalies of genital organs 3. Primary amenorrhea 4. Habitual miscarriage 172 5. Infertility Reasons: 1. Chromosomal abnormalities 2. Gene mutation 3. The presence of hereditary predisposition Markers of chromosomal abnormalities erased multiple somatic malformations and dysplasias changing the number of X-chromatin a) If the karyotype 46X or 45X0 - X-chromatin is absent. B) 47XXX - 2 Globke chromatic, ie, number of clumps = number of chromosome 1. X-chromatin was determined by scraping with a buccal mucosa - a slide with the fixation in a mixture of 3 parts methanol, 1 part glacial acetic acid. Types of anomalies of sex chromosomes: 1. Trisomy 2. Monosomy 3. Mosaicism Turner's syndrome: 45X/45X0, X - chromatin negative or greatly reduced, Uchromatin is not detected. Pure form of the DW: 46XY/46XY, at least - such as mosaicism 45/X0/46XX; 46XX/47XXX; 45X0/46XY Mixed form of the DW: 46XY/45X; 46XY/46 XX. Test control: 1.Testy functional diagnosis (TDF) can determine: A) two-phase of the menstrual cycle B) The level of estrogenic saturation of the organism B) The presence of ovulation 173 D) The usefulness of the luteal phase of the cycle D) All of the above 2. Continue to the statement, "a BMI over 30 ... A) is the norm ... " B) ... indicates a propensity to obesity ' B) ... indicates a moderate risk of metabolic disorders, " D) ... indicates a high risk of metabolic disorders, " 3. Specify the primary indication for the test with gonadotropins A) Suspicion of primary ovarian failure B) Suspicion of hyperprolactinemia B) Suspected giperandrogenemiyu D) All perechichlennoe 4.Ukazhite contraindications for hysteroscopy A) Acute genital diseases B) The presence of vaginal smears of trichomonads, yeast fungus, a large number of leukocytes B) Acute thrombophlebitis D) Pyelonephritis D) All perechichlennoe 5. Continue statement: "The symptom of" pupil "... A) ... there is only one phase of the normal menstrual cycle " B) ... occurs in phases 1 and 2 of the normal menstrual cycle " B) ... only observed in phase 2 of the normal menstrual cycle " D) ... is not observed in normal menstrual cycle " 6. Which functional diagnostic test indicates the presence of two-phase of the menstrual cycle? 174 Basal thermometry Kariopiknotichesky index Symptom pupil Analysis of vaginal discharge urinalysis 7. Tests of functional diagnosis (TFD) can determine dvufaznost menstrual cycle saturation level of estrogen the body the presence of ovulation the level of releasing factors all of the above 8. Functional test with dexamethasone to spend: clarify genesis of hyperandrogenism diagnosis of anovulation identify giperestrogenii diagnosis of typical forms of gonadal dysgenesis identification of luteal phase deficiency cycle Quiz Questions 1. What is the purpose of problem gynecology? 2. What is included in the assessment of women topobiologicheskuyu? 3. BMI. How is it calculated? The classification of obesity. Types of obesity. 4. Hirsutism. Classification of hirsutism. 5. TFD. Interpretation of the results TFD. 6. Functional Tests. Interpretation of the results of functional tests. 7. What additional methods of examination used in gynecology? 175 Recommended Reading Main Reading 1. Акушерство.Учебник для медицинских ВУЗов под редакцией Г.М. Савельевой. -М.:Медицина,2000. 2. Айламазян Э.К. Акушерство. Учебник для студентов медицинских ВУЗов. – СПб: Специальная литература, 1997. 3. Чернуха Е. А. Родовой блок. – М., 1999. Additional literature 1. Справочник по Акушерству и Гинекологии М. 1996. 2. Дуда И.В., Дуда В.И. Клиническое акушерство.- Минск, 1997. 3. Серов В.Н., Стрижаков А.Н., Маркин С.А. Практическое акушерство. Руководство для врачей. – М.: Медицина, 1989. Subject: Normal menstrual cycle and its regulation. Violation of menstrual function. Amenorrhea. Hypomenstrual syndrome. In the latter half of 21st century the firm a tendency to frequency growth of violations on the part of hormone background of women of different age period throughout the whole world, independent of computation method the given finding is outlined. According to the data of epidemiological studies, in industrially developed countries the average statistic frequency of amenorrhea is 1, 2-1, 4% in relation to total number and 0, 8-2, 4% - in relation to women РУз recently the disease incidence growth in two age groups is seen: among teenagers and women of 30 up to 39 years. 176 Amenorrhea Clinical-Objective survey methods: They is necessary to explain students about certain complaints: absence of menorrhea for 6 month and more or absence of menorrhea above age of eighteen. The pay attention outwardly of amenorrhea: Physiology absence of menorrhea during pregnancy, nursings, in period of the sexual maturation, old age. Cryptoamenorrhea imperforation owing to of cervical canal of the uterus, malformations of genital organs, atresia of hymen. Pathologic - absence of menorrhea in womens over 18 years of age (primary amenorrhea ), cessation of earlier former menstruations by 6 months and more ( secondary amenorrhea ). Hypothalamic form, hypophysial form, ovarian form, uterine form. Laboratory - instrumental technologies: To explain students about definition importance of hormone background of organism: A ) hormone examining: - monotone reduction in the number of estrogens; - increase in levels of progesterone; - lowering of tropic hormones (luliberin, follitropin, luteotrophic ). B ) the students must know the diagnostic value Test definition of functional diagnostics (ТФД; • Measurement of rectal temperature during 2-3 months (monophase temperature lower • Symptom definition «Pupil» (Absence +++); • Symptoms tension of шеечной mucilage ( In № 8-12 melanoma associated antigen when good hormone saturation of organism at a point of ovulation); • Arborization symptom («Fern» Has not been expressed); • The cytology of vaginal smear - the karyopyknotic index monotone in limits 30-40%, without increasing up to 80%, that provides evidence about ovulation. 177 Is needed to emphasise students about importance: Ultrasound of the uterus and adnexa to determine aplasia or malformations; X-ray examination: X-ray of the skull in two views to exclude pituitary tumor (changing shape of the sella turcica or an extension or thickening of the frontal plate ). Also valuable is hysterosalpingography to exclude malformations Internal genital organs. Students to explain from what disease is needed to distinguish. Differential diagnosis it is necessary to carry out with following by conditions: 1. Pregnancy - while always secondary amenorrhea, the presence of suspicious (Subjective feeling - nausea, vomiting, taste a whim ), probable (the change of shape, size, texture of the uterus, a pregnancy test positive or biological ), prolonged amenorrhoea reliable signs of pregnancy is not (the presence of the heart, small pieces and stir the fruit ), as well as ultrasound which specifies a pregnancy. 2. Differentiates the true from the false amenorrhea, when there are cyclical changes, but due to lack of blood outflow occurs amenorrhea. Cryptomenorrhea confirmed by inspection of the external genitalia, due to lack of openings in the hymen last tense, swollen cyanotic. Emphasize to students the following points Treatment When false amenorrhea the cruciform section of maindenhead accompanied by suturing by the two of opposite corners by the catgut suture is produced. Treatment of amenorrhea holds true specialist. Treatment is directed at the cause and begins with strengthening therapy, vitamin therapy, physical therapy (galvanic collar on Shcherbak, endonasal electrophoresis, acupuncture, hormone therapy, depending on the TFD. Efficiency evaluation of treatment menstruations emergence or menstrualsimilar of reactions, confirmed of TFD. Tactics complex therapy at specialist up to positive effect. Cure criteria: emergence of positive changes in TFD. 178 Prevention at the level of sick: taking into account the risk of development of infecundity in woman with amenorrhea, it is necessary to count it as the social factor. In connection with this is of importance the opportune diagnostics and treatment. Prevention at the level of family: begins by period of antenatal life of fruit, that the woman in gestation period from adverse effects (the ionizing radiation, chemical and bacteriological and so on ) and obligatory with early childhood (the rachitis prevention, frequent colds Prevention at the level of society: the risk group on the development of amenorrhea is the child of often who fall ill with infectious diseases, and also suffering chronical tonzillogennoy infection, rheumatismus, suffered the acute infection (the measle, the diphtheria, epidemiological. Mumps, hepatit ) in period of the sexual maturation, girl with infantilism signs. The contingent of risk group is being revealed during prof. inspections in pre-school and School educational institutions. Algodysmenorrhea Violation of menstrual cycle, expressed in paroxysmal, rarer nagging pain in the lower abdomen, in the area of? Sacral, low back during your menstrual period and accompanied with general misery. The algomenorrhea divide in primary or function, not engaged in organic changes of internal genital organs, and secondary, conditioned by pathological processes in bodies of small pelvis (the endometriosis, the chronical inflammatory diseases of appendages, the pelvic ganglionevrity. Clinic-instrumental methods: It is necessary that the students knew, the diagnosis of primary algomenorei is based on complaints the pains emergence at young girls through 1-1, 5 years after menarche. The pains begin in the first day of cycle or few hours before menstruation, have the paroxysmal character, localize in the lower abdomen and often radiating in the low back, the inner surface of the thigh, often is followed by the nausea, retching, loose stool, weakness, migraine the headache. Students let us explain, that valuable are anamnesis data: suffered as a child infectious and chronical inflammatory diseases (especially gastro-intestinal system ), traumatic labors, abortions, operations on uterus and appendages, and also data of superficial inspection: salient constitutional Feature-Asthenic Body addition, a tendency to lowering of body mass. 179 The students must know that the rectal examination at virgins and the vaginal touch (if lives by the sex life ) determines the absence of anatomic changes. Follows will stop, that may be the common blood analysis - in limits of normal quantities; bulk analysis Urine- with no pathology. analysis and tank. precipitations crop within the normal limits. Sharpen students attention about conducting importance: Tests of functional diagnostics TFD: 1. Measurement of basal temperature; 2. Symptom definition <pupil>; 3. Symptom tension of cervical mucus; 4. Symptom <fern> 5. Index calcitonin-like immunoreactivity; • Ultrasound-when function amenorrhea anatomic uterus change and appendages is lacking. Let us explain students, that is necessary to hold the differential diagnosis: with algomenorrhea of organic character developing when inflammatory diseases of internal genital organs, the uterus myoma, adenomyosis and adhesive disease is held. The secondary algomenorrhea is diagnosed on a foundation: complaints the pains emergence connected with menstruation. the pains radiate into the low back, the inner surface of the thigh. Anamnesis: consists of the book concerning of uterine myoma, suffered the surgical interventions on uterine cervix, operation on uterus and appendages. Will teach students carry out the gynecological inspection. Data gynecological inspection: the uterus increase, definition of particular units, that is representative for uterine myoma, definition the adhesion, limited excursion and bias, the appendages increase, that testifies suffered inflammation. Ultrasound - when organic algomenorei uterus increase and its appendages, presence of arresting the uterus regulation adhesion. Emphasize the need for students with a differential diagnosis of PID (pelvic inflammatory disease). 180 2. Inflammatory diseases of female genital organs. The complaints the pains emergence is not linked with the arrival of menstruation and the clinic is followed by signs of common and local inflammation: general misery, weakness fervescence, the rebound tenderness symptoms palpation is determined. Vaginal touch when endometritis - uterus debility, when adnexitis appendages increase with affected side the debility. Laboratory data - the leukocytosis, the left shift, accelerated the ESR, the analysis of vaginal precipitations discovers the increase of WBC up to 20-25 in sight, even in number, finding out of pathologic flora (the trichomonads, the funguses, the gonococci ) as evidenced by the bacteriological research. Ultrasound - uterus increase and presence in cavity of EchoNegative fluid, increase of uterine adnexa, inflammatory infiltration, effusion presence in Douglas' cul-de-sac. The endometriosis by the complication of that is the secondary Algomenoreya more often is sometimes in womens at age after 30-40 years, in anemnesis the abortions, the labors, the surgical interventions on uterine cervix, operation on uteruses and uterine adnexa are marked. When endometriosis nagging pain in the lower abdomen of constant character, which increase during your menstrual period and last during first 2-3 menstruation days, and when primary Algomenoreya of pain slack in the first 1-2 hour полсе launched menstrual flows. For endometriosis especially for internal (adenomyosis ) is typical the small temperature rice during your menstrual period, menorrhagia, the infecundity. Laboratory data: common blood analysis accelerated ESR. When gynecological examination the increase of uterine sizes (the adenomyosis ) appendages during your menstrual period and the cutback after menstruation is constant sign of appendages endometriosis. For adenomyosis typical the shape change and uterus regulation. The uterine body gains the sphere-shaped when diffusive form and irregular when nodose. Ultrasound-uterus increase in luteal phase, in uterus wall dotted or cystic echostructure per days of menstruation; increase and cystic change of ovaries. 1. Painful menstruation accompanied with sharp cramping pains, are seen in womens when submucous myoma. When nascent submucous units, when the unit achieves internal shed and uterine contractions is being pushed aside through the 181 cervical canal arise pain. Age of patient with uterus myoma more often elder 30-35 year. Complaint besides pains, acyclic bleeding, often with signs of anemization. When vaginal touch uterus increase, shape change, presence of particular units. Ultrasound: uterus increase, units detection, redetermination their dimensions and location. Treatment of primary almenoret lead preparations by the overwhelming the prostaglandin synthesis for 2-3 day yes menarche and in the first day of cycle Naprosyn 250 mg.2-three times per days, brufen 200 mg.2-three times per days, the indomethacin 25 mg.3 times, brufen 200 mg.3 times, the acetylsalicylic acid 200 6 mg.4-time. Treatment it is necessary to carry out during 3-4 menstrual cycles. Physiotherapy - electrophoresis with novocaine in the area of abdominal brain, needle-reflex therapy. It is necessary O & M all to combine with mean tranquilizers (the valerian, the relanium, trioxazine at bedtime, in half vtroroy of cycle. When lack of effect from performed therapy of it is necessary cyclical hormonotherapy with more active gestagens during not less than three months (regividon marvelon. Tactics when function algomenorei treatment on an outpatient basis. In case of treatment inefficiency of primary algomenorei and when secondary algomenorei connected with endometriosis or uterine they is necessary to direct sick to specialist. When secondary almenorei connected with chronic inflammation of internal genital organs treatment is held ambulatory. Efficiency evaluation of treatment is based on symptoms disappearance algomenorei. Cure criterion painless menstruation. Prevention at the level of sick of following of rule of personal sanitation, regime of work and rest. The prevention at the level of family shall be exercised by the warning of infectious and colds in children's and pubertal age, correct nutrition and the physical development of girl. Taking into account constitutional girls feature, they is necessary to organize the clear regime of work, rest, occupation, do not overstack them during your menstrual period by additional loads. The prevention at the level of society the girls improvement (dispensary observation, the detection EGD and their the liquidation), the conducting the work of San gap 182 among school-girls, to propagandize the sports facilitating gormonicheskomu physical development. The occupation will be held traditional way in sight of conversations and answers to questions, engagement to volunteers occupation, and also way of solution of situational missions. Situational mission: Mission 1. The girl 16 years appealed with complainings of not regular menstruation with 12 years, passing in long-term menstrual hemorrhage. Per vaginum: the uterus are smaller than normal quantity, the appendages is not determinated. Precipitation sanguine moderate. Diagnosis. Needed examination. Tactics Doctor of common practical work stoppage methods of juvenile bleeding Mission 2. Sick 49 years came at the reception to doctor of female dispensary with extract from gynecology department. From abstract follows that concerning of uterine hemorrhage was carried out walls abrasion of uterine cavity. Gynecological examining of scrape: glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia. From anamnesis: last 4-5 menstruation months of steel to come timelagged for 2-3 week and was accompanied by bleeding. Treatment failed to obtain. PV: uterine cervix cylindrical. The shed are closed. The uterus up to 4-5 weeks, mobile, is increased evenly. The appendages is not determinated. Archs deep. Precipitation milk. Diagnosis. Plan examination. Tactics Doctor of common practical work. Mission 3. At girl 16 years appeared sanguine the genital discharge, continuing during 8 days following 2-month delay first menstrual period appeared four months ago on 4 days through 28 days. Moderate, painless. The sex life denies the development correct, well of fiztcheski is complex. When abdominal recto-examining of pathology not been detected. Aerodynamic rotor - 80 grams / liter. Probable diagnosis. Tactics Doctor of common practical work. treatment. TESTS. 1. The features of the normal menstrual cycle are A) anovulation 183 B) The formation of the corpus luteum in the testis * B) the predominance of progestogens in the second phase of the cycle * D) ovulation * D) none of the above 2. For anovulatory menstrual cycle is characterized by A) long-term persistence of follicles * B) cyclical changes in the body B) atresia of follicles * D) the prevalence of progestogens in the first phase of the cycle A) ovulation 3. The hypothalamus produces hormones following A) FSH-releasing factor * B) estrogen B) progestogens D) gonadotropins D) releasing factor LH * 4. In the normal menstrual cycle, high levels of estrogen Saturation occurs A) on day 14 * B) on day 21 B) during ovulation * T) is true, both D) during deskvomatsii 5. Estrogens have the following action A) relaxes the smooth muscles 184 B) increase the process of ossification * B) stimulate the activity of cellular immunity * D) promote peristalsis of the uterus and tubes * D) all of the above is false 6. Tests of functional diagnosis (TFD) can determine A) dvufaznost menstrual cycle * B) The level of estrogenic saturation of the body * B) the presence of ovulation * D) the level of releasing factors D) all of the above 7. Proyomenoreya - it A) a short menstrual cycle * B) short periods (1-2 days) B) scanty menstruation D) all of the above D) frequent menstruation * 8. For anovulatory menstrual cycles with short-term persistence mature follicle is characterized by A) ovulation B) basal temperature single-phase * B) in endometrial scraping into the second phase of the cycle - late phase of proliferation * D) a symptom of "pupil" (+++)* D) none of the above 9. Primary algomenoreya due A) hyperandrogenism 185 B) retrodeviatsiey uterus * B) a high production of prostaglandins * D) * infantilism D) nothing of the above 10. If PMS is noted, usually in the second phase menstrual cycle A) * giperestrogeniya B) increased secretion of ACTH B) increase serotonin levels D) gipoestrogenemiya D) * mastalgia 11. At the climacteric syndrome in premenopausal women observed The following clinical symptoms A) vegetovascular * B) The psycho-emotional * B) metabolic-endocrine * D) inflammation D) none of the above 12. Amenorrhea - the absence of menstruation for A) 6 months * B) 5 months * B) 6 months or more * D) 4 months D) 1 month 13. The presence of ovulation, as evidenced by the research: 186 A) determining the concentration of hormones in the blood at 12-14 days of the menstrual cycle * B) ultrasound monitoring of the dominant follicle * B) histological examination of endometrial scrapings * D) analysis kariopiknotichesky index D) ultrasound monitoring for 19-20 day menstrual cycle 14. Gipomenstrualny syndrome - is: A) scanty menstruation * B) rare menstruation * B) scanty bleeding intermenstrual discharge D) None of the above D) heavy menstruation 15. Tuberculosis may be due to all the following except: A) for cervical dysplasia * B) congenital malformations of genital organs B) genital infantilism D) * dysfunctional uterine bleeding D) uterine fibroids * Checking problems 1. Regulation of menstrual cycle 2. Changes in the body of woman in different periods of life 3. Amenorrhea cause, algodysmenorrhea 4. Risk group 5. Amenorrhea classification; 6. Primary and secondary algodysmenorrhea 7. Principles examination 187 8. Scheme examination women with amenorrhea 9. Kind of algodysmenorrhea and tactics Doctor of common practical work 11. Woman treatment with amenorrhea in conditions GRP and air-cushion vessels. Subject: Dysfunctional uterines bleeding. Etiology and pathogenesis. Clinic, diagnostics, differential diagnostics. Treatment. Prevention and rehabilitation. Under term <the dysfunctional uterines bleeding> understand such bleedings, which are determined by the violation of rhythmic production by ovaries of sex hormones and which is not linked neither with structural diseases of genital organs, neither with common system diseases of woman organism. It should be noted that the data definition it is impossible to count fairly exact, because never it is impossible to hold of clear boundary between function and organic (morphological) changes. Indeed, as this is seen and as an example of dysfunctional uterines bleeding, in such patient the increase of uterine sizes, one-or the bilateral increase of cystic changed ovaries and some other the purely anatomic changes on the part of genital organs often are being revealed. However, in spite of these the circumstance, the concept <disfunktsirnalnye uterine hemorrhage> one can consider legitimate and them is wide is taking advantage of gynecological practice. The importance of dysfunctional uterines bleeding in gynecology of first of all is determined very high frequency of this form of pathology of menstrual function about 10-18% all gynecological diseases. The great variability of dysfunctional bleedings in age dependence is marked. So, about 50% all dysfunctional uterines bleeding falls to the climacteric period of woman life. In period of the sexual maturation 4-15% girls suffer these disease. Concerning high incidence of ovarian dysfunction and bleeding in infancy menstrual function and in the period of климактерия can be explained by big vulnerability the hypothalamus - the hypophysis - ovaries - the uterus in specified age stages of woman life. In period of the sexual maturation (12-16 year ) occurs the function formation of this neuroendocrine system. The hypothalamus centres, outlining the releasinghormones, which govern by the pituitary function regarding of generation of folliclestimulating (FSH ), luteinizing (LH ) hormones and prolactin (punched tapes ), operate still неполноценно and especially are prone to the different unfavorable 188 effects ( stressful situation, overworking, infection etc. ). This is why at such girls <the bust> function of hypothalamic system often occurs, that clinically occurs by the heavy and long-term dysfunctional uterine кровотечениями. In climacteric period occurs the normal aging of hypothalamic centres, which gradually lose his sensibility to action of gender ovarian hormones, due to the precipitation cyclicity of gonadotropins, and then and sex hormones breaks down. All it also leads to initiation of dysfunctional bleedings. Besides menarche and menopause, the dysfunctional uterines bleeding is not uncommon and in childbearing year, when, the mutual relations in system the hypothalamus - the hypophysis - the ovaries - the uterus are different by the stability. Within this period leading the importance in pathogenesis of dysfunctional uterines bleeding belongs to inflammatory processes of genital organs, especially salpingooophoritis. Under the impact of long-term the existence of inflammatory hotbed in small pelvis varys the receptors sensibility of ovaries to action of gonadotropin hormones, and also the uterus sensibility (the endometrium) to estrogens and progesterone. All these complicated change ultimately leads to violations of ovarian function and to long-term, often profuse hemorrhages. So that, age factor the great role in pathogenesis of dysfunctional uterines bleeding belongs to very. As already was marked above, the dysfunctional uterines bleeding are pluricausal diseases, i. e. they are caused by a great diversities of causes. To their number belong the aging features of organism, the neuropsychiatric factors, the different occupational hazards, the unfavourable living conditions, the dysfunctions of peripheral endocrine glands (thyroids, the adrenal glands), liver disease (in that body occurs the exchange of sex hormones ), acute and chronical inflammatory diseases (tonsillitis, viral flu and other common infection, inflammatory of genital lesion) etc .. All these factors, despite their big variations in character and mode of action, may exert adverse the impact on the different links of complex neuroendocrine system the hypothalamus - the hypophysis - the ovaries - the uterus, leading to violations of ovarian function and bleeding. This is why the prevention of pathology data of menstrual function first and foremost should be directed at warning and effective early treatment precisely these forms of common and local disease, especially in infancy of menstrual function. The fact that, often begun in juvenile age, dysfunctional uterine bleeding when is not sufficient good treatment changes to bleeding of childbearing year and even climacteric period. Such sick in practice all life with Backs Soon receive the different hormonal drugs, repeatedly undergo 189 diagnostic uterine curettages. And precisely at this contingent of sick most frequently arise pre-cancer the endometrial disease and the cancer. This is why effective treatment of dysfunctional uterines bleeding must get under way at the earliest using of all up-to-date means of therapy. This is frame of effective the cancer prevention of uterine body. Now of no unified, conventional classification of dysfunctional uterines bleeding. However, despite discrepant data, the researcher most divide these bleedings on anovulatory and ovulatory (last meet much rarer and not is of critical importance in gynecology). Among anovulatory bleedings bleedings, conditioned by the short-time rhythmic persistence of follicle (anovulatory month-long) and connected with long-term existence of follicle (the persistence) or atresia (regress) several follicles has been adopted to distinguish. The ovulatory bleedings is determined or shortening of first or second phase of menstrual cycle, or else lengthening of phase in development of yellow tel .. As was pointed out above, leading the importance in pathogenesis of dysfunctional uterine bleeding belongs to the anovulatory bleedings. These is why lower we will stop for review of pathogenesis, clinic, diagnostics, differential diagnostics and therapeutics which is precisely what bleedings. The name is said, at the foundation of anovulatory uterine hemorrhages rests the ovulation absence and consecutive development of yellow tel .. Itself and anovulation may appear as in two ways: in sight of short-time or longer follicle persistence; The short-time rhythmic persistence of follicle it is known still entitled <the anovulatory cycle>, i. e. the menstrual cycle without ovulation. Externally the anovulatory cycle almost nothing does not differ from ovulatory. The only distinguishing characteristic - the absence when anovulatory cycle of pregnancy, because without ovulation the pregnancy is not possible. Such anovulatory cycles very is common when formation of menstrual function, in lactating and in climacteric period. Case studies showed, as in copulative woman's age the anovulatory cycles may meet 1-2 time for a year. The entity of anovulatory cycle is in what in ovary one or more follicles are growing, achieve the maturation stages, but the ovulations does not happen. Then such follicle or the follicles during concerning short time (7 - 10 days) undergo regress, i. e. atresia. In response on the down grade of hormone (estrogens) in woman begins so-called the menstruation-like hemorrhage, which externally nothing does not differ from usual menstruation and appears exactly per days expected month-long. 190 The diagnosis is put on a foundation of monophase basal temperature, positive symptom of pupil in the latter half of cycle and data kolytotsitogrammy (calcitoninlike immunoreactivity varys in ranges from 20 up to 40%). In the endometrium on the eve expected month-long are discovered only proliferation of mucosa to the total exclusion any secretion signs. As already was pointed out above, the anovulatory cycles usually are alternated with ovulatory. This is why to determine diagnosis of refractory anovulation at such women should investigate the basal temperature over not less than 3-4 months. Only in cases of refractory anovulation when short-time persistence of follicles is needed corresponding therapy. Most frequent form of anovulatory uterine hemorrhages - bleeding, conditioned by the persistence or follicles atresia. When persistence one or more follicles gradually achieve maturation stages and not ovuliruya, extracting in raised amounts the estrogenic hormones continue long-time to exist, the redundant growing of endometrial what causes. These phase disease is followed by interim amenorrhea, duration usually 6-8 the week. In response on the down grade of hormone (estrogens) in the body endometrium begins gradually (rather than at once, as when ovulatory cycle) to reject, that always leads to initiation of long-term bleeding, often highly plentiful. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding of anovulatory character can meet and when follicles atresia. In this case pathology in ovaries the even maturing of many follicles, which, however, not having achieved complete ripeness is seen, undergo regress, i. e. atresia. The follicles atresia as opposed to of persistence is followed by not high, and lowered by the estrogens precipitation. However prolonged effect of estrogen on the endometrium even in low concentration leads to its hyperplasia. So that, the persistence and the follicles atresia give the similar pathohistological picture of uterine mucosa. As with persistence, when follicle atresia before bleeding initiation the amenorrhea is seen, however the duration it if the latter case usually more is significant (up to several months). After such amenorrhea begins the long bleeding, largely conditioned by the reducing the concentration of estrogens in the body. It should be noted that the hormones bust in the body is major factor of bleeding initiation. However only bust the estrogens concentration, as though and other hormones (when ovulatory menstrual cycle. The bleeding arises on the down grade as estrogens, and progesterone), it is impossible to explain all the compound mechanism of menstruation-like hemorrhage. Second driver are vascular change in response on 191 the down grade of hormones. The fact that the vascular system of the endometrium has specific response to fluctuations in blood of sex hormones. Due to of long-term estrogenic action is developing vascular distention accompanied by circulatory disturbance and bleedings. All these causes nutrient loss of uterine mucosa, its necrotic change with abruption of single units. Such abruption is carried out very long-time, as the long persistence of bleeding - the most typical clinical symptom of dysfunctional bleeding is responsible for. When anovulatory uterine hemorrhages the pathological process may render his adverse impact in practice in any one of system links the hypothalamus - the hypophysis - the ovaries - the uterus. However basic <the events> most frequently played out in system the hypothalamus - the hypophysis, that is expressed in insufficient production lh. at the same time well it is known that ovulation is carried out under the impact of two hormones: fsh and lh, in this case is of the great importance the insufficient production lh. Ranking among great significance of primary violations in system the hypothalamus - the hypophysis not lower value have and the primary changes at the level of ovaries accompanied by the implication in the pathological process of hypothalamushypophisis axis (the communication between hypothalamus-hypophisis axis and ovaries shall be exercised according to the law of double feedback). The clinical picture of anovulatory bleedings largely is made up from symptoms of suppression of menses accompanied by bleeding initiation. Disease is inclined to recurrences. The duration, bleeding tailors - over a wide ranges: from 2 weeks up to 1. 5 months and even more; when this amount lost blood also is sometimes by the different. When follicle persistence bleeding, as a rule, more plentiful, rather than when atresia. However when follicle atresia of bleeding very often receive the long character, that rarer is seen when persistence. In juvenile age of bleeding there is often very plentiful and are followed by the development of posthemorrhagic anemia. This is explained comparatively frequent combination of ovarian dysfunction with atresia of the uterus, whereas; in copulative and climacteric age of even long-term bleeding not always are followed by the sick anemizatsion. Long-term and the plentiful bloodlosses in some patient cause the development of secondary irregularities anticoagulant blood system (increase in levels of free heparin, fibrinolytic activity of blood, the lowering of platelet aggregating functions etc.). These disorders without corresponding the correcting by the drug preparation enhances the bleeding and leads to more severe anemia. After violation elimination of ovarian function and the normalization of menstrual cycle of change of blood-clotting also gradually vanishes. 192 Important symptom of anovulation - infecundity. It is usually several precede disease, since right before atresia or follicles persistence, accompanied with bleeding, in the patient the anovulatory cycles often arise. In childbearing year the infecundity often is sometimes is bound not only in violations of ovarian function, but as well with inflammatory changes of uterine adnexa, which precede such bleedings and accompany them. These is why at examination of woman the possibility not only endocrine, but as well of tube character, infecundity one should keep in mind. When gynecological examining several augmented the uterus and the cystic change of one of ovaries often find. The dysfunctional bleedings often group with uterus myoma, because for both disease the increased production of estrogenic hormones is typical. In such instances the uterus increases more much, and on its surface typical interstitial or the subserosal myoma units are discovered. The diagnosis of anovulatory uterine hemorrhages usually do not cause formidable difficulties. First and foremost it is necessary the direct attention to the typical symptoms of cases: suppression of menses, replaced by bleeding. Sometimes the delay of month-long can be absent; in such instances the ceaseless bleedings or the sanguine genital discharges are seen almost. From additional methods of examination made wide use of tests of functional diagnostics. For all types of anovulation typical monophasic complex of basal temperature - most exact and the reliable symptom of dysfunctional bleeding. The follicle persistence is characterized expressed by the pupil symptom (+ + +, + + + +), high calcitonin-like immunoreactivity (70-80%), great tension of the cervical mucilage over all. amenorrhea period. When atretic follicles, when giperestrogenemiya is lacking, all these symptoms has been expressed weaker. The most important diagnostic value has abrasion of the endometrium. This interference very is wide is taking advantage of climacteric and childbearing year for the diagnostics of bleeding character, exception of endometrial cancer, and also for the installation of bleeding. When microscopic study of scrape of mucosa it is more usual to find cystic glandular endometrial hyperplasia or the polyposis, while the least signs, indicative of secretory conversion of mucosa are lacking. When stubborn, recurrent bleedings pathologist may detect the sites of atypical endometrial hyperplasia, that is necessary regardaas the pre-cancer picture. In juvenile age to endometrectomy on vital indications (the lack of effect from recent species of therapy at hand of persistent hemorrhage and growing anaemia) come running only. In specialized gynecological permanent establishments hormones definition in blood and urine made wide use of, in this case find the changes in gonadotropins production 193 (especially the lowering lh before assumed by the ovulation term), excretion violation of estrogens and the low findings of urine pregnanediol. It should be noted that the diagnostics of anovulatory uterine hemorrhages in most case and without these timeconsuming examinings, calling for dedicated equipment. and corresponding the personnel qualification is possiblea. The big is of practical significance (or importance) has the differential diagnostics of dysfunctional uterines bleeding with many others common and gynecological diseases, in which the cardinal symptom is the uterine hemorrhage. When conducting the differential diagnostics first and foremost it is necessary to rule out blood disease, disturbance of function of thyroid and adrenal cortex. Along with this follows always to remember, that the uterine hemorrhages alike often arise and when structural diseases of genital organs (the myoma, the cancer etc.). In infancy menstrual function the juvenile bleedings follows from very early on are indistinguishable from blood disease, most frequently from Werlhof's disease (thrombocytopenia). For blood disease typical lead in anemnesis on nasal and ulorrhagia, the easy education when small bruises and injuries of subcutaneous hemorrhages. Blood disease more often is followed by the strengthening and lengthening of menstrual hemorrhages (menorrhagia), in this case the rhythm of menstrual cycle breaks down concerning rarely. In blood analyses is discovered the sharp level reduction of platelets. If during evaluation of the patient with juvenile bleeding she has find the Werlhof's disease or some other blood disease, then such sick the they is necessary to direct to hematologist. When liver diseases, especially owing to suffered the Botkin's disease, in some patient bis arise violation of menstrual function, having the metrorrhagia character. It's related to active role of liver in return of sex hormones. Such sick must first and foremost treat the medical man. Only the stiff character of violations of menstrual function at hand of signs of significant improvement liver disease may warrant for treating at gynaecologist. When diseases of thyroid and adrenal glands also can arise different violation of menstrual cycle (Meno-and metrorrhagia). This is related to the fact, as thyroid, and the adrenal glands are under the influence of tropic anterior pituitary hormones (the thyrotropic hormone and acth). Production violation of these hormones, often are followed by changes in production fsh and lh, and this leads to anovulation and uterine hemorrhages. These is why in the patient with dysfunctional uterine bleeding it is necessary during examination obligatory to exclude and these disease. The 194 uterine hemorrhages in age dependence follows to differentiate with following by diseases: in juvenile age - with tuberculosis of genital organs, granulezokletochnoy ovarian tumor and neck cancer and uterine body (rarely); in copulative - with pregnancy (beginning abortion, abortion in pitch incomplete abortion, nondeveloping the pregnancy), placental polyp, cholecystic sideslip, chorionepithelioma, uterus myoma, especially submucous, body cancer and uterine cervix, polyps, and cervical erosions; in climacteric period-with body cancer and uterine cervix, granulosa-and ovarian tekakletochnymi tumor, erosions and neck polyp Uterus. In connection with large number of different disease and limited volume of article consider it necessary of indicate only on basic and the most frequent disease, with which has to carry out the differential diagnostics of dysfunctional uterines bleeding. Discontinuing the uterine pregnancy may be accompanied as spread blood-stained discharges from the vagina (the beginning abortion), and heavy bleeding (the abortion in pitch the incomplete abortion). However on the view in mirrors always find the cyanosis signs of mucosa, slightly open or disclosed the uterine shed, the uterus softening and other probable signs of pregnancy. When non-developing pregnancy the uterus approach normal sized just at the beginning of pregnancy or else when very long-term finding of parts of foetal egg in its cavity. At the same time when ovarian dysfunction the uterus rarely increases to a great extent. The placental polyp usually arises owing to abandonment in the uterus of remainders of foetal egg (in anemnesis at such women the clue to abortion always is available, while woman with aiovulyatsiey suffer by the infecundity). The bleeding appears through 6-8 the week after abortion. When diagnostic curettage organized part of foetal egg are removed with very large labour, whereas hyperplastic the mucosa when ovarian dysfunction manages to create to remove without any special efforts. Is of the great importance the hystological research of scrape of the endometrium. Very often the ovarian dysfunction has to diagnose with uterus myoma (especially with submucous. However when myoma are lacking characteristics for dysfunctional uterines bleeding of suppression of menses. When hysterography is discovered the round structured shadow (submucous disposed the swelling unit). The cervix cancer with relative ease to exclude on the view with the aid of a speculum and colposcopy. Decisively the problem decides the biopsy. The corpus uterine carcinoma largely exclude, on a foundation data of pathmorphological research of scrape of the endometrium. The polyps and cervical erosion with relative ease to diagnose on the view of uterine cervix in mirrors, and also by means of colposcopy. 195 Feminizing ovarian tumor (granular-cell and tekakletochnye growth) externally are followed by typical picture of dysfunctional bleeding: suppression of menses, replaced by bleeding. When endometrial abrasion owing to prolonged exposure to mucosa of estrogen also are being revealed the hyperplasia and the polyposis of the endometrium. This is why in that cases they is necessary very carefully to palpate the appendages region. Tumor detection testify in behalf of diagnosis feminizing ovarian tumor. In questionable cases has been shown the laparoscopy. Treatment of dysfunctional uterines bleeding is doctor mission. This is why we will be limited only characteristic of shared principles of therapy of such sick. Treatment of dysfunctional uterines bleeding always they is necessary begin from common arrangements. The exception may contribute only the cases of heavy bleeding, when the delay with diagnostic uterine curettage or assignment of hormone haemostasis it is dangerous for woman health. Common treatment should be aimed at elimination in the patient the negative emotions, physics and mental overworking, the infections liquidation and intoxications. All this facilitates relationship normalization in system the hypothalamus - the hypophysis - the ovaries - the uterus. For that purpose lead the psychotherapy, designate the bromine preparations and caffeine, the tranquilizers, sedative and sedative. The conducting of these arrangements permits to normalize the menstrual function without the use of hormonal preparations at 50% sick in elemental disease stage. Along with this when great bloodlosses is wide resort to blood transfusions, introduction of dried plasma, designate the vitamins, the iron drugs, the physiotherapy (the galvanic collar on Shcherbak, the electrical stimulation of uterine cervix). When juvenile bleedings, in which especially often arise secondary irregularities anticoagulant blood system, have been shown such preparations, as protamin sulfate, the E-Aminocaproic acid. The symptomatic therapy, aimed at increasing of contractile properties of myometrium, when dysfunctional uterines bleeding not have a positive result, because By these means (the calcium chloride, the ergot preparations, the oxytocin and others) it is impossible the stop bleeding, conditioned by the presence of the uterus overgrown the mucosa. The wide distribution in treating of dysfunctional uterine, bleedings received the hormone therapy. It pursues two main aims: control of bleeding (hormone haemostasis) and regulation of ovarian function with reestablishment of ovulatory cycles or else cessation of menstrual function (in climacteric age). 196 To exercise hormone haemostasis made wide use of major dose of estrogens, the progesterone and the synthetic progestins. After control of bleeding it is necessary to pursue the hormones introduction, since on the down grade their the blood concentration the organism responds by the bleeding recurrence. The regulation of menstrual cycles lead by means of gonadotropins, combined use of estrogens and progesterone, and also by means of clomiphene - preparation, challenging the production lh and causing the ovulation. The treatment character subject to violations form of menstrual function (the persistence, the follicles atresia) determines the doctor. The auxiliary medical personnel may only perform treatment purposely and under control of doctor. Sick, suffering by stubborn dysfunctional uterine bleeding, are subject to dispensary observation in specialized studies of female dispensaries, where do you work the specialists, the well knowing problems of gynecological endocrinology. 197 Subject: Bleedings in I pregnancy half. Abortions. Abortion. Abortion during first 28 weeks. In most case the fruit happens to be nonviable. If thanks to critical care it survives, the abortion are regarded as the pre-term deliveries (marriage office gives the certificate of the birth of a child ). Differentiate early (up to 16 weeks ) and late (of 16 up to 28 weeks ) the abortion, artificial and spontaneous. When the spontaneous abortion is repeated more than two the time, then speak about habitual miscarriage. The abortion artificial is produced in the first 12 weeks of gestation in medical institution. At hand certain indications may be прервана and after indicated date by the decision of health authority. When pregnancy by the term up to 6 weeks with abortion one should not to hurry, since the marginal increase of uterus may be observed and in the absence of uterine pregnancy (the ectopic pregnancy, the ovarian dysfunction, the premenstrual period and so on ). Before operation the woman is to be inspected, that assumes the vagina examining and urinary tract on microflora, the blood test for syphilis and AIDS. Symptoms and current. When satisfactory post-operation condition - normal temperature, absence of stomach pains and bleeding signs the acceptor may be extracted from permanent establishment. The insufficient uterine contraction (the subinvolution ) is followed by usually elevated temperature, long-term bloody issues, 198 that often indicates the presence in uterine cavity of remainders of foetal egg. In such случах is produced repeated abrasion. Abortion spontaneous. The causes it often remain elusive. The great significance have the previous artificial abortions (especially the interruption of primary pregnancy ), the delayed puberty (infantilisms ), acute and chronical infectious diseases, the immunogenetic disparity of maternal blood and fruit on rh factor and blood group, disfunction of endocrine glands (the hypophysis, the ovaries, the adrenal glands, thyroids ) and the cervical incompetence (the pathology of uterine cervix ), the physical factors (the manual lifting task, injury, the bruises and so on ). Differentiate several stages of spontaneous abortion. The abortion posing a threat to - sick complain of the small pain in the lower abdomen and in low back. Кровянистых genital discharges no, the external shed is closed (when cervical incompetence приоткрыт ), the uterus quantity corresponds gestational age. Such condition it is considered convertible, and when successful early treatment the pregnancy in future are developing normal. Abortion begun - increased pain, emergence of mean spread of bloody vaginal discharges. The uterus quantity corresponds gestational age, the external shed is closed or slightly opened. Pregnancy conservation still it is possible, but forecast is worse than when abortion threatened. Abortion in the course - exfoliation of foetal egg from uterus walls and exile from its cavity through cervical canal. Sick complain of cramps in the lower abdomen and bloody issue (sometimes great ). The uterine sizes correspond gestational age or are smaller than it. Pregnancy conservation it is impossible. Abortion defective - delay in uterine cavity of parts of foetal egg, accompanied with, as a rule, plentiful bloody issues. The abortion complete - is seen more often in the early pregnancies. The uterus is void of remainders of foetal egg, decreases, the cervical canal of the uterus closes and the bleeding shall be stopped. Treatment. Subject to stage. When posing a threat to and incipient abortion the bed rest in hospital conditions has been shown. Psychotherapy, eliminating the negative emotions and positively influencing the advance of pregnancy. The medicated methods include the sedative therapy (the bromine preparations ), the hypnotics before bed, the vitamins (Whigs e, the ascorbic acid ), the hormonal drugs (the progesterone, combined the estrogen progestin preparations ). When abortion in the course and defective surgery extirpation of foetal egg or parts thereof has been 199 shown. When late abortion, not accompanied with great bleeding, wait spontaneous birth of foetal egg, endometrectomy has been shown in case of the delay in parts cavity of placenta. When posing a threat to or beginning abortion, conditioned by the cervical incompetence, surgical intervention is indicated: placing a suture on uterine cervix. Infectious complications of spontaneous abortion.1 ) uncomplicated feverish abortion: the infection is localized in the uterus, in the patient the weakness, the tachycardia, fervescence and leucocytes in blood.2 ) complicated by feverish abortion: the infection extends beyond uterus, but is limited by the region of small pelvis. Typical deterioration of systemic condition, pain in the lower abdomen, following the temperature rise, the chill, the great increase of leucocytes кропи and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR ).3 ) septic abortion. Occurs by the serious condition: pallor of dermal covers, shaking chills, has been expressed share backward wave tube Fever with phenomena of common intoxication and toxic changes of bodies - liver, kidneys, spleen. Treatment infected abortion. Leading the method - antibiotic therapy. When complicated by and septic designate the massive doses of antibiotics, sulfonamides, desensitizing the preparations, the vitamins. The remainders of foetal egg remove only when uncomplicated abortions heavy bleeding. Usually this operation produce after infection abatement. Bleeding in the first half of pregnancy. Most frequently is sometimes is linked to spontaneous abortion, when defective - growing the bleeding is seen, in which scrape the uterine mucosa and remove the remainders of foetal egg (refer to. Abortion ). The violation of tubal pregnancy is followed by dark spreading blood precipitations. Pregnancy diagnostics Clinic-Objective survey methods: In this case we must remember about certain complaints, the direct attention to history taking, the presence of doubtful signs of pregnancy, connected with subjective senses of woman, probable signs, conditioned by objective changes in gender sphere of women and reliable signs, specified by different methods of obstetric examination. Laboratory - Diagnostic examination methods: Such methods of examination of as colpocytological, definition in blood sera or in the urine of anterior pituitary-like principle make it possible to diagnose the pregnancy on early times. 200 Especially the pay attention follows on the ultrasonic diagnostic techniques of pregnancy, that makes it possible to put the cyesiognosis with 2-3 week term, to register the cardiac action with 4-5 week term, to educe the motor activity of fruit with 7-8 week term. They is necessary to calculate the gestational age: - On date of last menstruation; - On first presence in ГВП or СВП; - On objective survey methods (internal gynecological ). Concept about artificial abortion and terms its conducting Artificial abortion is artificial abortion by the term up to 12 weeks, being produced by will of woman or on medical and social indications, carried out by doctor observing of rules of asepsis and at contra-indications even number within walls of medical institution. Such period has been identified by the fact that in this case, it is possible, to remove the foetal egg with smaller risk of complications, than at a later dates. The less the gestational age, in which the it is interrupted those, is less marked consecutive hormonal disturbances. Methods for performing artificial abortion in accordance with a pregnancy. Depending on time separate several kind of artificial abortion. • When suppression of menses up to 2 weeks it is possible conducting "of MiniAbortion. This procedure is held under easy anesthetic or local anesthesia. Through uterine cervix in uterine cavity introduce the nozzle, which in their turn is attached to system, creating the vacuum. At expense of negative pressure the foetal egg remove from uterine cavity. • Up to 7 weeks of gestation the medicated abortion by means of preparation Mifegin RU-486 ) one can perform. The preparation causes the uterine contraction and the exit of foetal egg. Surgical intervention in this case is not required. • When term from 5 up to 12 weeks abrasion of uterine cavity is being used. Under intravenous anesthesia by means of tool cervical dilatation, whereupon abrasion of internal uterine surface and disposal of foetal egg by means of special purpose tools is held. • Artificial abortion by vacuum-extraction (when gestational age not more 9-10 weeks 201 Possible complications of artificial abortion and their diagnostics. The complications of artificial abortion is divisible into two group - early and late. To early belong following complication: • The perforation of the uterus arises during runtime abrasion owing to wrong of technician or wall thinning of uterus due to of inflammatory processes. In fault time uterus wall can be damaged the abdomen organs, that may require serious surgical interventions. • The bleeding arises owing to damage of blood vessels of uterus wall. The plentiful bloodloss can cause depressed case, which requires the immediate interferences of doctor. • Infection. Even with observance of all terms the emergence risk of acute infectious inflammation there are. The pathogenic microbes can exist in genital tracts and the artificial abortion only gives the impetus to their renewed activity. Late complication not less than are dangerous, than early. Among this are: • The violation of menstrual cycle can arise owing to sharp change of hormone background, violation activity of endometrial owing to abrasion, and also chronical inflammatory processes, which often are activated after artificial abortion. • Ectopic pregnancy. Owing to эндометрия damage, adhesive process, when consecutive pregnancy the fertilized egg goes out not in uterine cavity, and remains in uterine tube . The situation admission often leads to disposal of uterine tube, that may become infecundity cause. • Incompetent pregnancy. Due to damage uterus consecutive pregnancies may conclude spontaneous abortions. Damaged the uterine cervix can't withstand burden, arising in connection with developing by the fruit. • The infecundity arises from damage endometrum, inflammatory processes, resulting in impassability of uterine tubes. • Endometriosis. The artificial abortion leads to increasing of risk of development of this the disease, which is followed by the fabric emergence of эндометрия in uterine muscle, that is followed by the plentiful painful menstruations. • Increasing of risk of development of malignant tumor of reproductive system. It is known that the abortion increase the risk of developing cancers of mammary gland and ovaries cancers. Rehabilitation and postabortal contraception. 202 In postabortal period by the most important task is the infectious disease prophylaxis. After abortion up to following menstruation follows especially closely to observe the hygienic of genital organs. In the first two weeks the woman must have a bath only under a shower. And the sex life up to following menstruation is prohibited, since in this case become infected with the genital organs, inflammatory diseases are developing, and the uterines bleeding often arise. In order to avoid abortions, and thus, and their aftermaths, they is necessary ably and competently to enjoy correctly selected by contraceptive, that not only keep out unwanted pregnancy, but as well sex drive and the sexual satisfaction often raises. Measure on abortions lowering and frequency their complications. Sanitary educational work in this issue is given to especially the much attention. Subject: Ectopic pregnancy, cholecystic sideslip, chorionepithelioma. 203 In the latter half of 21st century the firm a tendency to frequency growth of ectopic pregnancy throughout the whole world, independent of computation method the given finding is outlined. According to the data of epidemiological studies, in industrially developed countries the average statistic frequency of ectopic pregnancy is 1, 2-1, 4% in relation to total number of pregnancies and 0, 8-2, 4% - in relation to labors. Recently is seen the disease incidence growth in two age groups: among teenagers and women of 30 up to 39 years. Classification The international classification of diseases (MCP 10 ) offers following the classification of ectopic pregnancy: A. Abdominal (ventral ) pregnancy B. Tubal pregnancy (1 ) pregnancy in uterine tube (2 ) break of uterine tube owing to pregnancy Tubal abortion. V. Ovarian pregnancy City. Another form of ectopic pregnancy 1 neck 2 combined 3 in horn of uterus 4 intraligamentous 5 in mesometrium 6 non-precise. In difference from MCP in national literature the tubal pregnancy divide by: 1. Ampullary. 2. Isthmial. 3. Interstitial. Ovarian categorize: 204 Developing at the surface of ovary. Developing inter follicular. The abdominal gestation is subclassified into: Primary (implantation in the abdomen occur originally ). Secondary (implantation in the abdomen occurs owing to exile of foetal egg out of the chimney ). Etiology of ectopic pregnancy A. bodies infection of small pelvis. Chronical salpingitis— Frequent find (30-50% ) when ectopic pregnancy. Often the ectopic pregnancy arises in womens with inflammatory diseases of bodies of small pelvis. 1. The infectious process in endosalpinx leads to fibrosis and rumen changes, disturbing the transport function of pipe due to its the narrowing, formation of false pitch of change of ciliated epithelium and defective peristalsis. All this feature hamper advance fertilized egg, promoting its implantation in pipe. Chronical inflammatory diseases of body of small pelvis usually hit the both uterine tubes. The frequency of repeated ectopic pregnancy in the second pipe is 10-15%. B. narrowing of uterine tube 1. Inborn defects of uterine tube (for example diverticulum and pockets ). 2. Benign tumor or pipe cysts. 3. Uterus fibromyoma in the area of tube corner. 4. Pipes endometriosis. 5. About tube soldered connection, arising bis when appendicitis or after operations on bodies of small pelvis and \ or abdominal cavity. Surgical interventions on uterine tubes. Frequency of ectopic pregnancy above after plastic operations on uterine tubes concerning of inflammatory diseases or reestablishment their cross-country capability after dressing. V. migration fertilized egg. At woman most the corpus luteum find out in ovary on the side, opposite localization of ectopic pregnancy. 205 1. When the external migration (for example from right ovary in the left uterine tube through the abdominal cavity or vice versa ) the blastocyst has time so to rise, that not passes through strait of pipe. 2. The fertilized egg may also to go through uterus (the in-migration ) and to hit in the opposite pipe. G. Navy. Often, ectopic pregnancy occurs when you use the IUD. D. Pregnancy obtained by in vitro fertilization. Pathogenesis of ectopic pregnancy In uterine tube, the abdominal cavities and rudimentary horn of uterus of no powerful specific mucous, which is inherent in usual place of implantation - uterine cavity. Progressive the ectopic pregnancy stretches fruit container, and the chorionic villus destroy the subjacent tissue, including the blood vessels. This process may elapse with different speed subject to place the localization and is followed by more or less expressed by the bleeding. If the foetal egg develops into Isthmial department of pipe, then the bazotropic growth the chorionic villus are taking place, which fast destroy all stratum of pipe. And already to 4-6 week this leads to pipe break and massive bleeding. The pregnancy, localized in interstitial department of pipe, however in connection with big thickness of muscular layer the duration existence of such pregnancy more analogously is leaking and achieves 10-12 weeks. When ampullar localization of foetal egg is possible ovoimplantation creasy of endosalpingsa. In that case the growth the chorionic villus possible apart of pipe lumen. In this case of owing to pipe reversed peristalsis it is possible exile detached foetal egg in the abdomen, i. e. occurs the tubal abortion. When close of fimbrial department of pipe given vent intraluminally of pipe the blood gives rise of gematosalpingsa. When open lumen of ampoule of blood, flowing out of the chimney and folding in the area its funnel, may form peritubarnuyu hematomas. When blood amassment in Douglas space the zamatochnaya hematoma, delimited from abdominal cavity by the fibrous capsule is organized. In rare occasions the foetal egg, exorcised out of the chimney, is not perishing, and implanted in the abdomen and continues to evolve. 206 In warranties it is possible the development of ovarian pregnancy, which rarely there is the long time and leads to plodovmestilischa break, accompanied with great bleeding. Signs of ectopic pregnancy Clinic of pipe break. The sharp pains in belly bottom and in the groin, panthodic in shoulder, the blade, the rectal intestine suddenly arise. Frequent symptoms: deathdamp, loss of consciousness. 1. Objective inspection. Discover fall hells, the running pulse, the pallor of dermal covers and mucosa. Belly on palpation is painful on the part of break, the ShchotkinBlumberg symptom slabopolozhitelen. Percussion - signs of free fluid in the abdomen. 2. Vaginal touch. The uterus insignificantly is increased, myagkovataya; more mobile, than usual (floating the uterus). Slight edema in the area of uterine adnexa. The posterior vaginal vault is flattened or is protruding, on palpation (the Douglas call) is extremely painful. In an attempt bias of uterine cervix the sharp pain anterior arises. . Clinic of tubal abortion. When abortion follow the pattern seen in tubal abortion arise the paroxysmal pains in belly bottom, appear the bloody issues. There is often short-time fainting. 1. Vaginal touch. The uterus myagkovataya, slightly is increased. The tumour-like formation in the area of one of appendages, painful on palpation, slow-moving is palpable. The debility when uterine displacement anteriorly and on palpation posterior vaginal vault have been expressed weaker, than when pipe break. Often from uterine cavity occurs precipitation of decidual cell, 2. When hystological research extracted the decidual cell or scrape of mucosa of uterine body discover the elements of decidual tissue without chorion elements. Diagnostics Presumable signs. Suggestion for ectopic pregnancy appears in complaints of pregnant on the pathologic bleeding and pain in inferior of belly. In anemnesis inflammatory diseases of body of small pelvis (PID) or operations on bodies of small pelvis. Differential diagnostics. The diagnostics of ectopic pregnancy is simple enough at acceptors with amenorrhea, signs of pregnancy, pains in inferior of belly and bleeding. It is necessary to rule out following condition. 207 1. The looping of ovarian cyst or the acute appendicitis are followed by unilateral pains in right iliac area; tongue is dry, positive the Shchotkin-Blumberg symptom. Other than the amenorrhea, swoons, anaemia and shock is sometimes. The blood analysis indicates the inflammatory process: leukocytosis, increasing ESRE. 2. Interruption of uterine pregnancy. When interruption of uterine pregnancy the external hemorrhage more has been expressed, than the pain syndrome, whereas when ectopic pregnancy the pain predominate over. When vaginal touch the uterus is increased respectively term of suppression of menses, the cervical canal openly, it is possible precipitation of foetal egg from uterine cavity. Matters and the precipitations character: when abortion they liquid, ruddy; when interruption of tubal pregnancy crumbly, colours of coffee-ground owing to mixing blood with desquamated necrotic of decidual cell. Bleeding in corpus luteum when normal uterine pregnancy (ovarian apoplexy). The bleeding in corpus luteum usually do not cause extremely bad pain and shock, typical for ectopic pregnancy. In addition, uterine hemorrhage usually no. The ovarian apoplexy may arise and at a point of ovulation (in domestic practice the ovarian apoplexy - the bleeding at a point of ovulation). Diagnostic techniques of ectopic pregnancy Level determination chorionic gonadotropin (chorionic gonadotropin). The test for definition in blood sera of the p-subunit of chorionic gonadotropins is positive in all instances of ectopic pregnancy, while the test for chorionic gonadotropin in the urine is positive it is only in 50% cases. A. The stepness rate chorionic gonadotropins in blood helps to differentiate normal and pathologic (ectopic or non-developing) the pregnancy; when normal pregnancy the level chorionic gonadotropins in blood doubles every two days. B. When threshold level chorionic gonadotropin 6000 mIU / ml the uterine pregnancy discover when Uzi. if in uterine cavity no embryo, it may be supposed the ectopic pregnancy. V. The standard urine probe on pregnancy is sometimes adverse in 50%) cases of ectopic pregnancy. One ought to bear in mind that often in cases interruption of ectopic pregnancy on a foundation of bleeding and pains the abortion threatened erroneously diagnoses. 2. Bodies Uzi of small pelvis helps to exclude the ectopic pregnancy, if in uterine cavity the foetal egg through seven weeks after last menstruation clearly is determined; this gestational age correlates with level chorionic gonadotropins 5000208 6000 mIU / ml. The detection augmented the womb and ovary when ultrasonography has no diagnostic value, since such picture may simply can be early the uterine pregnancy and the yellow tel .. Transvaginal ultrasonography. When ultrasonography, executed by means of transvaginal probe, the foetal egg it is possible to visualize earlier than when transabdominal echography. A. The foetal egg in uterine cavity can be found when level chorionic gonadotropin 1500-2000 mIU / ml, corresponding six weeks of gestation, B. Consequently, by means of transvaginal ultrasonography the ectopic pregnancy it is possible to exclude on 4-6 days earlier than when transabdominal ultrasonography. The culdocentesis lead to identify free blood in the abdomen when complainings of the acute pain in belly bottom in combination with pathologic bleeding, swoon or shock. A. The needle № 18 introduce through the posterior vaginal vault in Douglas' cul-desac. B. When culdocentesis they is necessary to receive the fluid. V. Is normal content syringe - 3-5 magnetic tapes of transparent fluid of nankeen. At hand of blood in the abdomen receive dark liquid the blood. Content in syringe may not to be when soldered connections or when organisation of blood clots, that do not remove diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. The laparoscopy and culdoscopy make it possible of inspection of uterine tubes and ovaries, if the diagnosis gives rise to doubt. Risk, connected with laparoscopy performance, much is smaller than risk of severe consequences when undiagnosed the ectopic pregnancy. Contra-indications for laparoscopy (by the opinion of Gryaznova) are suffered the peritonitis, rumen changes frontal abdominal wall, the meteorism, the heavy neuroses and cardiovascular disease in stage unbalance. Hystological research of the endometrium. When abrasion of uterine cavity concerning of pathologic bleeding (for example when suggestion for the spontaneous abortion), obtained the decidual tissue without the chorionic villus in samples of endometrium indicates the ectopic pregnancy. Additionally in study of strokes it is possible to educe the phenomenon Arias-Stella - the atypical cells in the endometrium with swelling, protoplasm vacuolization, giperhromaziey, nucleus hypertrophy with fragmentation, turning up in response to the hormonal changes when pregnancy. 209 Gryaznov with co-sponsors considers by this method by the permissible only for womens, which has no interest in pregnancy conservation or when suggestion for the incomplete abortion. 7. Bodies reography of small pelvis. This investigation permits to receive data on congestion of different organs and hence, about their the functional activity. Treatment of ectopic pregnancy In modern practice stills shall be used operative and the conservative treatments of ectopic pregnancy. Both this method have its advantage and disadvantages. Gryaznov with co-sponsors believes that operative therapy of ectopic pregnancy is optimum. In modern foreign literature (Gollesky, Goshert et al the authors) is information about successful application of synthetic hormone-like preparations and methotrexate for treating of tubal pregnancy. In our country shall be used integrated approach to treatment of ectopic pregnancy. It shall comprise: Operation. Fight against bleeding, hemorrhagic shock, bloodloss. Maintaining of postoperative period. Rehabilitation of reproductive function. Operations, applied to discontinuing the tubal pregnancy All described lower operation can be performed as laparotomicheskim, and laparoscopic means. To advantages of laparoscopic technique belong: Duration reduction of operation. Duration reduction of postoperative period. Build-down of duration of stay in permanent establishment. Reduction in the number of rumen changes frontal abdominal wall. Best cosmetic effect. Salpingoovarikoektomiya. Previously at hand of constant uterine adnexa on the opposite side this species of operation was used precisely, however now disposal of normal ovary it is considered unjustified. It's related to that now there is a possibility 210 for ekstakorporalnogo conception, What for it is necessary maximum reestablishment of generative potential (WW Beck). Salpingectomy. Now it is considered by the optimum treatment of ectopic pregnancy. Most of all this operation is convenient for treating discontinuing the tubal pregnancy in case of accession of massive bleeding (WW Beck, t. Wolff). The operation and the blood transfusion in such instance lead simultaneously. After autopsy of abdominal wall it is possible to use the refusion of blood (Ailamazyan EK with co-authors). The reinfusion is contraindicated when long ago pregnancy loss (WW Beck). Operation, applied to progressive of tubal pregnancy The frequency diagnosing progressive the ectopic pregnancy increased recently not only at expense of increase of total amount of ectopic pregnancies, but, essentially at expense improving diagnostic techniques. In the detection of the patient progressive of tubal pregnancy it is possible application of more sparing the treatments, rather than when discontinuing the tubal pregnancy. Extrusion. In the patient with progressive the tubal pregnancy (when localization of foetal egg in ampullary department of pipe) the foetal egg it is possible carefully push to out. This method now shall not be applicable by the fact that very there is a high probability of repeated initiation of tubal pregnancy Salpingostomy. Is being done the longitudinal salpingostomy. After disposal of foetal egg salpingitis, usually not sutured. Shinkareva L. F. and Aleksandrov M. S. in the event that the chorionic villus was not germinating in the muscular layer of pipe limited themselves to its abrasion. Segment resection of uterine tube. Remove the pipe segment, bearing the foetal egg, whereupon are exercising the anastomosis two pipe tips. When impossibility of execution salpingo-of salpingoanastomoza it is possible to cord both end and to impose the anastomosis later. Operation when abdominal gestation The operation technician when abdominal gestation depends on localization of foetal egg. Usually the operation is reduced to disposal of foetal egg and consecutive of hemostasis. Maintaining of postoperative period. The maintaining of postoperative period in these case the operations several is different from usual. 211 At once after the operation sick coat by heaters, on the follicle gritty belly put, which further substitutes for ice bag. When appropriate is going on infusion therapy and anesthesia. Absolutely needed consider the preclusive antibiotic treatment. Besides is needed the vitaminotherapy and appropriate nutrition. Conservative treatments of ectopic pregnancy At hand progressive the ectopic pregnancy of small term the methotrexate is used successfully. The methotrexate is antagonist of folic acid. It is sealing off the fabrics metabolism, having the high level of exchange, among which belongs and the trophoblast. Application complication of methotrexate is the acute massive bleeding from place the pregnancy localization through 1-2 weeks after preparation cancellation. Rehabilitation of reproductive function Lead action, dedicated to restoring pipe cross-country capability. Lead sanatoriumresort therapy. The information, that in womens, undergoing the tubal pregnancy, often defective and second the pipe are available. This is cause for carrying out of anti-inflammatory therapy in postoperative period. When they is impossible to of child conception by the naturally it is possible IVF. The cholecystic sideslip - the peculiar change of villous envelope, in the basis of which rests the degeneration the chorionic villus. When cholecystic sideslip occurs the sharp edema the villi, they expand and turn into bubbles, filled by the clear liquid, which remind grape clusters. The causes of origin of trophoblastic disease, including chorionepithelioma stills it is unknown. The cholecystic sideslip develops into as the aftermath the fertilized eggs presuppose that, which had lost his nucleus. Largely, the cholecystic sideslip is developing at young women. The cholecystic sideslip was complete and partial. When complete cholecystic sideslip regenerate all chorionic villus, when partial cholecystic sideslip - only part them. More often this occurs on early pregnancies. The embryo in this case dies and dissolves. May arise distructive (destroying) the cholecystic sideslip, in which the bubbles grow in uterus wall on different depth and destroy its the fabrics. 212 Cholecystic sideslip: signs of a disease The cholecystic sideslip is characterized following by main features, each of which not always occur: Repeatedly repetitive low portions the sanguine genital discharges, sometimes in them, are discovered bubbles of chorionepithelioma. Often is developing early toxemia of pregnancy. The quantity discrepancy of uterus gestational age (the uterine sizes is in excess of normal for this term). Absence of true signs of pregnancy: the fruit is not determinated by means of palpation, ultrasound investigation, the fetal heart sound is not heard and when apparatus the examining is not registered. When body Uzi of small pelvis is determined the picture "snowy storm" in the uterus. Sharp increase jump of hormone level of pregnancy of chorionic gonadotropin in the urine and blood. Level of this hormone in several times higher than when normal pregnancy. Often are developing bilateral the ovarian cyst. Not distant the cholecystic sideslip on 5-6 month often is being born independently. When distructive cholecystic sideslip may arise life-threatening the bleeding. Cholecystic sideslip: disease treatment After the establishment of diagnosis of chorionepithelioma produce disposal of chorionepithelioma from uterine cavity, for this use abrasion of uterine cavity by the abrasion spoon, vacuum aspiration. When the bleeding emergence, posing a threat to woman life, produce the operation of hysterectomy. All distant fabric obligatory are channeled into the hystological research. The danger of chorionepithelioma is in what after they very dangerous malignant tumor - the chorionepithelioma (the hardest form of trophoblastic disease This swelling is booming and gives massive metastazing (first and foremost in easy). This is why all sick cholecystic sideslip produce the roentgen the bodies examining of thorax for the diagnostics of possible complications. After the result acquisition of hystological research, the woman is channeled into consultation to cancer observer, for solving of question about chemotherapy need. Sick must underlie close medical supervision over two years in connection with 213 eventual risk of development of chorionepithelioma. In the earlier year it the level of chorionic gonadotropin monthly, in the second - each three months make examination and determine. The pregnancy is contraindicated over two yearst. Horioepitelioma The malignant tumor, wich is developing from epithelial elements of chorion. Arises primarily after chorionepithelioma, but meets and after births of children or abortion. As a rule, hits women of young age. The swelling has the salient configuration: nodes of bluish or garnet. To size nodes Greatest, quantity from about cherry. The chorionepithelioma call by the metastases disease, because it early begin to metastasize. Horioepitelioma: signs of a disease Chief complaint is the emergence of bleeding genital discharges. Sometimes they appear in connection with beginning of regular menstruation after abortion or labors. The duration and the bleeding volume is different. Their the distinctive feature is the lack of effect from endometrectomy. As a rule, to halt uterine hemorrhage resort to procedure abrasion of uterine cavity. In case of uterus defeat chorionepithelioma, after abrasion the bleeding on the contrary increases, in connection with swelling traumatization. When growth chorionepithelioma throughout the uterus wall arises the internal intraperitoneal hemorrhage. Sick temperature rise, pain in the lower abdomen, the general weakness, the fatigue, the weight loss also may to mark off. Due to blood potoeri is developing the heavy anaemia (the quantity reducing of erythrocytes and hemoglobin). Not less than important sign of chorionepithelioma are whites with bad smell, which testify resolution of the tumour. Deterioration of state of the patient occurs very quickly, because the swelling is booming and extends (metastasizes) round the human body. The chorionepithelioma metastasizes in easy, the brain, the liver, the kidneys and also grows in vagina, the uterine cervix, uterine tubes and ovaries. Horioepitelioma: disease diagnosiss The diagnostics rests on inspection data, ultrasound investigation, colposcopy and hysteroscopy, level determination of chorionic gonadotropin. When gynecological inspection is determined augmented uteruses, its the sizes rarely is in excess of 8-9 weeks of gestation. The inspection in mirrors permits to see swelling metastases in vagina and the uterine cervix. Most important is determination in blood and level urine of hoironicheskogo gonadotropin, the number of which in the patient horioneipteliomoy is increased in scores and the hundred the time. 214 Obligatory is the X-ray research of bodies thoracic cavity for opportune the detection of metastases. Subject: Inflammatory diseases of female genital organs of nonspecific and specific etiology. Survey methods and treatment. The structure of gynecological diseases inflammatory diseases of genital organs occupy the first place. Patients with inflammatory diseases of the genital organs are 60-65% of gynecologic patients, of whom 20-30% require treatment in hospital. One of the unfortunate consequences of this category of disease is infertility. Early diagnosis, management, treatment and rehabilitation can restore all the specific functions of the female body. Etiology Nonspecific inflammation depends on the violation of the proportion of bacterial species associated pathogenic microflora of the vagina, its strong estrogenozavisimost: dominant role of different lactobacilli of transient microorganisms - Staphylococcus epidermidis, korinobakterii, bacteroides and other specific inflammation is possible with the decisive importance of microorganisms such as gonococci, trichomonas, fungi Candida, urogenital viruses ureoplazmy, mycoplasma, chlamydia, etc. Pathogenesis Mixed infection is a serious problem, because in this case increases the pathogenicity of each of the pathogens. In these situations, inflammation is marked reaction from the tissue, accompanied by epithelial damage, destruction and dysplasia. Classification 1. To outward seeming of exciter: • Specific • Nonspecific (septic etiology ) 2. On localization: • Disease inferior of genital organs: edeitis, bartholinitis, colpitis, endocervicitis • Disease of superior of genital organs: endometritis, salpingitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, parametrit 3. On clinical course: 215 • Acute • Subacute • Chronical • Latent Clinic Clinical manifestations of inflammation vary, depending on the nosological form of the disease, the etiological factor. In the lower division of clinical disease genital symptoms dominate the local disorders (itching, burning, abnormal leukorrhea, redness, swelling, rarely - pain). The clinical picture of diseases of the upper reproductive system is more diverse and is characterized as general (fever, intoxication, and inflammatory changes in the blood, and local (pain, uterine enlargement, adnexal; variety of patterns of whites, peritoneal signs, etc.) symptoms. The clinical picture present in varying degrees of severity: 1. Syndrome of local inflammatory changes 2. Inflammatory intoxication syndrome 3. Syndrome of immune disorders 4. Dysfunction syndrome related bodies 5. The syndrome of menstrual function disorders Clinical and objective methods of examination: it is necessary to pay attention to history taking, signs of inflammation associated with subjective feelings of women, the objective changes in the genital area of women and credible evidence, determined by different methods gynecological examination. Laboratory diagnostic methods: Such research methods as bacterioscopic, bacteriological, determination of antibodies to a particular infection provide an opportunity to diagnose inflammatory diseases. Bacterioscopic and bacteriological methods of diagnosis can reliably diagnose. Виды лечения 1. Conservative: 216 - etiotropic - detoxification - antihistamine - immunostimulators 2. Surgical: volume of transactions depends on the prevalence of the destructive process, the causes of the infection (pus formation tubo-ovarian, is resistant to conservative treatment of endometritis, salpingoophoritis, pelvioperitonita etc.) genitals comorbidity, age of the patient. Irreversible morphological changes in purulent tubo-ovarian formations, depth and severity of the destructive process, the presence of polyorganic violations lead to the fact that the only rational method of surgical disorders is. Surgical treatment should be based on the principles of organ, but with a radical removal of the main foci of infection. Each patient-specific timing and extent of surgery should be individualized and optimal. Indication to surgical treatment when purulent tubo-ovarian swellings: 1. Purulent tubo-ovarian education, insusceptible of medical treatment (i. e. remain the pain, the fever above 38'C, the dim outlines, testifying inclusion in the process of adnexa ). 2. A tendency to generalization (parametrit, pelvic inflammatory disease and zone distribution temper peritoneum above hypogastrium. 3. Complications presence - threat the perforation and the pyosalpinx perforation, piovara, tubo-ovarian abscess with advance in peritonitis - sepsis - parametrit - vesico- adjunct, enteric-adjunct and abdominoperineal- adjunct Fistula - Peritoneal abscesses: interColon, hypophrenic, subhepatic 4. Purulent tubo-ovarian education in pre- and postmenopause 5. Combination of purulent genital infection with good tumor of uteruses and appendages 217 Rehabilitation stages 1. Termination of acute process by the reasonable treatment 2. Reestablishment of hormone of гемостоаза 3. Reestablishment of reproductive function Situational missions: Mission 1 In gynecology department from infectious diseases hospital sick 28 years with complainings of pain in inferior of belly, the retching, the chill is delivered. In connection with multiple loose stool was hospitalized in the infectious diseases hospital. With the objective of contraception 3 years ago was introduced Navy. for the past three year at gynaecologist have not been observed. Objectively: pulse 90 in minute. Hell 110/60 mm. w. c.. respiration rate 18 in minute. The tongue is furred by the whitish raid, суховат. Belly several is distended, painful when deep palpation in all departments, in hypo and mesogastric region the positive rebound tenderness symptoms. Vaginal touch: vagina free. Uterine cervix of cylindrical form, external shed gap, in shed – “ tendrils” Navy. from cervical canal - plentiful pyoid precipitations. Uterine body of round structured form, several more rate, мягковатое, painful. On the right and behind necks is determined bitterly the painful education soft body with dim outlines by the size 8, 5 CgA 6, 5 CgA 6, 0 refer to. The combustion arch truncated. Parametrial without infiltrates. When vaginal touch involuntary loose stool. Rectal examination: ampoule of the rectum free, mucous mobile. Through front the bowel wall the education with dim outlines by the size 8, 5 CgA 6, 5 CgA 6, 0 melanoma associated antigens, within позадиматочном space is palpable. On front the bowel wall is palpable the defect up to 0, 5 refer to. On the glove - pus. Problems: 1. Your preoperative diagnosis and its foundation 2. Plan examination 3. Treatment policy 4. Surgical treatment, if it is in what volume has been shown whether 218 5. What complications in intrauterine contraception you know, their the prevention Mission 2 The woman 22 years appealed with complainings of the acute pains in inferior of belly, sharp pain on urination, the plentiful pyoid whites. Sex life lives with 16 years outside marriage, irregular, from pregnancy not is protected. The last sexual connection was 10 days ago. The menstrual function is not abused. Which is called symptoms appeared on 3rd the menstruation day, which yesterday ended. Objectively: skin palish, temperature 38, 2 S.. Pulse 100 per minutes. The tongue is coated with white fur, dry. Belly bitterly painful in all departments, moderately is distended, in inferior, more on the right the positive Shchotkin-Blumberg symptom. When gynecological examination: circle cervical erosion, plentiful pyoid precipitations. When vaginal touch the bias for neck bitterly painfully, the uterus is not accrued, slightly painful, the appendages from both sides is not accrued, but the palpation them is extremely tender. Archs free. Complete blood count: hemoglobin 148g / l leykotsitov16 2 h109 / l n - 4, - 69 m - 6, l - 21. Hematocrit 41%. ESR 12mm / h Problems: 1. Your assumed the diagnosis, its foundation 2. Eventual causes of origin disease 3. Acceptor additional examining, if it is has been shown whether what 4. With than it is necessary to carry out the differential diagnosis 5. Appraise data of common blood analysis 6. Management program 7. Possible complications Mission 3 219 Sick 42 years entered the department of surgery with complainings of pain in the lower abdomen, the nausea, the retching. Came down with three days ago, was the temperature 37, 5 C0, the houses used the heater, but the pains not calmed down. On the day of receipt in permanent establishment has been identified: condition is moderately grave, the pulse 110, hells 110/70, the temperature 38S0, the overtone of dermal covers normal, obesity 3 degrees is available. Belly on palpation painful is larger in right iliac area, symptoms of rebound tenderness is positive. However the surgeons decided sick to show gynaecologist. It has been ascertained that the woman previously carried over appendagitis, but during five years not had considered themselves gynecologically sick. Last the menstruation was 2 a week ago at maturity. When vaginal touch: in mirrors mucous the normal colour, the uterine cervix cylindrical, the shed is closed, when bias of uterine cervix the extreme tenderness is marked, back and the right archs several is overhanging, when press is marked the debility, the uterine body clearly not contour are clearly visible, but one gets the impression that, it is deflected left and posteriorly. On palpation of right appendages is marked the debility is greater than left. Due to debility and thickness abdominal wall to define the appendages quantity fails. Precipitation, moderate of whites. Problems: 1. Your assumed the diagnosis, its foundation 2. Eventual causes of origin disease 3. Acceptor additional examining, if it is has been shown whether what 4. With than it is necessary to carry out the differential diagnosis 5. Management program 6. Possible complications 1. Checking problems 1. That relate to НВЗ inferior of genitalia? 2. What methods of examination are needed in formulation НВЗ 3. What therapy principles НВЗ 4. Enumerate disease transmitted by the genital tract? 5. What complication НВЗ 220 6. What survey methods is to pass the fume (the woman and man ) when infecundity? 7. What kind of infecundity you know? 11. Suggested reading Basic literature 1. Гинекология. Бодяжина В.И., Жмакин К.Н. 1997 2. Акушерство и гинекология под редакцией Савельевой Г.М., Сичиновой Л.К. перевод с английского М., 1997 1. Родовой блок. Чернуха Е.А. М., 1999. 2. Клинические рекомендации. Акушерство и гинекология. Выпуск 2. Под редакцией Кулакова В.И., М., 2006 3. Гнойная гинекология. Краснопольский В.И., Буянова С.А., Щукина Н.А., М., 2001 Additional literature 5. Руководство по неоперативной гинекологии. Бодяжина В.И., Сметник В.П., Тумилович Л.Г., М. 1990 6. Неотложная помощь при экстремальных состояниях в гинекологии. Айламазян Э.К., Рябцева И.Т. С-Петербург, 1992 7. Справочник по Акушерству и Гинекологии М. 1996 8. Атлас оперативной гинекологии М. 1996 9. Практическая гинекология Кулакова В. М.2001. 10. Оперативная лапароскопия в гинекологии. Стрижаков А.Н., Давыдов А.И., М., 1995 221 Subject: Uterine myoma. Endometriosis 1. Conducting place of occupation, equipment - based on chair of obstetric and gynecology located in methodological centre of reproductive health 3 clinics ТМА. (polyclinic, gynecological and abortive branch office, operational unit ) 222 - base of birth complex when Tapovich, birth complex №4, Birth complex №6 - necessary equipment: 1. Sick on the theme 2. Gynecological tools 3. Clinical and laboratory analysis data 4. Table 5. Cases 6. Phantoms and models 7. Videofilms 8. Internet 2. Study duration of subject Hours amount - 6, 3 3. Occupation purpose • To teach students of future Doctor of common practical work to carry out prophylactic measures, sanitary public education, opportune and correct diagnostics and treatment of endometriosis and uterine myoma • To elaborate knowledges and skills on sanitary public education • To form knowledges on early and correct diagnostics of endometriosis and uterine myoma • Develop knowledge of the correct interpretation of laboratory and instrumental studies in endometriosis and uterine myoma • To introduce the principles of prevention of endometriosis and uterine fibroids 4. Tasks The student must be aware: • About basic clinical symptoms of endometriosis and uterine myoma • About diagnostic techniques of endometriosis and uterine myoma 223 • About methods of treatment of endometriosis and uterine myoma • About methods of preventing of endometriosis and uterine myoma The student must be able: • To hold clinical examination of woman with endometriosis and the uterus миомой using of laboratory and instrumental methods of examination • To diagnose the endometriosis and the uterine myoma • To proces individual the clinical record • To interpret the results of laboratory and instrumental methods of examination • To carry out counselling on endometriosis prevention and uterine myoma 4. Motivation Uterine myoma - benign tumor in womens. The frequency it after 35 years achieve 35-45%. 0¦¦-LThe frequency increase of myoma in recent years it's unlikely that reflects the true picture. To be sure, the speech go on the perfection of diagnostics, namely echoscopy introduction, which permits to educe myoma of off too small size ( 3-5 MM across ), нге increasing the uterine sizes and not specified when double touchМио. The frequency of endometriosis is 10% of MS disease women and 50% in women who are screened for infertility. Note that most increased the frequency of so-called small form - single endometrioid heterotopias in the pelvic peritoneum - a diagnosis that is made only by laparoscopy. However, there may be severe pain. In view of these small forms of the frequency of endometriosis in infertile women is 80%. 5. Interdisciplinary and InsideSubject connection The teaching of subject data is based on knowledge by the basis students of anatomy, histology, normal and pathologic physiology. Obtained in the course of knowledge occupation will have been used when passing the by them endocrinological disciplines, therapy, surgery, hematology and other clinic disciplines. 6. Occupation content 6.1 theoretic part Uterus fibromyoma 224 The benign tumor, which meets at 20% women. Some scientists, that one out of every two of Woman over-40s has the uterus fibromyoma. The swelling has significant increase in availability period of menstrual function and undergoes regress in the menopausal period. Sometimes this gives grounds to wait of menopause as treatment. Unfortunately, this swelling can incur malignancy (0.6 - 1% ). Regenerates the fibromyoma in sarcoma since this STT. Is found in any age period, but most frequently in 40-50 year (find the myoma development at 65% women ). Of 30 up to 40 years also every so often meet the myoma - 25-35%. Before 25 years - single instances. More than one uterine myoma don't look like other. May consist of single node, but most frequently is sometimes the multiple uterine myoma. There is several uterus names. The term the uterine myoma became prevail over different names of swelling . The myoma is synonymous of fibroma, fibromyoma, leiomyoma. All depends only from one in what volume and quality connective tissue and muscular fibre. Location: often multiple, usually intramural, interstitial. Myoma emanates from the muscular wall, has a set of nodes, number and size are quite diverse. Interstitial localization prevails (60-70%). Pregnancy with uterine myoma is possible (3%), but sterility is dominant. During pregnancy with myoma is malnutrition of the fetus, since nodes can not be stretched and growth of the fetus is in the direction of free nodes. The biggest problem with carrying a pregnancy. With such a pregnancy develops weakness in labor, cesarean section performed because of fetal position, because of obstacles in the form of nodes. In the postpartum period can be complications bleeding. If the bleeding is not, then all subsequent contractions ishemiziruyutsya nodes (as food goes from the capsule) and developed necrosis of nodes developed endometritis, metroflebit. Against the background of gangrene develops sepsis. With multiple sites you need to amputate the uterus. Quite often submucous (submucosal) nodes. Located in the uterine cavity. These fibroids can be produced, which requires that the neck was revealed. From this clinic - bleeding, cramping pain. Submucous fibroids on a broad basis can not be born, and often give heavy bleeding with anemizatsii. Also quite common subserous fibroids. These fibroids are surrounded by only the serous membrane. They can be broad or narrow (foot) base. May be a combination of multiple intramural and subserous. Intraligamentarnye nodes - a rare localization - the node at this location is located between the sheets of the broad ligament. Node is in the parameters, often deep, lies 225 on the vessels, passing to the ureter, bladder presses. Therefore, this localization is very insidious. Cervical fibroids - mostly single units, and quite often large, and performing vkolochennyh in the pelvis. Vaginal part of cervix is almost never find. Another less common uterine round ligament. Pathogenesis Opinion on histogenesis formed early in the century - the origin of the mesenchyme of the vascular wall - there is degeneration of the mesenchyme of the vessel wall and formed the so-called active zone (the beginnings of the future growth of uterine fibroids). In these areas the growth of disturbed metabolism, and further growth is due dyshormonal disorders. In the beginning there is some major cause disturbances in the hypothalamus - pituitary - adrenal cortex - the ovaries, which leads to the organization growth of fibroids. Then begins the growth of fibroids without signs of differentiation, and then there is a clear differentiation and therefore some of these nodes contains connective tissue fibers, muscle fibers. This causes swelling dishormonal number of violations in the body, which also contribute to tumor growth: metabolic, functional failure of the liver (liver is the metabolism of steroids). Also contribute to the emergence of fibroids: a violation of lipid metabolism also contribute to the growth of fibroids. Inflammation, infectious processes, menstrual disorders, deficiency of the second phase of the menstrual cycle in which the content is not increased by estriol and progesterone are at the lower boundary. The number of nuclear estrogen receptor is below normal, while the number of total progesterone receptor on the bottom border. Therefore, for uterine myoma is always a defective second phase is aborted yellow body, so the total cumulative value of hormone is not modified, but still there is lack of a second phase. These disorders of the peripheral units are responsible for reproductive function are always present in uterine myoma, but disturbances in the central mechanisms are generally absent. There are new studies (Sawicki), which suggests a local gipergormonemii. Hormone-fibers in the uterus are smooth muscle cells, nerve fibers, vascular system. These receptors are active for estradiol and progesterone, and this dependence is obtained from the embryonic primordia of ovarian function, which takes place locally. Depending on the disorders of the ovarian hormones is a local consumption of these embryonic beginnings. Studies have shown that the vascular network of the total amount of hormone is much lower than in regional areas of the tumor. That is all the hormones that are produced by the ovaries are consumed by the zone. When uterine always has a place polycystic changes (degeneration) of ovarian 226 (Low active follicular cysts). While functioning ovaries, until growing fibroids. Allocated two pathogenic variants of growth and development of fibroids (proposed Vikhlyaeva): * The first option due to the fact that women are often in history has been a violation of the menstrual cycle, genital infantilism, juvenile bleeding. In this embodiment, is klinikopatogeneticheskom growth and tumor development. The tumors grow large size, have no specific symptoms. * The second variant is associated with the violation of the receptor areas, which usually is the result of local pathological manifestations (abnormal births, multiple abortions, intrauterine intervention, inflammation of the uterus, appendages). Under this option, often meet with small fibroids, but close to the receptor area. These fibroids although small, but extremely bleeding, giving a lot of clinical manifestations. Clinic The main symptom is bleeding. Bleeding associated with a number of factors changes in the endometrium, with contractile ability of the uterus. Changes in the endometrium - is most often expressed by proliferative changes (secretory dominate). Proliferative changes more often in the form of glandular, glandular-cystic hyperplasia of the endometrium. Long-term rejection, a mosaic of pictures rejected by the myometrium promotes further bleeding, uterine bleeding, so when anemia and pronounced. Most often the beginning of cyclical bleeding make submucosal uterine fibroids abundant Meno-metrorrhagia and. Then the bleeding become erratic in nature. Interstitial fibroids, particularly distorting the cavity lead to significant bleeding. By spotting, bleeding will acyclic forms as cervical, peresheechnaya. Bleeding is also associated with the violation of contractility. Bleeding with long-term, cyclic and acyclic then. Bleeding are also associated with a large area of rejection. Women tend to suffer from iron deficiency anemia. The second symptom - a symptom of pain. Different nodes, even small units can produce pain. Most often these occur and pain associated with nervous disorders. Nerves and blood vessels pass through the capsule, so the violations associated with perestyazheniem capsule. Pains are debilitating in nature. The pain may intensify after menstruation, due to compression, ischemia capsule site. Quite often, fibroids of the uterus combined with adenomyosis, and the uterus also increased in size due to cavities lined with the endometrium (uterine lining under adverse conditions, migrated to the intermuscular space.) With this combination, there are cyclical pain 227 before menstruation, during the first days of menstruation, and ends after, and then all repeated. Pain may be cramping in nature at birth fibromatous site. The growing nature of the pain occurs during ischemia node. This occurs quite often - suddenly there are pains in the abdomen, which is intensified. At the same time may be fever, urinary retention, bleeding. On palpation revealed local tenderness in one of the sites. In the site there are elements of necrosis - the node is gray, with areas of destruction. This is one of the indications for urgent ultrasound surgery. Larger fibroids are more likely to compression of the nerves, pelvic plexus. Impaired function of adjacent organs - the bladder, intestines. Even the host, growing out of the front wall of the uterus and pressure on the bladder can produce a variety of symptoms: frequent urination, painful urination, urinary retention. This leads to secondary changes in the urinary tract - cysts, fistulas and other big sites are localized on the front wall of the uterus, cervical and peresheechnaya localization sites are also close to the bladder. These sites often provide urinary retention. Such a violation leads to disruption of trophic arise vesico-vaginal fistula. When the location of the site intraligamentarnom - compression of the ureter, the major trunk vessels, nerve plexus. The ureter is pulled, thin and during surgery can injure. Such localization leads to disruption of passage of urine. There is hydroureter, hydronephrosis, kidney failure that is. Impaired function of the intestine - the type of constipation. Since there stagnation in the pelvis, which decreases intestinal motility, resulting in the formation of hemorrhoids. Women with uterine cancer are at risk from the onset of uterine adenocarcinoma because in the pathogenesis of frequent metabolic disorders (obesity), hyperplastic processes in the endometrium, the age period (hypertension, etc.). Infertility is often seen as well. Irregular menstrual cycle - the type of dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Survey methods to detect uterine fibroids Fibroids detected easily enough, but the differential diagnosis of small tumors difficult. Uterus during bimanual study has an uneven surface, and the tumor has a smooth surface, clear outlines, painless in the study, is shifted along the cervix. Other methods allow you to find an overall increase in cancer. Ultrasound provides a clearer topical information on the location and size of knots. You can see the structure of nodes (necrosis, calcification, etc.). Hysterosalpingography. A very important method in women with infertility (have to check patency of the fallopian tubes, the localization of the site.) 228 Sounding the uterine cavity and cytology, endometrial histology. These studies are important to rule out uterine cancer. Also performed diagnostic curettage. Hysteroscopy - a fairly new method. Visually inspected the entire uterine cavity in the air or water. At hysteroscopy can do a biopsy. CT, NMRI. Differential diagnosis * Swelling of appendages * Uterine pregnancy, ectopic Diferentsiruyut by ultrasonography. * Adenomyosis of the uterus - mainly on clinical findings, the data urography - Conservative treatment - Surgical techniques Surgical methods are the basis of treatment. Readings should be delivered in the identification of fibroids. There are absolute indications: * Submucous localization * Neck-node localization peresheechnaya * Necrosis fibromatous site * Large size of the tumor The combination of adenomatosis and fibroids * A combination of uterine prolapse, and (loss) of the uterus * A combination of uterine cervical cancer * Born myoma nodes In different age period, the volume of intervention is different. Up to 40 years old tactic is aimed at organ-saving operations possible. Running Conservative miomotomiya (enucleate site sutured bed). If a young age can not be done miomotomiyu conservative, there are a number of plastic surgery designed to preserve only of menstrual function. These include - high supravaginal amputation of the uterus, defundation. Blind supravaginal suggested amputation of the uterus with endometrial plastic blind. If you can not neither one nor the other, it is supravaginal 229 hysterectomy may be needed. Over 40 years - two volumes - supravaginal amputation of the uterus (uterine body is removed, the cervix is retained), and hysterectomy (removed the body along with the neck) - performed by changes in the cervix (polyposis, misplacement, etc.). In menopausal women is just a total gisteroektomiya (total hysterectomy), with appendages. Conservative treatment is directed (in practice it is not) to normalize the menstrual cycle - a hormonal treatment (maintenance of the second phase), treatment of anemia, stop bleeding, restorative therapy. Recently, a anatogonist lyuliliberina - zolodeks - used for dispersal of small fibroids, preparation for surgery. Tanazol used as a drug preparation for surgical treatment. Used on data occupation new pedagogical technologies: Interactive game: «Cat bagged» To operate it is necessary: 1. Variants compositions of problems 2. Номерки for draw in respect of a number of students in group 3. Clean sheets of paper, handle Progress of work: 1. All students are divided into groups by drawing lots in small groups of 3 students in class 2. Each subgroup sits at a separate table, preparing a blank sheet of paper pen 3. In the worksheet, write the date, group number, department, FI subgroups of students participating 4. One of the members of the subgroup is suitable to the teacher and takes the envelope option questions for each group - a separate option, but the difficulty level for all subgroups of approximately equal 5. Students re-write on a piece of your questions and note the time 15 minutes. For work 230 6. Small groups of their peers to discuss the job, write down the answer, as far as possible accurate 7. The teacher must closely monitor the students to not written off and did not communicate with other subgroups 8. At the end of 15 minutes. answer sheets are collected 9. teacher for classes checks for accuracy, completeness and accuracy of the job 10. All participants are a small group put up the same score Maximum - 0.8 points 0.8 - 0.7 "5" 0.6 - 0.4 "4" 0.4 - 0.1 "3" 0 - "2" 11. On the answer sheet, the teacher puts the mark and the signature 12. The resulting score of the students is taken into account when placing the current total employment as an estimate for the theoretical part 13. In the lower part of the magazine is free to hold the mark of the business game, the elder puts his signature 14. Teacher of students remain Interactive game: "Weakest Link" Requires: 1.Nabor questions printed on separate sheets 2.List paper with a list of games for logging 3 Stopwatch Progress: 1. Game conducts teacher and an assistant from among the students - the counter 231 2. Counter on a piece of writing a date, group number, department name, a business game and a list of student groups 3. The teacher asks questions to students in series of set questions 4. A student has 5 seconds to answer 5. Teacher with the word "right" or "false" evaluates the answer, if the "wrong" then he gives the right answer 6. Counter poses in front of the student name "+" or "-", depending on the answer is correct 7. Students are thus two rounds of questions 8. Field 2 rounds of questions the game is suspended and students who were eliminated from minus two games as a "weak link" 9. The game continues on a new round with the remaining students. Again, they offered a new round of questions and the students drop out again, which when added to the first two rounds came minus 10. Shown round by round the strongest of the players who responded to the increasing number of questions 11. On a sheet against each name the teacher records - who in any round of the retired and became a "weak link" 12. The game is estimated as 0.8 points. Students who withdrew after the first 2 rounds of responses receive 0 points. After Round 3 replies - 0.2 points, After round 4 answers - 0.4 points; After round 5 answers - 0.6 points. The strongest party gets 0.8 stars 13. The resulting score of the students counted in the scoring for the current occupation 14. In the lower part of the magazine is free to hold the mark of the business game, the elder puts his signature 15. Minutes of the game is saved 232 6.2 Analytical part Situational missions: Mission 1 Sick 27 years with primary infertility entered the gynecological permanent establishment for surgical treatment concerning of submucosal uterine myoma. 1. What the optimum extent of business And ) hysterectomy Б ) defundation C ) supravaginal amputation of the uterus without appendages D ) conservative myomectomy * E ) supravaginal amputation of the uterus, ovaries biopsy 2. Which of these states can be observed in the presence of submucosal fibroids A) giperpolimenoreya B) Acyclic bleeding B) cramping abdominal pain D) infertility D) all of the above * Task 2 Patient 43 years, was admitted to the hospital for gynecological surgical treatment for submucous uterine fibroids. At vaginal examination: cervix gipertrofirova ¬ on, deformed, the body of the uterus is increased up to 8-9 weeks of pregnancy ¬ sion, dense, painless, appendages on both sides have not changed; mucous discharge. 1. The optimal amount of surgery? A) Pangisterektomiya B) supravaginal amputation of the uterus without the adnexa B) Conservative myomectomy D) Hysterectomy without appendages * 233 D) defundation 2. Which factor influences the choice of operation in this observation? A) Localization of myoma node B) Dimensions of myoma node B) The presence of iron deficiency anemia G) condition of the cervix * D) Size of the uterus Task 3 Patient 37 complained of severe abdominal pain on the left, occurred as a sudden. Objectively: the uterus up to 12-13 of pregnancy, heavy, lumpy. One of the corners of the left walking, sharply painful. The appendages are not palpable. 1. Preliminary diagnosis A) torsion legs subserous site * B) interstitial site of uterine necrosis B) twisting legs ovarian tumors D) Ovarian tumors suppuration D) malignancy of uterine fibroids 2. What additional tests will help in the diagnosis A) laparoscopy B) Pelvic ultrasound * B) culdoscopy D) hysterosalpingography D) hysteroscopy 3. Recommended medical tactics A) an emergency surgery - amputation of the uterus without the adnexa * 234 B) The surgical treatment in a planned manner - amputation of the uterus without the adnexa B) emergency surgical treatment, conservative myomectomy D) a conservative anti-inflammatory therapy D) surgical treatment with no effect on anti-inflammatory therapy Task 4 Patient 36 complained of heavy bleeding during menstruation for 6-8 days. OBJECTIVE: queen size up to 14 weeks of pregnancy, a dense, rounded, mobile, painless. The appendages are not palpable. 1. Preliminary diagnosis A) uterine fibroids * B) adenomyosis B) endometrial cancer D) uterine sarcoma A) Endometrial polyp 2. What are recommending additional tests A) Pelvic ultrasound * B) separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous of the cervix and uterus * B) laparoscopy D) colposcopy D) tservikoskopiya 3. Therapeutic Tactics A) surgery * B) The conservative hormonal therapy with progestins B) Conservative hormonal therapy with combined estrogen-progestin therapy D) conservative hormonal therapy agonist of gonadotropin-releasing hormone 235 D) gormonalnpya therapy Target 5 Patient 46 applied to the antenatal clinic with a complaint to the mi ¬ ample long menstruation, fatigue, decreased work capacity. In the history of two urgent deliveries, five abortions, chronic inflammation of the uterus. In the last 6 years in order to use the intrauterine contraceptive, which was removed a year ago. He considers himself a patient at 6 months, the doctor does not vanish ¬ schalas. Pulse 78 minutes in I, regular, BP 125/80 mm Hg, the level of hemoglobin ¬ bean 80 g / liter. At vaginal examination: cervix not erode, the body of the uterus enlarged to the size corresponding to ¬ yuschih 7.6 weeks of gestation, round, movable, painless ¬ Noe, appendages on each side are determined that the range of painless codes are expressed, the parameters are free; vyde ¬ leniya of genital tract mucous membranes. 1. For which of gynecological diseases characterized by describing ¬ sleigh above the clinical picture? A) Myoma with submucous location of one of the nodes B) The internal endometriosis of the uterus * B) Chronic endometritis 2. What additional research methods can be used to confirm the diagnosis? A) Ultrasound scan of the internal genital organs * B) X-ray hysterosalpingography * B) with separate diagnostic hysteroscopy you ¬ skablivaniem mucosa and cervical canal walls with iatki gistogolicheskim examination of scrapings * D) Laparoscopy 3. What are the most likely reasons for this patient giperpolimenorei? A) Reduction of contractile activity of myometrial * B) Relative giperestrogeniya. B) Increasing the area of the uterus menstruating * D) Abnormalities in blood coagulation. 6.3 The practical part 236 The task of practical skills with step by step execution and evaluation of these skills: 1. To be able to assess the evidence ultrasound genitals, hysterosalpingography, rengenografii skull and teretskogo saddle 2. Assessment of functional diagnostic tests 3. Formulation of initial diagnosis (type of infertility) and direction if necessary to specialists 4. Measuring height and weight 5. Inspection and palpation of the breast 6. Bimanual gynecological examination 7. Study of Pupil symptoms 8. Fence urogenital secretions for research on the flora of the three points 9. Bacteriological examination selections 10. Inspection in the mirror 7. Checking problems 1. Enumerate two pathogenetic variant of growth and development of myoma. 2. Cardinal symptoms in myoma clinic. Than they are determined? 3. Most dangerous complications of uterine myoma. 4. Therapy principles of uterine myoma. 5. Laparoscopic classification of endometriosis. 6. Clinical symptomatology of endometriosis and its pathogenetic foundation. 7. Principles of treatment of endometriosis. 8. Operative and conservative methods of treatment of endometriosis. Subject: Benign and malignant ovarian tumors 237 Ovarian tumors are the second (after uterine fibroids) of all neoplasms of female genital mutilation. They occur at any age, but mostly after 40 years. Among them are prevalent forms of benign (75 - 80%), malignant tumors occur in 20-25%. From 1987 to 1997 frequency of genital cancers increased by 15%. The incidence of malignant tumors in St. Petersburg went out on first place in Russia and Europe. Malignant tumors of the ovary is mainly secondary to arise from benign or borderline mucinous cyst or serous (80-88%). Primary cancer is only 4-5%. Benign ovarian tumors exist for a long time without causing complications. However, some complications may require emergency care in a garrison. Torsion legs cysts - the most common complication (15%). Suppuration ovarian tumors with possible perforation and abscess development of peritonitis. Cyst rupture - may be associated with peritoneal signs and symptoms of internal bleeding. Ovary - female gonad, paired organ, a flattened ovoid body, medium length - 3-4 cm, width - 2-3 cm, weight 8.5 grams. The ovaries are located near the uterus, fallopian tubes and bowel. Own ligament is attached to the corner of the uterus. Funnel attached to the pelvic-ovary and to the side wall of the pelvis. Insertion of the ligament to the ovary - Ovarian gate, which consists of the main blood vessels supplying the ovary and depart venous and lymph nodes. The free surface of the ovary is covered by a single layer of cuboidal epithelium. The second layer consists of fibrous connective tissue poor in cellular elements - the tunica albuginea. Under the tunica cortex is located, covering the medulla. In the cortex laid follicles at different stages of development and corpus luteum. Medulla is rich in blood vessels and nerves. Main of ovarian functions - Generative, vegetative and hormone. Classification of ovarian tumor (on M. F. Glazunov and V. P. Mikhailov) 1. Cystic tumours (75% all swellings) Silio-epithelial A ) secernant B ) proliferative C ) malignant 238 To underscore that specified subgroups ("a", "b", "c" ) are stages of one process. They all are developing from Mullerian epithelium. Feature macro- and microscopic structure, clinic. Pseudomucinous cystoma: A ) secernant Б ) proliferative C ) malignant Features macro- and microscopic structure, clinic. Malignization in 25 % of cases. 2. Hormone producing ovarian tumor (5% all swellings ) Feminizing tumor: A ) granular-cell B ) ThecaCell Structure peculiarities. The clinic is determined by the excessive hormone (estrogenic) swellings activity and depends on age: At girls - emergences of month-long and signs of early sexual puberty, in ChildNative age - disorder menstrual cycle of menorrhagia type, in climacteric period and menopause - metrorrhagia. Rarity of carcinomatous degeneration feminizing tumor (4% ). Masculinization ovarian tumor Arrhenoblastoma and androblastoma (0, 3% ). Are developing from embryonic sites of brain tissues in the area of ovaries gates. First they arise as good, but fast malignancy. Clinic: first defemination (amenorrhea, atrophy of mammary glands, lowered the libido ), and then - masculinization (whiskers growth and beard, lowering of quality of voice and others ). 3. Stomatogen or connective tissue (2, 5% ) A ) fibroma 239 Structure. Meets primarily in elderly. Slowly are growing. Typical the Meigs triad: ovarian tumor, ascite, hydrothorax. B ) sarcoma Features micro - and macroscopic structure. Metastazing. 4. Teratoid or germinogen ovarian tumor (10% ) A ) mature TeraohmLump (adult teratoma ) - ectodermal the origin, differentiated, the benign tumor. B ) the teratoblastoma - is developing from three of germinal layers: Ectoderms, meso - and endoderm. Poorly differentiated malignant tumor. Meets at age 16-30 years. C ) dysgerminoma. Is developing from early cells of as men's, and female gonads. The clinic essentially does not differ from other oophoroma. 5. Metastatic ovarian tumor Arise due to metastazing malignant neoplasms of differential localization lymphogenous, blood-borne or имплмнтационным way. Krukenberg tumor swellings metastases of gastro-intestinal system. Metastases when mammary gland cancer. Micro- and macroscopic structure. 6. Ovarian tumor of not clear genesis - 7, 5 % This or so far gone the ovarian tumor, that it's hard to pass judgement from their genesis, or the rare swellings, type of brenner tumor. Psevdoopuholevy education (retention cyst ): Follicular cyst "chocolate" endometrial cyst Cyst of corpus luteum Luteal cyst when cholecystic sideslip and chorionepithelioma Short characterization of structure and clinical symptom of some cysts of this group Basic complications, linked with the presence of ovarian tumor: 1. foot looping of swelling (acute and chronical ) 240 Predisposing the moments: - big mobility of swelling - small tumor sizes - great stretching frontal abdominal wall - pregnancy - postpartum period. Clinic: - abrupt sharp stomach pains - nausea, retching - flatulence - rapid pulse - subfebrile temperature - objective evidences: debility on palpation of belly, strain frontal abdominal wall, abdominal distention; when internal examining - painful education alongside of uterus, limited in mobility, painful in an attempt bias . 2. Cyst break Predisposing moments: - injury - gynecological examining. Clinic: - acute stomach pains; - clinical symptoms of shock; - symptoms of acute of internal hemorrhage. 3. Malignization of ovarian cyst (from 20 up to 50% ) Especially malignizations silio-epithelial, rarer Malignization signs of ovarian cysts: 241 A ) dense, inhomogeneous consistency of swelling B ) emergence of ovarian tumor from both sides C ) rapid growth of the tumour D ) early fixing at expense of growth in neighbouring swelling E ) sign "of шпоры or beak" - in Douglas space due to of implantation of tumor cells in its peritoneum. Histological classification of ovarian tumor (WHO, 1973.) 1. Epithelial tumor: serous, mucinous, endometrioid, BrightlyCell, brenners tumor, mixed epithelial, nondifferentiable carcinoma, unclassified epithelial tumor. 2. Stroma swellings of genital cord: granulosa-stromal-cell, Androblastoma, гинандробластома, unclassified the stroma swellings of genital cord. 3. Lipid cell swellings. 4. Germ-cells tumor: dysgerminoma, swelling of endodermal sinus, embryonal carcinoma, полиэмбриома, chorionepithelioma, teratoma, mixed the germ-cells tumor. 5. Gonadoblastoma: clean and mixed. 6. Soft tissues tumor, not peculiar to ovaries. 7. Unclassified swelling. 8. Secondary (metastatic ) swelling. 9. Tumour-like processes. А. Pregnancy luteoma. B.Thecomatosis and hyperkeratosis. C. Massive edema of ovary. D. Single follicular cyst and cyst of corpus luteum. E. Of polycystons ovaries. 242 F. Multiple luteinized cysts. G. Endometriosis. H. Cursory epithelial inclusions. I. Simple cysts. J. Inflammatory processes. K. Parovarian cysts. The epithelial good ovarian tumor largely is cystoma (serous and mucinous). Distribution stages of злоокачественного process: (classification USSR Ministry of Health from 1956.) 1 stage - has been impressed only the ovary; 2 stages - the swelling came out beyond ovary, the second ovary, one or both of uterine tubes has been impressed; 3 stages - has been impressed all mentioned. In addition, the swelling spread to parietal peritoneum; metastases in regional lymph nodes (lumbar, paraAortal ), Salnikov; 4 stages - the ovarian tumor hits neighbouring bodies (the bladder, the rectal intestine, the loops of small intestine with dissemination on peritoneum beyond small pelvis ) or with metastasis in the distant lymphatic nodes and the internal organs. In addition, now by онкогинекологами the classification ovary cancers on the system Treatment of ovarian tumor A. treatment of benign tumor 1. Satisfy on swelling adequate quality during operation: while is not sutured the abdominal wall, the macroscopical study of swelling, to cut the swelling, at hand of papillae or otherwise equivocal signs (the solid structure, the consistency inhomogeneity ) to produce the express - the biopsy . Salnikov inspection, stomach, other internal organs, paraAortal lymphatic nodes. 2. If the ovarian tumor good, is removed only the swelling with corresponding by the uterine tube or without her. 243 3. When bilateral tumor at young women it is necessary conservation constant ovary fabric. 4. Twisted the cyst is removed without preliminary foot untwisting of cyst ( the thromboembolism prevention ). 5. During operation for ovarian cyst at pregnant woman of it is necessary gentle handling of pregnant uterus. The stump of funnel-pelvic binder to peritonize leaves adjacent the parietal peritoneum, not подтягивая to uterus corner (the prevention abortion ). In postoperative period to appoint the progesterone and others. especially, if with кистой is separated the yellow tel.. B. patient treatment with oophoroma Now woman treatment with oophoroma is held taking into account the peculiarity of organism of sick and distribution stage of tumour process. Largely shall be used combined therapy: surgery + chemotherapy or beam therapy + hormonotherapy. Volume of surgical intervention when oophoroma: disposal of ovarian tumor with corresponding by the uterine tube, supravaginal amputation of the uterus with appendages of opposite side, resection or extirpation of gastrocolic omentum. During the operation chemical preparations introduction in the abdomen and after the operation antiblastomic therapy. In recent years is recommended to generate not the supravaginal amputation, and the uterine extirpation, if this technically feasible. When III or IV stage of tumour process of ovaries patient treatment begins by polychemotherapy and after that the surgical intervention with cited above of business (when Possibility. Henceforth of repeated courses of Polychemioterapeutics or radiation therapy. As of полиохимиотерапии the following shall apply the preparations combination: cyclophosphamide + methotrexate + 5-fluorouracil cyclophosphamide + methotrexate + vinblastine actinomycin D + cyclophosphamide + fluorouracil. As of radiation therapy shall be used the gamma-ray teletherapy on apparatus GUT Co-400 or application way of solid radioactive agents in the vaginal vaults or in 244 uterine cavity, left in the operation. Is presently being used for megavoltage therapy on linear accelerators. It is necessary briefly to stop to the question of treatment at young women and girls with oophoroma of I of stage. On the assumption of afterhistory, now it is possible to take for as granted, that the unilateral adnexectomy in a situation like this it is permissible while only in isolated cases and when observance (obligatory) conditions number of: Only in the patient with dysgerminoma or with malignant cyst pseudomucinous In the absence aggravating the factors forecast (growth or capsule break of swelling, soldered connection or union with surrounding tissues, effusion in small pelvis); Dead certainty in metastasis absence. However the doctor, manufacturing unilateral овариоэктамию, assumes the grave responsibility and must systematically during a number of years observe this patient. 6. Conclusion The significant importance in system of fight against cancers have systematic (not less than two once a year ) the medical checks up of female population at age over 20 and strictly developed the dispensary observation system of sick with pre-cancer processes and cancer. In the fight against cancer the great significance has also the opportune direction of sick on treatment and the systematic educative activity among the population. All woman, at which was found or suspected the tumour process or the swelling of genital organs, are sent to specialized oncologic institution. The competence to diagnose the ovarian tumor, the tactics knowledge subject to swelling character, age of patient, occurred the complication, it is necessary each doctor. Subject: Wrong positions and developmental anomaly of female genital organs. The opportune diagnostics of developmental anomalies and wrong positions of female genital organs make it possible to warn complications, which are linked to beginning of catamenial and reproductive function and in a timely way to hold operative therapy. Causes of origin of developmental anomalies of genital organs is: 245 1 ) action of harmful environmental factors (intoxications, high and low temperatures ), occupational hazards (chemical production, radioactive substances ), domestic intoxications (alcoholism, tobacco smokings, drug abuses, abuses ) in the period of embryogenesis 2 ) chromosome and mutations 3 ) weighed down heredity 4 ) parent age elder 35 years Vagina aplasia - total lack of vagina. The aplasia is related to hereditary defects formation vagina. Cause its initiation is the developmental disorder of caudal of müllerian (paramezonephral ) ducts. Ranking among vagina absence in this case pathology the underdevelopment of other departments of reproductive system (ovaries, uterine tubes and uterus ) is marked. Occurs this pathology, besides absence vagina, specified when gynecological examination, amenorrhea, impossibility of sex life. Aplasia treatment of vagina surgical. Creation of artificial vagina from sites by the number of disposed the organs and tissues is produced: cutaneous shred of minor lips, site of sigmoid, peritoneums of small pelvis. At hand of contra-indication to surgical treatment shall be used the bloodless colpopoiesis - by means of special kolpoelongatora produce the phased stretching of skin of vaginal vestibule (within 20 day ). Atresia of maindenhead - atresia of hymen. Is being revealed in period of the sexual maturation, with menstruations beginning, when due to absence conditions for recess of catamenial blood from the vagina occurs the retained menstruation formation. Filled by the blood the vagina has the sphere-shaped, above it when rectal examination is determined the dense uterus of no sizable. When gynecological inspection are determined the absence of hole in maindenhead, its the cyanochroic colour and the swelling. The blood accumulation occurs by the absence of menorrhea (the false amenorrhea ), pain in the lower abdomen and low back. If the brake is not being removed, form hematometra and gematosalpinks. Treatment consists in performance of crucial incision of maindenhead. The additional closed vagina is located in one of archs of basic vagina and is determined in sight of tight elastic education. The additional vagina is connected with cervical canal of the uterus, from where during your menstrual period into him catamenial blood, sometimes in number comes from (in that case during your menstrual period the mean bloody issues are marked ). Due to recess absence of blood occurs the suppuration of content additional vagina, that is followed by the emergence of pyoid precipitations. Treatment: cavity emptying and wall excision of additional vagina. The medial longitudinal partition of 246 vagina may be different length, often shares the vagina on two unequal part. Surgical treatment is held only in the case, when the pary prevents normal sex life. Developmental anomalies of uterus. There is following types of developmental anomaly of uterus: didelphia, uterine cervix and vagina (uterus didelphus ); unicornuate uterus with is normal developed by the vagina (uterus unicornus versus, vagina simplex ); bifid uterus with two necks and normal vagina (uterus bicornis bucalis, vagina simplex ); unicornuate uterus with second rudimentary buffalo horn and normal vagina (uterus unicornis cum cornu rudimentario, vagina simplex ), the complete pary of body and uterine cervix (uterus septus ); partial bulkhead of uterine body (uterus subseptus ). One of rare the malformations of female genital organs appears in syndrome of Rokitansky-Kyustnera. In that case is marked partial or the complete ametria and vagina in combination with is normal developed by uterine tubes and ovaries. All malformations of uterus divide into three group: 1 ) with absence of menorrhea and impossibility of sex life - when ametria and vagina; 2 ) in violation of recess of catamenial blood (complete or partial ), retained menstruation education, hematometra; 3 ) without violation recess of catamenial blood. Vices, existing without recess violation of catamenial blood, are leaking asymptomatic and long-time not are diagnosed in womens, not living by the sex life. Basic manifestations of these vices are embarrassment when sex life, the infecundity or the customary incompetent pregnancy. At hand of vice, hampering the recess of catamenial blood, the aspect of disease is turning in period of the sexual maturation of girl, at the beginning of menstruation. Are marked the amenorrhea, periodical pain in the lower abdomen. When rectal examination is marked the presence of тугоэластического education in small pelvis. Treatment: in the absence of recess brake of catamenial blood vice treatment aren't held. When unilateral violation of recess of catamenial blood is held surgical treatment, aimed at disposal of additional vagina and functioning the horn of uterus. At hand of intrauterine pary or bifid uterus, source of infecundity, is held corresponding the operation. Wrong positions of genital organs. In rate at normal woman in reproduction period, not pregnant and not feeding, when finding it upright when deflated bladder and rectal intestine the uterus is arranged in the centre of cavity of small pelvis, on equal disposal from sacral, symphysis and side walls of small pelvis. The uterus is in a position anteversio-anteflexion - the uterine fundus not acts above entrance to the small pelvis and and кпереди, the vaginal part of the cervix - кзади and down, between bodies is directed at uppermost and uterine cervix the obtuse angle, open кпереди is organized. Wrong positions of genital organs the firm variations from 247 their normal the location, due to presence in woman of inflammatory processes, tumour educations, adhesive process, injuries, malformations, underdevelopment of genital organs and so on are called. Giperantefleksiya (Pathologic anteflexia of uterus). In this case condition the abnormal anteflexion of the uterus, with the consequence that between uterus bodies is marked and uterine cervix the acute angle (less 70 is organized? ). Basic causes of origin of this condition are the inflammatory processes of genital organs and other bodies of small pelvis, gender infantilisms. Basic manifestations of this condition are violation of menstrual cycle ( the oligomenorrhea, the hypomenorrhea, the opsomenorrhea, the algodysmenorrhea ), the infecundity. The diagnosis is put on a foundation of gynecological inspection - deflected кпереди, normal uterine sizes, the planarization of vaginal archs are determined bitterly. Treatment of this pathology consists in cause elimination, its who have called. When expressed the pain durations during your menstrual period the non-narcotic analgesic, the antispasmodic drugs, the anti-inflammatory drugs are charged. Backward-turned uterus— Deviation of uterine body кзади from medial axis of tel.. In this case between uterus bodies and uterine cervix the corner, opened dorsally is organized. Separate fixed and mobile of ретрофлексию. Cause fixed retroflexion is the adhesive process in small pelvis, arising due to of inflammatory process or endometriosis. The mobile retroflexion is seen when tonus lowering supporting, suspensory and anchoring uterus apparatus when asthenic body build of woman (subtle bony skeleton, lengthened thorax, excitability, irritability, enteroptoz ), infantilism, after births of children, as a corollary of sharp weight loss woman (when heavy diseases, improper feeding ). The presence of mobile retroflexion, as a rule, is leaking without clinical symptoms. Fixed the retroflexion has no pathognomonic clinical symptoms. Sick, as a rule, worry complaint, characteristics for disease, being by the cause of origin of wrong position of uterus (inflammatory process or endometriosis ). Long-existing the retroflexion often leads to omitting of genital organs ( owing to constant pressure of intestine loops on front the uterine surface ). When vaginal inspection is marked the deviation of uterine body кзади, the uterine cervix is located кпереди. When mobile backward-turned uterus easily is given in the normal position when double touch. Attempt to return in the normal position the uterus, within fixed retroflexion, lead to initiation sharp pains and often - to disturbance of function of pelvic bodies. Treatment is held at hand in the patient the complainings of violation of menstrual cycle, pains in the sacrum and inferior of belly, pains during sexual intercourse. At hand of endometriosis has been shown specific treatment (refer to corresponding the chapter ). If retroflexion cause became the inflammatory process in small pelvis, then is held therapy, aimed at elimination 248 its aftermaths. Shall be used the gynecological massage, the physiotherapy, the gymnastic, the vitaminotherapy, sanatorium-resort therapy. Turn and uterus looping around long axis. Is seen when unilateral inflammation of sacrouterine binders, conducting to their shortening, at hand of tumour process in small pelvis (the swelling is arranged кзади and alongside of uterus ). Treatment of this pathology consists in elimination of cause factor. Uterus looping— This turn of uterine body around long axis when fixed the uterine cervix. Cause of this condition are unilateral mass lesions of ovary (the cyst, the cystoma ) or подбрюшинно disposed the uterine myoma. Treatment - elimination of cause factor. Uterus elevation— Uterine displacement upwards. The physiology elevation of uterus when complete bladder and rectal intestine is possible. Cause of pathologic elevation are mass lesions of appendages, hematoma and other pathological processes in small pelvis. Treatment - elimination of basic disease. The omitting and the fallout of genital organs - such regulation of uterus, in which the uterine cervix is arranged lower spinal line. The fallout of genital organs - the uterus move out of interlabial space in part - only the uterine cervix (the partial fallout ) or fully (the complete fallout ). Classification on Malinowski I degree Fallout of genital organs - the omitting of genital organs - is marked the uterine prolapse, the external shed of uterine cervix lies below spinal plane, the vagina walls get to vaginal orifice. II degree - the defective fallout of genital organs - the uterine cervix goes beyond interlabial space, and the body is arranged above it. III degree - the complete fallout of genital organs - all uterus is arranged lower interlabial space. Causes of origin of these conditions are as follows the factors: 1 ) the muscles traumatization perineal and pelvic diaphragm in labors ( especially if perineal do not ушивают or it heals by the secondary tension ), the frequent labors; 2 ) muscles weakness perineal, not engaged in labors, arising in womens with asthenic body build, hypoalimentation, engaged in the hard physical labour, when stubborn chronical запорах, when gender infantilism, sharp weight loss; 249 3 ) fabrics atrophy in elderly and old age. Often the omitting and the uterine prolapse arise in womens with backward-turned uterus. When uterine prolapse occurs the elytroptosis, when its fallout - their the eversion. The omitting and the walls eversion of vagina leads to omitting and fallout intimately associated with them bladder (colpocystocele ) and rectal intestine (proctocele). Clinical symptoms: Worry the pain durations, heaviness in the lower abdomen, sensation of a foreign body in vagina, the defecation violation and urination, urinary incontinence and gases, strengthening in cough, the ptarmus, gravities rise. When fallout of genital organs on their the mucosa appear the bedsores, crack, trophic ulcer, joins the infection, which may spread to the urinary system. The prolapsed uterus has the cyanochroic colour, it is edematous (due to infringement крово- and flow of lymph, easily вправляется when patient's position in a horizontal position. Treatment: when uterine prolapse shall be used diet therapy, the vitaminotherapy, the gymnastic, the hydrotherapeutic procedures. The woman is hauled with heavy working for lighter. When partial and complete fallout of genital organs is held surgical treatment. Mission 1 The girl by the age 13y.o. complains of pain in region of the abdomen, low back and perineal, of referred in the rectum. It is delivered in gynecology department with signs of acute abdomen on ambulance. From anamnesis: menstruations no, the secondary sexual characters are developed. During an inspection of privates: noticeable nipple in the area of vaginal vestibule of bluish-purple colour. Your preoperative diagnosis? Doctor tactics GPs Mission 2 The woman 27 years appealed in gynecology department concerning of infecundity, married seven years, the complaints the offensive absence of pregnancy consists of. From anamnesis the menstrual cycle did not superven, menarche is lacking, the secondary sexual characters is available. Status genitalis: the privates are developed correctly. Inspection of uterine cervix in mirrors: uterine cervix clean, little sizes. Inspection of per vaginam: vagina nulliparous, narrow, folded structure. Uterus remnant, sizes 1, 5 * 2 0 * 1, 5. Appendages from both sides of normal sized, painless. Precipitations mucous. Your preoperative diagnosis? Doctor tactics GPs Mission 3 The woman 25 years appealed in gynecology department concerning of infecundity. The polyclinic doctor domiciliary assure the woman, that the infecundity cause in 250 misalignment of uterus - retro flexio versi. Correct whether the findings did the polyclinic doctor? Will be able whether come the pregnancy at woman data? What survey methods is needed to hold? Tests 1. To privates belong? Major lips Uterine cervix Big glands of threshold Cervical canal Minor lips 2. To internal genital organs belong? Clitori Uterine tubes Ovaries Bartholin irons Uterus 3. The uterus is located in small pelvis by the as follows: Are inclined in front The vaginal part of neck and the external shed are arranged at the level of Ischial spines Beyond interlabial space The uterine body is located in mouth of cavity of small pelvis The body and the uterine cervix are arranged at an angle to one another 4. The ovary is supported in the abdomen thanks to: Own of mesovarium Wide uterine binder 251 M. levator ani Sacrouterine binders Funnel-pelvic binder 5. The peritoneum covers the uterus, as a rule? On its of front face - with isthmus level On its of clearance face - almost to a level of external shed Uterine fundus and its inferior - fully Only uterine fundus Forms excavacia rectouterina 6. Parametrium (parametrials ): Surrounds the vaginal wall of uterine cervix Are disposed at a level of uterine cervix Is located in the foot wide uterine binders Provides the friable joining of peritoneum with uterus Completes the parametrium 7. Topographic- anatomic ovaries feature: Are connected with Taz walls by own binders Are derivative paramezonephral duct Lies in Douglas space Is covered by the peritoneum Are in small pelvis 8. Basic anatomy feature of ovarian artery is then, That it: anastomose with uterine artery Moves away just below renal artery 252 Occurs between leaves of wide uterine binder Along its of free edge Walk away from front face of abdominal aorta Is in unified box with ureter on the right 9. The regional anatomy of uterine artery has following the definitive signs: Divides into rising and descending branch On first overlap with ureter is arranged behind ureter Its the vaginal branch go on anterolateral wall of vagina from both sides Its the vaginal branch anastomose with renal artery anastomose with ovarian artery 10. The pampiniform veniplex is characterized following This ovarian plexus: It is going on ovarian Vienna It анастомозирует with uterine veniplex This veniplex, located in intestine mesentery located in wide uterine binderе 11. The suspensory apparatus of uterus and its appendages consists of: Wide uterine binder Own mesovarium Round ligament of uterus M. Levator ani Cardinal binder 12. Cardinal uterus binder: Hold the uterus from excessive biases Are passing place of lymphatic pathways 253 Occur in the foot wide uterus binders Are being fastened to side walls of small pelvis Are suspensory uterus apparatus 13. The front wall deflated the bladder comes in contact with internal surface ? Pubic symphisis Pubis Top branches of ischiums Frontal abdominal wall Is covered by the parietal leaf of peritoneum 14. To arresting apparatus of internal genital organs regard? Sacrouterine binders Cardinal binders Vesico-uterine binders Fascia of pelvic floor Wide uterine binder 15. The ovary blood supply shall be exercised? Branches of ovarian artery Ovarian branches of uterine artery Branches of internal срамной artery Branches of femoral artery anastomosis of ovarian with uterine artery 16. Cause of precocious sexual development can be disease: Micro pituitary adenomas Gonad dysgenesia Follicular ovarian cyst 254 Adrenogenital syndrome Dermoid 17. The endocrine infecundity may be determined all but: Impassability of uterine tubes Vaginal atresia Prolactin-synthesizing pituitary tumor Ovary Tecoma Hypothalamic-pituitary disfunction 10. Checking problems 1. Factors growing of anomaly FGM. 2. Factors growing of wrong positions FGM. 3. Risk group on developments of аноалии. 4. Suspensory, supporting the apparatus FGM. 5. Anatomy of pelvic floor. 6. Anomalies classification FGM. 7. Classification of wrong positions FGM. 8. What treatments more often apply to anomalies of female genital organs? 9. What survey methods most are informative when anomalies of female genital organs? 11. Suggested reading Basic literature 1. Гинекология. Бодяжина В.И., Жмакин К.Н. 1997 2. Акушерство и гинекология под редакцией Савельевой Г.М., Сичиновой Л.К. перевод с английского М., 1997 3. Клинические рекомендации. Акушерство и гинекология. Выпуск 2. Под редакцией Кулакова В.И., М., 2006 255 4. Гнойная гинекология. Краснопольский В.И., Буянова С.А., Щукина Н.А., М., 2001 Additional literature 5. Руководство по неоперативной гинекологии. Бодяжина В.И., Сметник В.П., Тумилович Л.Г., М. 1990 6. Неотложная помощь при экстремальных состояниях в гинекологии. Айламазян Э.К., Рябцева И.Т. С-Петербург, 1992 7. Справочник по Акушерству и Гинекологии М. 1996 8. Атлас оперативной гинекологии М. 1996 9. Практическая гинекология Кулакова В. М.2001. 10. Оперативная лапароскопия в гинекологии. Стрижаков А.Н., Давыдов А.И., М., 1995 256 Subject: Background and pre-cancer disease. Neck cancer and uterine body The neck are covered multilayer squamose epithelium which emanates from urogenital sine, of which the privates - the vulva and the vagina also are organized. This is why in pathogenesis of these areas some community in difference from oncological the ovarian disease is available, the uteruses where the great significance has the hormone disbalance in the body. In pathogenesis play the factors: behavior pattern of woman (in risk group enters the women which early become sexually active - up to 16 years, since up to 16 years the stratified epithelium extremely thins, easily vulnerable, and the early traumatization can result in development of oncological process ). Early primary pregnancy and early first genera (up to 16 years ) is also epithelium traumatization of uterine cervix. Frequent change of sexual partners (speak about carcinogenic effect of sperm on epithelium of uterine cervix - in sperm is two protein - Heston and the protamine, which is assigned to carcinogenic effect ). Inflammatory and venereal diseases (the endocervicitis, colpites. Traumatization during abortions, labors, abrasions. The smoking (there is the close relationship ). The primary cause - the viruses - the herpes virus of second serotype ( first type does not matter ); the human papillomavirus - occupies the first place (10, 16, 18 genotypes ) - contamination occur only genital tract - causes the development by the condylomas, verruca at the surface of uterine cervix, which inappreciably (on the view are not discovered ), well is seen when endoscopic examination - colposcopy ); when serological study can be found the specific cells, characteristics for defeat only human papillomavirus - changed cell of stratified epithelium - cell gain the air form (koylotsity, air cell ) - About nucleus is organized the air rim. When electron 257 microscopy the special encompassings by nucleus find out, that pathognomonic. The immunochemical method is also found out these viruses - the immunoperoxidase method - in cytoplasm and nucleus the special inclusions find out, that emerge only when defeat of multilayer squamose epithelium. By means of monoclonal antibodies and molecular biological means can be found viruses. Definition of antibody titer in blood did not actual. The viral theory actual because at 80-90% sick find out defeat by the viral infection. Cytomegalovirus in combination with herpes virus of second type. Cervix cancer this not only a medical problem, but as well social. Since there are the women group at which the risk of development cancers of uterine cervix achieve 90%. Classification disease of uterine cervix. Clinicopathologic classification. Background processes of uterine cervix: erosions, pseudoerosion, leucoplakia, polyps, condyloma. Pre-cancer process - dysplasia. Cancer stage zero - carcinoma in situ. Microinvasion cancer. Invasive carcinoma. The background process not necessarily precedes neck cancer. Background processes. Occur the hyperplasia processes of epithelium cells, that of new glandular structures, and following proliferation and the tumour process gives rise. The true erosion is the epithelium injury (the epithelium absence on some site ), and it as any fabric always apt to regeneration, and there is within a few day. In future the erosion refreshes, or to coats by the multilayer squamose epithelium, or to coats by the cylindrical epithelium, which inherent for cervical canal. If the erosion being not ectocervix will be capped cylindrical epithelium then is organized псевдоэрозия this areas of cervical mucosa, which is covered by the irregular epithelium, not those which should be there. Are being founded condition for processes of proliferation. Leucoplakia. Appears in sight of white spot on uterine cervix, the site of redundant cornification. 258 Eroded ectropion. Due to of labor, abortions can be the side cervical rupture, and then occurs the channel eversion of neck, that is misplaced by the fabric, i. e. fabric submitted to unusual her the Wednesday, and consequently will take place proliferation. Condyloma, verruca. Nature their viruses. The polyps, as a rule of cervical canal, is sometimes various sizes, as a rule on foot. The basis their connective tissue, and are covered they as a rule by the glandular epithelium. Can be the glandular-fibrous polyps. Diagnostics: inspection in mirrors, endoscopy (colposcopy), cytologic examination. Pre-cancer process - dysplasia. The dysplasia is sometimes easy, moderate, heavy. Offer the term - the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. The dysplasia is the atypia of cover epithelium of uterine cervix, in violation its lamination, but during is not involving the germinal epithelium and the stroma. Outside as a rule of pathology not to find, only if there is the conformity with backgrounds by processes. When easy dysplasia occurs moderate proliferation of low layers of epithelium of basal and parabasal. The moderate dysplasia are affected all stratum, but to a greater extent, can be found changed cells, the cells аtipizm of lower cells - the nucleus hyperchromatosis is available, in them varys the nuclear-cytoplasmic relation. This is determined only when cytologic and hystological research. So that the cervical dysplasia shall be established on a foundation of histological and cytologic examination. If the dysplasia group with colpitis, then dysplasia cause may be the inflammation, cured the colpitis may withdraw and the dysplasia. Cancer stage zero. Carcinoma in situ. Sometimes it is very difficult to hold the facet between heavy dysplasia and cancer stage zero because when last by the prolapsed bedding, the violation of cytoarchitectonics - the change of nuclear-cytoplasmic correlation are taking place. The cancer stage zero differentiate those that it does not врастает in строму and is not introduced in the muscular layer. Respectively no metastases. May not to be clinical symptoms, but if there is then this contact bloody issues. These bleeding arise after physical load, sexual connections, inspection. In the area of external shed meet two different epithelium - cervical and multilayer flat, there of most frequently the cancer stage zero is developing. This is why when take cytologic are trying to achieve this areas. 259 Microinvasion cancer. Corresponds 1а of disease stage. There is the invasion, there is the infiltrative growth, the basement membrane has been impressed, but the invasion is limited three by millimeters. Separated this form this is why that if is affected 3 MM of muscular layer, then this more or less compensated the process, with less aggressive current, with smaller percentage of metastases development. The diagnosis shall be established only after histological conclusion, the cytologic examination not is crucial. So is the invasion, then in clinical picture may appear except spontaneous bleeding, can be pain, of whites. Whites is linked to damage of lymphatic vessels, under which go early metastazing. Watery бели is lymphorrhea. Invasive carcinoma. There is the invasion in строму more 3 MM. Clinic: pain, whites, bleeding. If go expressed the infiltrative growth, then can be violation on the part of neighbouring bodies - the acraturesis, pain, the defecation violation, can be hydronephrosis phenomena. The cervix cancer may be endophytic, exophytic and mixed mode of growth. When exophytic form, already on the view in mirrors can be seen growth of uterine cervix, in sight of cauliflower - shapeless the education, the ruddy, when the Touch easily are bleeding. Is found in 50-55%. The endophytic form in sight of ulcer, crater, with purulent territories, at the bottom can be necrotic mass, is found in 35%. Mixed form. When exophytic form the metastases are found in smaller percentage of cases (13% ), and when endophytic of more often (35%). On minute structure differentiate : Mixed form - more aggressive current. Flat cell cornified the cancer. Flat cell not keratinizing cancer. Adenocarcinoma. Adenosquamous carcinomas. undifferentiated swelling. Most heavy adenocarcinoma and undifferentiated swellings. Diagnostics. In order to correctly make a diagnosis, separate 2 stage examination: 260 In the first stage go the detection - the screening. At the second stage - deepened the diagnostics. For primary screening the cytologic examination is being used. The smears take from cervical canal, from endocervix, from the surface of neck - ectocervix. The double touch will help the process stagement, the place the going to parametrial cellulose has whether. Colposcopy - inspection of uterine cervix. Simple colposcopy - 15 multiple increases, inspection of uterine cervix. Extended the colposcopy, - for best identification process by the vinegar, methylene blue. MicroColposcopy. Schiller trial. To identify distribution hotbed. process the mucous uterine cervixes, and the cells of germinal epithelium keep the glycogen, which is reactive with iodine and gives the brown overtone. Normal mucous if treated with will be colored in the brown colour. When integrity violation then cell do not stained in the brown colour. For stagement redetermination use the aiming biopsy, which gives the material for hystological research. Before used the lymphography - presence definition of metastases in the lymphatic nodes. Abrasion of cervical canal and uterus. Ultrasound with vaginal probe. CT and NMRI. Classification cancers of uterine cervix (1985 ). Precipitation of process stage it is necessary for choice of tactics of treatment. 0 stage - cancer stage zero. 1А stage - microinvasion cancer. Invasion up to 3 MM. Swelling diameter not more 1 refer to. 1B the stage - the swelling is limited only by uterine cervix, but the invasion is limited by the uterine cervix. 2А the stage - the cancer infiltrates top vagina third, or on uterine body. 2B the stage - the process shift to parametrial cellulose, not gets to uterus walls. 3А stage - extension to lower third of vagina, on body and appendages. 261 3B the stage - with parametrial the process gets to Taz walls. Appear in the regional lymph nodes. Then if the metastases have developed in the lymphatic nodes then this 3 stages. The hydronephrosis - growth in the urine path may be. 4А stage - defeat neighbouring bodies. 4B stage - distant metastasis. Regional metastases. Blood supply of uterine cervix. The uterine artery go from internal iliac artery. At the level of internal shed the uterine artery divides into rising and descending branches. Primary metastasis will units defeat ranging on internal and external iliac arteries, in obturator pit. Units - internal, external iliac and obturator. Classification of TNM. Treatment. Background treatment of process. Basic treatment is the destruction method. Before treated by the buckthorn oil that wrong, since inspires the irregular regeneration. If the conformity with inflammatory process then add antibiotics. Destruction by the electric current - diathermocoagulation. At the site action the ulcer is developing, which to coats normal epithelium. Let-downs: the painful procedure, often the Stroop drops out on 7-10 days and appears the bleeding; the cicatrice is organized, under which can walk the break in labors; no material for hystological research, then before procedure it is necessary to make the biopsy. Action by the cold - cryodestruction. - 30 degrees in zone of erosion. The Stroop of more mellowy, the bleeding is sometimes rarer, the cicatrice of less expressed, without serious consequences. Laser destruction - most optimum action - evaporation of irregular epithelium. Without serious consequences, bleeding never is sometimes, are not organized rumen change of uterine cervix. Chemical degradation. Conization: Electric conization Cutter conization. 262 Conization is exercising when the background process is combined with deformation of uterine cervix. For instance when eroded ectropion. The external shed - the site from where go take away most frequently swelling. Is being done when heavy dysplasia, cancer stage zero. Moderate and easy the dysplasia can be healed by the laser exposure. Invasion and the microinvasion cancer are being treated: Combined method: surgical + beam. Complex method - use of all types of action - surgical method, beam, chemotherapy. When stage one use the surgical method - the Вергейма operation (1911 ) - the uterine extirpation with appendages, disposal of top third of vagina, the pelvic lymphadenectomy. If the process 2-3 stage then use the combined method. Radiation therapy - distant, internal. Chemotherapy on 3-4 stage. 263 Subject: Sterile marriage. Contraception problems. To-day on land more 6 bln of inhabitants and a tendency to bigger population increase of planet is marked. However, the increase in the number of population does not conform quality of people's health, as demonstrated by world statistics. Doctor of common practical work has to propagandize the healthy way of life, and as one of fundamental frequency components the it - the healthy maternity, battle over improving of living standard of population, bringing up of healthy and full-fledged younger generation. Concept of reproductive health: “relay protection is condition of complete physics, mental and social well-being, and is not easy diseases absence and diseases in all questions over reproductive system and its function”. UN World statistics. 264 - lethality from complications of pregnancy and births 500 thousand annually - Lethality of infants 9, 6 million /Year - Up to 5 summer age 4, 8 million /Year - Number of artificial abortions 40-60 million. - Of them illegal 25-30% One of most Grosny findings in statistic relay protections is the maternal mortality the woman death from conception moment up to 40 days after births of children. Findings of maternal mortality on 100 thousand. Viviparities: - US 8, 0 - Great Britain 12, 0 - Japan 2, 0 - Kazakhstan 77, 3 - Kirgizia 43, 0 - Tajikistan 82, 0 - Turkmenia 56, 0 - Uzbekistan 26, 4 The causes of maternal mortality (incineration facilities ) are numerous, however, in all mills on statistic WHO the equal tendency for reasons ms. is marked. Cause incineration facility (WHO ). - Bleeding - Hypertension (gestosis ) - Septic conditions - Pathologic labors - Complicated by abortions 265 Ranking among such findings there is still a variety of other characteristics, determining the quality relay protections. On WHO figures: Fact RH Incineration facility at age> 35 years 5 time> than in young Down's disease 19 - 35 years - 1: 1000 35 years - 30: 1000 intergenetic interval about 30 % Labors amount = abortions amount extragenital diseases about 60 - 70 % of fertile age Given the fact that the findings incineration facilities is in no doubt and other complications straight such finding as the fertility are interlinked with. Fertility finding: - Spain 1, 2 - Italy 1, 2 - Japan 1, 5 - Great Britain 1, 8 - Turkey 2, 7 - Nigeria 7 - Uzbekistan 4, 4 Statistic evidences for Узбекистану созвучны with world statistics. Additionally to this one may refer to such facts: In Uzbekistan lives about 2, 5 million families. More population halves, that is more 12 million man - women. Annually in Uzbekistan are being founded about 250, 000 new families. If up to 1998 on 500 thousand labors 500 thousand had to. Abortions, then to-day this had declined in number up to 340 thousand. but ratio survived. 266 Such fact merits the attention of, that among patient with breast cancer women, interrupted the primary pregnancy by the abortion way are dominated. 00020. Only 20% women of fertile age observe intergenitic the interval 2, 5-3 year. The finding extragenital diseases among womens of fertile age and pregnant is very high. In certain regions, for example, Каракалпакстане this figure achieve 80-90%. In connection with this, naturally, increasing the number of sick childrens, nascent from sick mothers. Conservation RH is complex of medico-social actions, comprising the entire a number of problems. Conservation RH include: Consultation-Information, enlightenment and services in service field of pregnant, woman in births, parturient women - Breast feeding - Maternal health and child - Warning and fertility treatment - Warning disease, transmitted by the genital tract - Hygienic of sex life - Responsible attitude toward its RH The problems quality improvement of life and health of people is constantly in the public eye not only health care personnels, but as well of many international communities and organisations. In 1952 in Bombay the first sitting of international federation family-planning was held, where notion definition family-planning was given. Family-planning - the possibility of marital pairs freely choose and responsibly to decide questions about amount and time of childbirth, to have the information and the means, allowing do this the election freely. UN At the same place were valid and are worked out 5 principles family-planning. - Contraception of pregnancy <19 years - Contraception of pregnancy> 35 years 267 - Observance of intergenitic interval 2, 5 - 3 years - Crossing of genus number - Contraception of pregnancy in the patient with extragenital diseases. To-day the medicine have the opportunity to help families in observance of the principles of RH/FP. By the fact that in recent years in our state are a major preoccupation health subadult generation, mothers and seven in general МH RUz and government the big measures on admission of these problems is performed. The mother's health and child преаратилось in state problem. 2000 had been denoted as «Соглом авлод йили», 2001– «Соглом она ва соглом бола йили». In this case the entires the programs with engagement not only health care personnels, but as well of sociologists, lawyers and public bodies, and also financial and different спонсирующих international organizations and funds are being developed. МH RUz the commands № 154 - <about women improvement of fertile age> and № 155 <reorganization of structure of obstetric complexes> are published. On these commands and other normative documents 100% women dispensary observation of fertile age, the detection and the improvement of female patients is provided. Group definition of woman with absolute contra-indications to pregnancy, accompanied by salvage service in election of contraceptive methods. Woman with relative contra-indications must also reorganize with temporary exception of pregnancy. Also the normal womens draw the attention, which the observance need of intergenetic interval 2, 5-3 year is explained. On the assumption of other countries' experience and international community the medical workers of Uzbekistan is to build his working for medical bringing up of population and improving of services of contraceptive technologies. Principles of our work are as follows: • Do not give birth very soon • Do not give birth too late • Do not give birth, if the patient • Do not give birth a lot of 268 • Do not give birth often To fulfill these principles, and full assistance to families in the choice of contraceptive methods to date, our state and Medicine raspologaeyut absolutely all contraceptive techniques adopted in the world. Contraceptive classification Natural methods: (ENP - Calendar method - Magnetic tape - Coitus interruptus Navy Barrier methods - Condom - Caps, diaphragms - Spermicides Voluntary surgical sterilization - Pipes Okklyuzziya - Vasectomy Hormonal contraception Oral (Coca, FTC Injection (IR) Norplant Implants To-day for the population of our state all enumerated the contraceptive are available. In this case it should be noted that during last 5-6 years all contraceptive, especially in the countryside, was granted free. The state made purchases of these funds for the population and the big спонсорскую help exert the international organizations and the funds. Among all enumerated contraception means there is one protecting from disease of passed by the genital tract is the condom. The distribution of this fund among the 269 population will aid great number reduction sexually transmitted diseases of such as HIV, the chlamidiosis, the syphilis, the gonorrhoea, the cytomegalovirus, the hippy hepatitis and other. Along with this is needed to mark and very important the not contraceptive property of this метода- men engagement to process family-planning To-day at us in republic found the wide diffusing method of voluntary surgical sterilization of women - tube occlusion. Each just listed contraception means has its advantages and disadvantages therefore gains the great significance correct counselling and the provision of services of contraception. Problem of protection relay protections, counselling and provision of services of contraceptive technologies first and foremost the general practitioners, within direct contact with the people are to deal. The general practitioner must clearly know the mode of action of each means, its the advantage and disadvantages, be able to advise patients, to provide services of hormonal contraception, the inserting and spiral disposal, will able to liquidate side effects of heavens and earth. As to voluntary surgical contraception, DCPW must be able advise on this method and prepare patients to carrying out such operation by the specialist Situational missions: Mission 1 Sick 46 years entered the permanent establishment in connection with complainings of the strong pain in the lower abdomen, the nausea, the oneshot retching, fervescence up to 39, 5 "S. during last 12 years with the objective of contraception uses VMA. Came down with 10 days ago, when appeared pulling pain in the lower abdomen, panthodic in the rectum, the body temperature rose to 37, 5 C. To doctor was not addressing, was treated independently without effect. In connection with sharp worsening of health is delivered in permanent establishment by the brigade of first-aid medical help. On the view condition is moderately grave, the pulse 120 in 1 mine, hell 120/80 MM mouth. Art.. The abdomen is distended, is extremely painful in all departments, is determined atrophy of percussion sound, the Shchotkin-Blumberg symptom of bitterly positive. The uterine cervix of эрозирована, are seen filaments VMA, in small pelvis painful, the fixed the conglomerate, overall sizes 12-14-I8 melanoma associated antigens, separately the uterus is palpable bitterly and the appendages to palpate fails, the posterior vaginal vault is overhanging, bitterly painful, genital discharge pyoid. 1. What is the diagnosis most is probable? 270 And ) endometritis against application VMA; suppuration of ovarian cystoma . Б ) endometritis against application VMA, acute bilateral salpingitis; pelvic inflammatory disease. C ) endometritis against application VMA; perforation of tubo-ovarian abscess; diffuse peritonitis. D ). Uterine myoma with necrosis of one of units; acute purulent salpingitis; diffuse peritonitis. E ). Ovarian cancer IV of stage. 2. Pastime tactics and volume of operation? And) disposal VMA accompanied by combined antibacterial and infusion-transfusion therapy during 7 day. In case lack of effect - abdominal section on Pfannenstiel, bilateral adnexectomy. B) drainage of paraplasm under control of transvaginal sonography accompanied by antibacterial and infusion therapy. C) medical and diagnostical laparoscopy; sanitation and drainage of abdominal cavity. D) extraordinary abdominal section; nizhnesredinnaya laparotomy; panhysterectomy; drainage of ventral cavity * E) extraordinary laparotomy; abdominal section on Joel-Cohen, above vaginal of uterine amputation with uterine tubes; omentektomiya. 3. What the main directions of etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy in postoperative period? And ) affecting the pathogenic microflora using of antibacterial, antiseptic and physics means. Б ) fight against endogenic intoxication. C ) reestablishment affected functions of different organs and systems. D ) prevention of surgical implications. E ) all enumerated выше* Mission 2 271 During abortion the perforation of the uterus by the abrasion spoon is made. 1. Your tactics? And) monitoring, cold on the abdomen, antibacterial and uterotonic therapy B) residue removal of foetal egg under control of hysteroscopy, in future antibacterial and uterotonic therapy C) extraordinary abdominal section, suturing of perforating hole, bodies inspection of ventral cavity D) abdominal section in case lack of effect from conservative therapy, rise signs of intraabdominal bleeding E) laparoscopy for exception of inside ventral bleeding 2. What complications can be in the patient And) wounding of abdomen organs B) intraabdominal bleeding C) peritonitis D) sepsis E) all the above * Test questions 1. To you appealed the woman requesting us to select the contraceptive. Unmarried. Sex life lives 2-3 once a month, at other times and rarer. Partners different. Pregnancies was not. Your recommendation A) intrauterine contraceptive device B) condom C) postinor D) oral contraceptive 2. Married woman 28 years, having one sex partner, suffering by the chronical thrombophlebitis of Vienna of lower limbs, mother of one child, are needed: A) oral contraceptive Б ) surgical sterilization 272 C ) intrauterine contraception D ) mechanic contraception 3. Divorced woman 32 years, having one child and rare (1-2 in two month) the sexual relations with one sex partner, follows to commend: And) marvelon B) anteovin C) postinor D) trikvilar E) abortive of sexual connection 4. Married woman, suffering by the diabetes mellitus, gallstone disease, thrombophlebitis, having one child, follows to commend: And ) oral contraceptive Б ) surgical sterilization C ) intrauterine contraception D ) surgical sterilization of husband 5. Woman 40 years, somatically not weighed down, having 3 childrens, are preferable: And ) surgical sterilization Б ) hormonal contraception C ) intrauterine contraception D ) postinor E ) condom 6. Woman, consisting on active taking into account in Neuropsychiatric outpatient clinic, has been shown: And ) surgical sterilization Б ) hormonal contraception C ) intrauterine contraception 273 D ) postinor E ) condom 10. Checking problems 1. What marriage should be considered sterile? 2. Primary causes of female infertility? 3. Primary causes of male infertility? 4. Tests of functional diagnostics? 5. Grade of purity of vaginal content? 6. Hysterosalpingography? 7. Definition 17-KS in the urine? 8. Sizes of womb and ovaries of women of reproductive age? 9. Postcoital test? 10. Index definition of body mass? 11. Fertility definition of sperm (WHO )? 12. What there is ovulation stimulators? 13. Therapy principles of endocrine infecundity? 14. Treatment of tubal sterility of inflammatory genesis? 11. Suggested reading Basic literature 1.Гинекология. Бодяжина В.И., Жмакин К.Н. 1997 2.Акушерство и гинекология под редакцией Савельевой Г.М., Сичиновой Л.К. перевод с английского М., 1997 3.Бесплодие в браке Пшеничникова М 1990 4.Клинические рекомендации. Акушерство и гинекология. Выпуск 2. Под редакцией Кулакова В.И., М., 2006 5.Семейная медицина. под ред. Краснова А.Ф., Самара, 1996 274 Additional literature 6.Руководство по неоперативной гинекологии. Бодяжина В.И., Сметник В.П., Тумилович Л.Г., М. 1990 7.Справочник по Акушерству и Гинекологии М. 1996 8.Атлас оперативной гинекологии М. 1996 9.Практическая гинекология Кулакова В. М.2001. 10.Оперативная лапароскопия в гинекологии. Стрижаков А.Н., Давыдов А.И., М., 1995 275